MIDS 167 finals...
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
What are these symptoms associated with?
crushing or squeezing (typical symptoms)
Nausea/vomiting
Diaphoresis (profuse sweating)
Chest pain
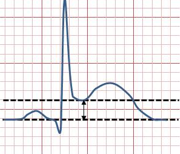
What is this + what does it mean?
ST elevation, MI, pericarditis or other
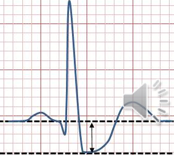
What is this + what does it mean?
ST depression, MI, ischemia, angina, bundle branch blocks (BBB)
What can inverted T wave mean?
MI, ischemia, electrolyte imbalance, cardiomyopathies etc
What kind of angina?
Chest pain when exercising that goes away once the patient stops and rests
Stable
What kind of angina?
Constant chest pain that occurs with minimal activity or rest
Unstable
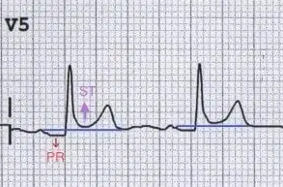
What kind of heart issue is this + symptoms?
pericarditis, sharp stabbing pain that is relieved when sitting up or leaning forward
What is this?
pericarditis
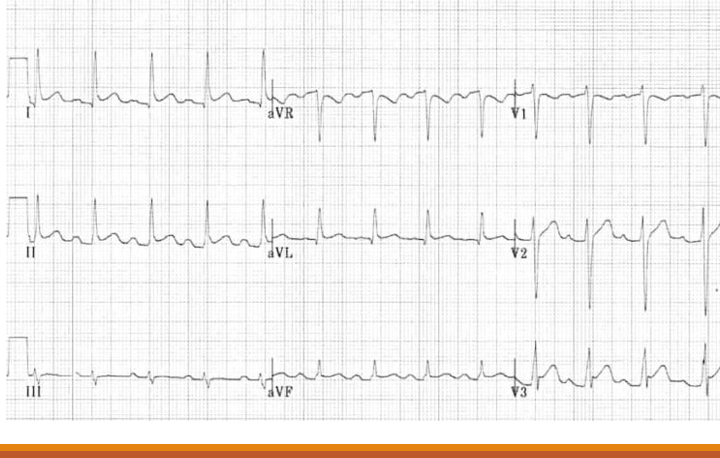
what is this?
pericarditis
What kind of MI is this?
Right coronary artery
ST elevation in leads II, III, AVF
Inferior MI
What kind of MI is this?
Left circumflex artery (LCX)
ST elevation in leads I, AVL, V5, V6
Lateral MI
What kind of MI is this?
Left anterior descending artery (LAD), the septal branches
ST elevation in V1-V2
Septal MI
What kind of MI is this?
Left anterior descending (LAD), the anterior branches
ST elevation in leads V3-V4
Anterior MI
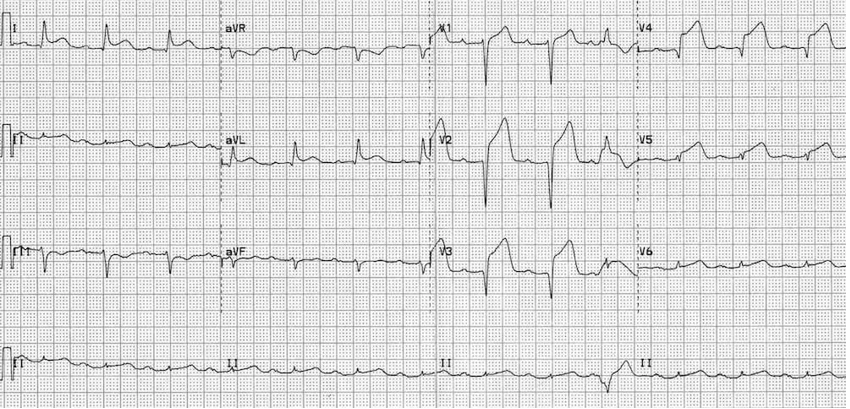
What kind of MI is this?
anteriolateral MI
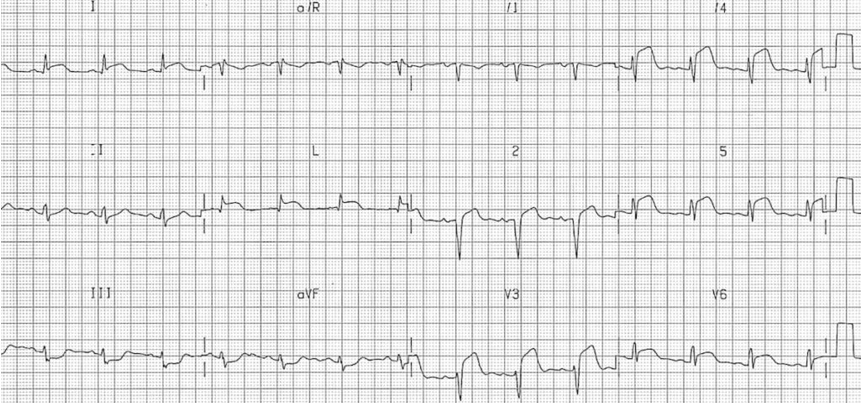
What kind of MI is this?
anteriolateral MI
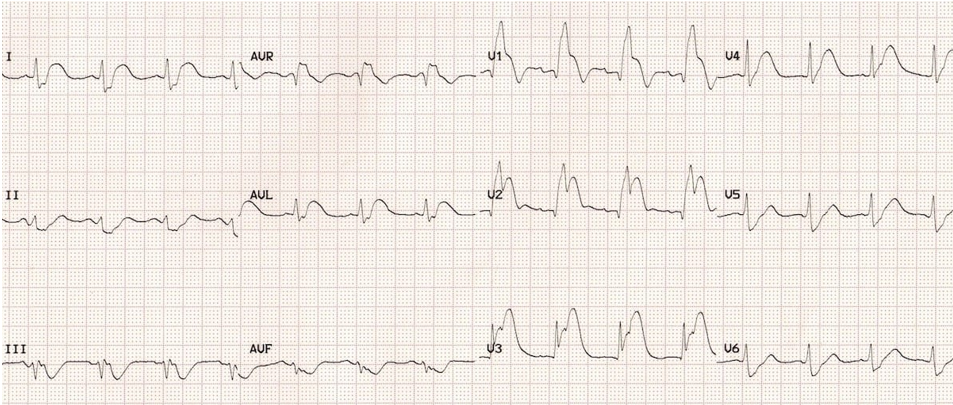
What kind of MI is this?
anterior MI
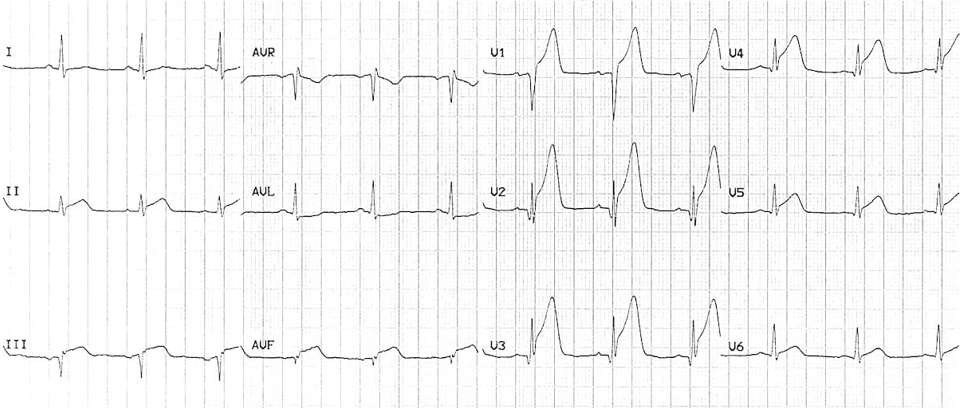
What kind of MI is this?
