ACS management and stable angina
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What does ACS stand for
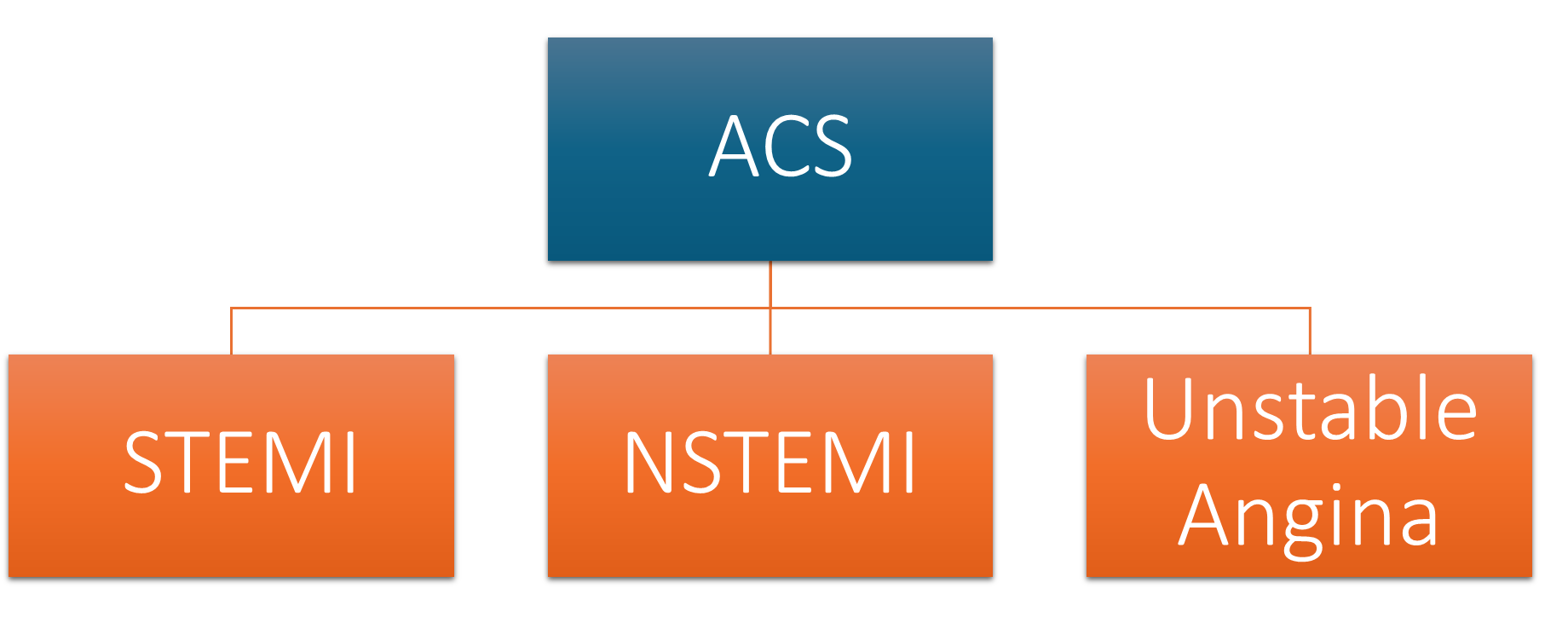
Umbrella term
Coronary anatomy
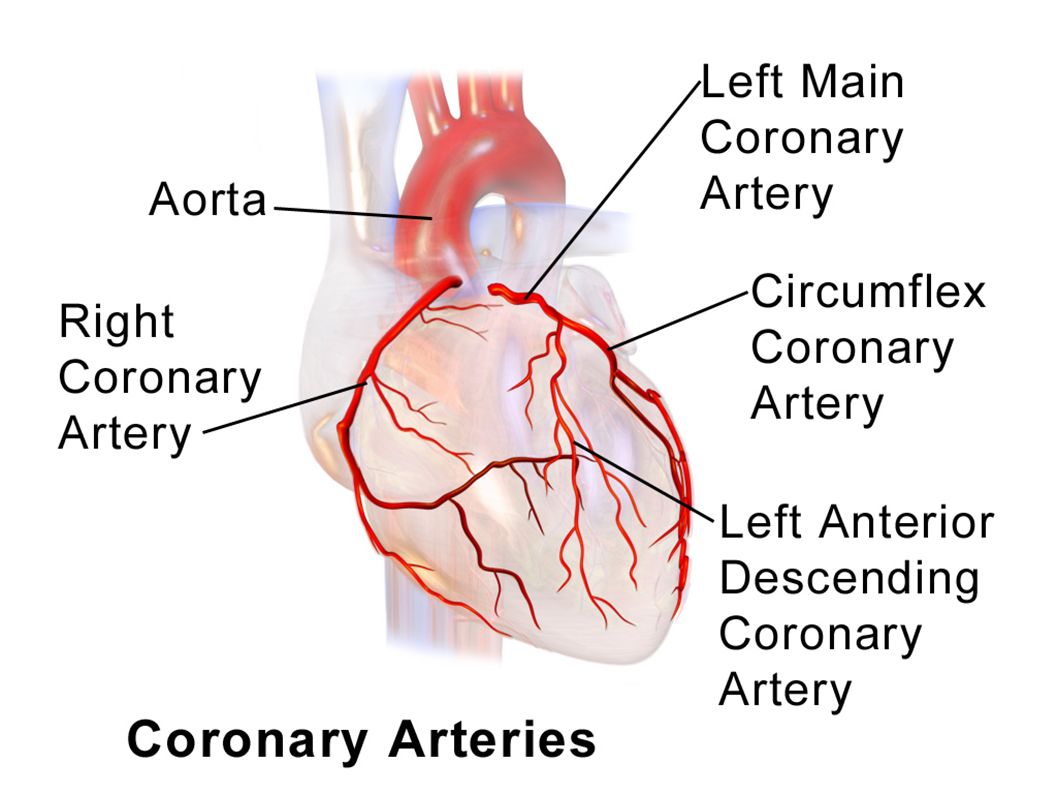
4 coronary arteries sit on the heart and supply blood to the heart while its pumping blood to the rest of the body
RF for ACS
•Hypertension
•Diabetes - classed as cardiovascular disease, causes damage to the blood vessels - microvascular disease
•AF
•Smoking
•Obesity
•Diet and Lifestyle - increased risk of clotting due to atherosclerotic process - limited motility
•High Cholesterol
•Gender - males more likely
•Age
•Family History
Signs and symptoms
chest pain - like someone is sitting on top of them
S.O.B
radiation down arm and jaw
sweaty
fatigue
epigastric pain
can vary between gender
What’s the difference
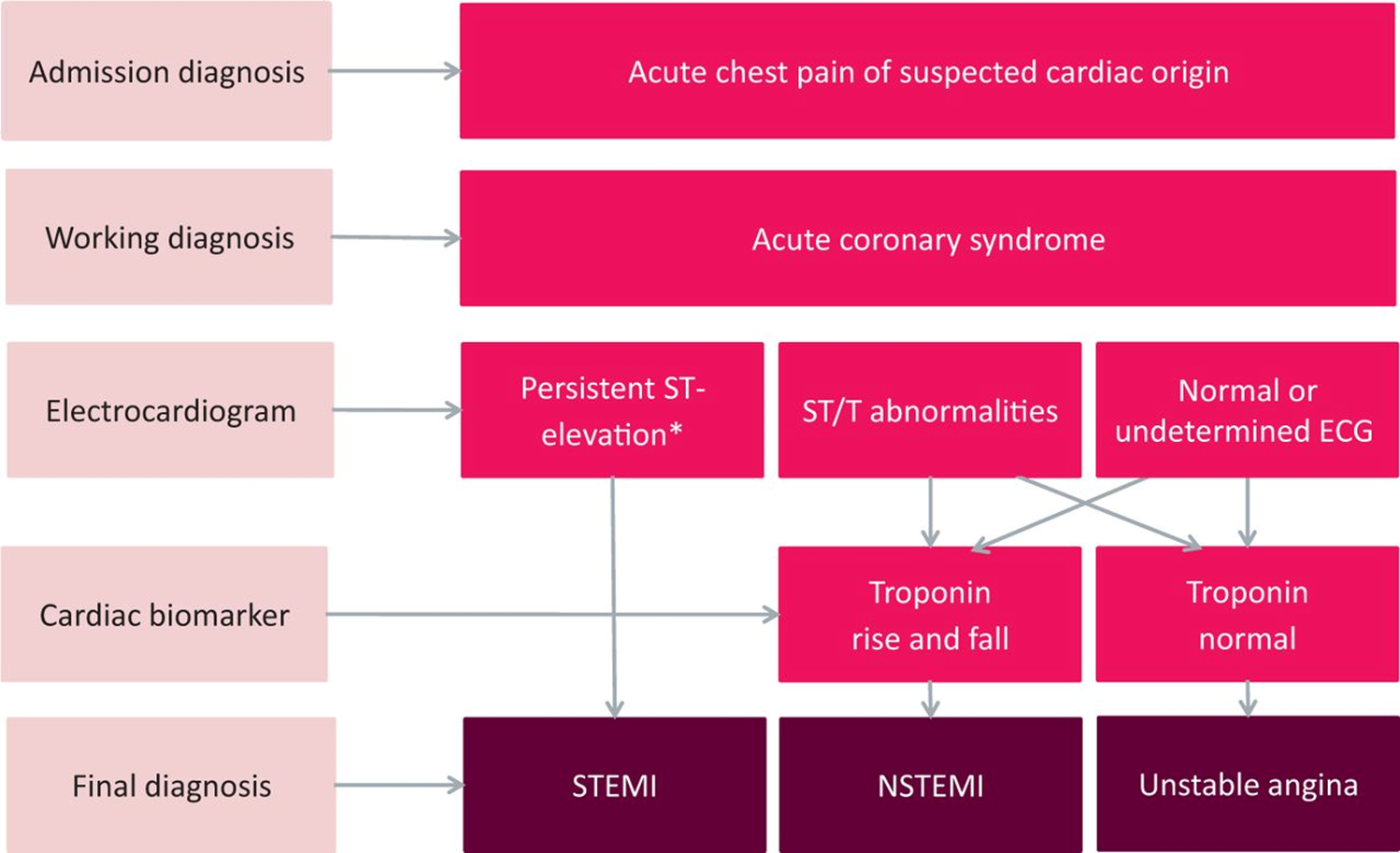
STEMI
•Total occlusion - no blood can go through so muscle can die - seen on ECG
•ECG Changes (ST segment)
•Stenting
•Troponin Raised
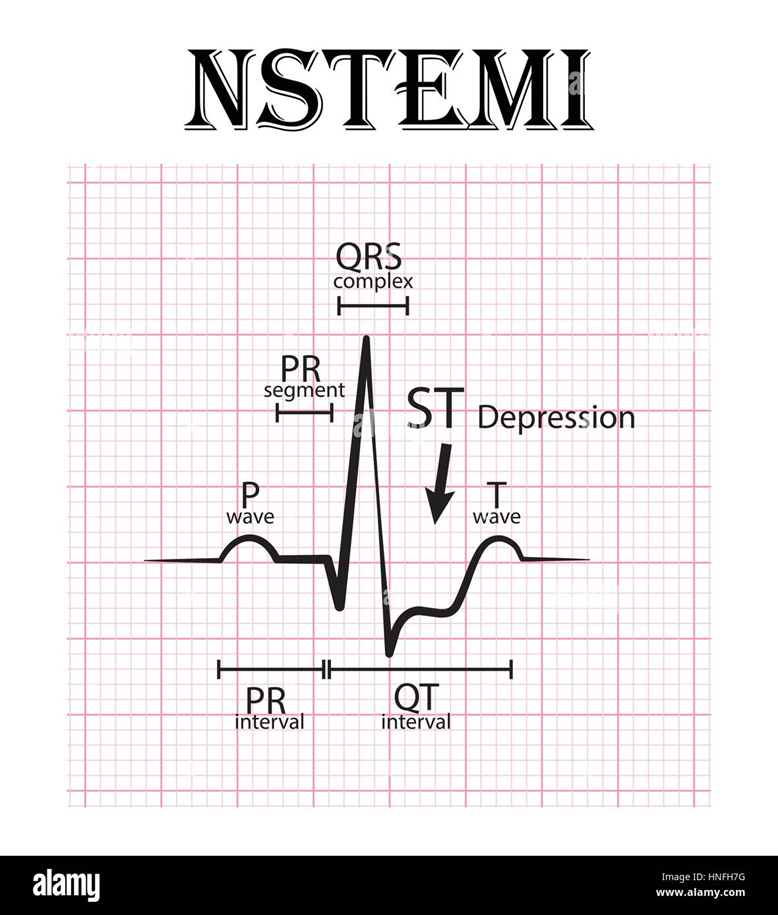
