Lecture 10: Monte Alban (part 2)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
why do we think that the cistern was an important monument?
because it was placed in the middle of the plaza
what was the whale bone in the Suken Patio used for?
as a music instrument
what’s creame ware and when did it appear?
a new ceramic style that appeared during the Nisa phase
true or false: the clay used for crema ware came from far away
false: it was probably created there or close
true or false: crema ware was a ceramic style adopted by everyone at Monte Alban
false: elites tried to control the style to have it for themselves, but some copies were created
how do we know that crema ware was associated with Cociyo, god of the rain?
because it was decorated with lightening iconography
true or false: we found crema ware owned by other leaders
true: it was probably a gift
what were the social inequalities during the Nisa phase? (5)
crema ware was only for the elite and they controlled the production
transformation of the main plaza (orientation, buildings)
elaborate mortuary contexts and residences for the elite
elite control of obsidian and marine shells (that had to be imported)
elite eating more venison
how did we know that there was a drop in population during the Tani-Pitao phase? (3)
decrease in architectural development
population influence in region starts to fade (Monte Alban doesn’t control the valley)
elite ate less venison
what was found in the grave 1994-61 and what did we conclude from it?
burial of a 3 months old
had good offerings, buried in the north platform (elite area)
food offering so that the baby could continue to grow in the afterlife
→ baby of an elite since we didn’t bury babies
what was the role of the terraces along the hill? (2)
living and food production
stop erosion
what happens if the terraces aren’t being taken care of?
mudslides: could destroy other houses and kill people (dangerous)
how did we know that there was a relationship between Teotihuacan and Monte Alban?
at Teotihuacan: Tlailotlacan, AKA the Oaxaca neighbourhood (for Monte Alban people)
at Monte Alban: different material culture
true or false: Teotihuacan was always occupied by the Aztecs
false: it was abandoned by the previous residents before the Aztecs came
what was Tlailotlacan?
a neighborhood occupied by Zapotecs (Monte Alban people) in Teotihuacan
how did we know that Tlailotlcan was occupied by Zapotecs? (5)
zapotec style pottery (only found there)
zapotec mortuary conditions (people were buried like in Monte Alban)
zapotec glyphs
zapotec-style multi-room temple
isotopic studies: looking at bones and migration patterns
what were Teotihuacan influences at Monte Alban? (9)
Teotihuacan-style pottery
Mica deposits
Tableros appearing on the North Platform
new residences on the North Platfrom without formal tombs
possible Teotihuacan burials
decline in construction of monumental buildings
use of offering boxes stopped
absence of new iconography representing Zapotec deities
grave 1993-43: 18 kids buried together
how did Teotihuacan and Monte Alban differ in pottery style?