anterior-inferior MI
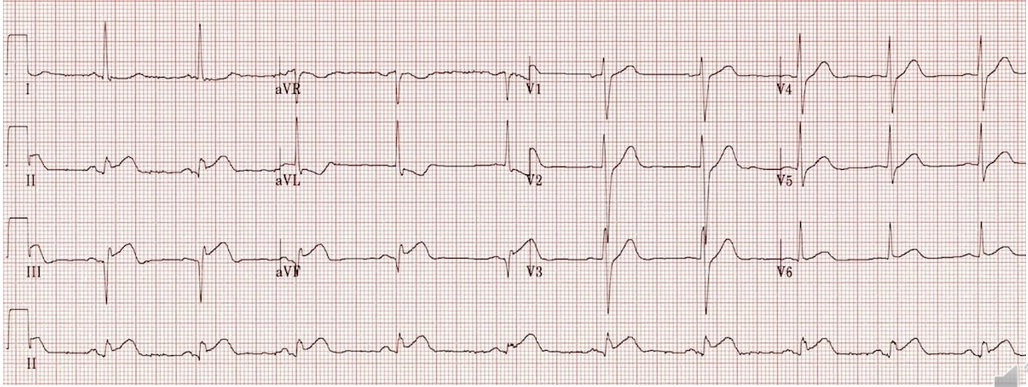
What kind of MI is this?
anterior-inferior MI
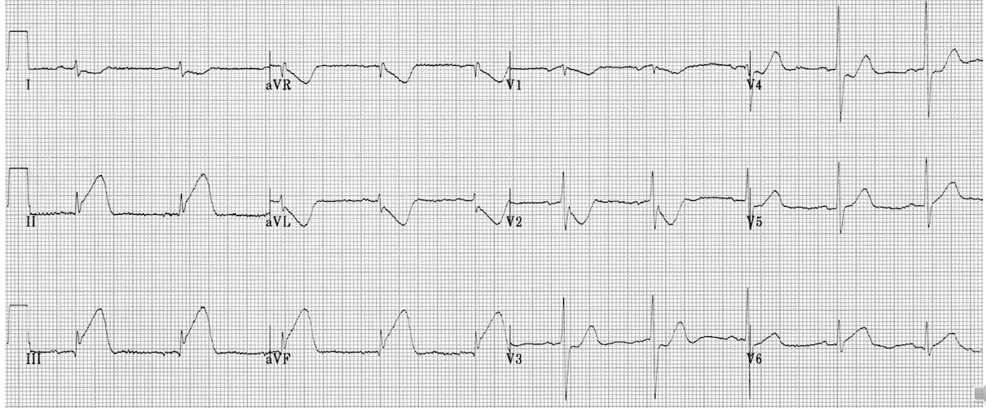
What kind of MI is this?
inferior MI
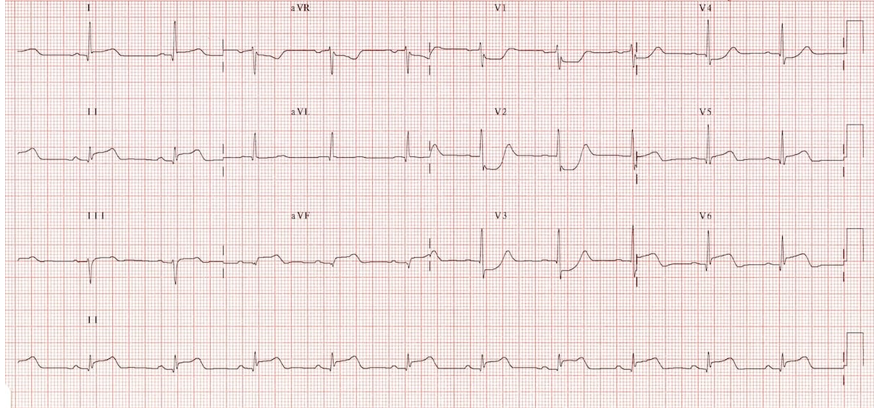
What kind of MI is this?
inferior-posterior MI
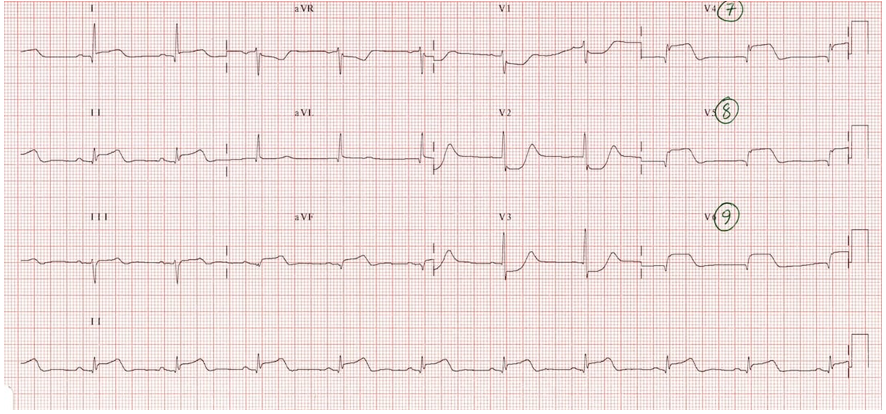
What kind of MI is this?
Inferior-posterior MI
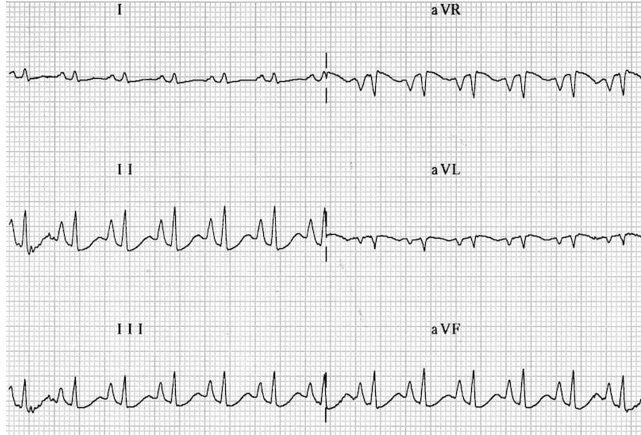
What kind of heart problem is this + how to spot it?
right atrial enlargement, p wave more than 2.5mm (about 1 big box)
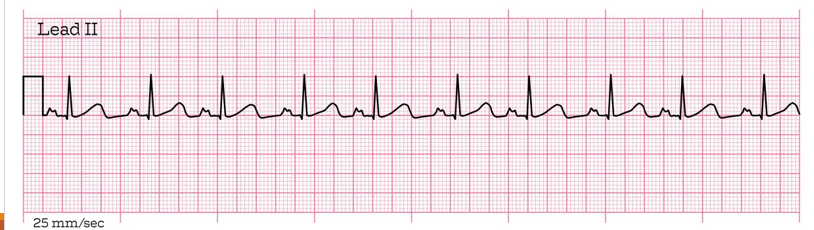
What kind of heart problem is this + how to spot it?
left atrial enlargement (LAE), p wave looks like an m
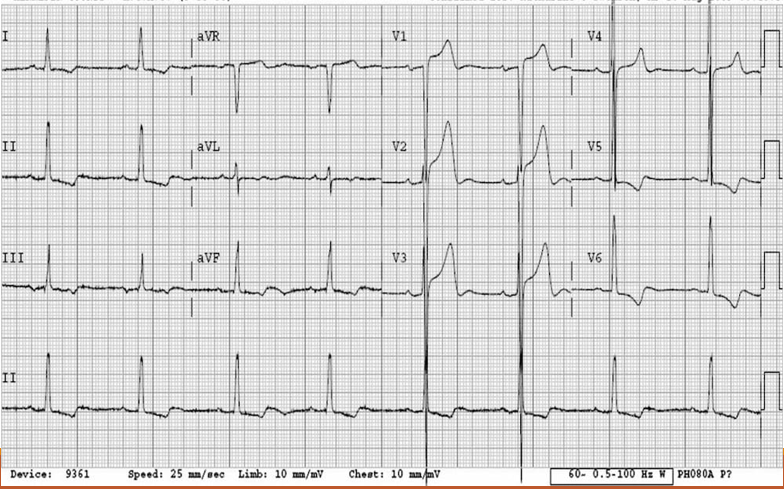
What kind of heart problem is this + how to spot it?
left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), tall R waves in V5 and V6, deep s wave in V1 and V2
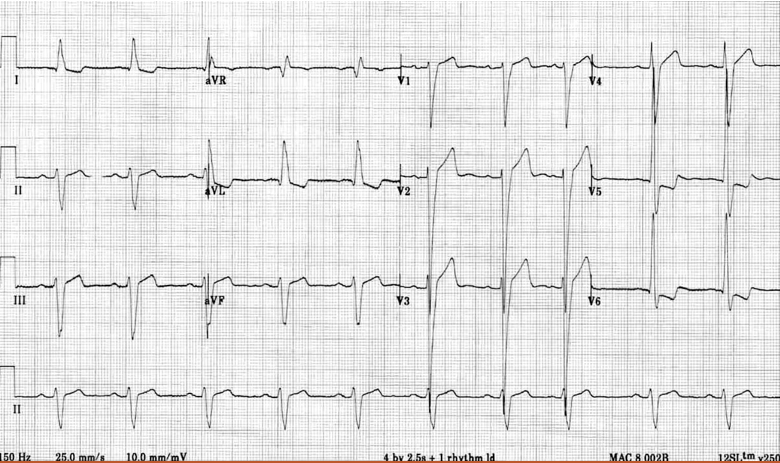
What kind of heart problem is this + how to spot it?
left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), tall R waves in V5 and V6, deep s wave in V1 and V2
There are only permanent pacemakers. T/F?
f
when are temporary pacemakers used?
emergency
types of temporary pacemakers?
