[HEAL 3106] Midterm 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Systems
are high order structures that perform a specialized function
Heart; Right side; Left side
CENTRAL part of the cardiovascular system; performs same action repetitively
acts as a double-sided pump
_____ - pumps blood to/from the lungs
_____ - pumps blood to the rest of the body
Blood; Whole blood; Plasma; Formed elements
FLUID of the circulatory system
_____ - blood w/ all components
_____ - liquid matrix
_____ - cell and cell fragments
Vessels
conduct blood between the heart & rest of the body
it is a closed system
interacts extensively w/ other fluid compartments
Arteries; Veins; Capillaries
_____ - carry blood AWAY from the heart; aka EFFERENT VESSELS; does NOT have VALVES
_____ - carry blood TO the heart; aka AFFERENT VESSELS; has VALVES (valves maintain UNIDIRECTIONAL blood flow)
_____ - exchange substances bet. BLOOD & TISSUES; LARGEST CROSS-SECTIONAL AREA
Transport gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes
Regulate pH, fluids and ion of the interstitial fluid/cells
Restrict fluid loss at injury sites within blood vessels
Defend against toxins and pathogens
Stabilize body temperature
FUNCTIONS OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (TRRDS)
Etiology; Pathogenesis; Molecular changes
_____ - the CAUSE of the disease
_____ - how the disease process EVOLVES
_____ - MORPHOLOGY - fundamental structure/form of cells & tissues
Clinical manifestations; Diagnosis; Clinical course
_____ - how the disease PRESENTS itself (SYMPTOMATIC/ASYMPTOMATIC)
_____ - NATURE/CAUSE of a health problem
_____ - the EVOLUTION of a disease (ACUTE/SUB-ACUTE/CHRONIC)
Transthyretin; Tafamidis
is a protein that circulates in our blood
due to age/mutations, it misfolds and accumulates in the heart
leads to a disease known as ATTR-CM (heart weakness, failure, death)
there is a therapy for this disease known as _____
blood flow; blood pressure; arterial; venous; capillary
_____ as _____
_____ pressure - force exerted by blood against ARTERIES
HIGHEST and PREDOMINANTLY determines SYSTEMIC PRESSURE
_____ pressure - force exerted by blood against VEINS
_____ pressure - force exerted by CAPILLARIES
aorta; 120mmHg; systemic circulation; systolic; 120mmHg; diastolic; 80mmHg
highest pressure is at the _____ which generates pressure about _____
_____ - pressures are HIGHER than Pulmonary circulation pressures
_____ - PEAK PRESSURE measured @ _____
_____ - MINIMUM PRESSURE measured @ _____
systolic - diastolic; diastolic + (systolic - diastolic) / 3
(1) PULSE PRESSURE FORMULA
(2) MEAN ARTERIAL PRESSURE (MAP)
is more DIASTOLIC because it spends 2/3 of its time relaxing = resting state
stretchability; compliance; systole; diastole
ARTERIES and PULSE PRESSURE is determined by _____
how easily a vessel stretches is known as _____
[!] pressure must be HIGHER than resistance; blood needs to flow NORMALLY not backwards!
during _____ influx of blood stretches the arterial walls → INCREASES PRESSURE
during _____ walls recoils, MAINTAINING PRESSURE
sphygmomanometer; cuff inflated to pressure; pressure released; korotkoff’s sound; lower pressure
blood pressure can be measured using a _____
_____ > SBP (No flow, no sound)
_____ < SBP (Some flow, some sound; turbulent flow aka _____)
_____ < DBP (Normal flow, no sound)
tissue perfusion; autoregulation; central regulation
_____ - blood flow through TISSUES; must match in demand of tissue
_____ - SHORT TERM; local changes in blood flow within CAPILLARIES; regulated by PRECAPILLARY SPHINCTERS (causes vasoconstriction & vasodilation of vessels)
_____ - SHORT & LONG TERM; regulated by cardiovascular centers in the brain; involves NEURAL and ENDOCRINE systems; can & alter blood flow to nonessential/inactive tissues; HOMEOSTASIS (normal range of BP) can decrease BP = restored!!! :)
3 parts:
cardioACCELERATORY center (increases heart rate)
cardioINHIBITORY center (inhibits heart rate)
VASOMOTOR center (causes vasoconstriction/vasodilation)
baroreceptors
NEURAL REGULATION is initiated by pressure receptors aka _____
receptors found in the AORTA and CAROTID SINUS
stimulate centers in the medulla to control heart rate & vasoconstriction of vessels
SHORT TERM!
