Final Study Guide
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What does Cephalic Angle mean?
The tube is angled towards the head
What does Caudal Angle mean?
The tube is angeld towards the feet
What does projection mean?
The positioning term that describes the direction or path of the CR of the x-ray beam as it passes through the patient, projectin an aimage onto the IR. Ex. PA, AP, Oblique
What does position mean?
The general body’s position and specific body positions
What are the general body positions?
Supine, Prone, Erect, Recumbent, Trendelenburg, Fowler, Sims, Lithotomy
What are the specific body positions?
Lateral, Oblique, LPO, RPO, RAO, LAO, Decubitus, Right/Left Decub AP or PA, Dorsal Decub Left/Right Lateral, Ventral Decub Right/Left
Where do you center at for PA Chest
At T7
Where do you center for AP Chest?
3-4 inches below from jugular notch which should be T7 level
What are you looking for in a PA/AP chest?
Lungs, Clavicles, Apices, costophrenic angles, 10 ribs minimum
What are you looking for in a Lateral Chest?
Lungs, Apices of lungs, costophrenic angles, sternum anteriorly, posterior ribs with no rotation,
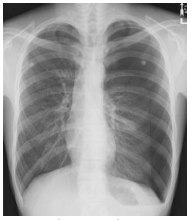
What chest projection is this?
PA Chest
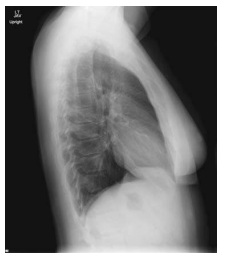
What chest position is this?
Lateral
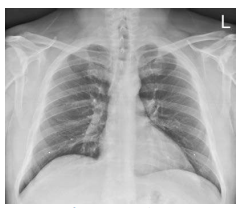
What projection is this?
AP
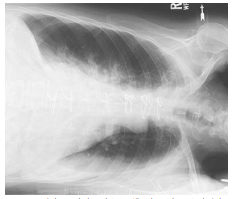
What projection/position is this?
Left Lateral Decubitus (AP)
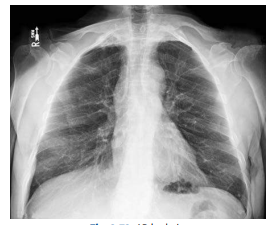
What projection is this?
AP Lordotic
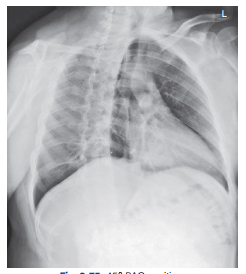
What positions is this?
RAO
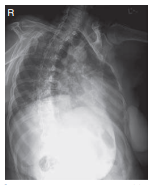
What position is this?
RPO
What is a routine abdomen include?
KUB
Whats included in a routine acute abdominal series.
AP Supine, AP Erect, PA Chest.
How is patient positioned for KUB/AP abdomen? Where is the CR at?
Patient is supine with arms away from the body. CR is perpendicular and center is at the level of iliac crest
How is patient positioned for AP Erect abdomen? Where is the CR at?
Patient is standing (for a minimum of 5 mins) and arms away. CR is 2” above the iliac crest.
What breathing technique for abdomen?
Exposure made at end of expiration
kvp range for abdomen?
70-85.
For AP/PA, PA Oblique/lateral thumb where is the CR located at?
First MCP
For AP axial thumb where is the CR located at.
At the first CMC joint with a 15 degree angle. For Lewis, you are using a 10-15 degree angle at MCP.
For an oblique hand, what angle should the hand be at
45 degree, no angle
Where should the CR be at for an oblique hand?
Third MCP joint
What should you be looking for in a oblique hand?
Third/Fourth/Fifth midshaft metacarpals aren’t overlapping, MCP and IP joints open w/o foreshortening, fingers parallel to the board
Whats the kvp range for PA Wrist?
55 to 65
Whats the kvp range for Oblique/Lateral Wrist?
60 to 70
Where is the CR for PA (AP), oblique and lateral wrist?
Midcarpal area (middle of wrist)
Where should the collimation field be field for these wrist projections?
Slightly pass MCP joints and seeing distal radius/ulna.
Whats visualized in an oblique wrist?
Trapezium and scaphoid should be visualized with slight superimposition of other carpal bones
To reduce OID for a thumb x-ray, would you use an AP or PA?
AP. If you did a PA, your thumb is naturally in an oblique position.
To reduce OID for 2nd/3rd fingers, what projection should you do?
Lateromedial Projection
To reduce OID for 4th/5th fingers, what projection should you do?
To reduce OID for the wrist, would you do AP or PA?
PA since the wrist has a natural arch so there would be increased OID
Whats kvp range for a lateral elbow?
65 to 75.
How should the elbow be positioned for a lateral elbow.
Elbow joint at center of IR, humerus and forearm should be at the same level, flex elbow/forearm into 90 degrees, rotate hand and wrist into a lateral position, thumb up.
Where is the CR at for the lateral elbow?
Mid-elbow joint (easy to palpate.
Whats the kvp range for AP, Lateral humerus.
70-85
How should an AP humerus be positioned?
Arm should be in AP position, extend arm away from body
How should the epicondyles be positioned for an AP humerus
Parallel to the IR
Where should the CR be for AP Humerus?
Midpoint of humerus and match humerus angle.
How should the epicondyles be positioned for an lateral Humerus?
Perpendicular to the IR.
What is the kvp range for ankles?
60-75
What are the two oblique positions for the ankle?
Mortise and Oblique
How much rotation is required for a Mortise projecton?
15 to 20 degrees
How much rotation is required for an oblique ankle projecton?
45 degrees
What view shows only the laterial and superior view of the mortise?
Oblique
What view shows the lateral, superior and medial view of the ankle?
Mortise
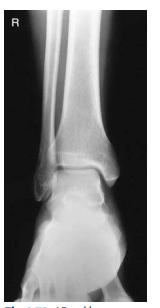
What ankle view is this?
AP
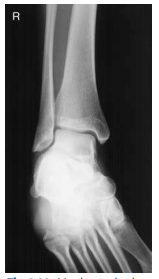
What ankle view is this?
Mortise
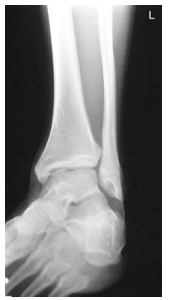
What ankle view is this?
Oblique
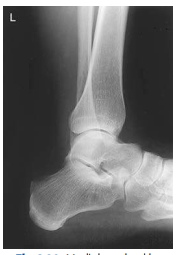
What Ankle view is this?
Mediolateral Ankle
Anatomical landmarks of the ankle consist of
Distal Tibia/Fibula and Talus
Whats the kvp range for Ap, obliq, lateral knee?
65-80
Where is the CR placed for an AP that has an average thigh and buttocks?
CR at 1/2” below the apex of patella with 0 degree angle.
Where is the CR placed for an AP that has an thin thigh and buttocks?
CR at 1/2” below the apex of patella with 5 degree caudad angle
Where is the CR placed for an AP that has an thick thigh and buttocks?
CR at 1/2” below the apex of patella with 5 degree cephalad angle
How is an AP knee positioned?
Leg in AP position, rotate internally 3 to 5 degrees for a true AP or untill interepicondylar line is parallel to plane of IR.
How is a lateral knee positioned
Have the patient rotate their body so the knee is in a lateral position, flex the knee 20-30 degrees, angle the tube 5 to 7 degrees cephalad and place CR 1” distal (toward ankle) to medial epicondial
What joint space opens up with the AP/Oblique/Tunnel/AP Axial Knee?
Femorotibial Joint Space
What joint space opens up with the Lateral Knee?
Patellofemoral Joint
For an AP Axial Outlet projection, where is the CR placed?
tube angled 20 to 35 degrees for males and 30 to 45 for females (cephalad angle), then CR is at 1-2 inches below the top of the symphis pubis or at the level of the greater trochanter
For an AP Axial Inlet projection, where is the CR placed?
Tube angeld at 40 degrees cauded and at the level of ASIS
For an Pelvis - Acetabulum (Judet), where is the CR placed if the affected side is down?
CR perpendicular starting on ASIS that is down, you go 2” distal and then 2” medial.
For an Pelvis - Acetabulum (Judet), where is the CR placed if the affected side is up?
CR perpendicular starting on ASIS that is up, you go 2” distal.
For an Pelvis - Acetabulum (Judet) (Pelvic Ring), where is the CR placed?
CR perpendicular starting on ASIS that is up, you go 2” distal and 2” medial.
For PA Axial Oblique: Acetabulum (Teufel Method), where is the CR Placed
tube is agled 12 degrees cephalad and CR is 1” superior to the greater trochanter (approximately 2” lateral to midsagittal plane)
Standard hip projections*******
Prosthetics*********
External rotation for a shoulder AP will show
The greater tubercle in profile
Internal rotation for a shoulder AP will show
the lesser tubercle in profile
Positioning steps for Neutral Rotation: Shoulder (Trauma)?
Patient’s arm is in a neutral position, CR is at the mid-scapulohumeral joint (3/4” inferior and slightly lateral to coracoid process).
Positioning steps for PA Oblique Scapular Y View (Trauma)?
Rotate patient (either RAO or LAO), palpate the superior angle of the scapula and AC joint articulation, abduct arm slightly if possible, CR is directed to scapulohumeral joint
Positioning steps for Tangential Projection - Supraspinatus Outlet Shoulder (Neer) (Trauma)
Same as Y view, but the CR is angled 10–15° caudally, centered at the superior margin of the humeral head
Positioning steps for AP Apical Oblique Axial: Shoulder (Trauma)
Patient is RPO or LPO, CR is angled 45 degrees and centered at the scapulohumeral joint, Collimate closely.
Whats the clinical indication for Y View?
To see dislocation of proximal humerus and scapula.
What are you looking for in a Y view?
The body of the scapula and the acomion and coracoid process. Humeral head is superimposed.
For AP Axial Clavicle, what is the angle for this projection?
15 to 30 degree cephalad to midcalvicle.
Why are multiple projections required for x-ray?
You might see the injury in a different view.
AP vs PA Imaging Tech: AP
Heart is magnified, higher dose to thyroid/breast, scapulae cover lungs
AP vs PA Imaging Tech: PA
Heart is accurate size, low dose to thyroid/breast, scapulae removed from lungs.
What are the eight Carpal bones?
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
What is the most fractured carpal bone?
Scaphoid
What are some other injuries for carpals?
Lunate dislocation, triquetral fracture, hook of hamate fracture.