Transcutaneous pacing (TCP), Transvenous Pacing
permanent pacemakers are either single or dual chambered. T/F?
T
3 types of pacemakers:
1) Atrial
2) Ventricular
3) ?
AV sequential
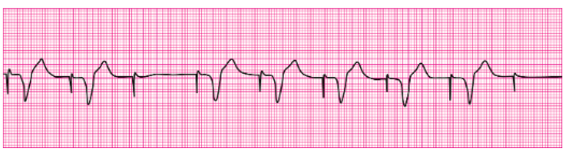
what happened here?
failure to capture
what is it called when the pacemaker feels that the atria/ventricle contracted on its own + when it has to shock it to get it to move?
sensing, pacing
When the ECG shows there is no relationship between the P wave and the QRS complex, you should suspect:
3rd degree block
Wenchkebach differs from complete heart block in that a complete heart block usually has: (normal or abnormal RR interval?)
Regular RR interval
The keys to interpretation of second-degree heart block, Mobitz type II, are the presence of constant PR intervals and the fact that there are more P waves present than QRS complexes. T/F?
t
In order to calculate heart rate accurately by the R-to-R interval method, the patient must have a regular rhythm. T/F?
t
often, Mobitz type II heart block will not progress to third-dree heart block. T/F?
f
Typically, first-degree block results from excessive conduction delay in the:
AV node
The heart block rhythm that most closely resembles a normal rhythm is:
1st degree block
It is important to note that the PR interval in Mobitz type II is constant, or regular, for every conducted beat. T/F?
t
If the ventricular pacemaker is the escape pacemaker, the ventricular rate will most commonly be between 20 and 40BPM. T/F?
t
A constant and prolonged PR interval is the hallmark of __________ degree block and is most commonly the only variation in the ECG strip.
1st
The first type of second-degree block is more serious than the second type because bradycardia is less likely to be present and because cardiac output is less likely to be seriously decreased in a second-degree type I block. T/F?
f
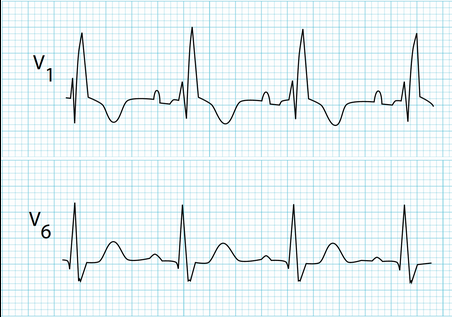
type of abnormality + characteristics?
RBBB, M in v1, W in v6, RSR (bunny ears)
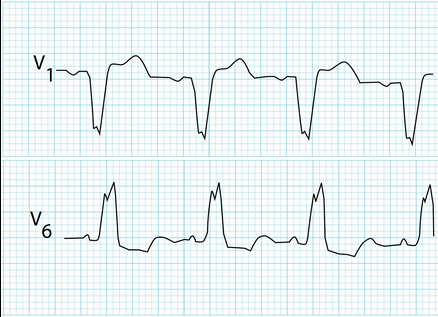
type of abnormality + characteristics?
LBBB, W in v1, M in v6, deep s wave in v1, monophasic (only 1 direction) s wave
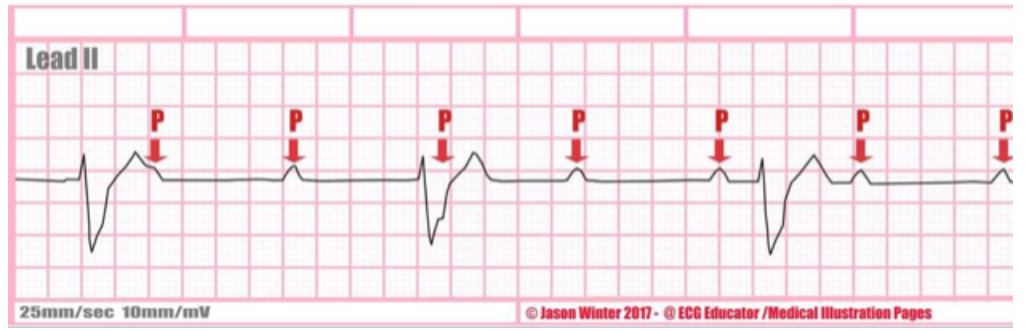
type of abnormality + characteristics?
3rd degree block, marching p waves, wide qrs, p waves and QRS don’t agree with eachother, normal RR ratio
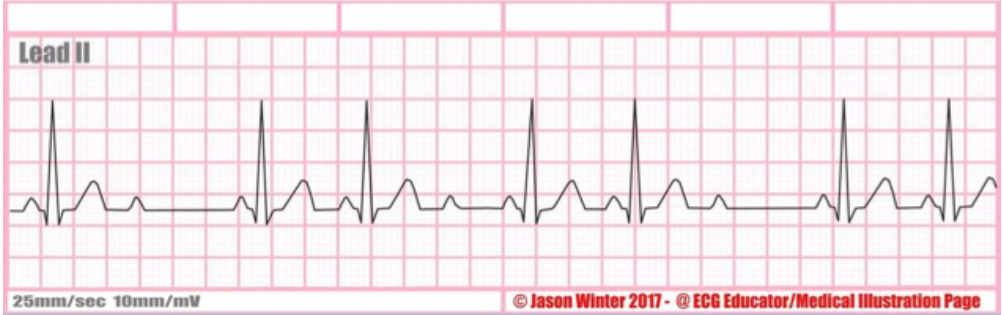
type of abnormality + characteristics?
2nd degree block mobitz type 2, some p waves dont have a QRS, can drop more than 1 QRS
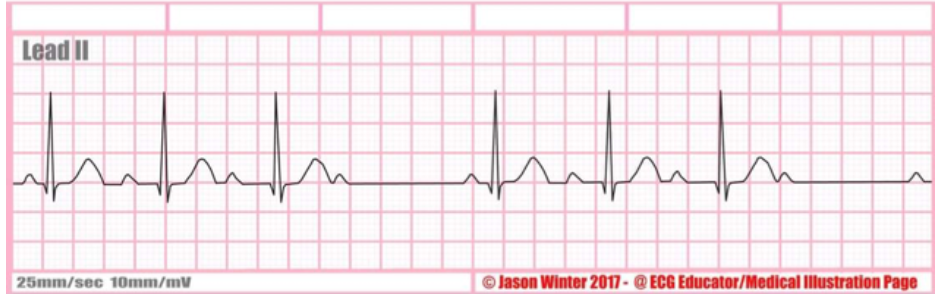
type of abnormality + characteristics?
2nd degree block mobitz type 1 (wenckebach), pr interval gets longer and longer until it drops the QRS completely and then resets
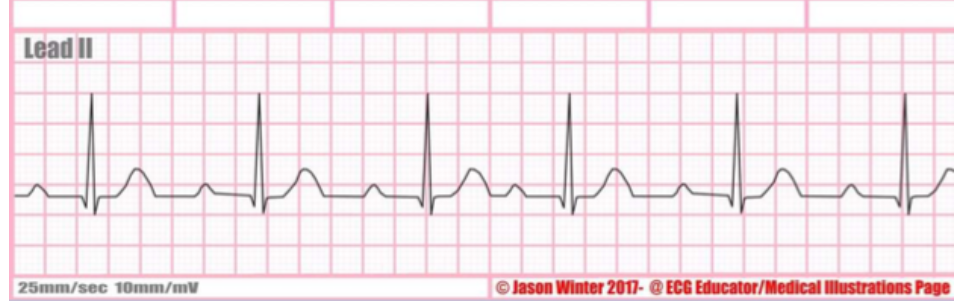
type of abnormality + characteristics? (PR interval > 0.20 secs)
1st degree block, PR interval longer than 0.20
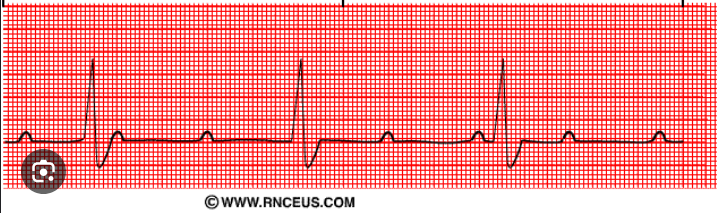
type of abnormality + characteristics?