kidney; RAAS system
_____ = plays a vital role for long-term regulation of blood pressure
_____ = activates a cascade of hormones to control BP LONG TERM; involves MANY organs & hormones; main system involved in control of blood volume and BP; results in VASOCONSTRICTION; REABSORPTION OF WATER & SODIUM; INCREASED THIRST
(1) KIDNEY senses a drop in BP
(2) releases RENIN
(3) ANGIOTENSINOGEN → ANGIOTENSIN 1 → ANGIO 2
ANGIO 2 causes VASOCONSTRICTION → BP rises
ANGIO 2 activates ALDOSTERONE → REABSORPTION OF WATER and SODIUM → BP rises
hypertension; primary; secondary; office bp measurement; out of office
ELEVATED blood pressure
SEX-DEPENDENT
normal is 120/80 (normotensive)
2 types:
_____ = essential or idiopathic (no idea what’s happening)
_____ = other disorder (kidney disease)
_____ = measurement taken in a clinical setting, prone to the white-coat hypertension and masked hypertension
WHITE COAT HYPERTENSION - BP can be falsely elevated due to the stress of a medical visit.
MASKED HYPERTENSION - BP can be normal in the office but high at other times, leading to misdiagnosis.
_____
HOME BP MONITORING - Patients take their own BP readings at home over days, weeks, or months.
PROS: provides long-term BP information in a familiar, stress-free environment and has been shown to better predict health outcomes than office readings alone
CONS: requires proper patient education on how to take accurate readings and can be subject to user error.
AMBULATORY BP MONITORING - portable device worn by the patient for 24 hours, taking BP readings at regular intervals throughout the day and night
PROS: Captures the 24-hour BP profile
CONS: Can be expensive, requires repeated monitoring, and can be affected by poor measurement techniques
low normal - <120, <80
normal - 120-129, 80-84
high normal - 130-139, 85-89
stage 1 - 140-159, 90-99
stage 2 - 160-179, 100-109
stage 3 - >=180, >=110
STAGES OF HYPERTENSION
non-modifiable risk factors; modifiable risk factors
_____ = are inherent and cannot be altered (ex: family history, gender, race, age)
stiffening of large arteries (more stiff = less compliance/stretch)
decreased baroreceptor sensitivity
increased vascular resistance
decreased renal blood flow
_____ = are those that can be changed through lifestyle or environmental adjustments (ex: sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits, diabetes, smoking, drug use, stress, salt intake)
raises blood volume
increases sensitivity to sympathetic nervous system
*red underlined PRIMARY!
primary hypertension; heart; brain; systemic vascular
typically ASYMPTOMATIC
_____ = thickening of the left ventricle (hypertrophy); atherosclerosis of the coronary vasculature
it’s detrimental because it’s getting smaller and smaller, blood is less
_____ = strokes, dementia, and cognitive impairment
_____ = atherosclerosis
ACE; ARBs; B-blockers
_____ = prevents the CONVERSION of Angio I to Angio II
_____ = blocks Angio II from BINDING to Angio II receptors
_____ = reduce heart rate and cardiac output (decreases BP)
artery; capillary