P is the small spike before the big spike, QRS is the biggest spike, ST segment is highlighted
ST is above baseline
normal procedure is stenting - done ASAP within 48 hours
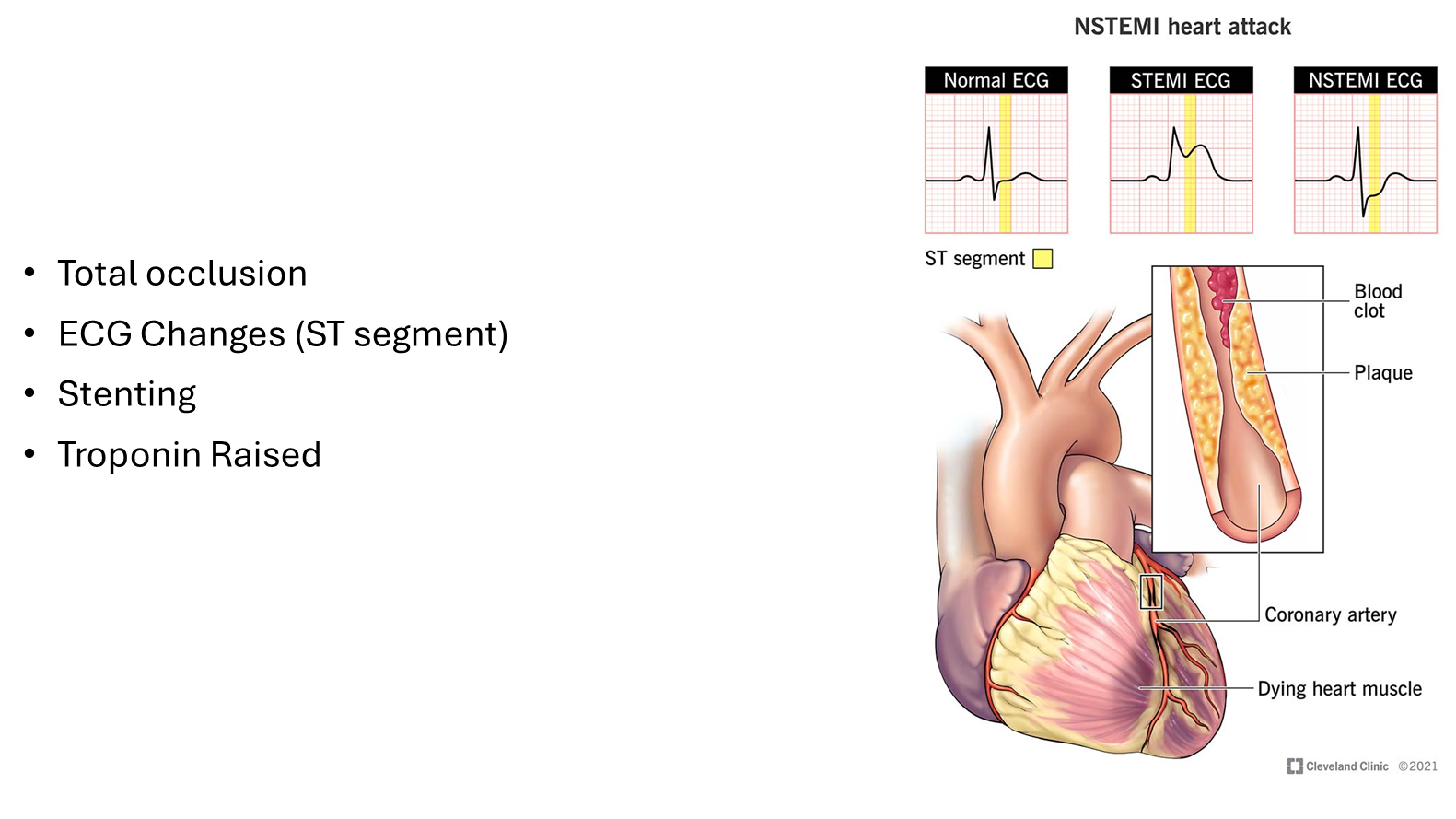
NSTEMI
•Troponin rise
•Partial blockage due to plaque rupture
Unstable angina

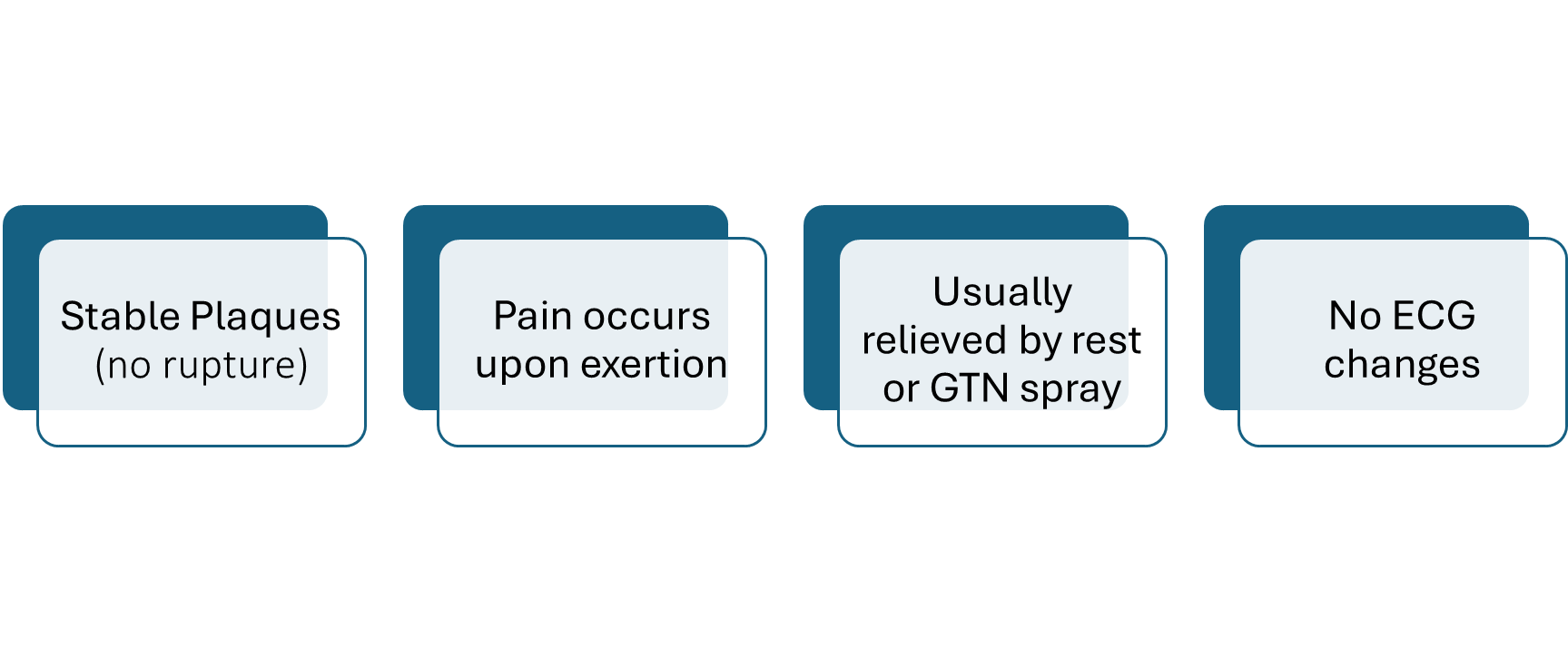
Stable angina
Treatment of STEMI
•300mg Aspirin to prevent clots from happening
•Oxygen
•GTN - dilate blood vessels so oxygen can get through
•Diamorphine - for pain
•cyclizine for nausea and vomiting - anti-emetic
•Angiogram
•STENT
Angiogram
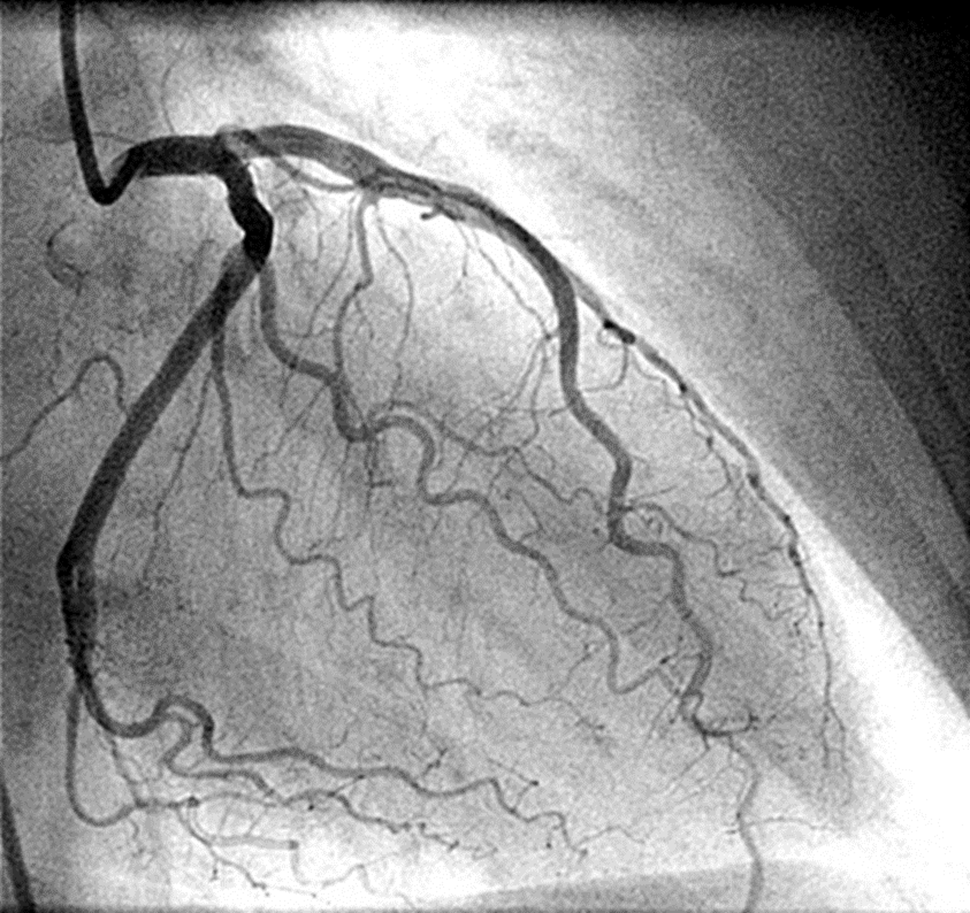
dye is injected into the radial artery to see where the blockage is
if patient is on metformin then hold the metformin for about 48 hours as dye interacts with metformin and can cause a build up of lactate, can cause patient to go into kidney failure
Stent
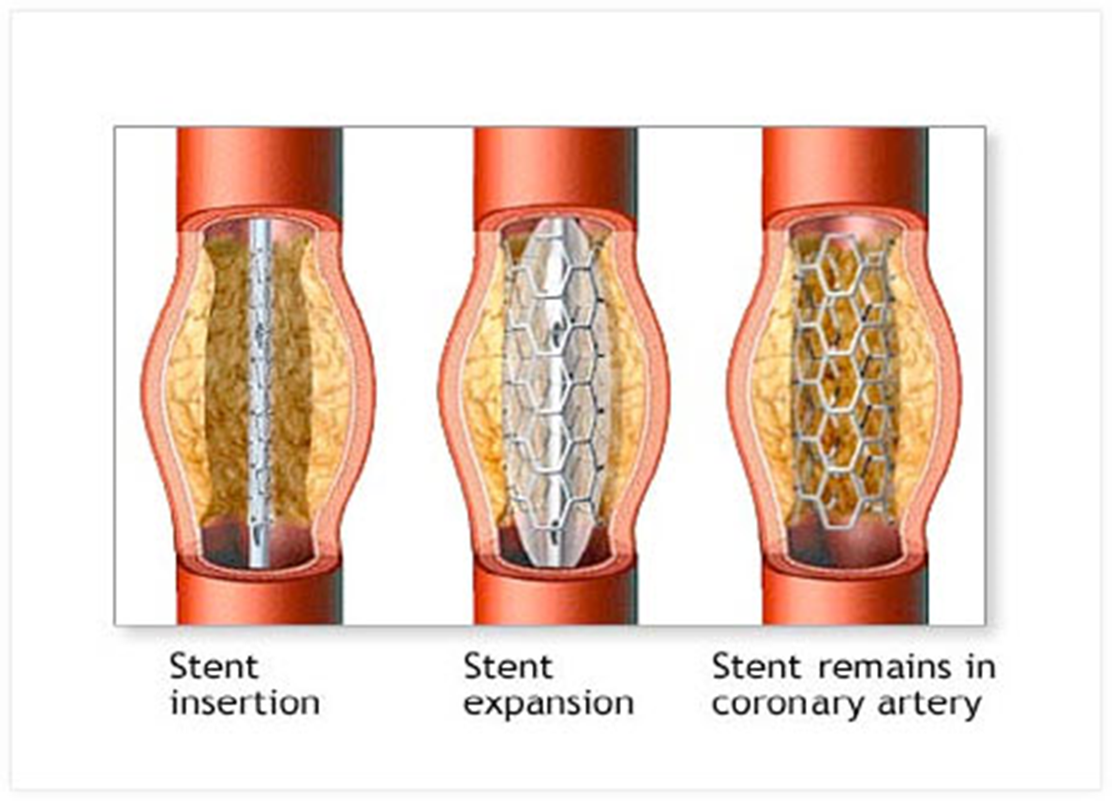
Stent expands with inflation of balloon, balloon is then deflated and is removed, stent meshes to walls of coronary arteries coronary arteries are dilated