3rd degree av block, p waves and qrs complexes dont match, marching p waves, regular RR interval
PVCs characteristically have a _____________ pause.
compensatory
Atrial activity is not discerned on an ECG strip in all the following rhythms except:
A) V tach (Ventricular Tachycardia)
B) AIVR (Accelerated Idioventricular rhythm)
C) A fib (Atrial Fibrillation)
D) IVR (Idioventricular rhythm)
c
The QRS interval should normally be ______seconds or smaller.
0.12
Oscilloscopic evidence of ventricular fibrillation can not be mimicked by artifact. T/F?
f
It may be difficult to distinguish asystole from very V-fib; therefore, you must always check how many number of different leads?
2
What does PEA stand for?
pulseless electrical activity
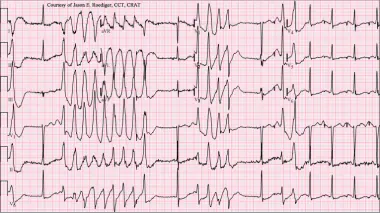
What rhythm resembles a turning about or twisting motion along the baseline (isoelectric line)?
Torsades de pointes, looks like that one arctic monkey’s album cover
PEA, a life-threatening arrhythmia, may result from:
A) Hypokalemia
B) Hypomagnesemia
C) Tricyclic antidepressant drug overdoes
D) All of the above
d
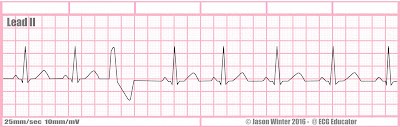
Rate + characteristics?
NSR with isolated PVC, has uniform shape
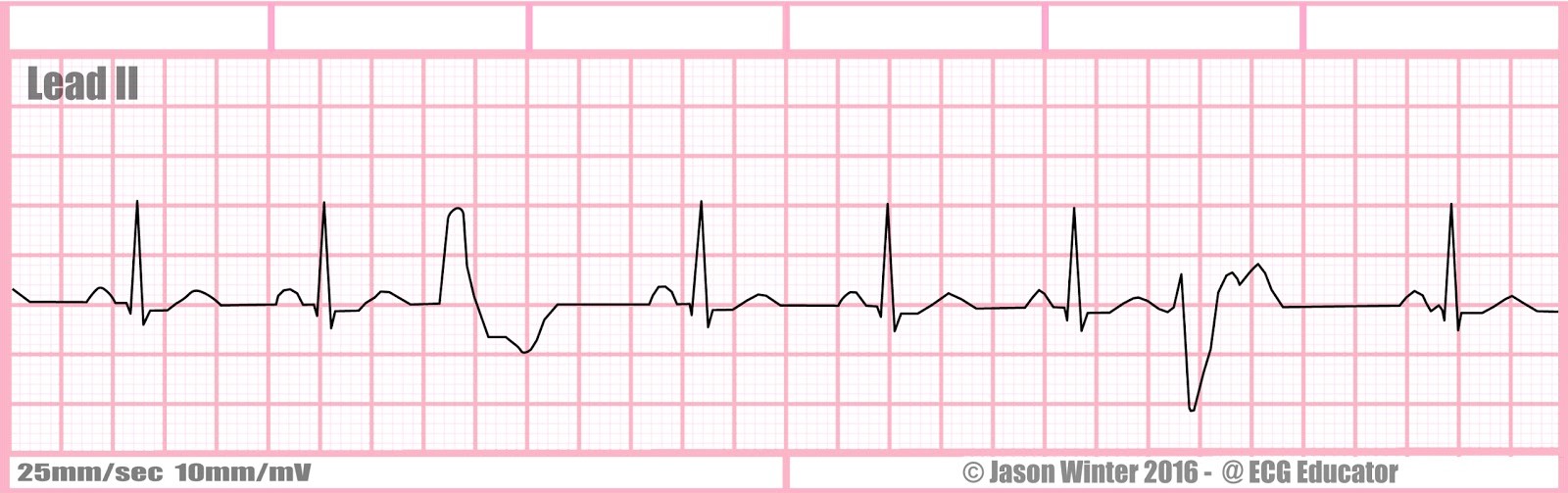
Rate + characteristics?
multifocal PVC, has different shapes
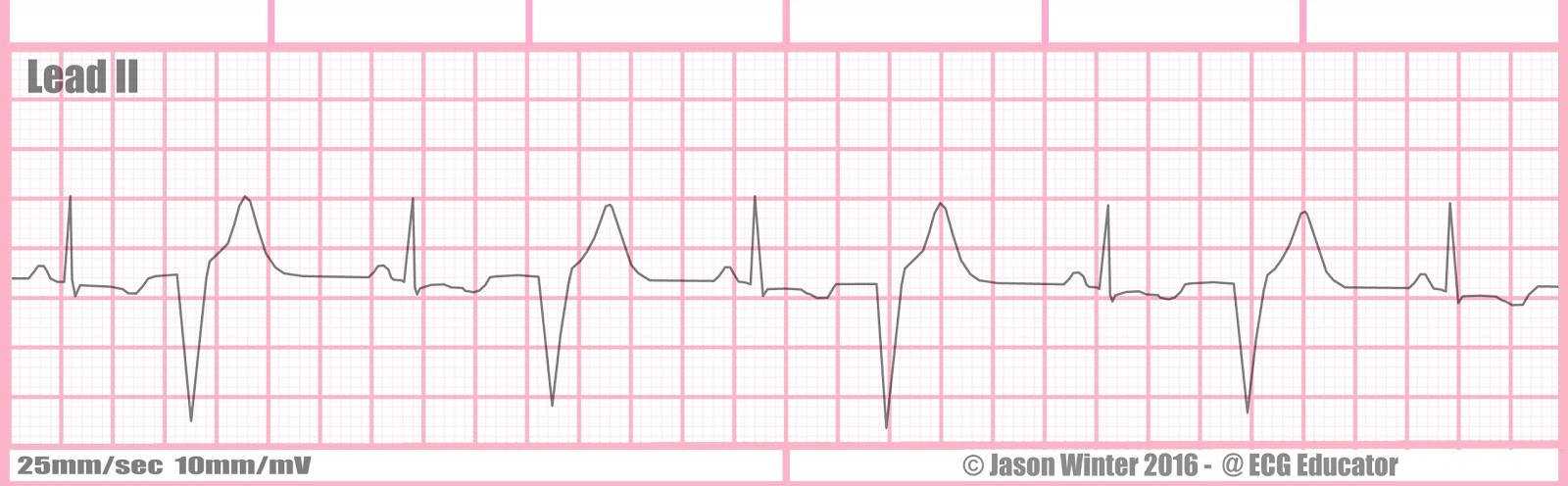
Rate?
Ventricular bigemini
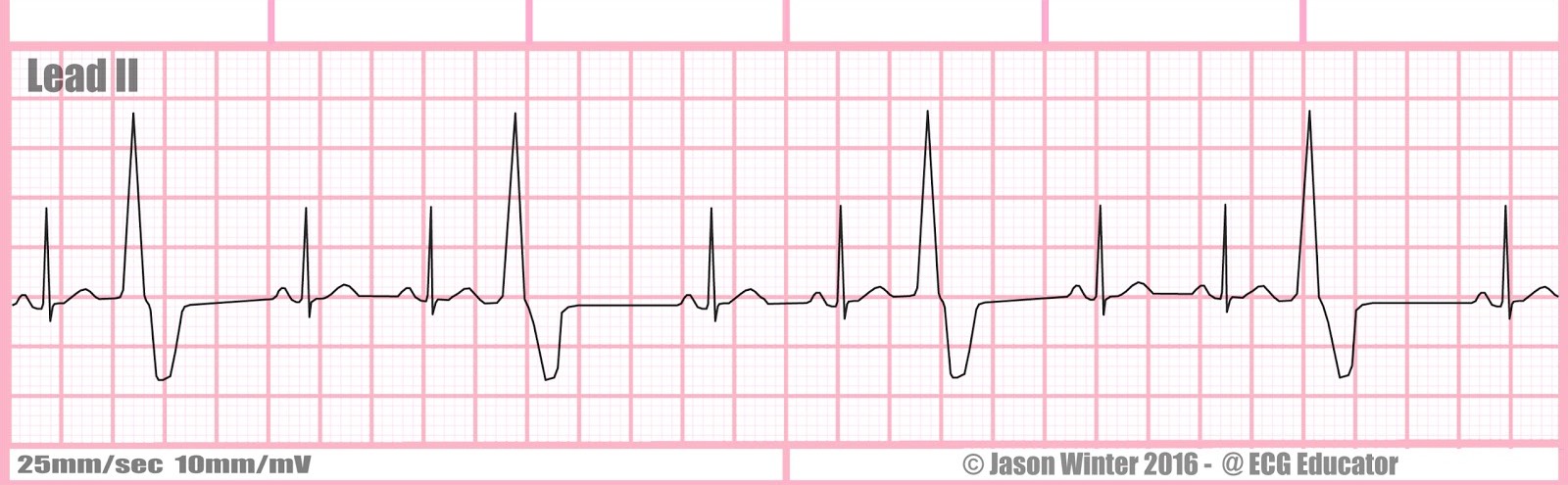
Rate?