_____ = LARGEST vessel
_____ = SMALLEST vessel
consists of a continuous tube of endothelial cells w/ basement membrane (lacks tunica media & externa)
very thin important for movement
slow movement; many capillaries = low total resistance; atherosclerosis
_____ is needed to promote substance exchange between capillaries and tissues
resistance is affected how? _____
_____ is an example of resistance
CHP; filtration; BCOP; reabsorption
_____ = blood pressure within capillary beds; highest near the arteriole side of the capillary
_____ = PUSHES water and small solutes OUT of capillaries
_____ = pressure exerted by plasma proteins within blood; remains the same throughout the capillary
_____ = PULLS water and small solutes INTO capillaries
Edema
_____ = swelling produced by the EXPANSION of interstitial volume; SWOLLEN = DECREASE IN BLOOD FLOW
4 causes:
increased capillary pressure
increased capillary permeability
decreased colloidal osmotic pressure
obstruction of lymph flow
LOCATION SPECIFIC
BRAIN, LARYNX, LUNGS can be life-threatening
JOINTS interfere with movement
capillary filtration pressure; capillary permeability; capillary colloidal osmotic pressure; obstruction of lymph flow; lymphedema
_____ = causes fluids to ENTER interstitial fluid; PRESSURE RISE = MORE FLUID; generalized EDEMA, heart failure, kidney disease, pregnancy
_____ = ENLARGED = CAPILLARIES DAMAGED = MORE PLASMA ENTER; inflammation, allergic reactions
_____ = PULLS fluid BACK into capillaries; DECREASES = LESS FLUID RE-ENTERS; decreased production/loss of plasma proteins
_____ = when this one is blocked, an EDEMA is formed aka _____; most often seen in the LIMBS
pitting test; compression stockings; diuretic therapy; administer albumin
_____ = pressure on a swollen area for 5-15s; GRADE will be dependent on deep it is & quickly it rebounds
GRADE 1 - IMMEDIATE rebound, 2mm pit
GRADE 2 - <15s, 3-4mm pit
GRADE 3 - 15-60s, 5-6mm pit
GRADE 4 - 2-3min, 8mm pit
_____ = increase interstitial fluid pressure; RESISTANCE to outward movement of fluids
_____ = common to other chronic diseases (heart failure, kidney disease)
_____ = used in individuals with liver failure and kidney disease
pulmonary circuit; systemic circuit
_____ = moves blood through the LUNGS; aka central circulation
right ventricle, left atrium, lungs, pulmonary vasculature
_____ = moves blood through the REST OF THE BODY; aka peripheral circulation
left ventricle, right atrium systemic vasculature, peripheral tissues
tunica externa; tunica media, tunica intima
_____ = OUTERMOST LAYER; anchors vessel to surrounding tissues; THICKEST IN VEINS
_____ = MIDDLE LAYER; contains sheets of smooth muscle; THICKEST IN ARTERIES; VASOCONSTRICTION & VASODILATION
_____ = layer that faces the LUMEN/INSIDE of the vessel; single layer of endothelial cells; creates continuous barrier
F = triangle P / R
FORMULA FOR BLOOD FLOW
plaque; occlusion
hardening of the arteries
formation of a _____ within the subendothelial layer of INTIMA of arteries
