bio final
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
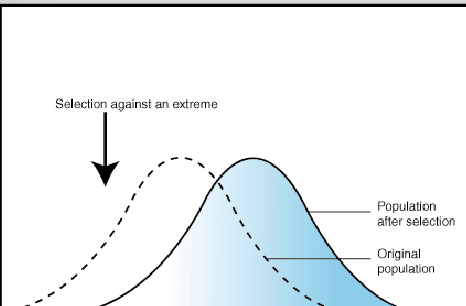
directional
selection for one extreme
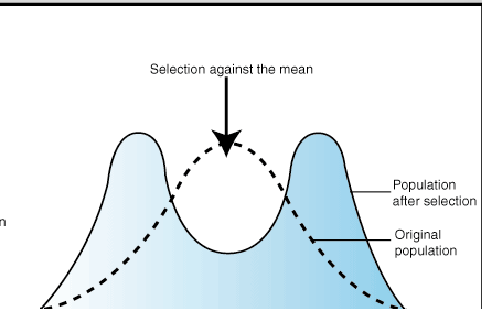
stabilizing
selection for the median
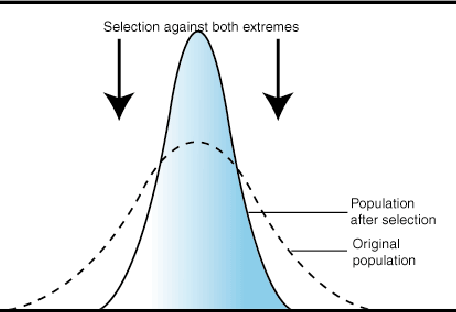
disruptive
selection for both extremes
allopatric speciation
Barriers split populations.
Populations face different environments
Natural selection leads to different results.
sympatric speciation
no geographical speciation
pre and postzygotic barriers
how are different species prevented from mating with each other
prezygotic
before fertilization
postzygotic
after fertilization
hybrid variability
the hybrid is weak or dies early
reduced hybrid fertility
the hybrid can’t have kids
hybrid breakdown
Later generations of hybrids are weak or sterile.
taxonomy
the scientific practice of classifying biological diversity
taxa
any named group of organisms (ex. a species)
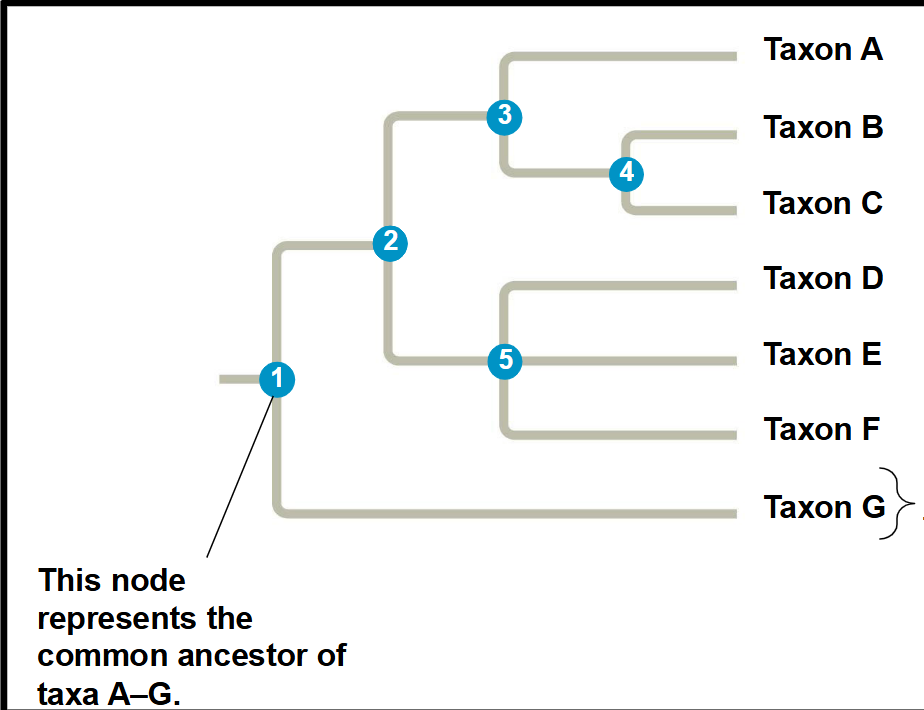
nodes
where linages diverge
..
basal taxon
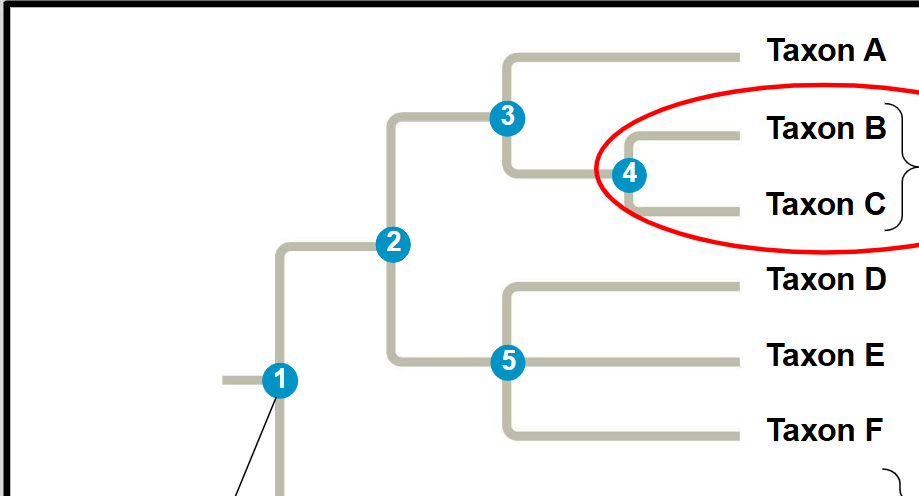
.
