Engng Math 145 Partial Fractions
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Degree of numerator < denominator
No long division required and partial fractions can be applied immediately.
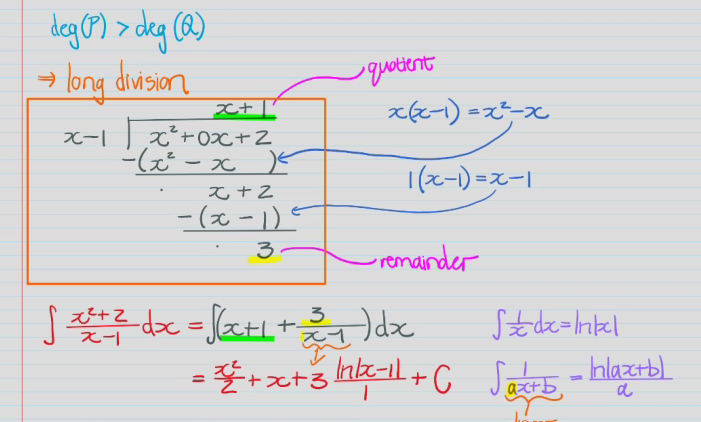
Polynomial long division
If degree of numerator greater than degree of denominator, then do long division.
Divide dividend by the x term if divisor and write quotient
Multiply quotient by the same x term and subtract it from dividend
Add dividend of term one lower than the quotient’s current degree
Repeat process but on the “difference + dividend term” until degree of the difference term is lower than the degree of the divisor
Remainder is remainder divided by the divisor
Polynomial long division shortcut for equal degrees
Divide leading terms for quotient (y) and then subtract dividend by divisor times quotient (y) for remainder.
eg. (2x2 + 2x + 1) / (x2 + x + 1) → 2x2 / x2 = 2, (2x2 + 2x + 1) - 2(x2 + x + 1) = -1 → 2 + (-1) / (x2 + x + 1) [answer]
Distinct linear factors
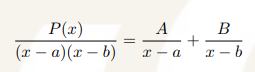
Repeated linear factors
A1, A2, …, are unique constants A, B, C, D, …
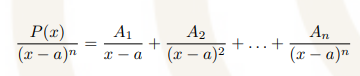
Distinct irreducible quadratic factors
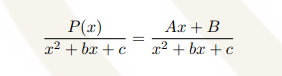
Repeated quadratic factors
A1, A2, … & B1, B2, … are unique constants A, B, C, D, …
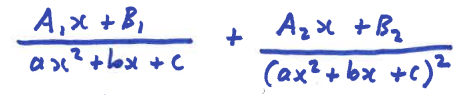
Integral of 1 / (x2 + a2)
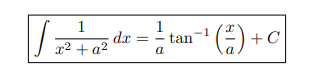
Irreducible quadratic test
If discriminant < 0, then irreducible.
Solving partial fraction constants
Simultaneous equations OR equating coefficients.
If simulatneous not possible make a variable equal to i = sqrt(-1).
xn factor
xn is a repeating linear factor: (x - 0)n