Botany 2 exam 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Taxonomic classification
Life
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Closely related species are grouped together into a _____
genus
Phylum/Division ending
-ophyta
Class ending
-opsida
Order ending
-ales
Family ending
-aceae
DNA replication —> transcription into RNA —> translation into proteins
transcription happens in the nucleus
translation happens in the ribosomes
Two different gene region types
Exons: Sequences of nucleotides that are eventually expressed as amino acids in proteins
Introns: sequences of nucleotides that are not transcribed, but are in-between exons
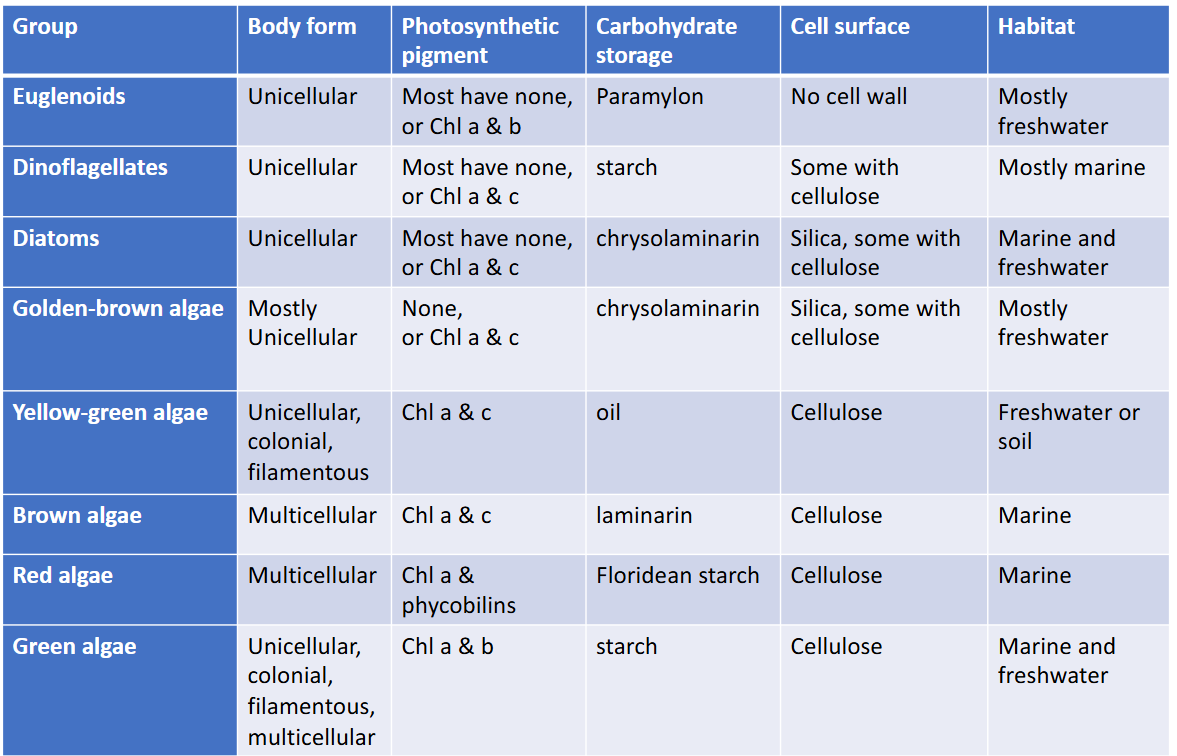
Brown algae have a variety of pigments called _______
xanthophylls
Where are eggs localized in Marchantia
archegonium
male reproductive cells in liverworts & mosses:
antheridium
Hornworts striking feature?
presence of a single large chloroplast in each cell opposed to numerous small plastids present in other nonalgal plants
DNA forms complex with proteins called _____
histones
Viridiplantae is a _____phyletic group
mono
group contains all descendants of their common ancestor
When reproductive algae cells are released only the ____ remains
cell wall
Sporangia and gametangia of plants are….