it contains fats, cholesterol, calcium and cell debris
occlusion
leads to ______ (blockage) of the arteries
leads to more TURBULENT blood flow
MORE TURBULENT = MORE RESISTANCE = SLOWER BLOOD FLOW
HIGHER BP
type of fluid flow w/ eddies and swirls (NON-LAMINAR)
opposes resistance, promotes blood flow (F=△P/R)
leads to INADEQUATE NUTRIENT & O2 DELIVERY
leads to TISSUE WASTING (ATROPHY)
artherosclerosis; resistance
the largest effect that ______ has on blood flow is due to _____
lipoproteins
lipids are primarily transported in circulation as _____
composed of triglycerides, cholesterol, and proteins aka apoproteins)
more associated with ATHEROSCLEROSIS (ApoB-100 → most common)
LDL; HDL
_____ = considered “BAD”; carries cholesterol to cells; if too much cholesterol → buildup of plaque within arteries = atherosclerosis!!
_____ = considered “GOOD”; acts as a “scavenger”; picks up extra cholesterol from blood vessels & carries to liver for processing/removal
familial hypercholesterolemia; ApoB
_____ = inherited condition when individuals have severe levels of circulating cholesterol/LDL
_____ = people with this have a mutation in which protein?
endothelial cell injury, migration of inflammatory cells, lipid accumulation and smooth muscle cell proliferation, development of a plaque
DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS (4) (EMLD)
endothelial cell injury
repeated and multiple injuries to the ENDOTHELIUM
endothelium is disrupted and the subendothelial layer becomes exposed → lipid accumulation increases
migration of inflammatory cells
due to injury, endothelial cells express adhesion molecules to recruit inflammatory cells such as MONOCYTES
monocytes migrates to the intima, matures into macrophages
repairs damaged area
engulf accumulated LDL
lipid accumulation and smooth muscle cell proliferation
macrophages laden with lipid transform into FOAM CELLS
foam cells releases growth factors → causes PROLIFERATION of smooth muscle cell
accumulation DEFORMS the vessel wall (creates ATHEROSCLEROSIS lesion → PLAQUE formation)
development of a plaque; fibrous cap, core, shoulder
consists of smooth muscle cells, immune cells (macrophages, leukocytes) and dense extracellular matrix (connective tissues)
3 COMPONENTS? (FCS)
fatty lesions; fibrous atheromatous plaque; complicated atheromatous plaque
_____ = thin, yellow discolorations; initial, very common
_____ = grey/pearly white; MORE DYSFUNCTIONAL, dangerous → occlusion of vessels can occur
_____ = dark red discoloration; MOST DYSFUNCTIONAL, high risk of ulcerations, hemorrhages, thrombus
thrombus; embolism; stable thrombus; unstable thrombus
_____ = blood clot
_____ = when a thrombus is dislodged & get lodged in a distant vessel that is too small to pass
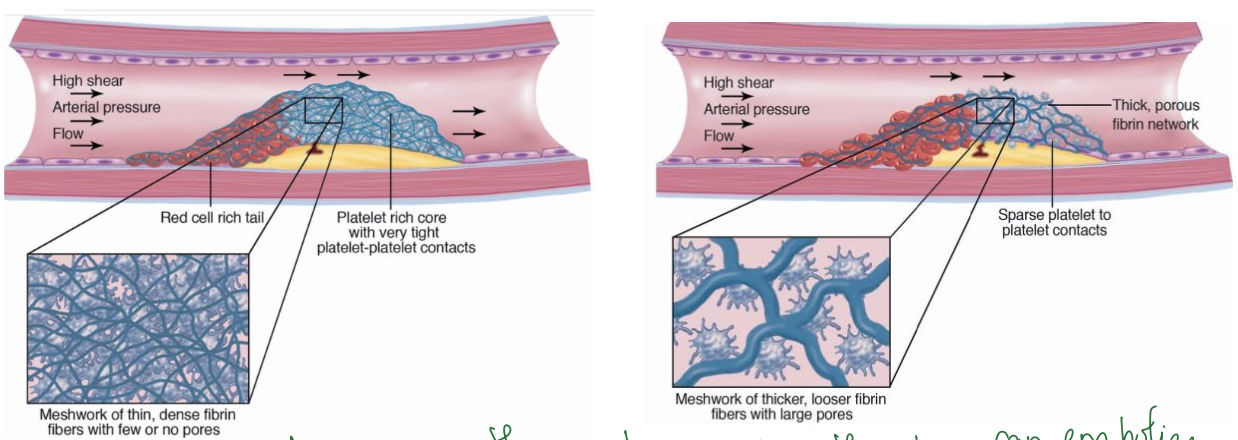
_____ = meshwork of THIN, dense fibrin fibers with FEW OR NO pores; OCCLUSIVE THROMBUS
_____ = meshwork of THICK, looser fibrin fibers with LARGE pores; higher chances can be dislodged; SERIES OF EMBOLISM
statins; HMG-CoA reductase