sister taxa
clade
A group of taxa that encompasses all members descended
from a common ancestor (ex. primates)
monophyletic
Includes a common ancestor and ALL of its
descendants
polyphyletic
Includes organisms and no common ancestor
paraphyletic
Includes a common ancestor and SOME of its
descendants
parsimony principle
simple explanations are preferred over more
complicated ones.
less evolutionary steps are better than more steps to explain relationships. The tree with the least number of steps is the most parsimonious.
what does parsimony have to do with phylogenic trees
the red queen hypothesis
why is sexual reproduction so common?
last universal common ancestor
what does LUCA stand for
bryophytes
what are mosses, hornworts, and liverworts?
eukaryotic signature proteins
what did the asgard archaeans produce?
Highly acidic or saline environments
Which environment is most commonly associated with known archaean species?
paraphyletic eukaryotes
Which is true regarding the classification of protists?
shallow freshwater with sunlight
where did ancient charophytes like to live?
gametophyte
Which Bryophyte generation will be haploid?
xylem
water
phloem
sugar and nutrients
The gametophyte generation is dependent on the sporophyte
Which is dependent on the other in Gymnosperms?
monecious
both male and female
dioecious
have male and female parts of separate plants
anther
produces pollen
stamen
made of anther and filament (male)
filament
supports anther
pistil
made of stigma and style (female)
style
connects stigma to ovary
stigma
receives pollen
nitrogen
An environment poor in which nutrient may lead to fungi adapted to carnivory?
dikaryotic
two nuclei
diploblast
two gem layers
triploblast
3 germ layers
Pathogen pressure forces C. elegans to mate with others
what does the red queen hypothesis have to do with C. elegans?
externally digesting, chitin in cell walls
what are the general traits of eukaryotes?
yeast
unicellular and has pseudohyphae
mycelium
collection of hypha
septum
divide cells
vascular tissues
transport water between roots and shoots
vascular plants
what type of plant is more able to colonize terrestrial habitats?
bacteria and archaea
what are the two main groups of prokaryotes?
anaerobic
What type of metabolism is associated with Asgard archaea?
chloroplasts
What did cyanobacteria become?
animals fungi and plants
Which three major groups evolved from aerobic eukaryotes?
parazoa
lack of defined tissue types
eumetazoa
defined tissue types
diploblast
two germ layers
triploblast
3 germ layers
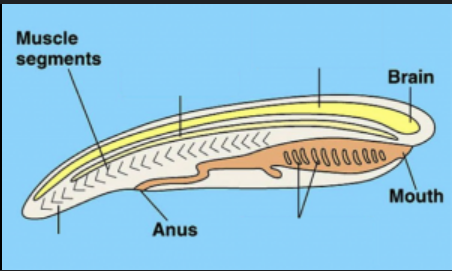
Dorsal, hollow nerve cord
top right
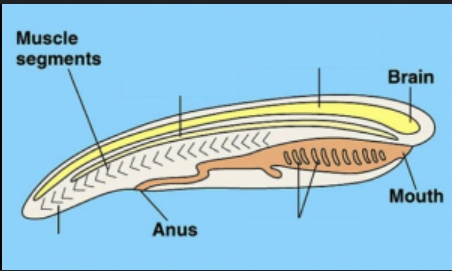
notochord
top left
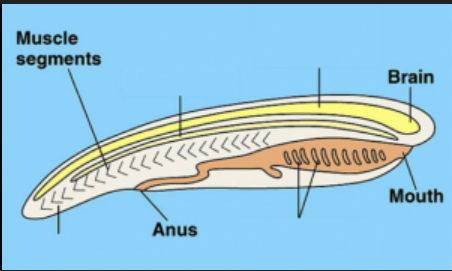
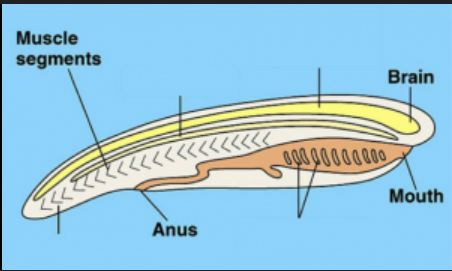
Pharyngeal pouch/slits
bottom right

post anal tail
bottom left
germline
what type of mutation is defined by its ability to be passed
on genetically via Meiotic reproduction?
frameshift
Which word refers specifically to the type of mutation which involves the addition or deletion of a nucleotide?
missense mutation
A mutation which results in a different protein being produced
nonsense mutation
A mutation which fails to produce a protein
silent mutation
A mutation which still produces the intended protein
allele, population
Evolution describes the change in ___________ frequencies in a ________________
homologues structures
Similar structures in related organisms which results from common ancestry.
fishers model
female mate choice and male ornamentation advantage
Zahavi’s model
The sexual dimorphism is an honest signal of genetic quality
gas exchange and increased weight on limbs
What issues do we have moving from sea to land?