Inserting something that can cause platelet aggregations s dual antiplatelet therapy is required
Coronary artery
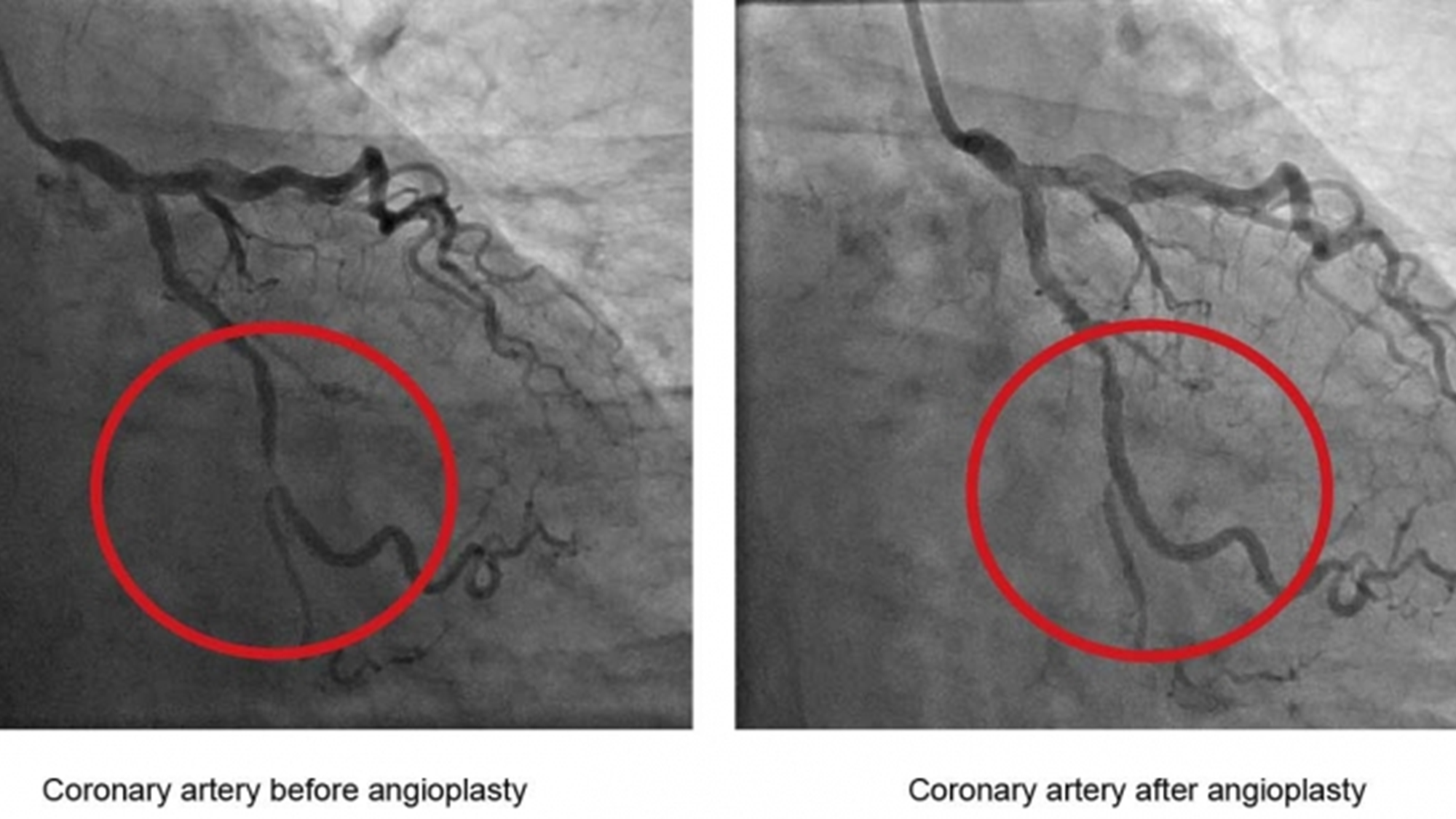
narrow vessels means heart muscle can be dead if it isn’t opened up
Secondary prevention post MI
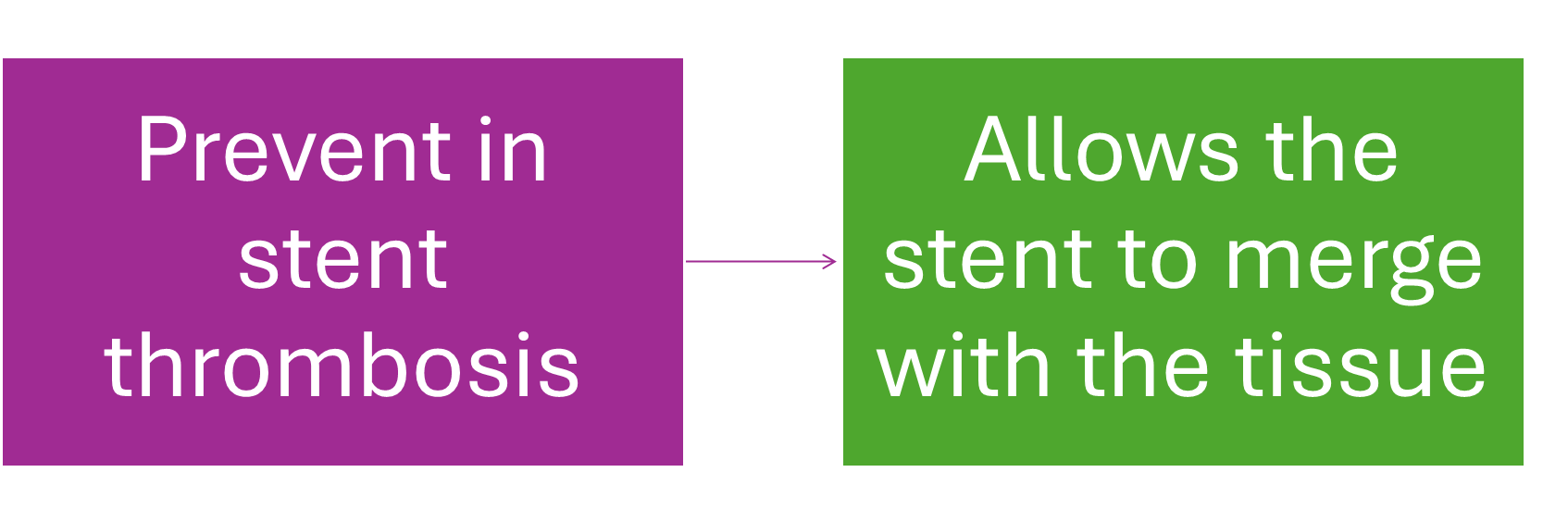
Aspirin + Clopidogrel/Prasugrel/Ticagrelor - 12 months, to prevents thrombosis due to stent - depends on comorbidities, extent of damage etc, clopidogrel has lowest chance of bleeding while ticagrelor has highest. After 12 months only continue with aspirin - life-long to prevent in stem thrombosis. If patient also has AF and has to be on something like warfarin/DOAC then duration would be different - 3-6 months? Only given with clopidogrel not the others as risk of bleeding is too high
Beta Blockers: Bisoprolol, cardio selective, greater affinity for beta 1 receptors, reduces work on the heart
ACE inhibitors - Ramipril, protect the kidneys and lower the BP, but if somebody has heart attack then its used to prevent cardiovascular remodelling - changes the way it pumps blood
Statins - atorvastatin 80mG - high intensity statins, may be reduced to 40 in elderly or decreased kidney function, look for side effects such as muscle pain - more common in elderly
PPI - lansoprazole to protect stomach, due to side effects of anti - platelet therapy. Omeprazole inhibits CYP enzyme which is needed to metabolise the clopidogrel so lansoprazole given instead
GTN spray
Eplerenone if ECHO shows HF - MRA, aldosterone antagonist, potassium sparing diuretic, also prevents cardiovascular remodelling
Dual antiplatelet
Beta Blockers
ACE inhibitors

Statins

GTN
counsel patients on how to use it
Monitoring

titrate medication to maximum tolerated dose - less likely to die
target of 60 to 70 bpm
cant increase ramipril dose of they have hyperkalaemia or decreased kidney function as ramipril causes hyperkalaemia
in community can’t titrate all medications at the same time
Post MI management
•Cardiac rehab
bedside ECHO -ulrasound of heart that detects abnormalities in ventricles or the atria to suggest the patient could be in HF as thats the next step after heart attack
•Follow up in cardiac clinic
•Follow up in the community
•Titrate to maximum tolerated dose in the community
What is stable angina
Form of IHD
Ischaemic means
A reduction in oxygen supply to the tissues due to narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries via atherosclerotic processes - build up of fat and cholesterol, leading to…
Imbalance between with the supply of oxygen and the myocardial demand – resulting in chest pain.
Coronary arteries
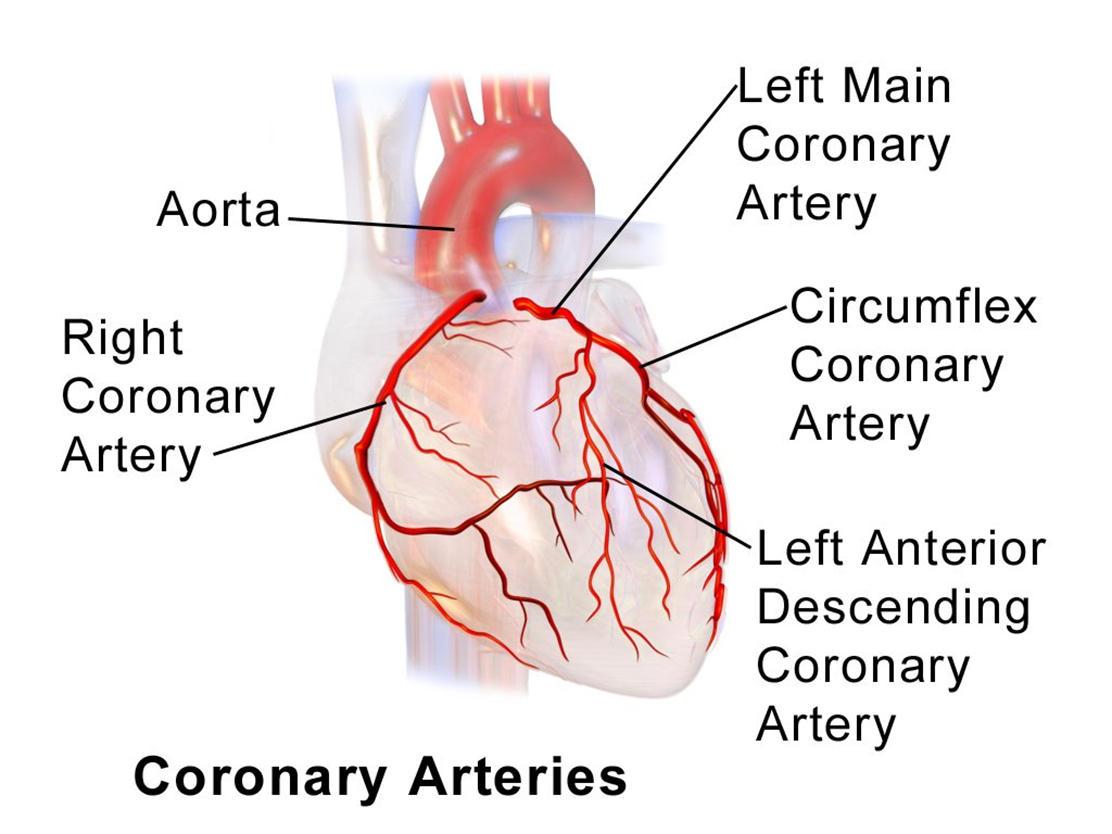
4 coronary arteries where potential blockages can happen - lumen narrowing causing chest pain
Risk factors for angina
smoking - narrows vessels
diabetes
HT
hypercholesterolaemia
Causes damage to the endothelium e.g. cocaine use causes spasticity to the blood vessels, causing narrowing of the lumen
always ask about recreational drugs
Angina
Stable angina
chest pain on exertion relieved by rest
Unstable angina
chest pain occurring at any time
Signs of angina
pain
tachycardia
N/V
sweating
Remember SOCRATES - where is pain, is anything making pain better or worse - helps identify which angina
Diagnosis
ECG - to see abnormalities, T- WAVE inversion sign of uneven palpitations
heart sounds - turbulence in valve and heart murmurs
BP in both arms rule out aortic dissection - RED FLAG requires immediate surgery
pulse check - tachycardia
oedema check - rule out HF
lung auscultation to rule out of infection
Blood tests - U + E’s, LFT’s, TFT’s, FBC, CRP, lipids. Electrolyte imbalances can cause arrythmias which can then cause angina. Deranged thyroid levels can be reason for arrythmias occurring. Anaemia can cause breathlessness. Lipids = cholesterol
CXR - rule out pneumonia
angiogram - helps determine if chest pain is cardia or non cardiac
Non - pharmacological management
weight reduction
stress reduction - yoga, walk, having pet
smoking cessation
healthy eating - green vegetables contain natural stuff that allows vessels to dilate
Managing comorbidities
•Diabetes
•Hypertension
•Use ACE inhibitor/ARB - ACE INHIBITORS are tripe threat - protect kidneys, cardioprotective, lower BP
•Lipid modification with statins - If LDL and non HDL high - Atorvastatin 20mg which is titrated up
Aspirin and beta blockers
•Aspirin reduces the risk of platelet aggregation within the coronary arteries and reduce risk of thrombus around the affected area.
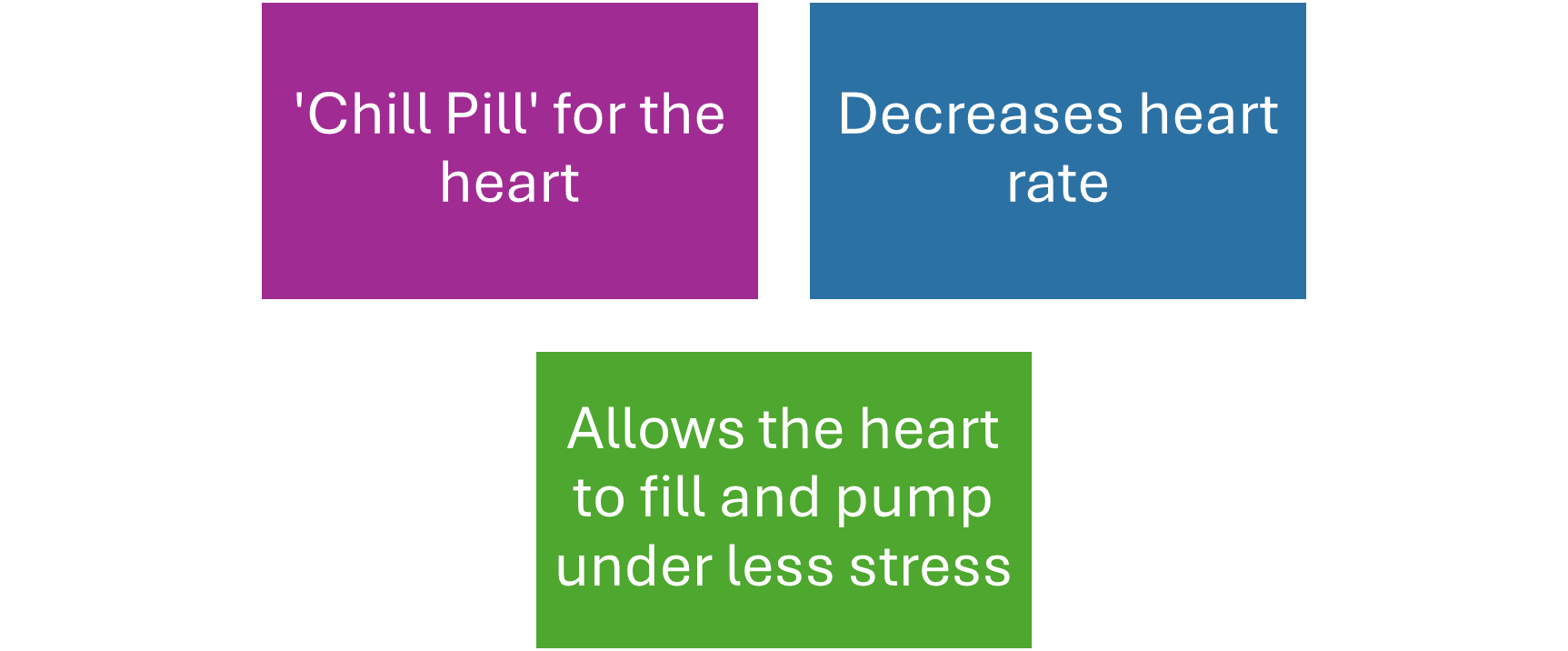
•Beta blockers are choice to reduce the cardiac workload and decrease stress on the heart. Great if there is LV dysfunction . Chill pill for the heart, great for chest pain induced by stress etc. Contraindicated in people with low HR, some asthma patients can be intolerant to beta blockers - trial and safety net
•Can help in people whose angina is triggered by anxious state
•CI: bradycardia, 2nd degree av block, sick sinus, some asthma
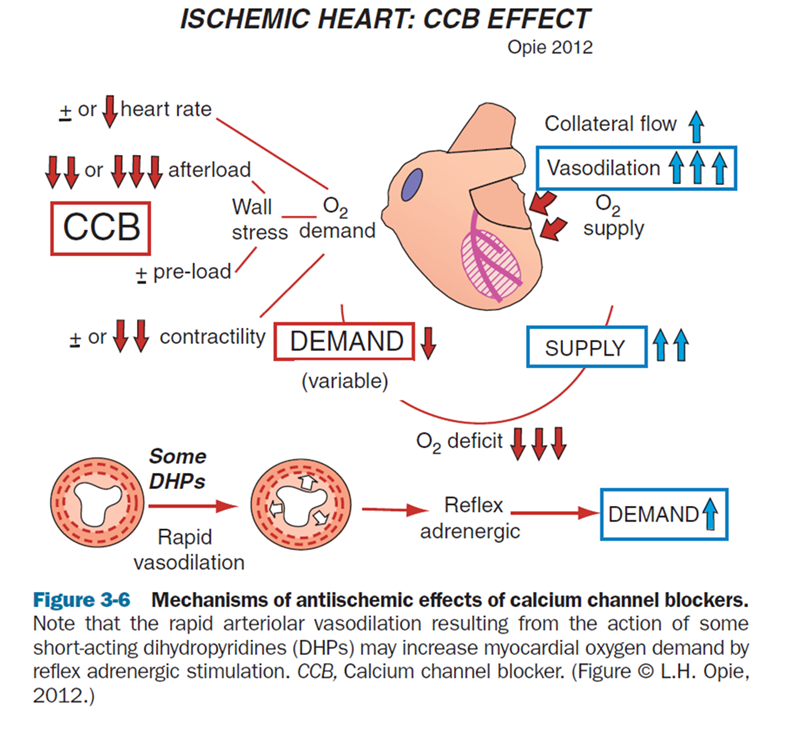
CCB
•Dihydropyridines (Amlodipine) - Good first line choice if the patient has hypertension (can be used in combination with beta blocker)
•Non – dihydropyridines (Diltiazem and verapamil) - slow the heart rate down
•Should not be used in combination with beta blockers due to heart block.
