CHEM 1 FINAL - THE STACK OF LEGENDS
1/287
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
288 Terms
Why don't we use EDTA lavender tubes for Na, K, or Ca tests?
EDTA chelates Ca; EDTA contains K and sometimes Na
Gray tops (sodium fluoride) is not used for the ______ test.
BUN (inhibits urease)
Hemolysis elevates:
KLAMPi - K, LD, AST, Mg, PO4, iCal
Intracellular fluid is __/3 of TBW, extracellular fluid is ___/3 of TBW
Intracellular fluid is 2/3 of TBW, extracellular fluid is 1/3 of TBW
Osmoreceptors in the ______ (part of brain) detect _____ (analyte) concentrations in the blood.
Hypothalamus, Na
When kidneys sense a low blood volume, they secrete _____.
renin
Renin cleaves ________
Angiotensinogen
How do we measure osmolality? (Colligative property)
Freezing point depression (sample is supercooled while being stirred via an osmometer)
You can calculate osmolality using this formula: ____________.
Posm = 2(Na) + (glucose/18) + (BUN/2.8)
Reference range for plasma osmolality:
275-295 mOsm/kg
Osmolal gap formula: O.G. = _______________________
O.G. = measured osmolality - calculated osmolality
What is an osmolal gap?
Other "things" that contribute to the osmolality besides the big players (Na, glucose, BUN) which are not in the calculated osmolality formula. Exampes: Lactic acid, keto acids, EtOH, ethylene glycol
What is pseudohyponatremia?
Na: ↓
Osmo: NL
Hyperlipidemia (lipids: ↑)
Hyperproteinemia (protein: ↑)
Metabolic states that can ↑ Osmo and ↑ Osmolal gap: ______ or _______
DKA, EtOH-KA (ketoacidosis)
Reference interval for Na:
135 - 145 mmol/L
MAJOR extracellular cation and plays role in H2O homeostasis and osmotic pressure:
Na
Reference interval for Cl:
98-109 mmol/L
Most ABUNDANT ANION in the ECF:
Cl
Most ABUNDANT ANION in gastric and intestinal secretions:
Cl
Reference interval for K:
3.5-5.5 mmol/L
MAJOR intracellular cation:
K
Bicarbonate reference interval:
22-28 mmol/L
Formula to calculate total CO2: _________________
Total CO2 = CO2 + HCO3-
Reference interval for Mg:
1.5-2.4 mg/dL
What is the anion gap?
The small fraction of anions that are not measured
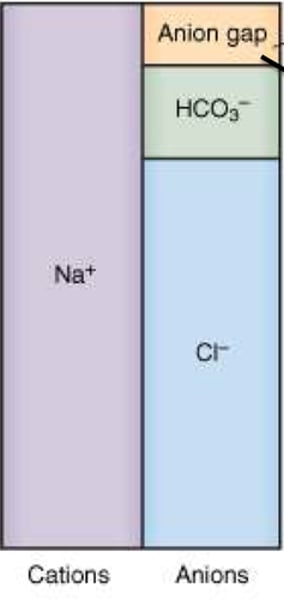
Formula for anion gap: AGap = ____________________
AGap = (Na + K) - (Cl + HCO3)
The anion gap is equivalent to the unmeasured anions minus the unmeasured cations: (huge formula)
(protein + organic acids + PO4- + 2SO42- ) - (K+ + 2Ca+2+ Mg+2)
When the anion gap increases, this is usually due to an ______ (↑/↓) in one or more unmeasured _______ (anions/cations).
When the anion gap increases, this is usually due to an ↑ in one or more unmeasured ANIONS.
An increased anion gap is useful in diagnosing what?
Metabolic acidosis
Stuff that increases the anion gap: (MUDPILES)
METHANOL, uremia, DKA, paraldehyde, iron/isoniazid, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, ETHANOL/ETHYLENE GLYCOL, SALICYLATE/Aspirin
Name a reason why a pt might have acidosis but their anion gap is normal
DIARRHEA (tons of bicarb is lost, blood quickly becomes acidic without the bicarb buffer).
Renal tubular acidosis can have same effect.
What is the most common reason why the anion gap can decrease (for example, close to zero)
Instrument issues (anion gap should never be too small)
In potentiometry, the __________ generated is proportional to the _________
Potential, activity/concentration of the ion
Describe the mechanism for an ISE (ion selective electrode)
Semi permieable membrae. MOST COMMON type of electrode.
The potential produced at the membrane/sample solution interface is proportional to the logarithm of the ionic activity/concentration
Describe the mechanism for a redox electrode
potential generated due to the transfer of an e- to an inert metal (platinum/gold)
Name some redox electrodes:
Hydrogen electrode (pH), saturated calomel electrode, silver-silver chloride
Which analytes use the pCO2 gas-sensing electrode?
