symbiosis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
endosymbiosis and ectosymbiosis
symbiont living either on the surface of the host or intracellularly
metamonads
found in the gut of specific species of termites
lives in symbiosis with other bacteria: 2 endsymbiotic bacteria which degrades cellulose and replaces mitochondria and 3 ectosymbiotic bacteria which provide motility by possessing 4 non-functional flagella
symbiotic associations in hemipteran insects
several bacterial species are found in insects which includes intracellular and extracellular bacteria. These are found in specialised structures called bacteriocytes can aggregate to form organs called bacteriomes
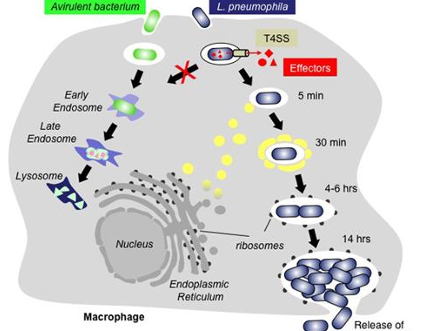
L.pneumophila is found in fresh water. Parasite of amoeba that can also replicate with alveolar macrophages
B.bacteriovorus attacks gram-negative bacteria. It invades the perupslams feed on host cell
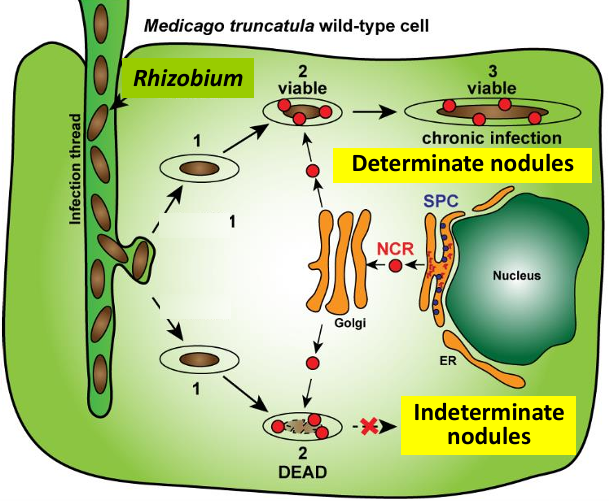
plant nodulation as a model symbiosis
plants are unable to use atmospheric N2 and so some legumes can fix N2, via a symbiotic interaction with soil bacteria (rhizobia). The symbiotic process called nodulation is increasing growth and yield
rhizobia
alphaproteobacterial (gram-negative)
soil dwelling bacteria is part of the rhizosphere
complex genome (5-10Mbp, several plasmids)
nodulation process
bacterial attraction: bacteria establishes contact with roots (production of roots exudates (flavonoids attract bacteria → activation of nodulation genes))
production of nod factor (nod factors are short oligosaccharides)
root curling
formation of infection threads
bacterial differentiation into bacteroids
Nitrogen fixation
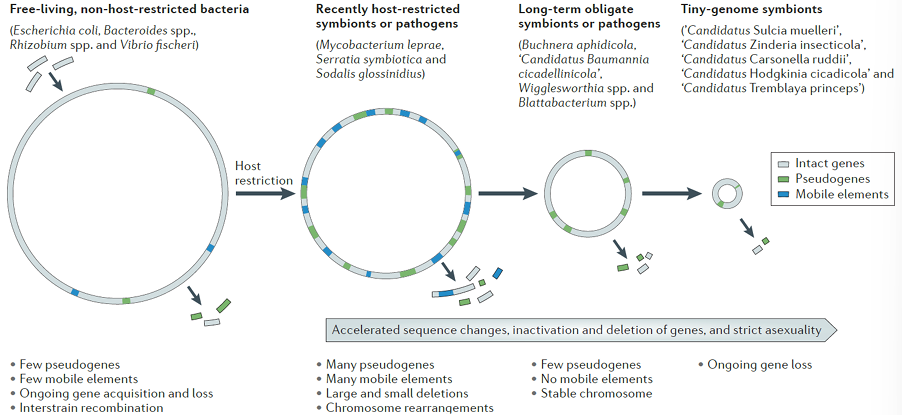
what distinguished obligate symbionts, parasites, organelles and viruses?
organelles are usually conserved across a wide range of organisms and are essential
parasites are harmful for the organism they infect
symbionts are often seen as beneficial organisms that live in association with other organisms
new approaches allowed to define new species and shook the concept of minimal genome
most bacterrial species have been studied in axenic cultures (independently of any other living organism)
metagenomics allowed to identify thousands of bacterial species that cannot be grown in lab conditions
what is the origin of small genomes in symbionts?
phylogenetic studies indicate that these organisms do not have an independent origin
genome size is the result of gene loss
a mosaic bionsynthetic pathway underpins…
amino acid biosynthesis