Monte Alban pottery is green, but Teotihuacan is brown
true or false: the tableros found in Monte Alban and in Teotihuacan are the same
false
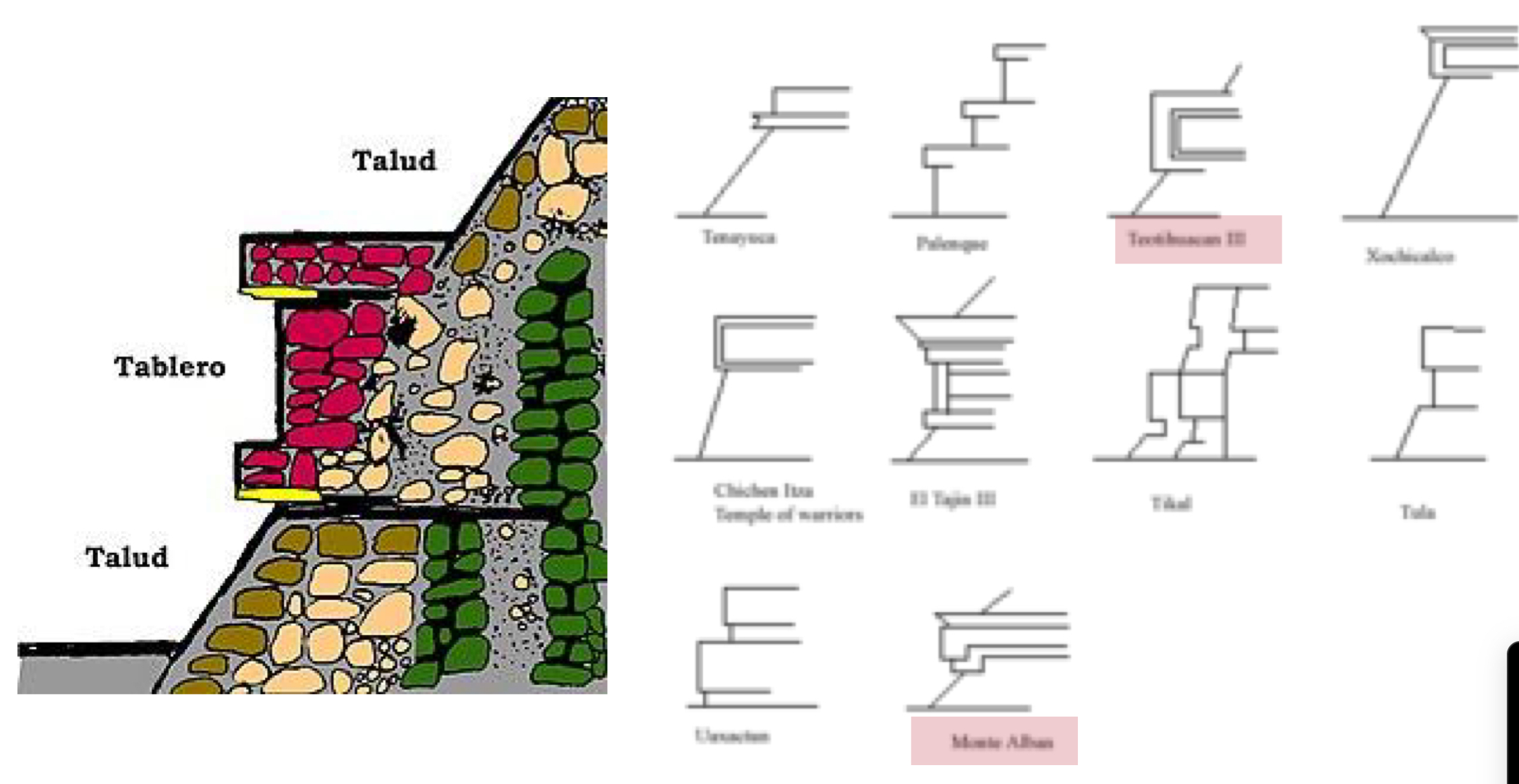
what’s the difference between burials in Monte Alban and in Teotihuacan?
Monte Alban: formal tombs
Teotihuacan: no tomb, people are in foetal position
what was found in grave 1993-43 and the conclusion?
18 kids buried together and some adult bones
found in North Platform
possible Teotihuacan influence because they did something similar with 18 kids buried under an altar
18 to represent the 18 months of the ancient calendar
secondary deposition: skulls had different levels of preservation
skulls were wrapped in leaves
what’s the difference between primary and secondary deposition?
primary: you bury the person
secondary: you bury the person and then take them out to put them somewhere else
what are the possible nature of relationship between Monte Alban and Teotihuacan? (3)
military: Teotihuacan controlled Monte Alban
Monte Alban changed to copy Teotihuacan because they were more powerful
reciprocal: nobles moved between both cities without friction
what happens during the Peche-Xoo?
zapotec cultural renewal: all Teotihuacan influence disappears
what was done during the Xapotec cultural renewal? (4)
construction of new monumental buildings starts again
reappearance of Zapotec deities in iconography
abandonment of Teotihuacan-influenced rituals
no known concentration of Teotihuacan artifacts
what are some changes done during the Peche-Xoo period? (3)
political influence fading: more rivals
main plaza reorganization: smaller temples
changes on practices: people from Teotihuacan left
why did we start building smaller temples?
so that rituals could be more restricted, showing more power
what was found in grave 1994-69 and what was the conclusion?
body but with missing parts like the head
people were buried close to their home so that their ancestors could protect them… but what if you went far away?
you took a home from your ancestor (big bone, tibia, femur)
why were arrowheads (plant) found in graves? (2)
maybe dead person like eating it during their living
water is associated with the lightening god
how did we know that there was a new focus on domestic rituals (at home burial) during the Peche-Xoo phase? (3)
increase in offerings: both in formal tombs and simple graves
more elaborate mortuary contexts: both type of tombs too, more decoration
more altars in domestic contexts: now 2-3 per house
why was Monte Alban abandoned? (5)
security reasons: terraces collapsed, too dangerous (more people leave = more collapse)
changes in ideologies: people didn’t like Teotihuacan influence
wish for different political organization: elite controlled a lot. once elite had no one to control, they left
environmental consequences: a lot of erosion = less fertile lands
economy: others stopped trading with Monte Alban
what was found in tomb 8 and what was the conclusion?
9 bodies from adults
were disturbed and damaged, probably secondary deposition
more than 500 artifacts offering
was after Monte Alban abandonment: when Mixtec reoccupied Monte Alban