Blood-gas analytes: pH, pCO2, PO2
Direct ISE vs indirect ISE:
DIRECT: non-diluted whole blood or plasma.
INDIRECT: sample is first diluted
How does the Clark pO2 electrode work?
________ is proportional to the _____ in the sample.
Current, PO2 (amperometric measurement)
This method is the gold standard for sweat chloride testing for CF patients:
Coulometry (measures the absolute amount of Cl)
Peptide bond is formed between what groups?
Carboxyl group and amino group
Transamination does what?
Moves an amino group between compounds (transaminase catalyzes transfer of amino group to an alpha-keto acid).
Total serum protein is measured via what reaction?
Biuret reaction
How does the biuret reaction work? Detects presence of _________ which reacts to form a purple complex with __________ in _______(alkaline/acidic) solution.
Detects presence of 2+ PEPTIDE BONDS which react to form a purple complex with COPPER SALT in ALKALINE solution.
Name 3 dye-binding proteins (methods for measuring proteins, very sensitive):
1. BCG/BCP for albumin
2. Pyrogallol red (in urine/CSF)
3. Coomassie brilliant blue (for immunoglobulins)
Early methods of protein measurement relied on _______.
Turbidity
_______ (Cathode/anode) attracts _______ (anions/cations)
Cathode attracts cations.
Anode attracts negative charged anions.
In electrophoresis, ______ become ______ charged in a pH of _______.
In electrophoresis, PROTEINS become NEGATIVELY charged in a pH of 8.6 (separated based on charge-to-mass ratio)
What is electroendosmosis/endosmosis?
The "stuff" in the gel (positively charged ion cloud) moves in the opposite direction of all the proteins during gel electrophoresis, causing smearing of the bands (causes gamma globulins to migrate towards cathode instead of anode)
Urine electrophoresis is similar to serum electrophoresis, except the urine is ______ and is used to detect __________
concentrated, Bence-Jones proteins (free monoclonal IgG light chains)
Hyperproteinemia is often _______ due to _________.
Hypoproteinemia is often due to _______.
Dilutional, dehydration, protein loss
Most sensitive APR (sensitive, not specific):
CRP (may increase x1000)
hsCRP is used as a marker for what?
Acute Myocardial Infarction
What is in each peak of electrophoresis?
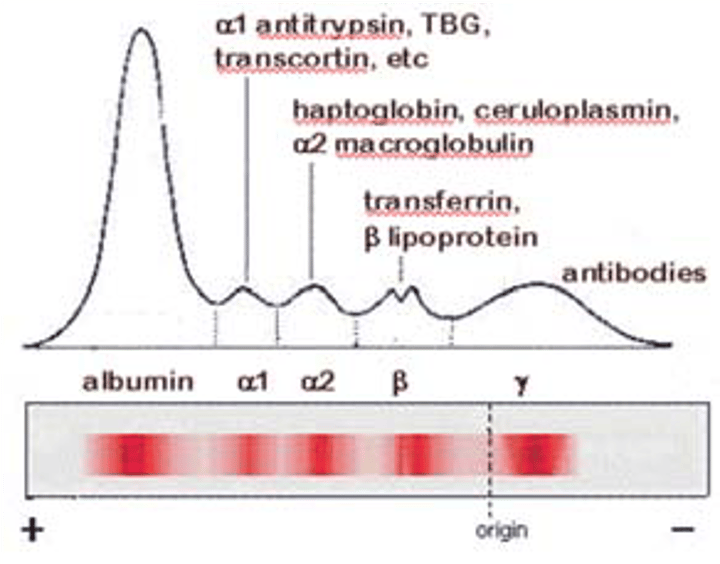
Albumin is made in the ______ and maintains ______ ________ _______ _________.
Liver, blood colloidal osmotic pressure
Causes of hypoalbuminemia (5):
1. Liver disease (make less of it)
2. Renal loss (leak lots of it)
3. GI loss (can't absorb it)
4. Skin loss (burns decrease ALB)
5. Inflammation (ALB is a negative APR)
Microalbumin is _____ (↑/↓) sensitive and measures a lower concentration of ______.
↑, albumin
Microalbumin is awesome for monitoring ____-_____ _____ ______ and is measured in 6-mo intervals in a 24-hr urine.
early-stage renal disease
Prealbumin transports _______ ______ and migrates _______ (before/after) albumin. ____-_____ _____ is bound to prealbumin. It is often used as an indicator of _______ _______ due to its short half-life and high amount of _________ _________.
Thyroid hormones, before, retinol-binding protein, protein nutrition, essential AA's.
Prealbumin ________ (↑/↓) in inflammation, cancer, cirrhosis, or protein-losing diseases
↓
Alpha-1-antitrypsin is a ________ __________ ________. Deficiency of AAT allows LE in the lungs to cleave more elastin, losing architecture of the lung, which causes ______ often in neonates. Genetic deficiencies of AAT can result in severe _____ _______.