ventricular trigeminy
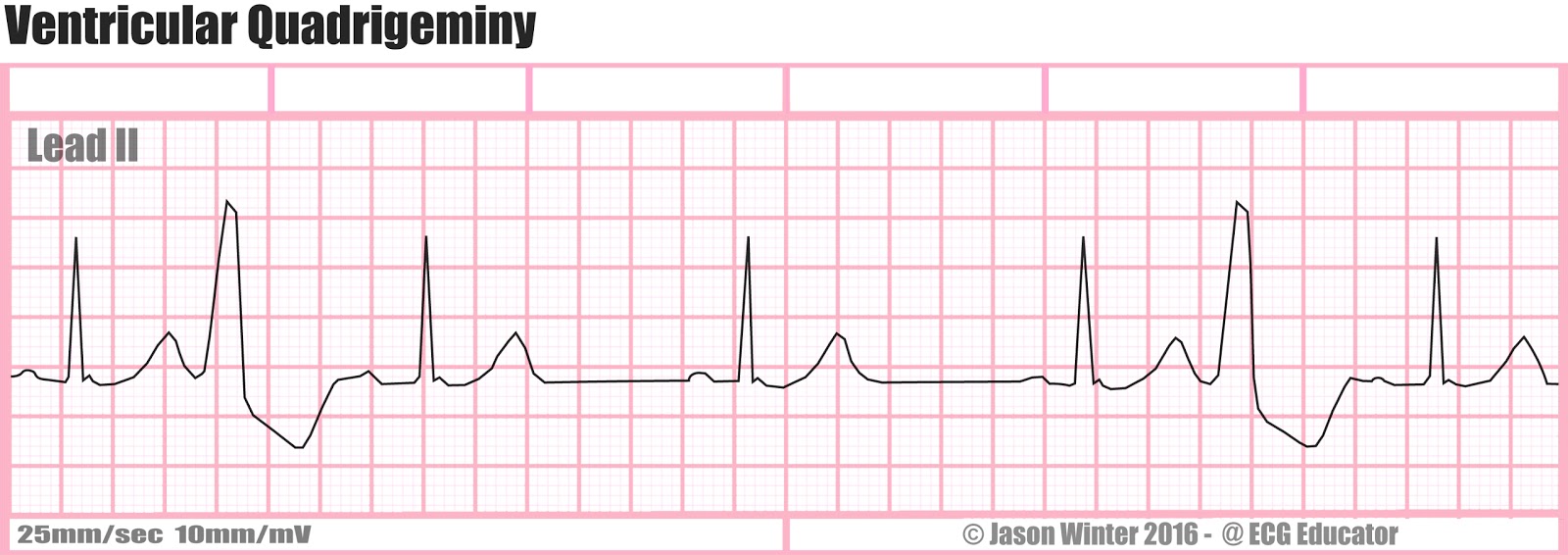
Rate?
ventricular quadrigemini
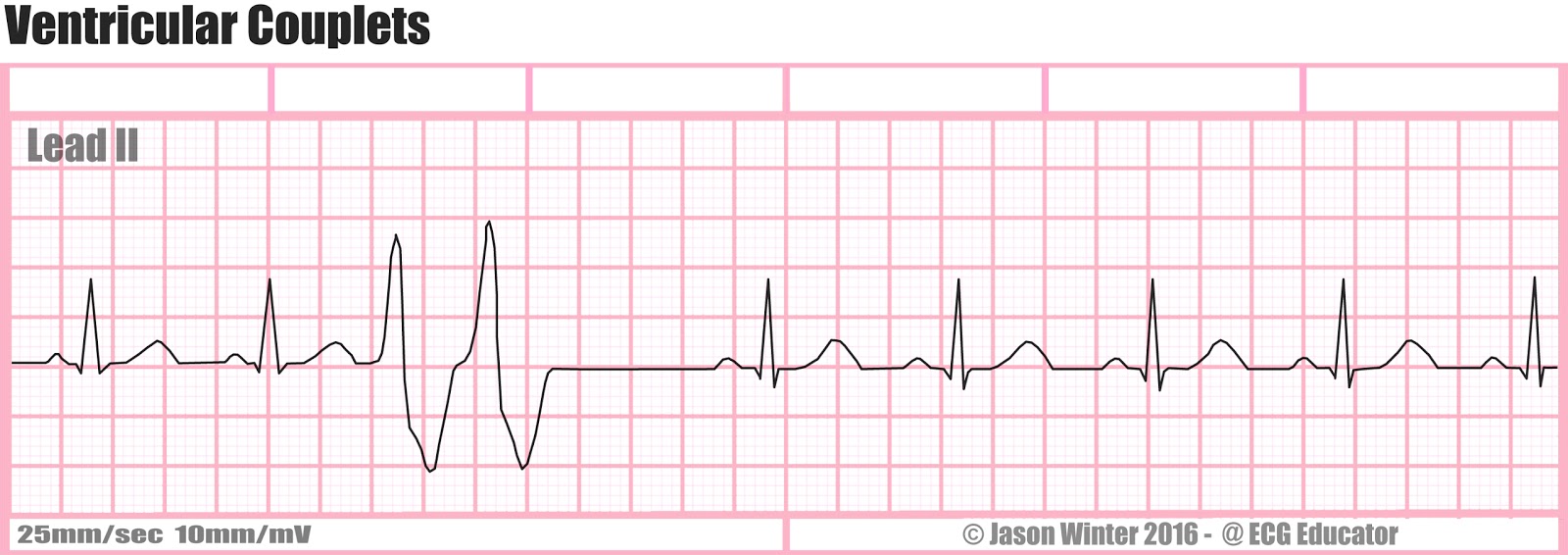
Rate?
ventricular couplets
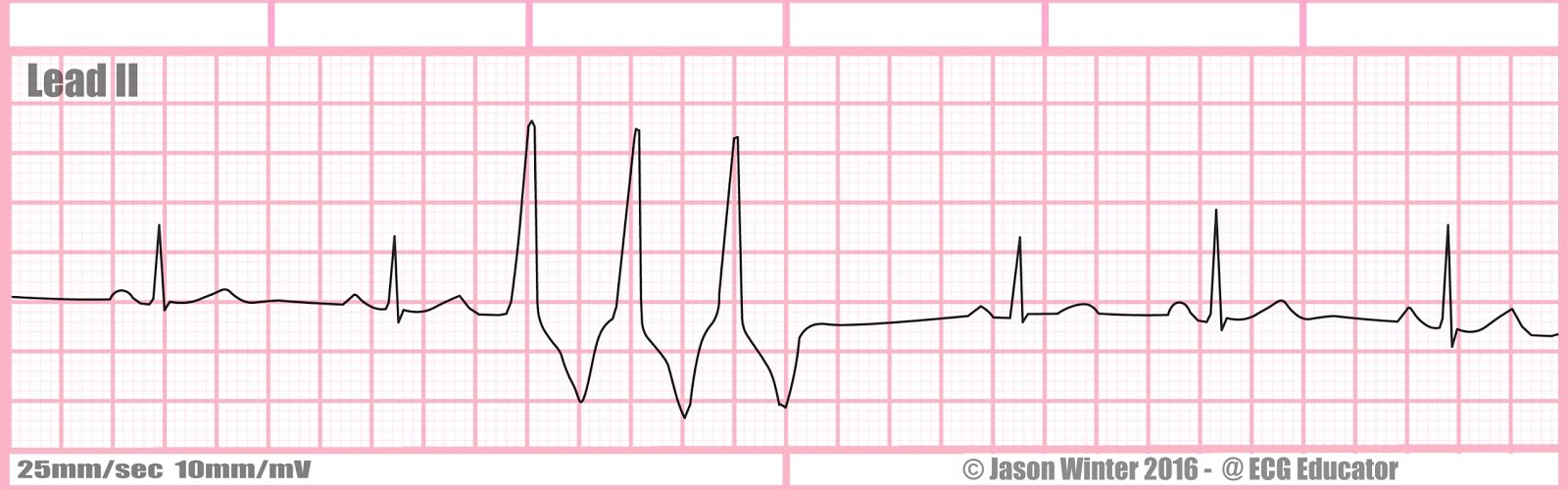
Rate?
