Chem H Unit 1
1/42
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Democritus
Discovered the atom
Atomos
Greek for invisible
Matter is made of atoms
John Dalton’s atomic theory (true)
Atoms combine in specific ratios forming compounds
John Dalton’s atomic theory (true)
In reaction atoms are rearranged
John Dalton’s atomic theory (true)
Atoms of an element are identical
John Dalton’s atomic theory (false)
Atoms cannot be divided
John Dalton’s atomic theory (false)
Plum pudding model by JJ Thompson
J. J. Thompson
Discovered electrons (were embedded in a positive mass)
Nuclear model by Earnest Rutherford
Earnest Rutherford
Discovered nucleus and protons
Earnest Rutherford
Determined atoms are predominantly empty space
Earnest Rutherford
Electrons are far from the nucleus
Earnest Rutherford
Nucleus is small, dense, and positive
Planetary Model by Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr
Determined electrons orbit in specific energy levels
Moseley
Arranged elements by atomic number
Mendeleev
Russian scientist; first noticed that elements arranged by increasing mass showed similar properties
Law of definite proportions
Ratio of elements in a compound does not change with the mass of the compound
Law of multiple proportions
Different ratios of the same elements can form different compounds
Conservation of mass
Matter is neither created nor destroyed by chemical reactions or physical changes
Protons
Positive
Changes the element
Neutrons
Neutral
Changes the mass
Electrons
Negative
Changes charge and form bonds
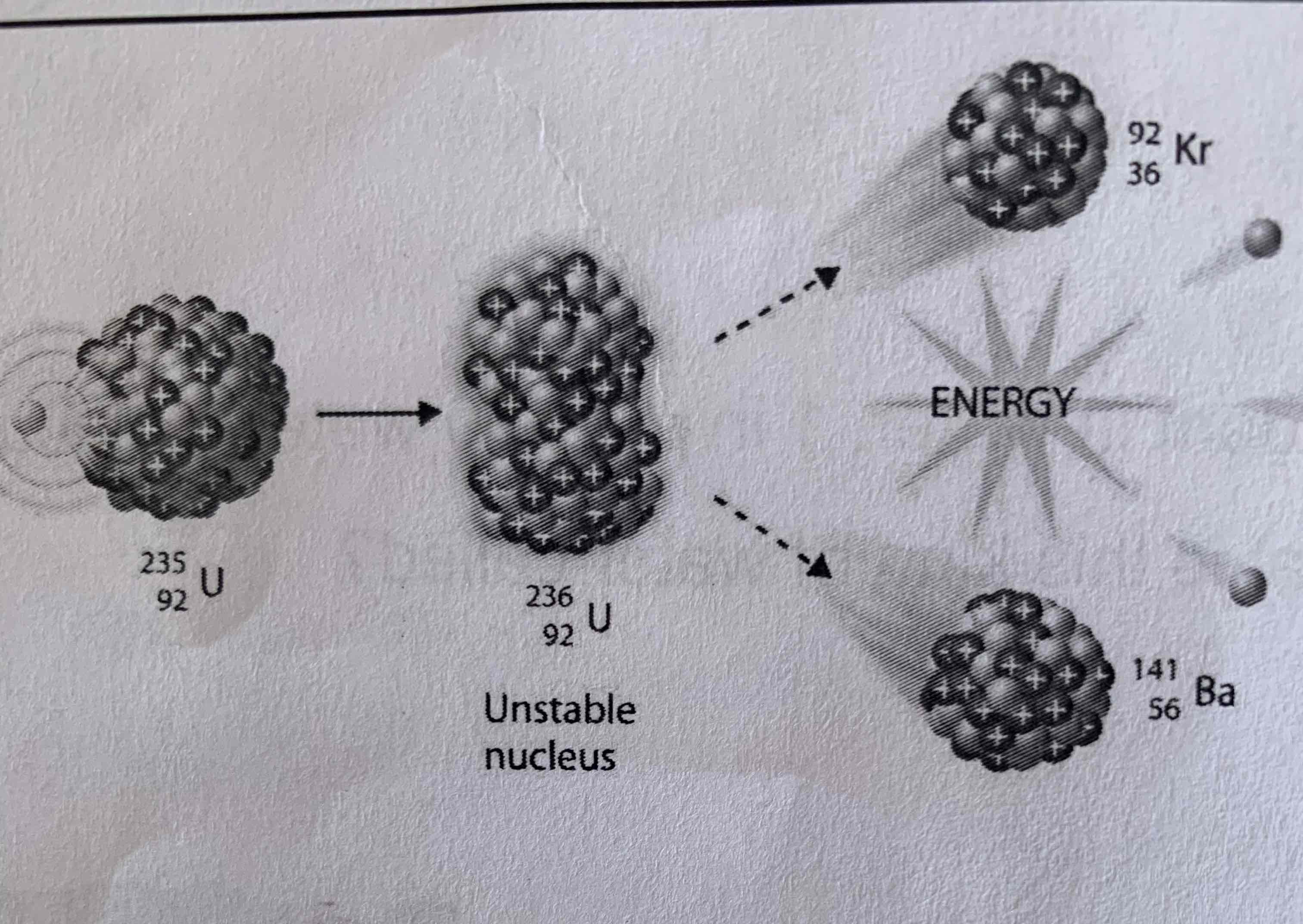
Fission
Breaks apart
Fission
Utilized in power plants
Fission
Reacts don’t always make the same products
Fission
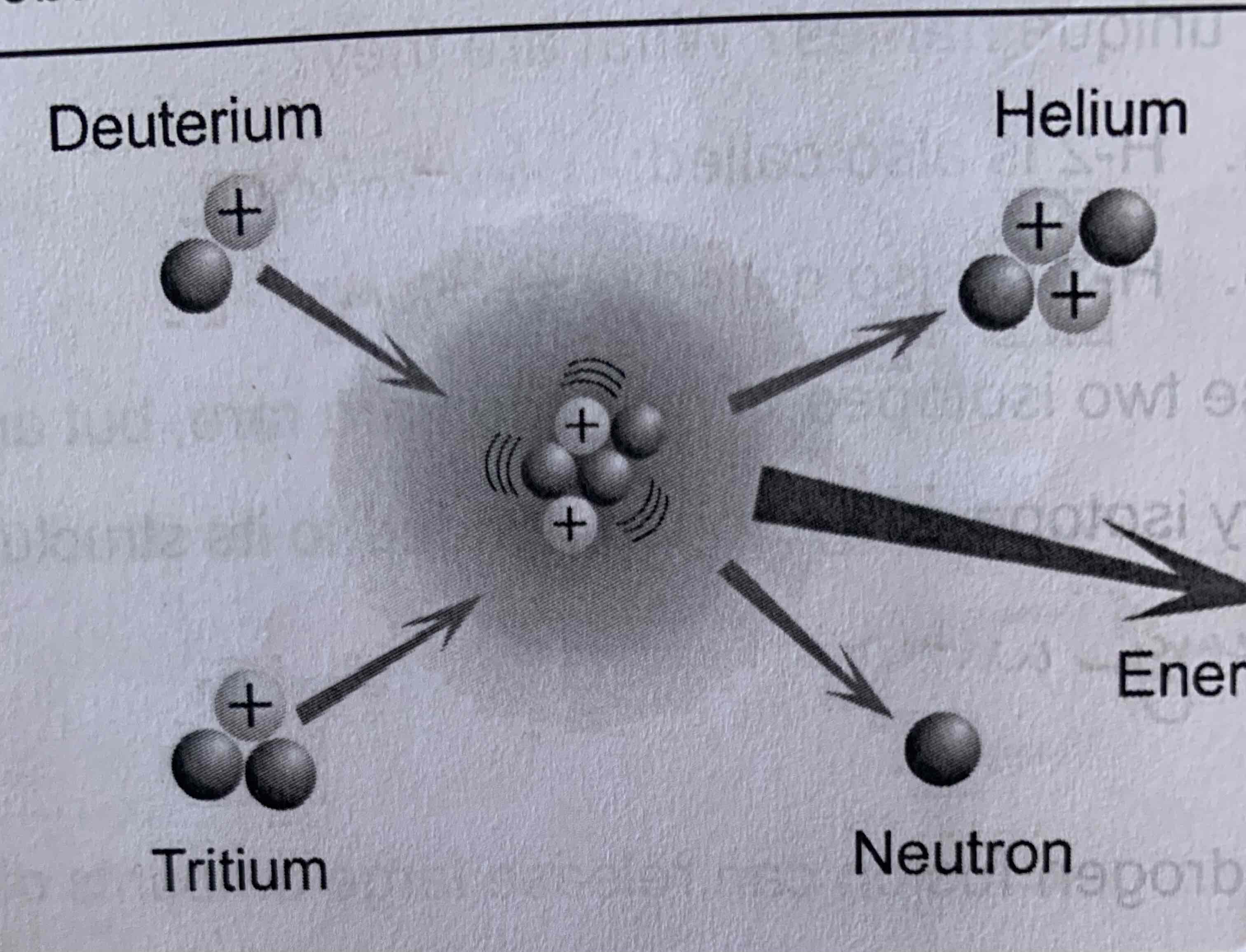
Fusion
Combination of nuclei
Fusion
Deuterium
Fusion
Fusion and Fission
Tzar Bomb
Fusion and Fission
Energy = Mass x Speed of light squared (E=MC2)
Fusion and Fission
Total number of protons and neutrons stay the same during nuclear reactions
Fusion and Fission
The arrangement of protons and neutrons changed (and this the element) in both fission and fusion
Heavy water
1 in 1000 water molecules with a heavy isotope of hydrogen bonded
Transmutation
The changing of one element into another
Nuclide
The protons and neutrons in a nucleus
H-2
Deuterium
H-3
Tritium
Periodic Law
The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic number
Valence electrons
The electrons occupying the outermost energy levels of an atom. Most elements want to have 8.
Atomic radius
The average distance from the center of an atoms nucleus to its outermost electrons