Serine protease inhibitor, emphysema, liver disease
Alpha-1-globulins include _____ and ______.
Alpha 1 antitrypsin, alpha 1 fetoprotein
Alpha 1 fetoprotein is made by the fetal liver; when it is _____ (↑/↓) in amniotic fluid, it often means baby has ______ _______ defects. If it is ____ (↑/↓) in mother's serum, it often means baby will have __________________. It is also a ______ marker for _________ cancers.
↑, neural tube, ↓, trisomy 18/21 or down syndrome, tumor, liver
Alpha 2 globulins include: (3)
1. Alpha 2 macroglobulins
2. HAPT
3. Ceruloplasmin
Alpha 2 macroblobulin is the major plasma ______ ________. _____ (↑/↓) levels are seen in severe acute pancreatitis. _____ (↑/↓) levels = _____ syndrome.
Proteinase inhibitor, ↓, ↑, nephrotic
HAPT is ____ (↑/↓) during hemolysis.
↓
Ceruloplasmin transports _____ and _____ (↑/↓) in ______ disease.
Cu, ↓, Wilson's
Beta 2 globulins includes: (2)
Transferrin, beta 2 microglobulin
Beta 2 microglobulin is used to assess ____ ______ function and will ____ (↑/↓) in renal failure, inflammation, and neoplasms.
Renal tubular, ↑
Where does fibrinogen appear in electrophoresis?
Between beta and gamma peaks
You notice a peak between beta and gamma peaks on gel electrophoresis. What type of sample must this be?
PLASMA because serum does not have fibrinogen.
Gamma globulins/immunoglobulins are ____ (↑/↓) in immunodeficiency, _____ (↑/↓) in polyclonal gammopathy or monoclonal paraproteins.
↓, ↑
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Acute inflammation
↓ ALB, ↑ alpha-1, ↑ apha-2
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Chronic inflammation
↑ alpha-1, ↑ apha-2, ↑ gamma
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Cirrhosis
Polyclonal ↑ gamma with beta-gamma bridging
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Monoclonal gammopathy
Sharp peak in gamma (M spike), ↓ in everything else
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Polyclonal gammopathy
Diffuse ↑ in gamma
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Hypogammaglobulinemia
↓ gamma
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Nephrotic syndrome
↓ albumin; increased alpha-2
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Alpha-1-antitrypsin def.
↓ alpha-1
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Hemolyzed specimen
↑ beta or unusual band between alpha-2 and beta
Describe the electrophoresis pattern: Plasma
Extra band between beta and gamma (fibrinogen)
Define the following:
Glucose-
Glycolysis-
Gluconeogenesis-
Glycogen-
Glycogenesis-
Glycogenolysis-
Glucose- sweet stuff
Glycolysis- breaking down glucose to lactate/pyruvate
Gluconeogenesis- making glucose from non-glucose stuff
Glycogen- glucose storage
Glycogenesis- process of making glycogen
Glycogenolysis- process of breaking down glycogen
In ketoacidosis, ________ and ________ accumulate. This stuff is made faster when a patient has diabetes because of ____ ________ ________ mobilization.
Acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, free fatty acid
Glucose reference range:
66-99 mg/dL
Glucose critical for 0-60 days old:
Glucose critical for adults:
The body's only hypoglycemic agent is _______
Insulin
Describe the two phases of insulin release
1st phase: rapid release of stored insulin.
2nd phase: steady insulin synthesis (60-120 min).
Diabetes type 1 is when ______________. Diabetes type 2 is when ______________.
cells exhibit minimal/no response to insulin;
retain 2nd phase but 1st phase/pulsatile secretion is lost
When you need to increase blood glucose, _____ and _____ are released first. Afterwards, other hormones that increase blood glucose are ____ ______ and _____.
glucagon, epinephrine, growth-hormone, cortisol
_______ (process) occurs first when glucose in the blood needs to be increased, then __________ (process).
glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis
A blood glucose of ______ is considered hypoglycemic.
Adrenergic and neurologic symptoms may be due to ______.
Hypoglycemia
______ (exogenous/endogenous) insulin is used in diabetes mellitus.
exogenous
A blood glucose of ____ is considered hyperglycemic.
Fasting glucose of > 99
In DM, ______ is underused, causing _______.
glucose, hyperglycemia
Patients with DM are at risk of developing diabetic ______, diabetic ______, ____ damage, and _______.
retinopathy, neuropathy, nerve, atherosclerosis
Polyuria, polydipsia, and rapid weight loss = DM type 1, which is insulin ______ (dependent/resistant) and is often due to ________.
dependent, auto-antibodies/autoimmunity (destruction of beta cells by T cells)
In type 1 DM, autoantibodies are usually against ______ itself (rarely against the receptors)
insulin