ventricular triplets (salvo)
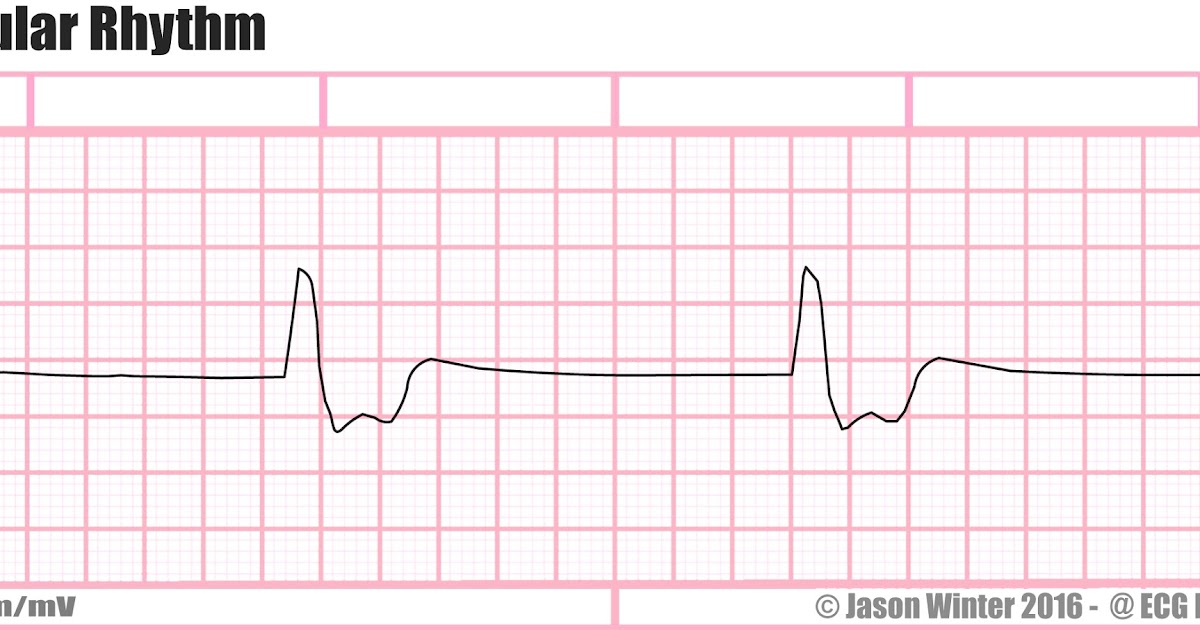
Rate + characteristics?
idioventricular rhythm, no p wave, wide and weird QRS, 20-40 bpm, made by purkinje fibers
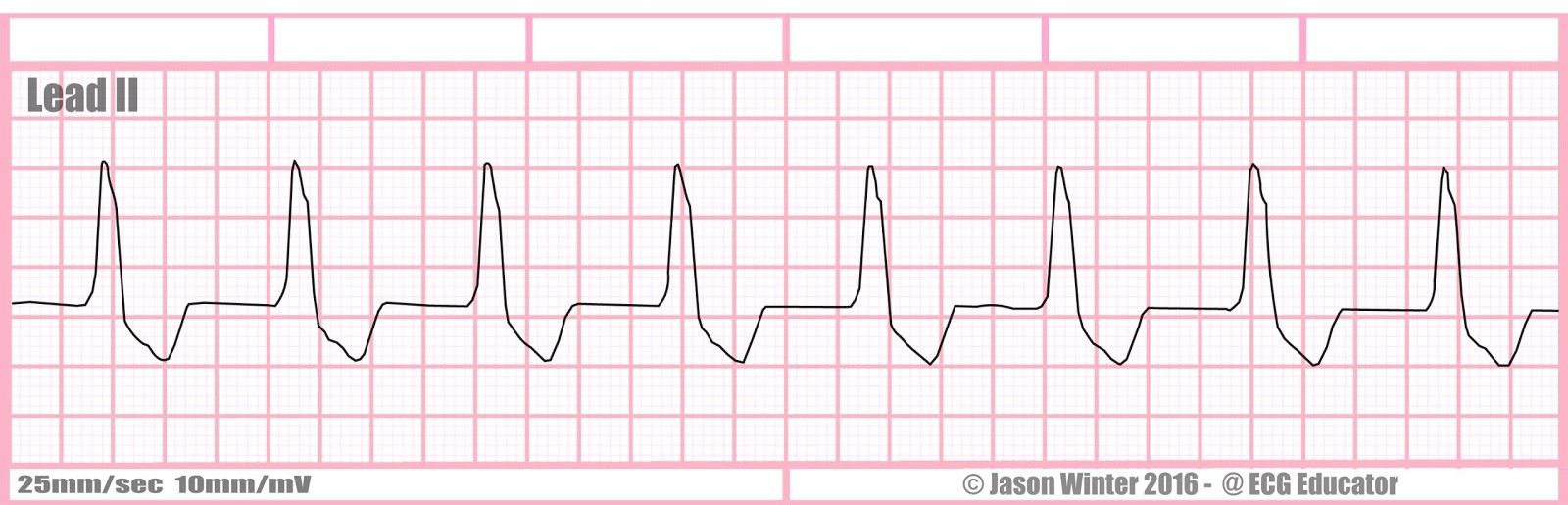
Rate + characteristics?
accelerated idioventricular rhythm (AIVR), 40-100 bpm, no p waves, wide and weird QRS
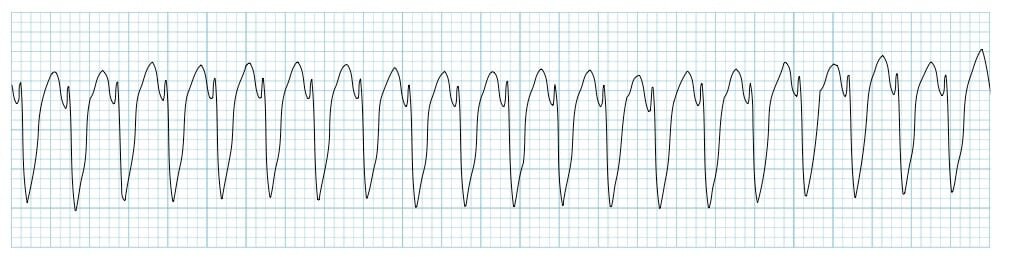
Rate + characteristics?
Ventricular tachycardia (VT), bpm 100-250, no p wave
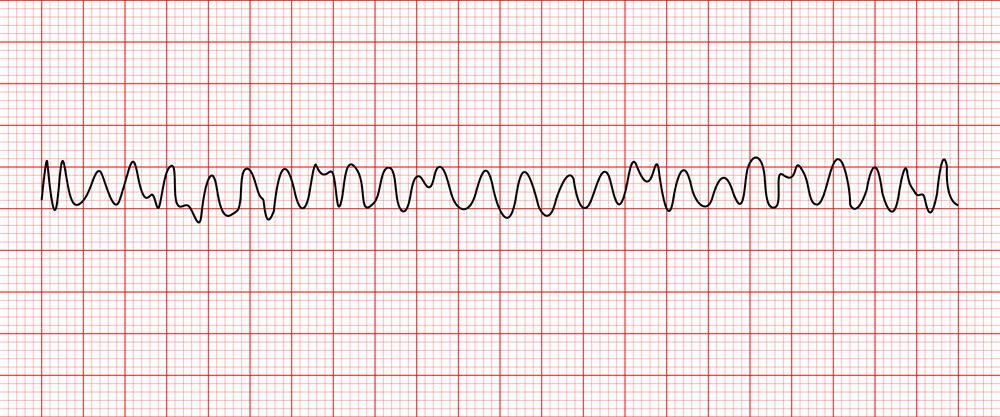
Rate + characteristics?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF), no p waves, chaotic irregular squiggly lines
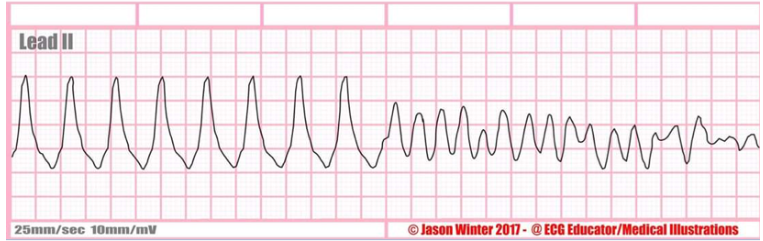
Rate?
Ventricular tachycardia to ventricular fibrillation
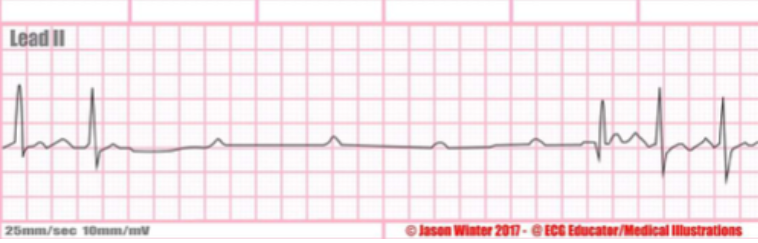
Rate + characteristics?
Ventricular standstill, p waves with no QRS
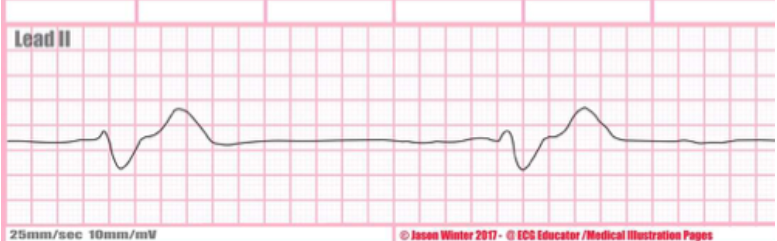
Rate + characteristics?
agonal rhythm, 15-20 bpm, very wide complexes, happens before asystole
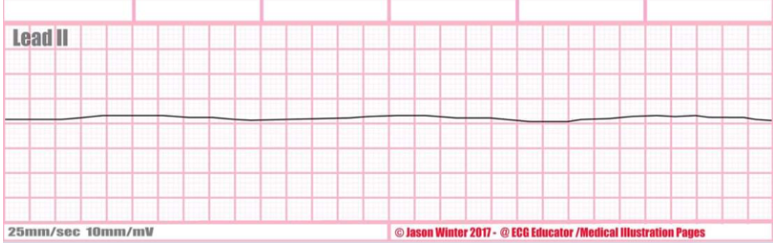
Rate + characteristics?
asystole, mostly a flat line
Difference between isolated PVC vs Multifocal PVC? What does the shape tell us?
shape depends on the site origin, if shape is uniform its isolated PVC, if it has different shapes its multifocal PVC
Ventricular fibrillation will always generate a pulse, whereas cardiac arrest won't. T/F?
F
Characteristics of junctional rhythm?
p wave can be inverted, late, or hidden
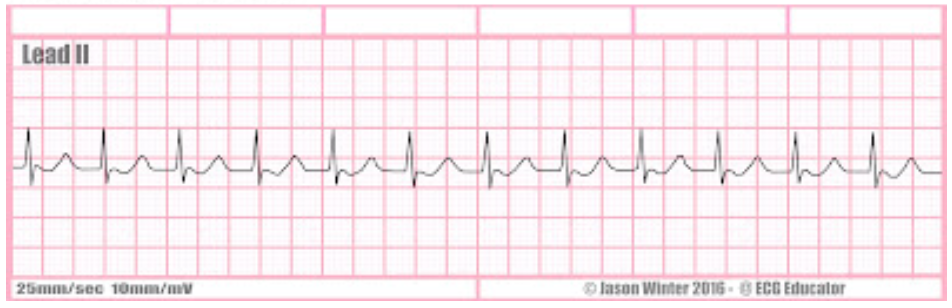
what is this rate + characteristics?
junctional tachycardia, absent or backward p wave, bpm over 100
junctional rhythms: more than ___ per minute is considered frequent
6
accelerated junctional rhythm is serious no matter what. T/F?
F
PJCs usually not serious. T/F?
T
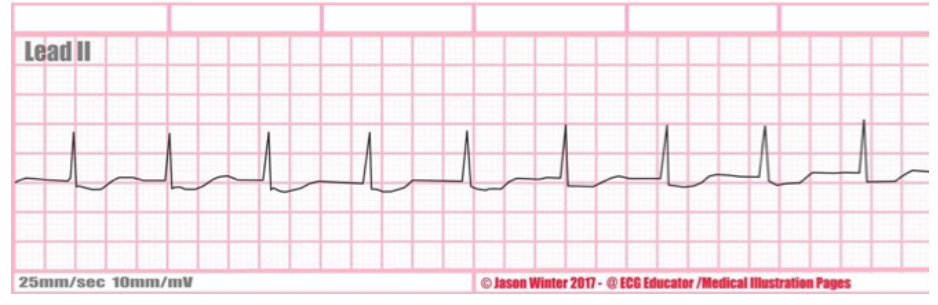
what is this rate + characteristics?
accelerated junctional rhythm, absent or backward p wave, bpm 60-100
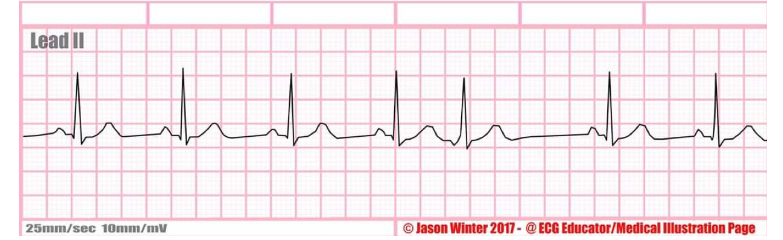
what is this type of rate?
premature junctional complex (PJC)
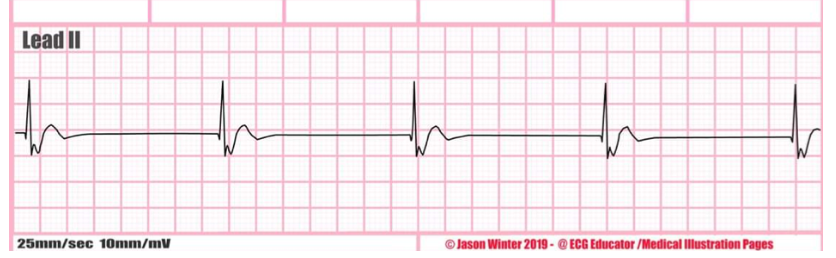
what is this rate + characteristics?
junctional rhythm with retrograde conduction
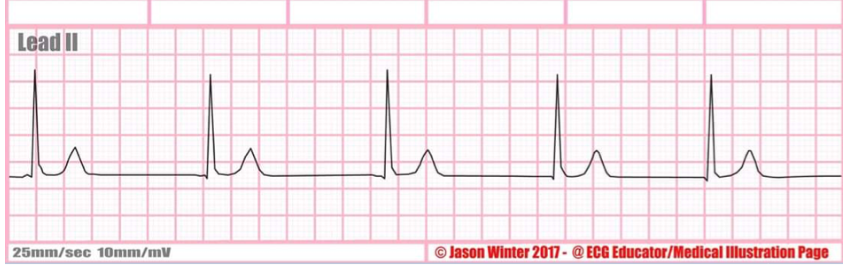
what is this rate?
junctional rhythm
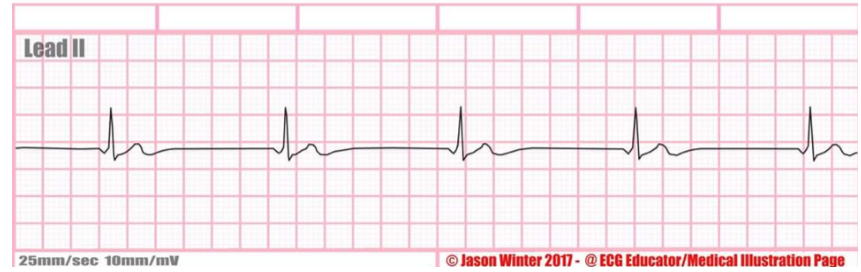
what is this rate?
