BIOC 503 - Protein Functions I
1/30
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
reversible
___ binding of ligands is critical for protein/enzyme function
induced fit model
ligand is coupled to conformational changes, sometimes dramatically
conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding model
discovered by Daniel Koshland in 1958
allows for tighter binding and high affinity
both ligand and protein can change their conformation
cooperativity
in multisubunit proteins, conformational changes in one subunit can affect the others
functions of globular proteins
storage of ions and molecules (myoglobin, ferritin)
transport of ions and molecules (hemoglobin, serotonin transporter)
defense against pathogens (antibodies, cytokines)
muscle contractions (actin, myosin)
biological catalysis (chymotrypsin, lysozyme)
ligand
molecule binding to a protein
typically small
binding site
region in the protein where the ligand can associate with it
noncovalent
ligands bind via the same ___ interactions that dictate protein structure, as they allow the interactions to be transient
hydrophobic effect
Van Der Waals
association rate constant
ka
rate at which the protein and the ligand bind to form the protein-ligand complex
dissociation rate
kd
rate at which the protein-ligand complex breaks off into the protein and the ligand as separate elements
equilibrium
when the association and dissociation rates are equal
rate
small k used to designate ___ constant
equilibrium constant
big K used to designate ____
Ka
__ = [PL]/([P]*[L]) = 1/Kd
theta
the fraction of occupied binding site
__ = [PL]/([PL]+[P]) = bound/total = [L]/([L]+Kd)
free ligand, Kd
the fraction of bound site (theta) depends on the ___ concentration and ___
Y
fractional occupancy symbol
saturation binding curve
fractional occupancy plotted against (usually experimentally known) substrate concentration
50
On a saturation binding curve, Kd corresponds to the intersection between the ___% line and the curve
equal
At equilibrium, when 50% of protein is bound, the concentration of unbound protein and the concentration of protein complexes are ___
[P] = [PL] AT EQUILIBRIUM
kon
formation of complexes
M-1 s-1
quick bonding/recognition
koff
dissociation of complexes
s-1
stability
koff,kon
Kd = __/__=stability/recognition
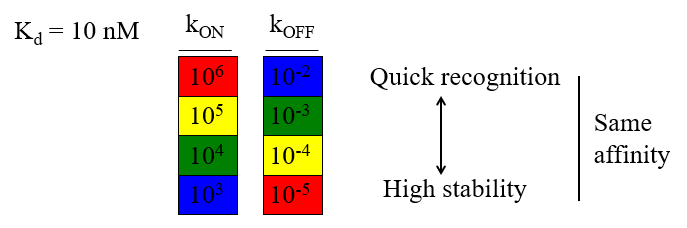
affinity
__ and kinetics are related
complexes can have the same __ aka same Kd despite being made of different combinations of kon & koff rates, and thus either more stability or quick recognition.
decrease
to increase affinity, you need to ___ Kd
partial pressures
when the ligand is a gas, binding is expressed in terms of ___
low
myoglobin has a very ___ Kd, aka a very high affinity for O2, which makes sense because its function is to store it
molarity
dissociation constant Kd is expressed in units of ___ (M)
kJ/mol
free binding energy delta Go is expressed in units of ___
DGo = DHo −TDSo
DGo = −RT ln Ka = RT ln Kd
strong interactions
Kd < 10nM
weak interactions
Kd > 10nM
lock and key model
high specificity binding model
based on the complementary of the binding site and the ligand, complementary surfaces are preformed
size
shape
charge
hydrophobicity
discovered by Emil Fisher in 1894