Tandem Repeats and RFLPs
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
Tandem repeats
Sequences of nucleotides that repeat, occurring one after the other in an uninterrupted fashion
2
New cards
Where are tandem repeats found?
In prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes in coding and non-coding regions
3
New cards
Tandem repeats differ in?
Length as well as in the number of repeats
4
New cards
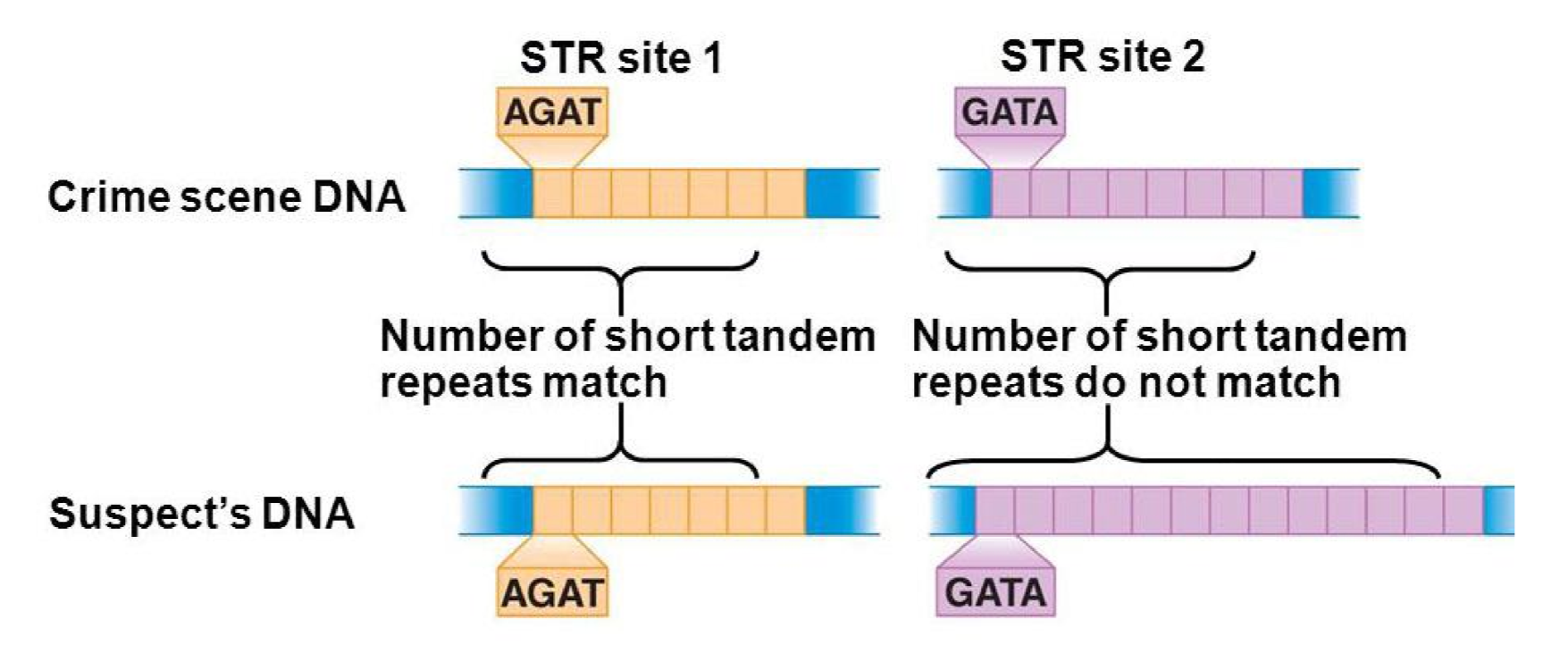
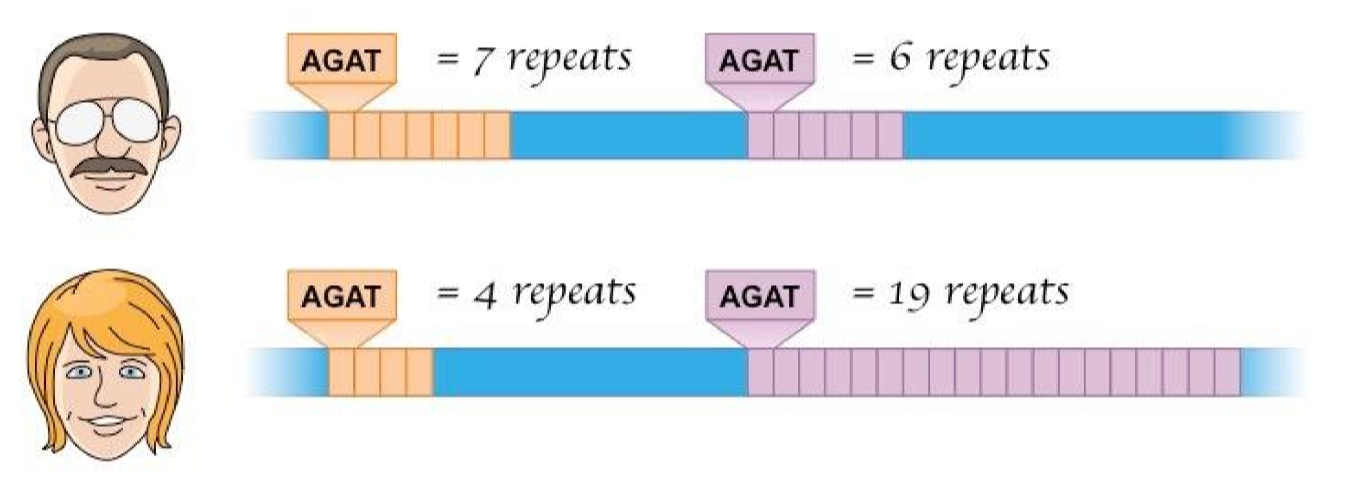
From one person to another, what is the same, and what varies?
* The repeated sequences are the same
* The number of times they repeat varies
* The number of times they repeat varies
5
New cards
What are the two types of tandem repeats?
* Short tandem repeats (STRs)
* Variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs)
* Variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs)
6
New cards
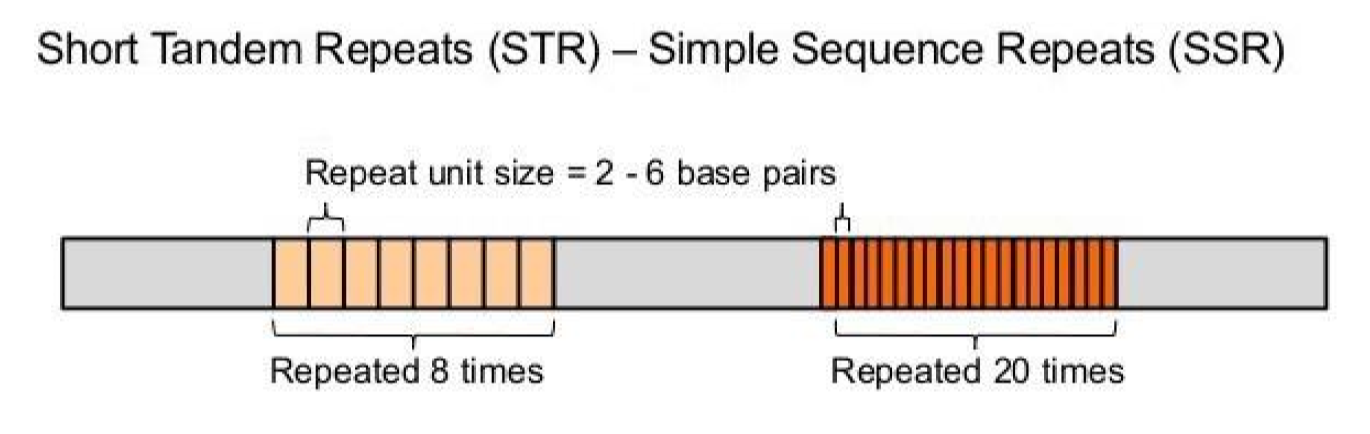
STRs
* Short tandem repeats
* 2-10 nucleotides
* May be repeated several dozen times
* 2-10 nucleotides