Long acting nitrates
Monotherapy - if cannot have beta blockers or CCB
Isosorbide mononitrate non modified release tablets - at 8AM and 2PM - Have to have nitrate free period otherwise vessels get used to it - vessels always dilated
isosorbide mononitrate M/R - once daily dosing in the morning
isosorbide mononitrate - the nitrate dispersed in the tablet is within a matrix, so when you cut the tablet in half it is equally distributed.
dilates coronary vessels through NO
therefore reduced preload and workload
side effects = headaches, safety netting
Short acting nitrate
•When a short-acting nitrate is being used to treat episodes of angina, advise people:
•
•to repeat the dose after 5 minutes if the pain has not gone
•
• to call an emergency ambulance if the pain has not gone 5 minutes after taking a second dose.
tell them to sit down, as under the tongue there is rich blood supply and skin is very thin so can penetrate through the skin
dilates blood vessels in brain causing headache
1 to 2 sprays under the tongue and wait for 5 minutes, repeat if pain hasn’t gone, repeat again if pain hasn’t gone, and if pain still persists then take it and call ambulance
e.g. GTN
Ivabradine
if either calcium channel blockers or beta blockers are not an option, Ivabradine is an option
Cannot be used in people with atrial fibrillation
Reduces heart rate without affecting blood pressure.
CI: HR <75 BPM esp in chronic or acute HF. Patients with a pacemaker
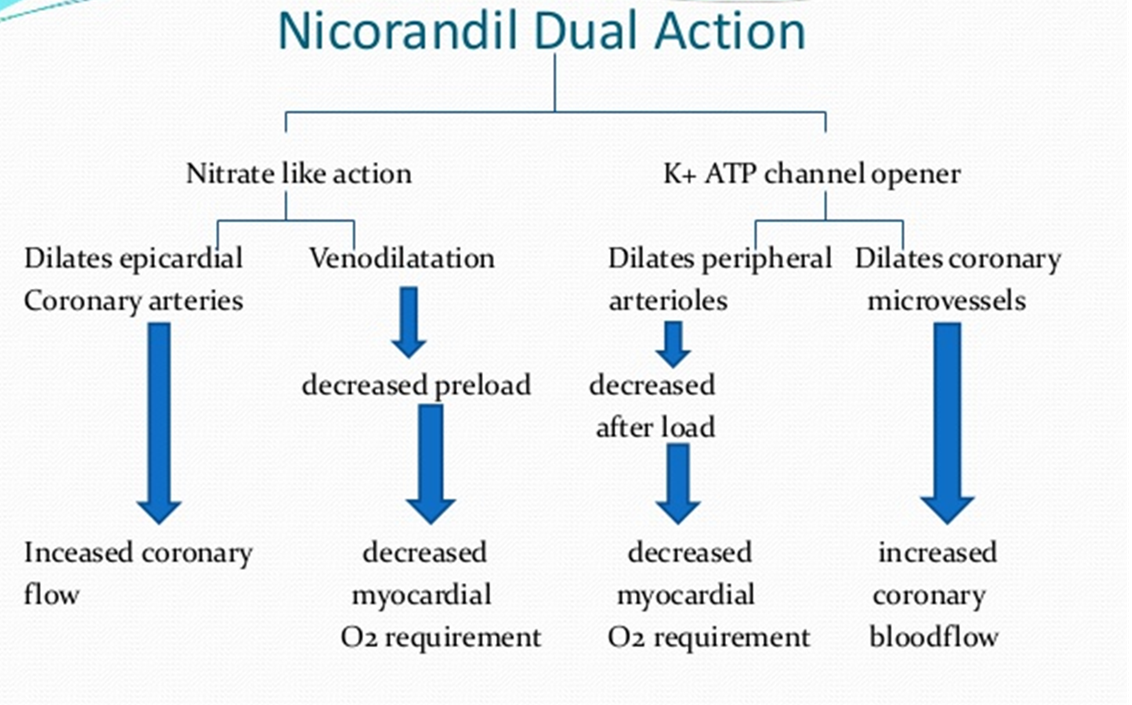
Nicorandil
•- Twice a day dosing
can’t go in Dossett box has to stay within the packet - adherence, check with patient if they can take it.
•Can get a head ache
•Monotherapy
•Assess every 2 – 4 weeks and continue to titrate
Titrate if necessary until symptoms controlled
Ranolazine M/R
MONOTHERAPY
initiated by specialist in hospital by cardiology consultant, not done in community
375mg twice a day for 2 – 4 weeks then titrate to response according to response
Multiple mechanisms of action to improve coronary blood flow.
If none of the interventions work, the patient should be referred to specialist for intervention such as PCI or CABG - motorway, creates new diversions from the part where it’s blocker to the part where its perfused so blood can go alternate way so heart muscle dies