Motor Control Assessment
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is motor control?
The ability to regulate or direct the mechanisms essential to movement
Motor learning theory
relatively permanent changes in performance due to practice or experience
What three systems does movement emerge from?
1) Sensory/perceptual
2) Cognitive
3) motor/action system
Spinal cord for motor control
Lowest level of motor control hierarchy, voluntary control of the body
What information does the brainstem process?
Somatosensory information
What part of the brain carries out the motor plan?
Cerebellum
What are the sensorimotor areas of the cerebral cortex?
Primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, supplementary motor area, and parietal cortex
What brain centers do the UMN connect to?
Basal ganglia and cerebellum
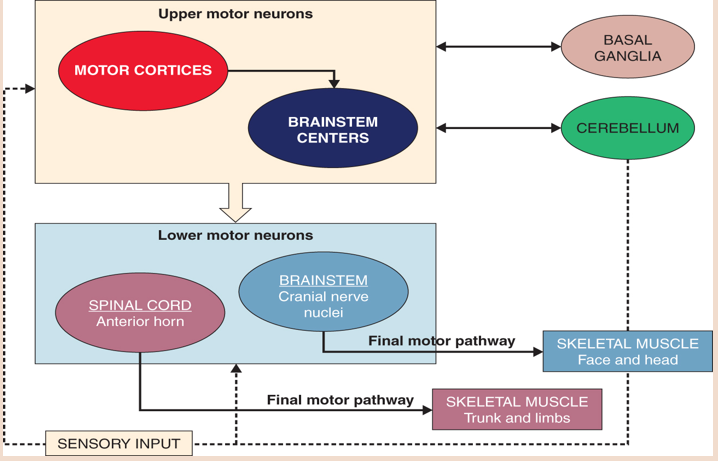
What brain centers do the LMN connect to?
Brainstem and spinal cord, signaling skeletal muscle → trunk, limbs, face, and head
What do higher levels in hierarchical processing do?
Planning and programming movement
What do lower levels in hierarchical processing do?
Carry out head, face, trunk, and limb movement.
What is parallel processing?
Involves multiple brain regions that simultaneously process the same signal
What brain center is the highest level? What does it do?
Cerebral cortex; controls sensorimotor areas and primary motor cortex
What brain system is the lowest level? What does it do?
Spinal cord; sends reflective and voluntary control of posture and limb movements
What does the brainstem do?
Regulates posture and movement. Also contains cranial nerve nuclei that receive somatosensory information from head and face and control motor output to the neck, head, and face muscles.
What does the cerebellum do?
Receives information from cerebral cortex about intended motor plans and compares that information with sensory information received from spinal cord and brainstem
What does the basal ganglia do?
Receives input from many cerebral cortex areas and sends information back to cerebral cortex motor areas to modulate UMN activity.
Apraxia
Inability to perform purposeful movements despite having the desire and physical capability to do so. Ex. Difficulty maintaining the orientation of grooming objects towards the body.
Ataxia
Lack of coordination and balance. Ex. Not able to coordinate reach patterns during bathing or leisure activities.
Bradykinesia
Slow movements, increased time needed to perform daily activities.
Chorea
Flailing limbs
Dysmetria
Overshooting or undershooting items when attempting to retrieve them from cabinets
Hypotonicity
Decreased ability to maintain an upright posture or standing position
Intention tremor
Contractures that get worse as the individual approaches a target. Ex. Spillage of food during feeding
Paresis
Weakness or partial loss of voluntary movement. Ex. Decreased ability to stabilize or manipulate grooming objects
Spasticity and rigidity
Tension in muscles creating stiff movements. Ex. Difficulty placing the affected limbs into clothing during dressing
What are UMN signs caused by?
Damage to cell body or axons proximal to anterior horn cells in spinal cord.
What LMN signs caused by?
Damage to cell body or axons distal to anterior horn cells in spinal cord.
UMN Signs
Spasticity
Hypertonicity
Hyperreflexia
+ Babinkski
Paresis
Plegia
Disuse atrophy
LMN Signs
flaccid paralysis followed by atrophy
fasciculations
hyporeflexia or areflexia
hypotonia
Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS)
Measures motor skills in natural settings using client-chosen occupations. Therapists evaluate motor and process skills within context of basic and IADLs.
Motor Assessment Scale
Performance-based measures that evaluates motor function as it relates to everyday life. Evaluate eight areas of motor function.
Action research arm test (ARAT)
Quick and easy assessment that uses simulated everyday activities to evaluate upper limb function
Wolf Motor Function Test
Document outcomes related to upper limb interventions and included a variety of tasks such as basic reaching tasks and functional activities involving fine motor control
Motor Activity Log
Self-report questionnaire related to use of involved UE outside structure therapy time - uses semi-structured interview format
Muscle tone
involuntary resistance of muscle to passive stretch.
What does normal muscle tone rely on?
Neural factors and mechanical
Characteristics of normal muscle tone?
Feeling of slight resistance to passive joint movement, and ability to maintain body part position against gravity
What does normal postural control allow for?
Steady states in sitting and standing, reacting to perturbations to balance and in prevention of falls
What are two assessments of postural control that OTs could use?
Berg balance scale and functional reach test.
Coordination
ability to produce accurate, smooth, and controlled movements
How is paresis assessed?
OT observes resting posture of the limbs and trunk and by assessing patients’s ability to produce voluntary movement during ADL performance
What are assessments for coordination?
Finger-to-nose, finger-nose-finger, pronation/supination, mass grasp, finger opposition, tapping, heel-shin, box and blockes, purdue pegboard test, nine hole peg test