* May be repeated several dozen times
7
New cards
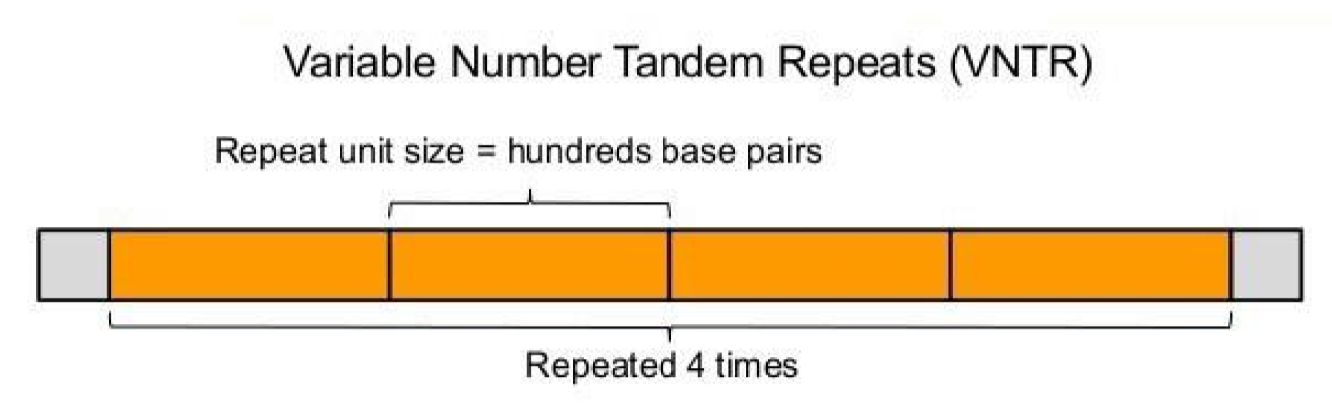
VNTRs
* Variable number tandem repeats
* 10-100 nucleotides
* Much longer than STRs
* 10-100 nucleotides
* Much longer than STRs
8
New cards
What is the difference between STRs and VNTRs
The number of times each unit is repeated
9
New cards
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLPs) refer to:
Restriction fragments that differ in size from each other
10
New cards
Restricting DNA in haploid and diploid (polyploid) species will frequently yield fragments of ? sizes in different individuals
1. varying
11
New cards
What are the causes of RFLPs?
1. Point mutations
2. Large-scale insertions and deletions
1. Transposable elements
2. Tandem repeats
3. Translocations
12
New cards
What are some applications of RFLPs
* VNTRs are used for DNA fingerprinting
* STRs are used in law enforcement
* STRs are very similar between closely related individuals
* Unrelated individuals are extremely unlikely to carry the same STRs
* STRs are frequently used in genealogical and paternity tests
* They can be used to identify the presence of genetic (and thus heritable) diseases
* VNTRs can be used to determine the origin of an outbreak
* RFLPs can be used to measure genetic divergence between different populations or related species
* Measure of the total number of RFLP differences represents a measure of genetic difference
* RFLPs are important in studies of evolution
* STRs are used in law enforcement
* STRs are very similar between closely related individuals
* Unrelated individuals are extremely unlikely to carry the same STRs
* STRs are frequently used in genealogical and paternity tests
* They can be used to identify the presence of genetic (and thus heritable) diseases
* VNTRs can be used to determine the origin of an outbreak
* RFLPs can be used to measure genetic divergence between different populations or related species
* Measure of the total number of RFLP differences represents a measure of genetic difference
* RFLPs are important in studies of evolution