Parasitism and Infectious diseases`
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are the two types of parasites
ectoparasites and endoparasites
where do ectoparasites reside
on the outsides of organisms
what are the advantages of ectoparasites
easily move between hosts
not exposed to host immune system
what are the disadvantages of ectoparasites
exposed to the environment
exposed to predators and parasites
what are endoparasites and where do they reside
they live on the insides of organisms and can be intracellular (like viruses, that live and replicate inside host cell) or extracellular (like intestinal worms, that live and replicate between host cells)
what are the advantages of endoparasites
safe from the external environment
hosts rarely have internal, physical defenses to prevent feeding
what are the disadvantages of endoparasites
exposed to the host immune system
hard to move between hosts
t/f: parasites cause population cycles of hosts
true
what are emerging infectious diseases
newly evolved strains of diseases, where some mutations allow a pathogen to jump to a new host species or become a more virulent strain
what is white-nose syndrome in bats
a disease caused by a fungus that causes a large number of bats to die
what are zoonotic diseases
those that jump from non-human animals to humans and are the main source of emerging infectious diseases in humans, resulting in many epidemics
what are zoonotic epidemics related to
habitat fragmentation and climate change
what is the S-I-R model
the simplest way to model the transmission of an infectious disease (i.e., if an epidemic will happen or not) that incorporates immunity of the host
what is S in e S-I-R
susceptible to the pathogen
in the S-I-R model what percent of individuals begin as S
100%
what is I in S-I-R
infected
of the susceptible individuals, some percentage become
infected
of the infected individuals some percentage develop
resistance via immunity
what is R in S-I-R
resistance via immunity
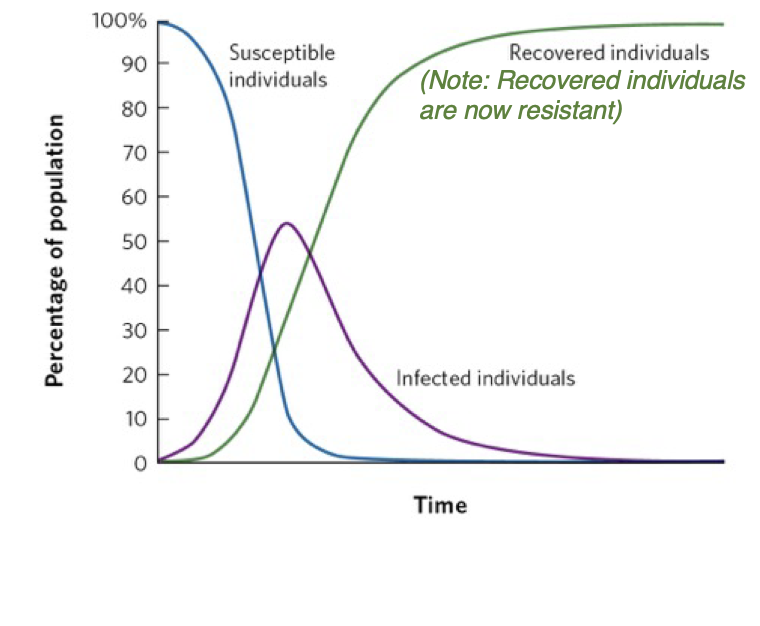
what model does this graph represent
S-I-R model
What is the equation for N, the total population size
S+I+R
I —> R is
the recovery rate (g)
S—→ I is what
transmission rate (beta)
S—→ R is
immunization
for most endoparasites (viruses and bacteria) what is counted instead of individual parasites
the number of hosts infected with parasites
what is Rnot
the basic reproductive number of an infectious disease (i.e. the number of new hosts who are infected by a single infectious host in an entirely susceotible population)
t/f: R0 is not a per captia growth rate
false
when the transmission rate is greater than the recovery rate what happens
disease spreads
what does it mean when R0 > 1
the infection will continue to spread through the population (potential epidemic)
what does it mean when R0 < 1
the infection will not spread (on average, each infected individual fails to infect another individual)
what is a spillover event
occurs when a disease that exists in a reservoir host population is transmitted to ahuman
what all can direct effects be caused by
predation, parasitism and other types of interactions
indirect effects are always a reault of what
multiple direct effects