_____ = main drug class used to treat high LDL/atherosclerosis
it inhibits/blocks _____ → rate-limiting step in the synthesis of de novo (made in the body) cholesterol = LOWERING LEVELS OF LDL
aneurysm; tunica media; aorta
abnormal localized dilation of a blood vessel; abnormal bulge/ballooning
it develops primarily in the _____
MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases) → breaks down extracellular matrix @ the t.m
! STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY OF VESSEL WALL IS AFFECTED !
most common in the _____
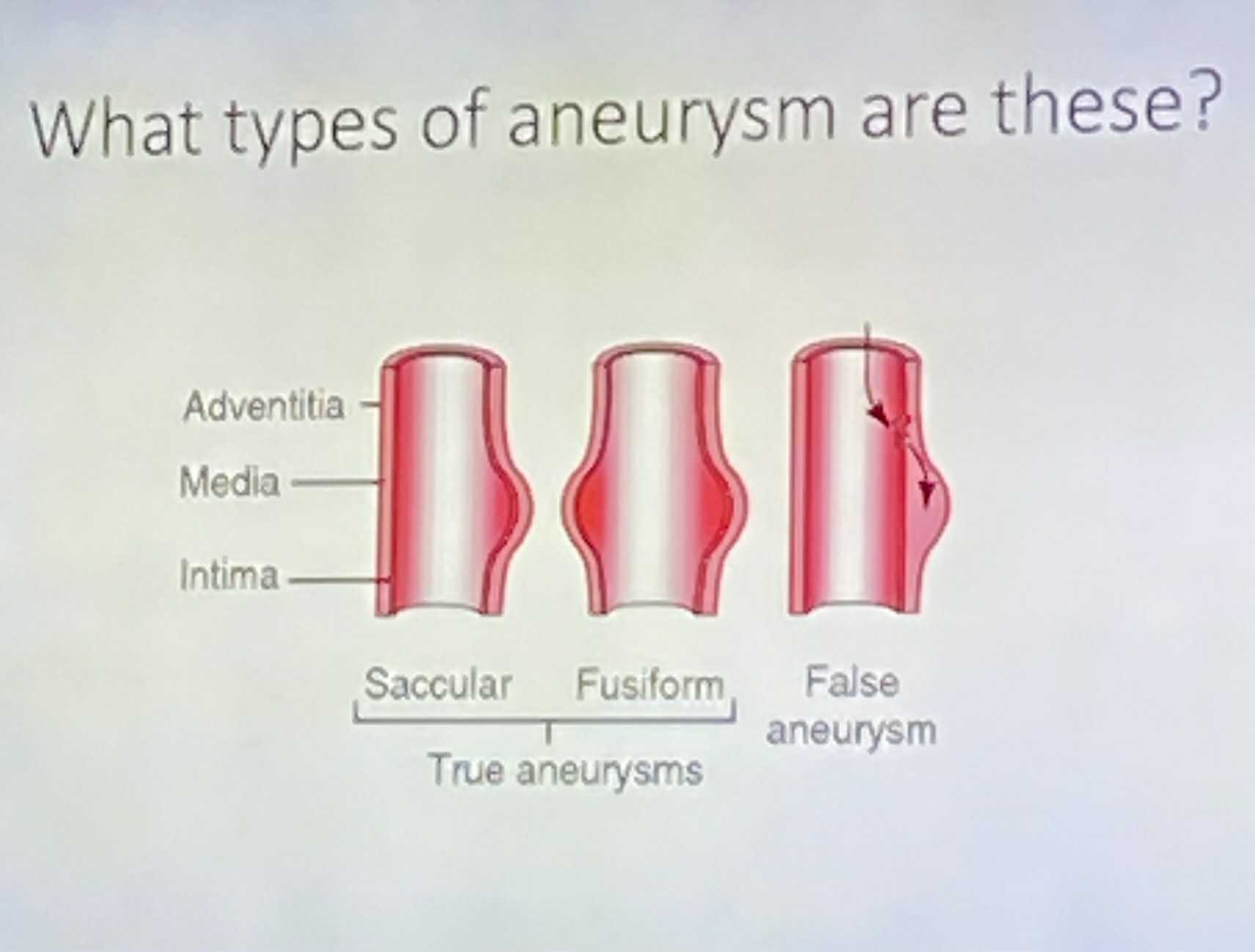
saccular aneurysm; fusiform aneurysm; berry aneurysm; all layers
_____ = weakness on ONE SIDE of the vessel
_____ = weakness on BOTH SIDES of the vessel
_____ = small SPHERICAL dilation of the vessel at a bifurcation
_____ = what layer is FALSE ANEURYSM?
vessel dissection; vessel rupture; aortic dissection; aortic rupture; size dependent
_____ = tearing of the INTIMAL LAYER
_____ = tearing of ALL 3 VESSEL LAYERS
_____ = separation of the layers of the aorta; creates “FALSE LUMEN”
_____ = tearing of ALL LAYERS OF THE AORTA; no lumen
risk of rupture is _____
may also be SEX-DEPENDENT (depends on the diameter & sex)
atherosclerosis/aneurysm, hypertension, connective tissue diseases, blunt chest trauma
WHAT CAUSES AORTIC DISSECTIONS?
- _____ = ulcers and/or thrombus weaken/penetrate aortic walls
- _____ = elevated BP creates wall tension
- _____ = “Marfan syndrome”
- _____ = x
Debakey system; type I; type II; type III
- _____ = most used for aortic dissection
- _____ = involve the ASCENDING/DESCENDING aorta; 60% of cases
- _____ = involve the ASCENDING aorta only; 10-15% of cases
- _____ = involve the DESCENDING aorta only; 25-30% of cases
symptoms of aortic aneurysm/dissection/rupture
severe chest/upper back pain
severe stomach pain (abnormal aortic aneurysm)
loss of consciousness
shortness of breath
similar symptoms of stroke
leg pain
difficulty walking
medical management; surgical treatment; open; tevar
_____ = anti-hypertensive medication, lipid lowering therapies “STATINS” (drug)
_____ = open heart surgery, TEVAR (thoracic endovascular aortic repair), Hybrid (open & minimally invasive)
_____ = placement of a graft as false vessel by opening the chest & blocking blood flow while repaired
_____ = placement of a graft using a catheter (minimally invasive because no opening of chest)
<5.0cm; >5.5cm; grey zone
_____ = surgery NOT RECOMMENDED → medical management
_____ = surgery RECOMMENDED to replace the aorta
_____ = aorta BETWEEN 5.0-5.5
Anatomy; Pathology; Physiology; Pathophysiology
_____ = identification & description of the body structures of living things
_____ = study of structural & functional changes in cells, tissues, and organs
_____ = functions of the human body under normal conditions
_____ = how disease states affect body function
abdominal aorta and iliac arteries, coronary arteries
2 SITES OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS?