Palmer- Spinal- Exam 1 Learning Objectives
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What are the primary and secondary curvatures
primary: thoracic and sacrococcygeal region, curve points posteriorly. AKA kyphotic, posterior curves
secondary: cervical and lumbar region, curve points anteriorly. AKA lordotic, anterior curves
Lordotic curve is formed by greater ______________ than ______________ IVD height in cervical and lumbar reigions
anterior; posterior
primary curvature is formed from the difference of
vertebral bodies
secondary curvature is formed from the difference of
IVD
what are the typical lateral curvatures of the spine
Upper thoracic and lumbar regions due to handedness, genetics and environmental factors
What causes lateral curvatures? (TQ)
deviations result from asymmetrical muscle tone
Describe the intervertebral disc (IVD) functions
Function:
-attach and separate vertebral bodies from each other
- help form the spine
-act as a powerful ligament
- forms anterior border of vertebral canal and IVF
-shock absorber
what are the components of the IVD
-nucleus pulposus (water, collagen, proteoglycans)
-annulus fibrosus (Type 1/2 collagen)
IVD height diminishes with...
age
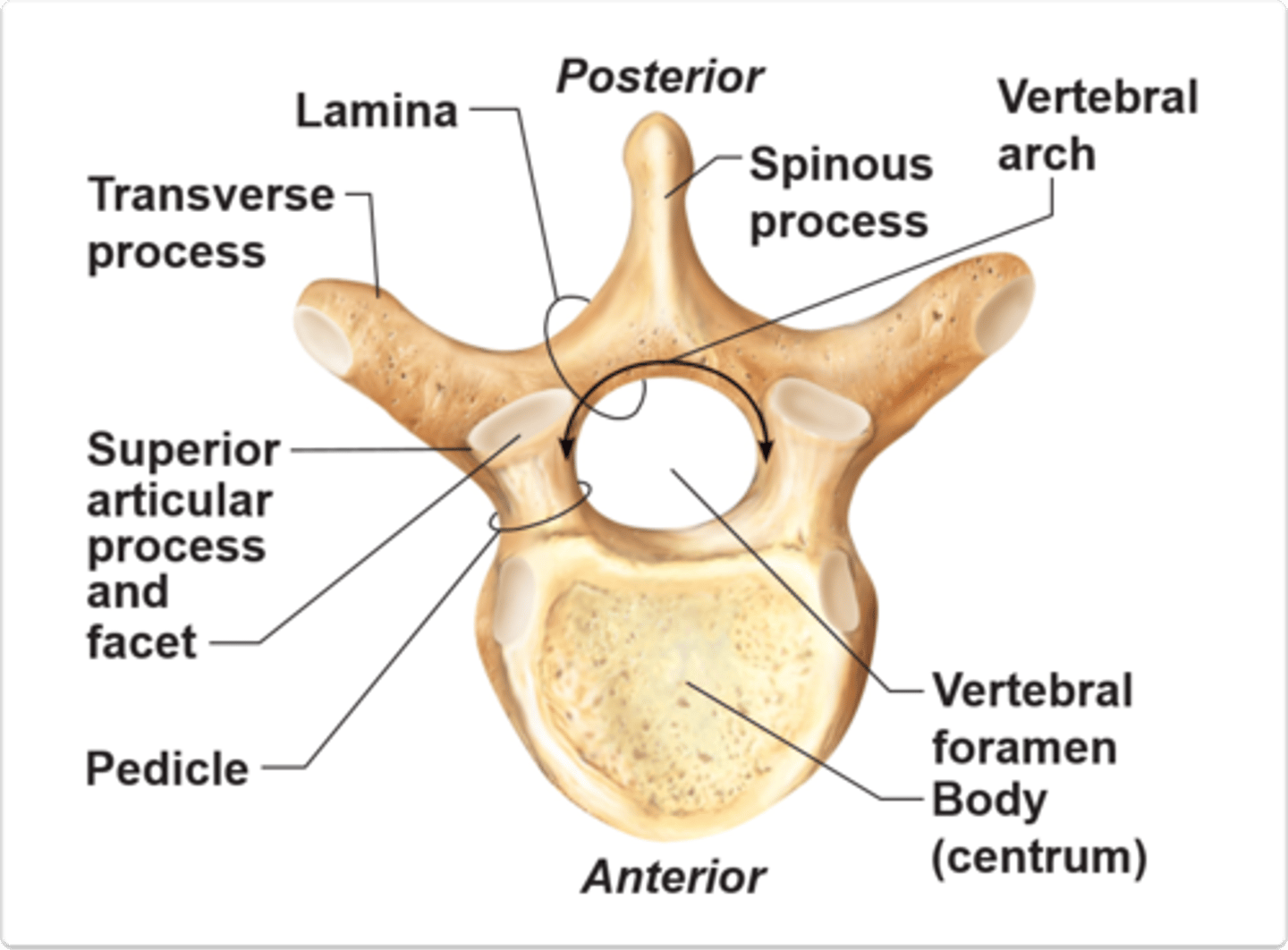
What is the general anatomical features of a typical vertebrae? (12)
-Superior and inferior epiphyseal rim
-Pedicle
-Body
-Vertebral Arch
-Vertebral foramen
-Lamina
-Superior and inferior vertebral notches
-Transverse process
- Transverse tubercle
- Spinous process
- spinous tubercle
-Superior articular process AND facet
which somites give rise to the vertebral column
sclerotomes
what are perichordal discs and intrasclerotomal fissures? What do they give rise to?
perichordal discs: embryonic IVD that arise from intrasclerotomal fissures
intrasclerotomal fissures: between scleotomites or a perichordal blastema. Divides perichordal blastema (marshmellows) into two parts
How many pairs of chondrification centers of there on a typical vertebrae? Where are they located (TQ)
3 pairs (6 total)
1 pair in the neural arch
1 pair for L/R transverse processes
1 pair in the centrum (body)
TQ- What is the order of ossification for vertebrae
membranous-->Chondrification-->ossification (bone)
membranous vertebral blastema is the same thing as ?
perichordal blastema
how many primary center of ossification are there? Where are they?
3 total
1 in the centrum (body)
2 in the neural arch
primary centers grow toward each other and cartilage decreases until small ___________ _____________ joints remain
cartilage synchondrosis
synchondrosis (cartilaginous joint) formed between the centrum and neural arch is called
Neurocentral synchondrosis
how many secondary center of ossification are there? Where are they? (TQ)
5 total
2- superior/inferior epiphyseal plate
2 tips of transverse processes
1 tip of spinous process
C1 spinal nerve exits ____________C1 vertebrae
above
How many cervical vertebrae are there? Cervical spinal nerve?
7 vertebrae, 8 cervical spinal nerves
C8 spinal nerve exits______________ C7 vertebrae
below
T1 spinal nerve exits _____________ T1 vertebrae
below
Explain the arteries within the spinal canal (TQ) (6)
Segmental arteries- from aorta
Spinal Branch arteries- mixed spinal nerves
Medullary (Feeder Arteries) - supply Ant/Post spinal artery
Anterior spinal artery- only 1
Posterior spinal arteries- 2
radicular arteries- supply rootlets
Explain the veins within the spinal canal (TQ)
Internal vertebral venous plexus
anterior and posterior spinal veins
basivertebral venous foramina- provides venous return
Describe meninges of the spinal canal
Dura Mater- tough external layer
Arachnoid mater- web-like real space filled with CSF
Pia Mater- adheres to spinal cord
Describe the spaces of the spinal canal (TQ)
(know where CSF is flowing and what meninges they are between TQ)
Epidural space- external to the dura, filled with fat
Subdural space- potential space between dura and arachnoid
Subarachnoid space- between arachnoid and pia and contains CSF
which ligaments forms the anterior and posterior boundaries of the spinal cord AND where they attach. TQ
anterior boundary: posterior longitudinal ligament attach tightly to bodies and IVD
posterior boundary: ligamentum flavum, attach to lamina
What action does the PLL prevent
prevents hyperflexion and posterior spinal disc herniation
What action does the Ligamentum Flavum prevent and allow?
allows for upright posture
straightens column after flexion
prevents hyperflexion
What is the purpose of the filum terminal and what is it derived from?
Anchors cord to the sacrum and coccyx and prevents vertical movement
derived from the pia mater
What is the filum terminal an extension of (TQ)
Pia mater
which spinal cord anchor prevents vertical movement?
Filum Terminal
What is the purpose of the denticulate ligaments and what is it derived from?
Anchors the cord laterally to prevent side to side movement
derived from the pia mater
What is the embryonic development of the nucleus pulposus (TQ)
embryonic notochordal tissue becomes the nucleus pulposus
What are IVDs developed from
notochord and sclerotomes
what is the annulus fibrosis developed from
somatic mesenchyme surrounds notochordal cells
what is a mechanism the body has to respond to stress on IVDs
osteophytes (bone spurs) to stabilize segements
describe the composition cartilaginous end plates (TQ)
composed of Hyaline (at centrum) and Fibrocartilage (at IVD)
describe the function cartilaginous end plates (TQ)
-prevents centrum (VB) from undergoing atrophy and pressure
-keeps IVD withing anatomical borders
-extremely porous for diffusion of gases, nutrients and waste material
What is the joint classification of the IVD (100% TQ)
Cartilaginous (amphiarthrosis) symphysis joint
What are the three different innervations of the IVD (posterior, anterior, lateral) and what are the "aka" terms. (100% TQ)
Posterior: sinu-vertebral nerve (aka recurrent meningeal nerve)
Lateral: gray ramus communicans
anterior: sympathetic branches/sympathetic trunk ganglia
posterior outer 1/3 of the annulus fibrosis receives innervation from? (TQ)
sinu-vertebral nerve (aka recurrent meningeal nerve)
What are the boundaries and contents of IVF (intervertebral foramina) (100% TQ)
Superior
Inferior
Anterior
Posterior
Superior: inferior vertebral notch (aka pedicles) or segment below
Inferior: superior vertebral notch of the segment below
Anterior: IVD, vertebral bodies, PLL
Posterior: Pre/post zygophophyseal joints, capsular ligament, ligamentum flavum
Describe the artery of Adamkiewicz, where it enters and what it is a principle supplier to
the Anterior medullary feeder artery!!
-enters T9/10
- ONLY major arterial supply to the anterior spinal artery
-Principle supplier of lumbar enlargement (L2/L3)
75% of thoracic IVD herniations occur below t8 which can compromise artery
The principle supplier of the lumbar enlargement (L2/3) is?
artery of adamkiewicz (anterior medullary feeder artery)
Explain the neural contents of the IVF (100% TQ)
Neural tissue:
- Ventral and dorsal nerve roots
- dorsal root ganglion (DRG)
- Mixed spinal nerves)
Explain the arterial contents of the IVF (100% TQ)
Arteries:
- spinal branch arteries arising from segmental artery (puserior/posterior intercostal arteries)
several branches given off before entering IVF: osseous branches and anterior/posterior spinal plexus
Explain the vein contents of the IVF (100% TQ)
intervertebral veins in epidural space
external vertebral venous plexus (Batson's plexus)
drains into segmental vein
Explain the lymphatic contents of the IVF (100% TQ)
Lymphatic capillaries in epidural space
Which transforaminal ligament attaches vertebral bodies to inferior articular processes of the same vertebrae?
superior transforaminal ligaments
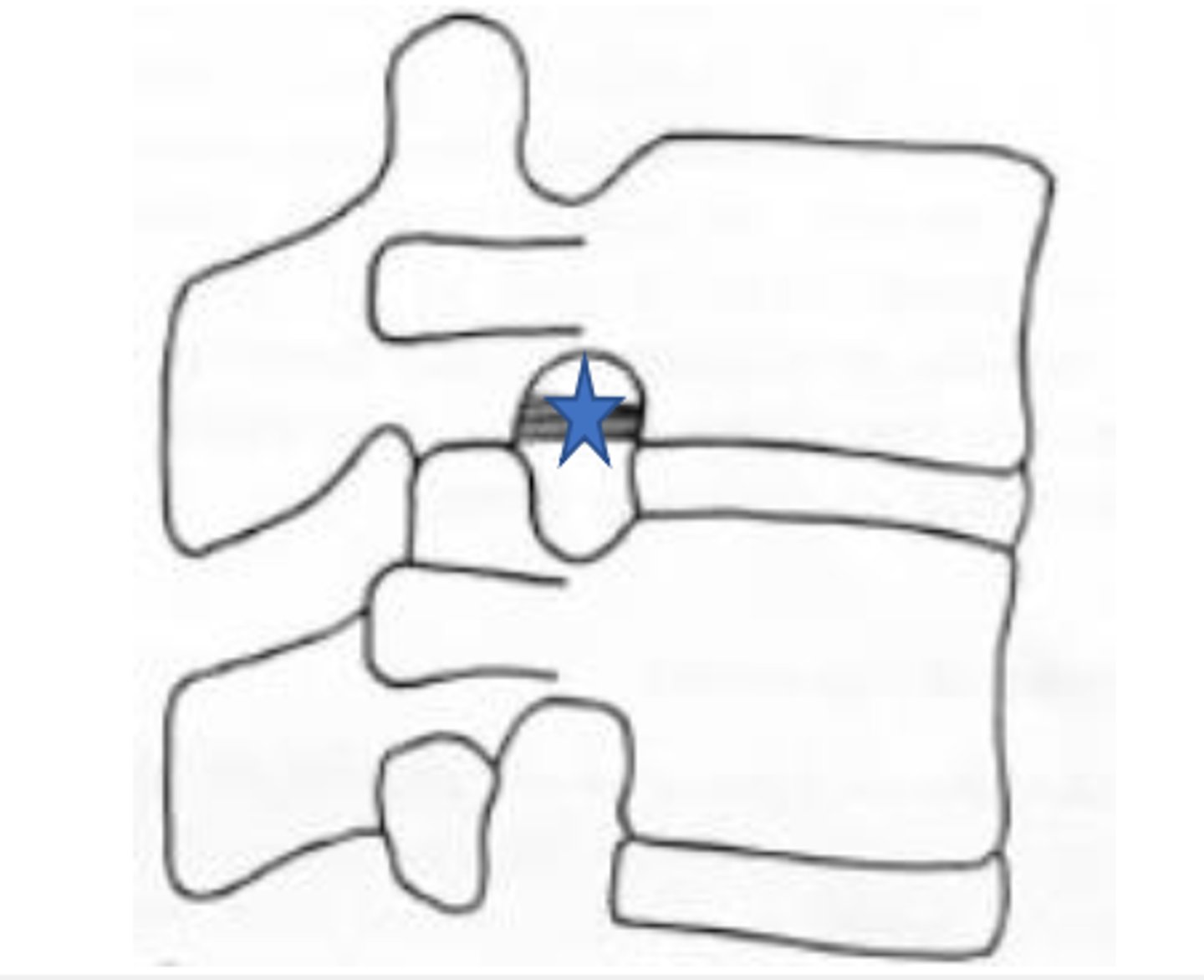
which transforaminal ligament attaches IVD to inferior articular processes of the segment above?
Middle transforaminal ligaments
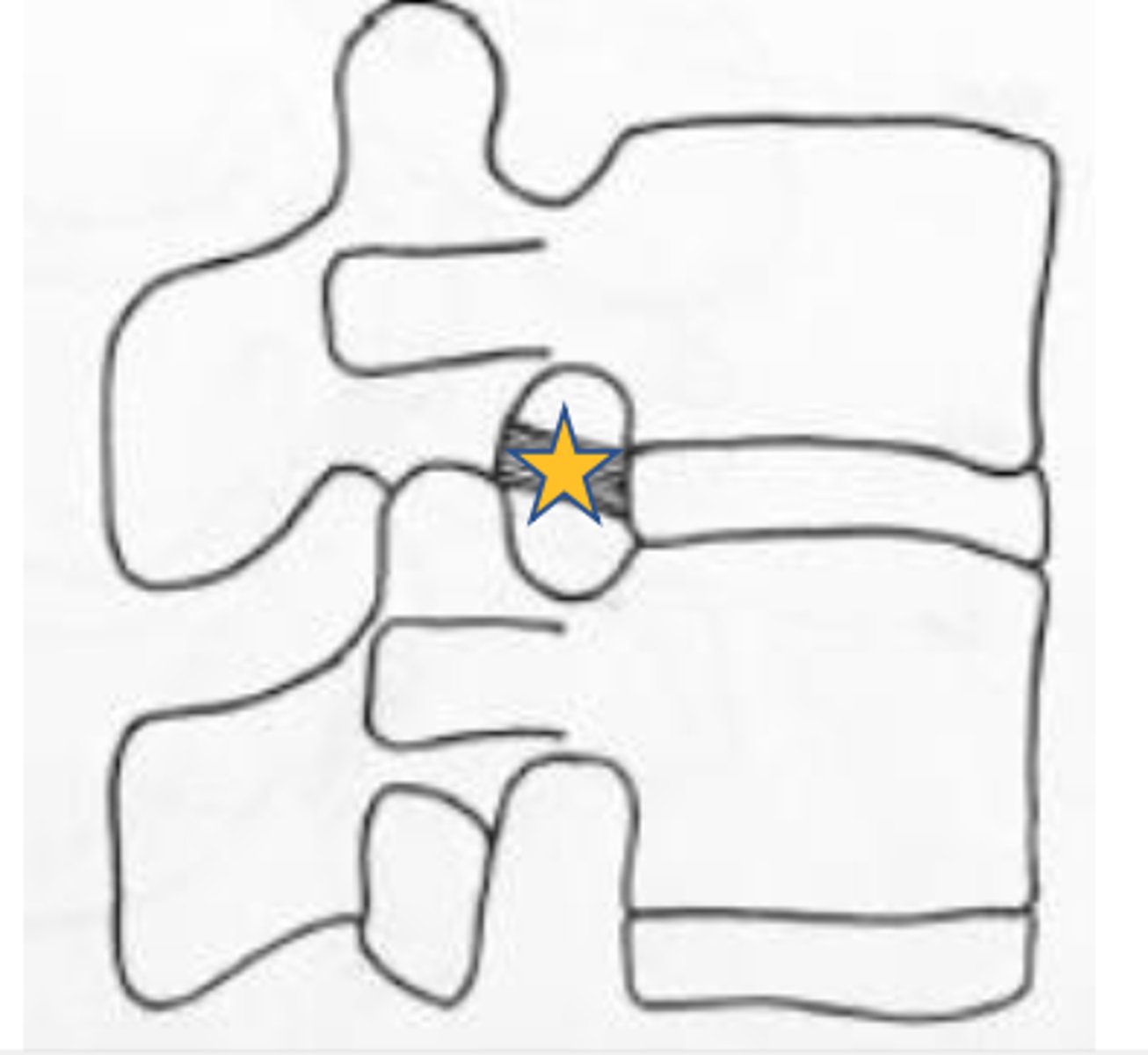
which transforaminal ligament attaches vertebral bodies to the superior articular process of the same vertebrae?
Inferior transforaminal ligament
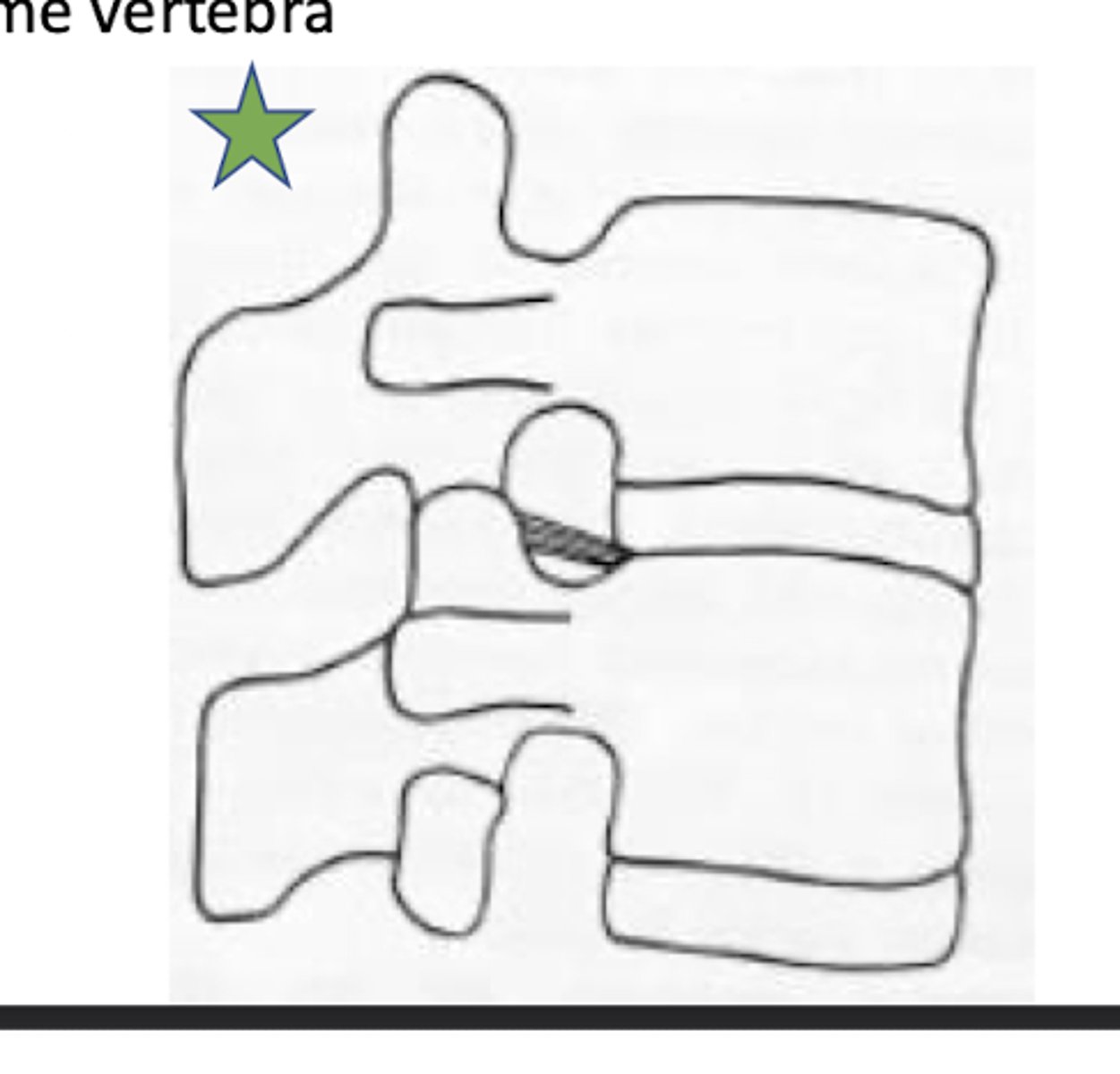
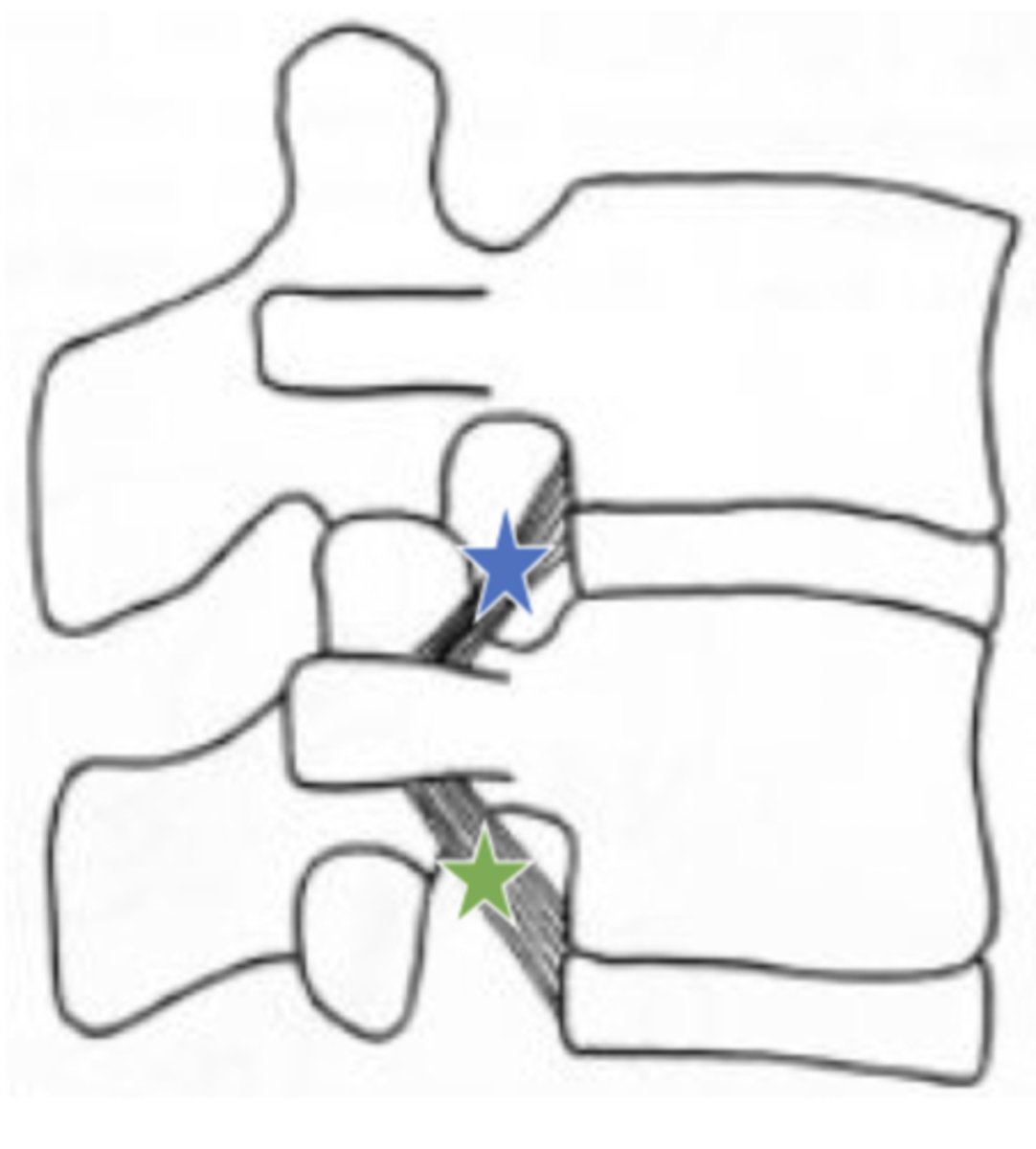
Which ligament attached vertebral body and ICD to transverse process of vertebra below?
superior corporotransverse ligaments (blue star in image)
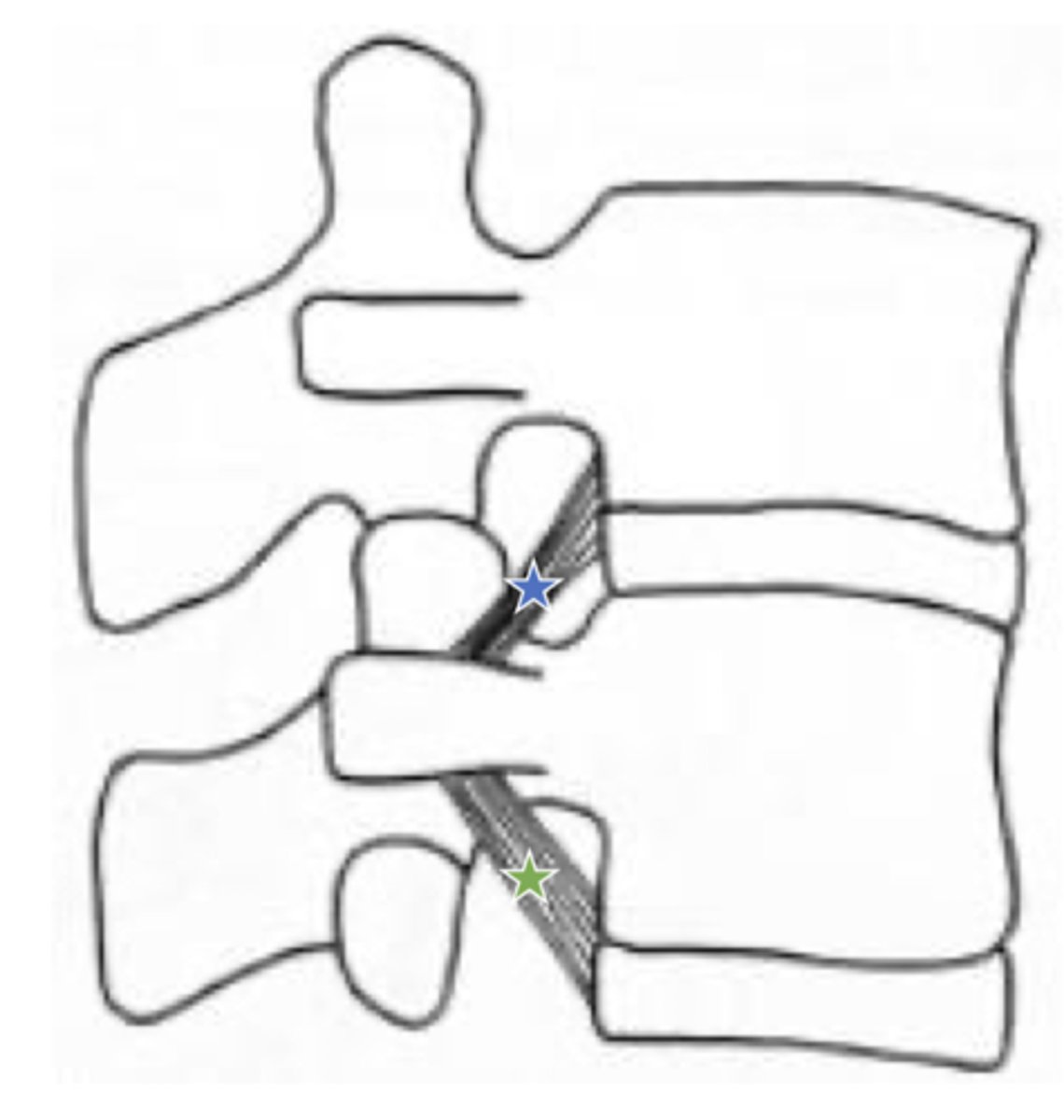
which ligament attaches vertebral body and IVD to the transverse process of vertebra above?
inferior corporotransverse ligament (green star in image)
Give the 4 examplea of fibrous joints including movements allowed and classifications
fibrous joint= more than two boney surfaces connected by a thin layer of Dense CT (ligament attachment)
Suture- syndesmosis (immovable)
syndesmosis- ALL JOINTS connected by a ligament, amphiarthrosis (interosseous membrane between radius and ulna)
Gomphosis- teeth in alveoli
Schindylesis-vomer bone with rostrum of sphenoid articulate together
what is it called with a suture ossifies?
synostoses
Give examples of cartilaginous joints including classifications (synchondrosis, symphysis) and which type of cartilage each uses
cartilaginous joint=cartilage fills space between opposing bones
Symphysis used Fibrocartilage: ex- IVD, pubic symphyses
Synchondrosis uses Hyaline cartilage: ex- epiphyseal plate, costochondral bones
Symphysis joints are only occurring where in the body?
Do they allow movement or not?
the median plane (midline)
allow slight movement (amphiarthrotic)
Give examples of synovial joints including movements allowed and classifications
synovial joints= joint cavity filled with synovial fluid
Any joint with a synovial membrane!
what 4 consistent structures are present in a synovial joint (100% TQ)
1. Articular capsule
2. Synovial membrane
3. Articular cartilage
4. Synovial Fluid
What is a uniaxial degree of freedom
move in one plane (ex: hinge joint)
what is biaxial degree of freedom
move in two planes (ex; condylar)
what is multiaxial degree of freedom
move in more than two planes (ex: ball and socket joints)
what is nonaxial degree of freedom
bones push against each other and do not move ex: plane joints in carpal bones
What are the three ways synovial joints are classified?
1) # of bones
2) Types of movements allowed at joint
3) morphological appearance
How do we classify synovial joints based on # of bones?
A) Simple- two bones form a joint
B) Complex- two bones joint and form two joint compartments
C) Compound- more than two bones form joint
What are the different ways we can classify bones based on morphologic appearance? (HINT you must know both names)
- Synovial plane (diarthrosis arthrodial)
-Synovial saddle (diarthrosis sellar)
-Synovial ellipsoidal (diarthrosis condylar)
-Synovial pivot (diarthrosis trochoid)
-Ball and socket (spheroid)
Synovial Hinge (ginglymoid)
Describe the articular capsule (aka fibrous capsule) (TQ)
4 different mechanoreceptors located in superficial and deep layers
Type 1-3: Encapsulated mechanoreceptors with proprioceptive function
type 4: non-encapsulated; unmyelinated free nerve endings
What are type I-III mechanoreceptors in the articular capsule specialized for?
proprioception with being encapsulated
What do type 4 mechanoreceptors in the articular cartilage respond to ?
potential mechanical extreme injury (nociceptors)
describe the synovial membrane modifications (3) 100% TQ
1- Synovial villi- finger like projections that increase surface area for secretion-absorption
2- Articular Fat Pads- Fibrous layer filling gaps between joint tissue
3- Synovial menisci and intra-articular discs- fibrocartilage projections that separate joint articular surfaces (meniscoids)
Descibe the articular synovial membrane (2 layers) and what their role is
outler fibrous layer:
- conn tissue, blood vessels, lymphatics, nerve endings; continuous with articular capsule
inner cellular (luminal layer)
- synovial fluid secretion
which articular synovial membrane layer is continuous with the articular capsule?
outer fibrous layer
what is another name for the inner cellular layer of the articular synovial membane? (TQ)
Synovial lamina intima
What two types of cells are found in the cellular layer (synovial lamina intima) of the synovial membrane? What are their roles? (TQ)
Type A synoviocytes- phagocytic
Type B synoviocytes- secrete protein and hyaluronic acid for synovial fluid
Describe the articular cartilage:
What is the articulating surface covered with?
How does it get nutrients?
- covered with hyaline cartilage
-avascular, lacks innervation and lymphatics
-nutrition/waste elimination provided by synovial fluid
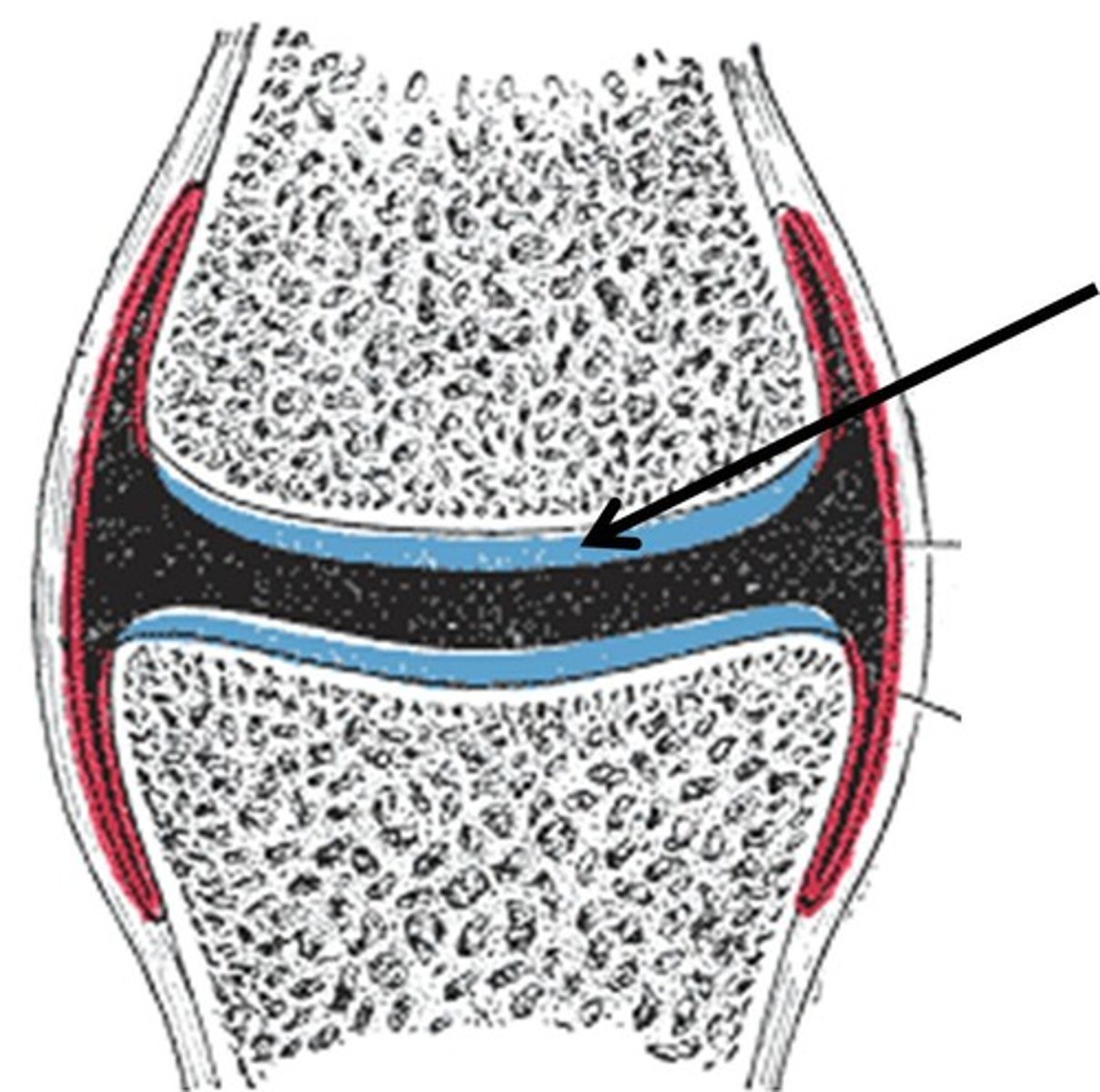
What percent of volume does water account for in articular cartilage
what is the remaining volume consisting of?
60-80% water
12-24% collagen type II fibers
8-16% proteoglycan gel
What is responsible for water retention in articular capsules
GAGs
Describe the function of synovial fluid (100% TQ)
provides nutritional source for articular cartilage and supplying lubricant, which increases joint efficiency and reduces erosion of articular surfaces
synovial lamina intima cells in synovial fluid secrete what for the final consistency?
wandering blood cells (WBCs) and connective tissue cells
T/F: there is a high volume of synovial fluid found in human joints
FALSE: there is a low volume in human joints
Differentiate between typical and atypical cervical vertebrae
Describe the orientation of superior and inferior articular facets
What forms articlar pillars?
Which muscles attach to articular pillars
Describe which osseous structure houses the vertebral artery
Describe the anterior and posterior tubercles and their associated structures
Understand the 5 osseous parts of typical cervical transverse processes
Which nerve structure runs along the costotransverse bar
Describe the carotid tubercle (C6)
Describe a typical cervical vertebra including joint surfaces and muscle and ligament attachments
Understand and describe the cervical lordotic curvature
Describe osseous structures located on the anterior and posterior arch of C1
Understand homologous structures of C1
Describe ligaments and joint surfaces associated with C1
Describe the ponticulus posticous, vertebral artery, acuate foramen, and retro transverse foramen of C1
Describe muscles, ligaments, and joint/surfaces associated with C2 and C7
Describe the vertebral artery: embryology, subdivisions (branch of which artery?)