Unit 6: Freshwater
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What percentage of Earth’s surface is covered by water?What percentage of Earth’s water is fresh water?
75%
How much of Earth's water is fresh water?
2.5%
Why is most of Earth's water not usable by humans?
Because it is saltwater in oceans
Where is most of Earth's fresh water stored?
In glaciers and ice caps (68%)
What percentage of fresh water is groundwater?
30%
What percentage of fresh water is surface water?
2%
How much of all fresh water is easily accessible for human use?
Less than 1%
How many people lack adequate access to safe drinking water?
2.3 billion
How many people have no access to clean water?
1 billion
How many people lack access to proper sanitation facilities?
2.6 billion
How does population growth affect water availability?
It increases water shortages, especially in developing countries
Which region is expected to be most impacted by water shortages?
Africa, due to a lack of infrastructure for water access and sanitationWhen there is not
What is physical water scarcity?
When there is not enough water to meet the population’s needs
Where us physical water scarcity common?
In areas with high population density and heavy water use
What is economic water scarcity?
When there is enough water, but poor infrastructure prevents acess
What is an example of economic water scarcity?
Sub-Saharan Africa, where water exists but many people cannot reach safe supplies
How does U.S. water availability compare to other regions?
Relatively high per capita water availability.
What is the major water source for the Southwestern U.S.?
The Colorado River
How long is the Colorado River?
1,450 miles from headwaters to the sea
What is the size of the Colorado River drainage basin?
246,000 square miles
Why is water distribution a challenge in the Southwest?
The region is arid, and water is limited without infrastructure
How many people and acres of farmland rely on the Colorado River?
About 30 million people and 4 million acres of farmland
Which major cities depend on the Colorado River?
Phoenix, Las Vegas, San Diego, and Los Angeles
How much water does the region use per year from the Colorado River?.
15−17 million acre-feet
What happens to most of the Colorado River’s water?
It is heavily manipulated and used before reaching the Sea of Cortez
How much of the river's flow reaches Mexico?
Only about 10%, mostly used by cities
What percentage of water use in the U.S. is residential?
13%
What are common residential water uses?
Drinking, bathing, cooking, cleaning, and landscaping
How much household water is used for landscaping in some regions?
33−66%
What percentage of household water is used for toilet flushing?
About 24%
What percentage of U.S. water use is industrial?
47%
What are some industrial uses of water?
Factories, power plants, and other manufacturing processes
What is the largest global use of water?
Agriculture (70% worldwide, 40% in the U.S.)
Why is water important in agriculture?
It is used for irrigating crops, stored in dams, and pumped from groundwater
What is consumptive water use?
Water that doesn’t return to its source or comes back polluted
What is an example of consumptive water use?
Agriculture—water used for crops evaporates or is absorbed
What is nonconsumptive water use?
Water that is returned to its source after use
What is an example of nonconsumptive water use?
Household and industrial water that’s cleaned and sent back to rivers
What is virtual water?
The hidden water used to make products
What are examples of virtual water use?
Producing food, clothing, and electronics
What maintains the flow of the Colorado River?
The hydrologic cycle, which continuously recharges the river
What are the major reservoirs of water in the hydrologic cycle?
Atmosphere, oceans, rivers and lakes, groundwater, snow and ice
What are fluxes in the hydrologic cycle?
Transfers of water, including evaporation, transpiration, evapotranspiration, and precipitation
What is evaporation?
The process where water changes from liquid to vapor and enters the atmosphere
What is transpiration?
The release of water vapor from plants into the atmosphere
What is evapotranspiration?
The combined process of evaporation and transpiration
What is precipitation?
Water returning to the surface as rain, snow, sleet, or hail
Where does the Colorado River source its water?
The Rocky Mountains, which are essential for its flow
How does the hydrologic cycle supply water to the Colorado River system?
Through evaporation, rainfall, and snowmelt
What is a stream?
The movement of surface water in a defined channel
When does a stream become a river?
When streams converge and larger tributaries contribute to it
What is discharge in the context of streams?
The volume of water flowing past a specific point in a stream over time
What do hydrographs display?
Discharge levels over time, showing change
What happens during flooding?
Discharge increases and exceeds the stream's banks, which can replenish surrounding ecosystems
Why are many rivers channelized?
To manage flooding and control water flow
What is a watershed?
The entire drainage system that collects and channels water
Name a process of water movement in a watershed
Sublimation, infiltration, percolation, or runoff
What is sublimation?