Junctional rhythm
PJCs may never occur without any definite underlying cause. T/F?
F
Causes of PJCs may include:
A) Fever
B) anxiety
C) drugs
D) all
d
what is the 5 step approach?
HR, rhythm, P wave, PR interval, QRS complex
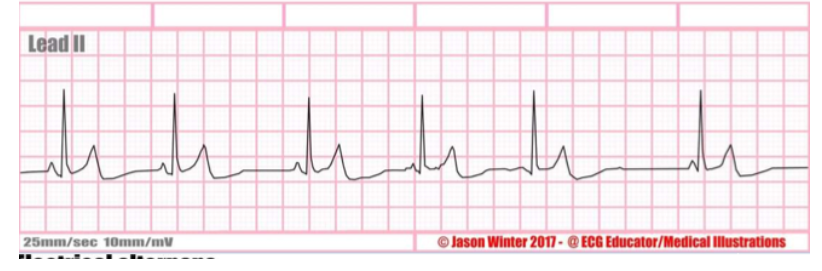
rate + characteristics?
wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP), 3 different P waves (upright, inverted or absent), 60-100 bpm
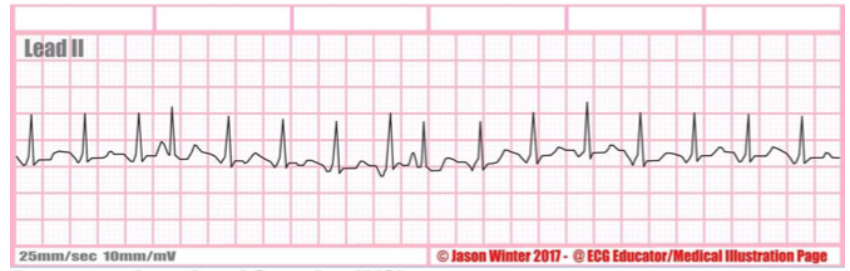
rate + characteristic?
multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT), 3 different P waves, can be irregular, bpm over 100
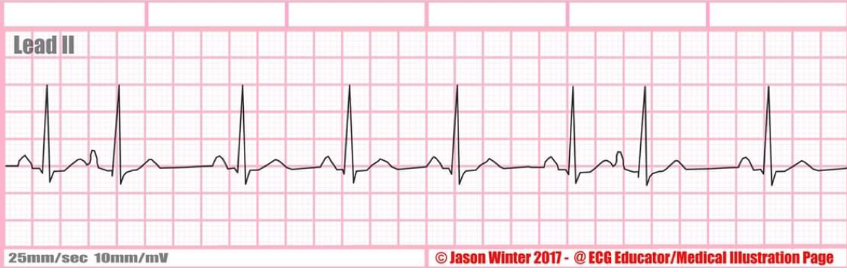
TYPE of rate + characteristics?
premature atrial complex (PAC), early P wave usually followed by a QRS complex
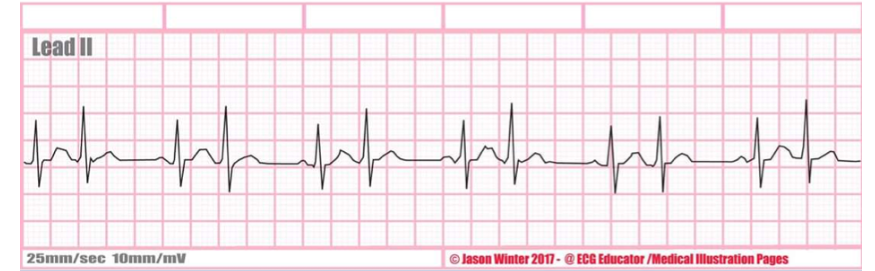
rate + characteristic?
atrial bigeminy, every second beat is premature
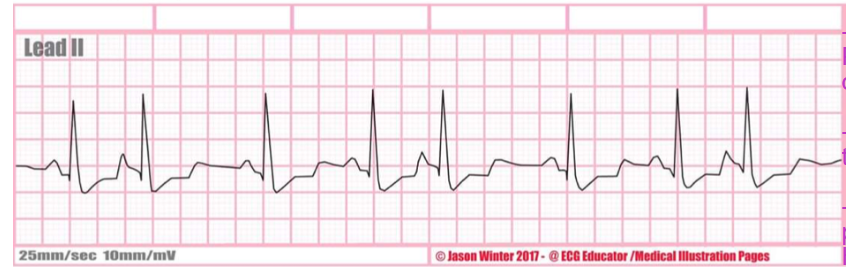
rate + characteristic?
atrial trigeminy, every third beat is premature
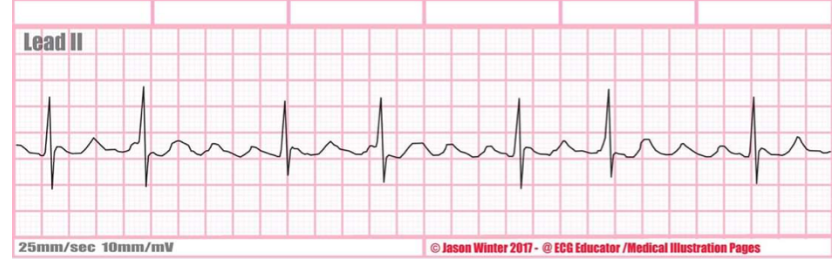
what rate is this + characteristics?
atrial flutter, flutter waves, saw tooth pattern, single irritable foci
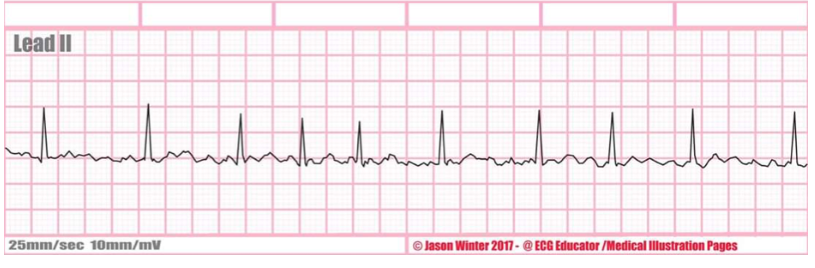
rate + characteristic?
atrial fibrillation (AFib), Irregularly irregular, no P waves, multiple irritable foci
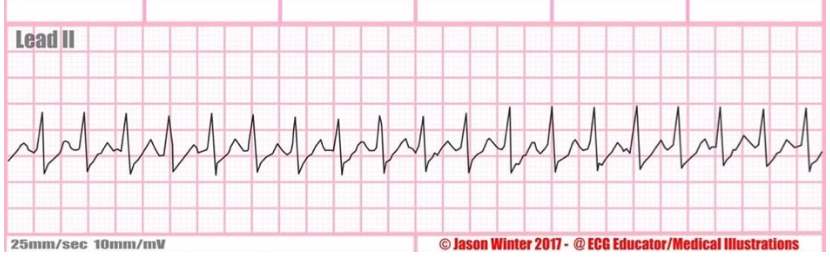
rate + characteristics?
supra ventricular tachycardia (SVT), bpm over 100, p waves usually hidden, slanted s wave
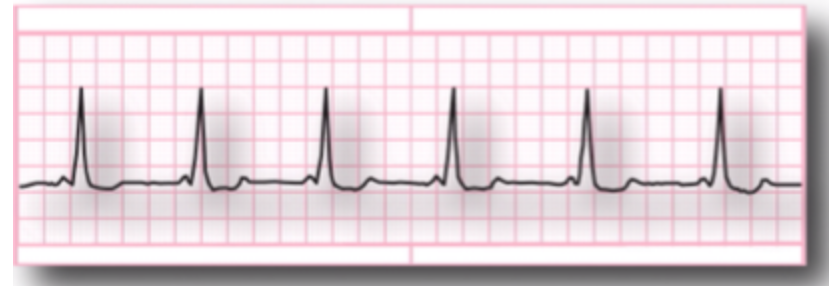
characteristics of Wolff-parkinson-White (WPW)?
Delta waves beginning at QRS complex
what does PAT refer to?
sudden atrial tachycardia
used to stimulate baroreceptors and used to slow heart rate
Vagal maneuvers
single irritable site in the atria initiates many electrical impulses at a rapid rate
atrial flutter