After they are released a ___________ remains
multicellular reproductive organs (only the inner cells differentiate into spores or gametes)
layer of sterile cells remain
Taxonomy-
principle that systematically identifies, names, and classifies organisms based on shared traits
systematics-
uses taxonomy, evolutionary history, and knowledge of environmental adaptations to understand the diversity of life
All organisms are grouped into three domains:
bacteria, archaea, and Eukarya
Artificial classification
based on a few characteristics; often do not share a close common ancestor
Natural classification
groups organisms together based on maximum number of natural characteristics
Phylogenetic classification
based on organism’s evolutionary history, as determined by DNA analyses
Modern classification systems use a combination of natural and phylogenetic classification*
Cladistics
They have descended from a common ancestor
similar features are synapomorphies (homologous features)
They have undergone convergent evolution
features like this are homoplasies (analogous features)
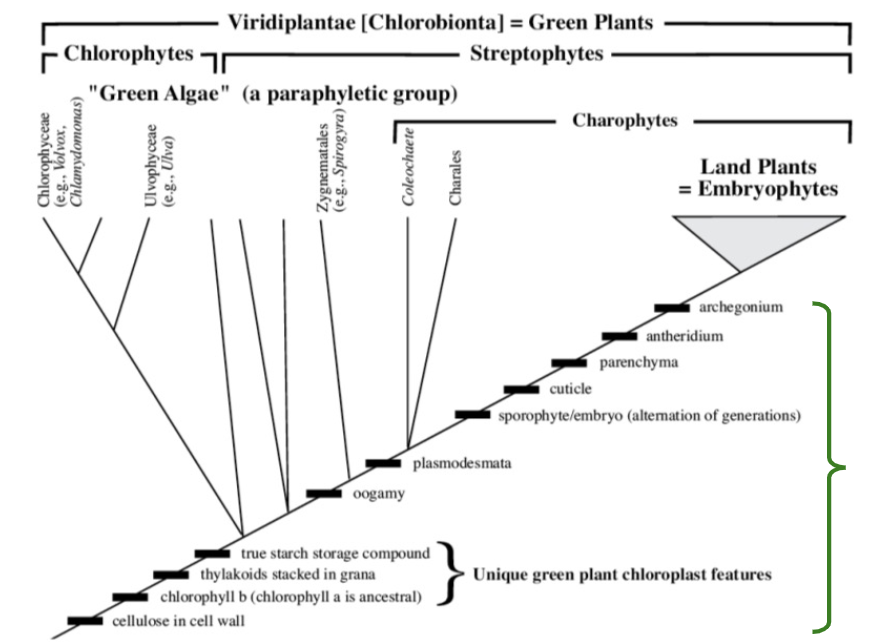
*Cyanobacteria: blue-green “algae” are prokaryotes (aka not closely related to other algae)
Division Chlorophyta and (part of) Stretophyta
green algae
Division Rhodophyta
Red algae
Division Chrysophyta
diatoms, golden-brown algae, yellow-green algae
Division Phaeophyta
brown algae
Algae are a ___phyletic group
poly