The process by which water changes from solid (ice or snow) directly to gas (water vapor) without becoming liquid.
What is infiltration?
The process by which water penetrates the soil surface and becomes part of the groundwater supply.
What is percolation?
The movement of water through the soil and rock layers, filtering down to recharge groundwater.
What is runoff?
The flow of water, usually from precipitation, that travels over the land surface and eventually returns to rivers, lakes, and oceans.
What is the size of the Colorado River watershed?
Spans 246,000 square miles and includes all its tributaries
Is water availability in the Colorado River watershed year-round?
No, water is not available year-round; its flow varies with seasons and demand
What are water rights?
Legal entitlements that allow individuals or entities to use a specific amount of water from a designated source
What is the Colorado River Compact?
An agreement that allocates water between the upper basin states and lower basin states to manage and share resources
What are riparian zones?
Narrow strips of vegetation along rivers that are lush and green, even in deserts like Colorado
What are the benefits of riparian zones?
They provide important habitats for wildlife, trap pollutants, and stabilize soil to prevent erosion
What nutrients do streams move?
Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), along with sediments rich in organic material
How can human activities affect streams?
Can increase the levels of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in streams, leading to contamination
What is a major issue with river water in some regions?
Are running out of water for human use, which can affect future growth and development
What are two solutions to address water scarcity from rivers?
Use water more efficiently in homes, farms, and industries.
Reduce farming or bring in water from other places.
Why do many places rely on groundwater?
Because of areas without big rivers or lakes for their water supply
What happens if more groundwater is extracted than nature can replace?
It will drop, leading to potential shortages
Why is groundwater considered the freshwater resource most at risk?
Because it can be depleted faster than it can be naturally replenished, with some sources taking hundreds to thousands of years to recharge
What percentage of U.S. drinking water comes from groundwater?
39% of U.S. drinking water comes from groundwater
What are the percentages of drinking water from groundwater in Europe and the Asia-Pacific region?
75% and 32%
What is groundwater?
Water that moves through rocks and sediments under Earth’s surface
What is porosity?
The amount of open space in the material, indicating how much water it can hold
What is permeability?
Is how easily water can flow through the material
What does high porosity but zero permeability mean?
It means the material has space for water but water cannot flow through it
What does high porosity and high permeability indicate?
It indicates that water can both be stored in the material and move through it easily
What is the unsaturated zone?
The area above the groundwater where the soil contains both air and water
What is the water table?
The top surface of the saturated zone where all spaces are filled with water
What is the saturated zone?
The area where soil and rock are fully filled with water
What is an aquifer?
Underground layers of rock that can hold and transmit water
Why are aquifers concerning in terms of water use?
Can take a long time to fill and are being drained quickly due to overuse
What is an aquifer?
A layer of rock or sediment that lets water flow easily
What is an aquiclude (or aquitard)?
A layer that blocks water from flowing easily
What is an unconfined aquifer?
An aquifer that has no overlying layer to restrict water flow, allowing direct recharge from surface water
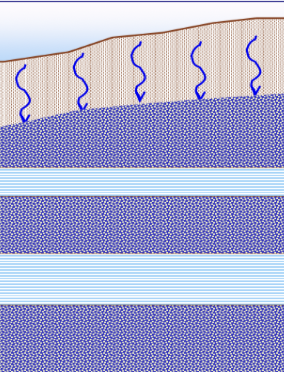
What is the main difference between an aquifer and an aquiclude?
An aquifer allows water to flow easily, while an aquiclude blocks water from flowing easily
What recent environmental issue has affected water levels in the Colorado River?
Droughts
How much water was lost in the Colorado River Basin between 2004 and 2013?
53 million acre-feet of water
What portion of the water lost in the Colorado River Basin came from groundwater?
41 million acre-feet
What has contributed to the reduced water levels in the Colorado River?
High water demand and drought conditions
What type of water is refilled as quickly as it is used?
Renewable water (like rivers and lakes)
What type of water is used faster than it can be replaced?
Nonrenewable groundwater
What are wetlands?
Areas that are wet either part-time or all the time
What are hydric soils?
Wet soils that are rich in organic material but low in oxygen
What are hydrophytes?
Plants that thrive in wet, low-oxygen environments
What ecological services do wetlands provide?
Filter pollutants from water, provide homes for animals (especially birds), and reduce flooding by absorbing extra water