contains members that do not share a recent common ancestor
Unicellular algae body type
Chlamydomonas, Micrasterias
Colonial algae body type
Pediastrum, volvox
Filamentous algae body type
spirogyra
Multicellular algae body type
ulva
Liverworts= division _____
Mosses= division ______
Hornworts= division _____
Marchantiophyta, Bryophyta, Anthocerotophyta
Embryophytes are a ____phyletic group
mono
group contains all descendents of their common ancestor
For plants to survive on land they need…
A cuticle to prevent from drying up
to absorb & retain water
to protect their gametes & sporocytes
Synapomorphies shared by all embryophytes
Archegonium & Antheridium
Parenchyma
Cuticle
Sporophyte/embryo
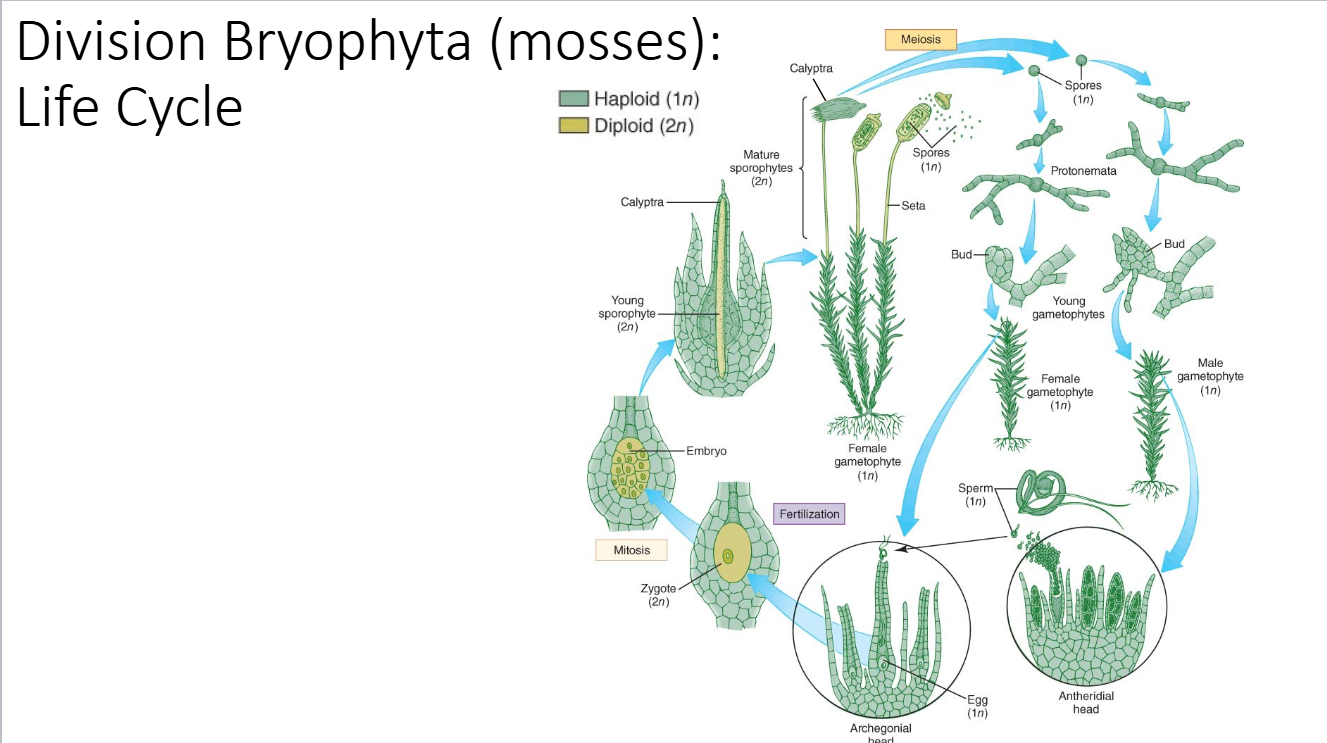
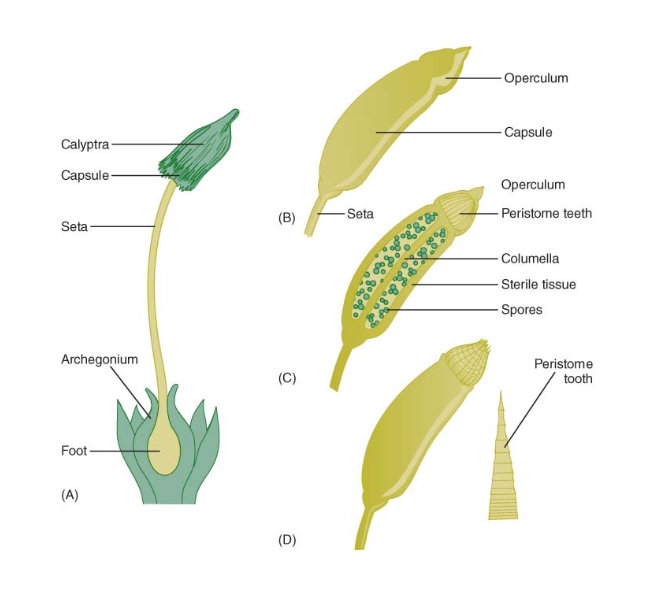
Bryophyta ecology
small size and no conducting tissues
non-vascular plants
inability to retain water
many mosses thrive at low temps near or below 0 degrees C-
can grow on hard, impervious surfaces because they have no roots that require substrate penetration
Selective mutations
upright body that grow into brighter light
production of pollen in seeds, to eliminate water for reproduction
vascular tissue allows for evolution of complex tissues and organs
“-gameto”= _____, -”phore”= ____
gamete, carrier/producer
When bryophytes spore germinates it divides via mitosis to forma filamentous _____, the beginning of the multicellular gametophyte body
protonema