Physics 11: Mechanical Waves + Sounds
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What’s periodic motion
Hint: EQUAL INTERVALS
Motion repeated in equal intervals of time
Eg. vibrating guitar string, bobble head, swing, bouncing ball
What’s vibration
Wiggling/shaking, back+ forth motion
What’s damping
Tendency of vibrating object to lose/fade out/dissipate energy over time
Eg. hit tune fork+ slowly fades
What’s A
Amplitude of disturbance/max distance from equilibrium position (m)
What’s equilibrium
Usually drawn w dotted lines
Resting position, all forces balanced here

What’s node
Hint: Points in a standing wave where the amplitude is always zero
Min disturbance/no movement
Think: Wave on string where nodes (certain points) don't move at all while rest of the string vibrates
What’s antinode
Hint: Antinodes are At the maximum
Max disturbance, highest distance of disturbance
In vibrating string, points that move the most (up and down the most) = antinodes
What’s T
Period (s)
Time to complete FULL cycle of one wave to pass
Eg. time for waves hitting feet, how long btwn wave hits
Full cycle: full motion completed btwn one point to next (eg. crest→crest)
What’s resonance
When forces applied to vibrating/oscillating object @ time interval = to period of oscillation→ amplitude increases
Eg. push friend on swing, correct timing to maintain pendulum clocks accurate (so don’t lose their energy during woo woo swings)
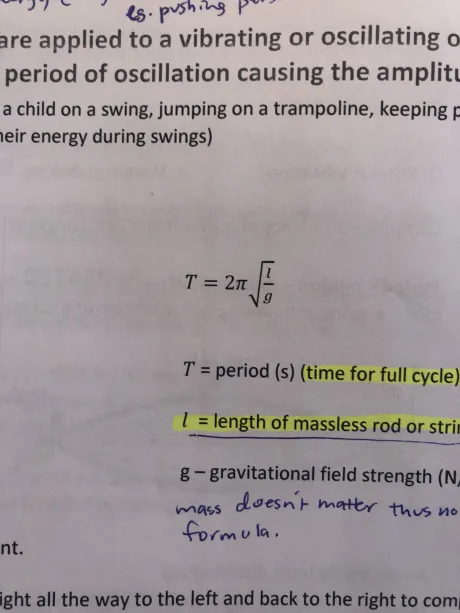
What’s all these variables in the formula
T=period (s) (time for full cycle)
l=length of massless rod/string (m)
g= gravitational field strength (N/kg or m/s²)
*Mass and amplitude are irrelevant→ not in formula
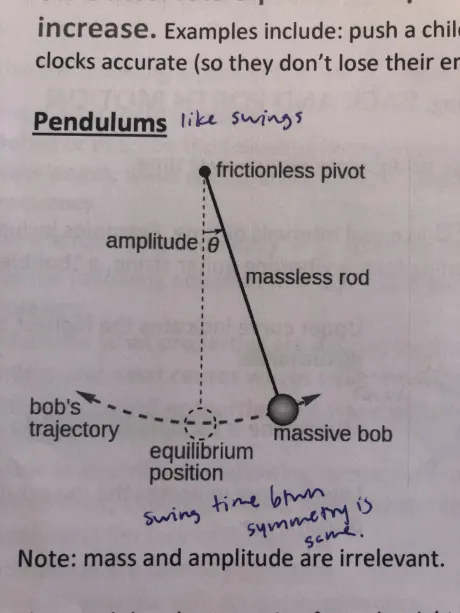
For this pendulum, to complete a full cycle and be ready to repeat it has to..?
Swing from right→left→back to right
If you put any mass on a spring vertically→it’ll ____????
Oscillate/bound up+down
On d-t graph: looks like since curve
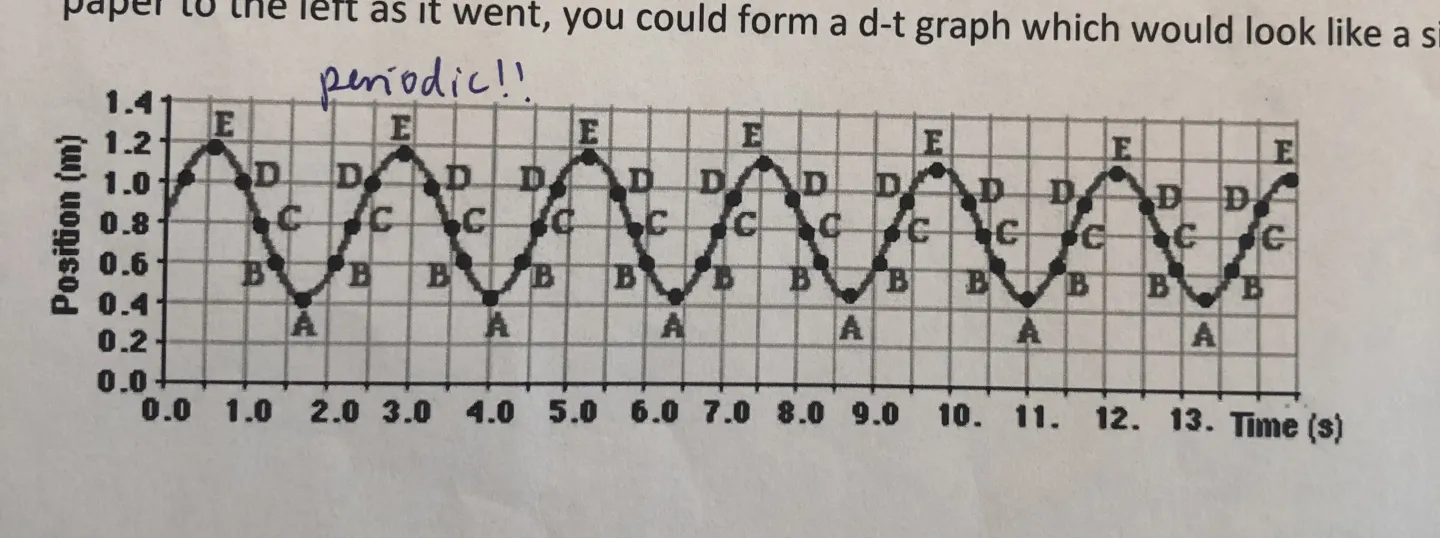
What’s a wave
Disturbance (basically make string go wee weooo) that carries energy thru matter/space
What are mechanical waves
Waves that need physical medium (stuff, matter) to travel thru
Eg. water waves, sound waves, waves along a rope
What’s a medium
Any physical matter like air, water, rope, etc
What’s transverse waves
Think: spider man goes up and down
Waves that displace medium w pulse disturbance that’s perpendicular to direction of wave itself (basically has amplitude)
What’s longitudinal waves
Waves that displace medium w pulse disturbance that’s parallELLLL to direction of wave itself (basically front n back)
What’s surface waves
Made up of both longitudinal + transverse waves → circular waves
What’s A
Amplitude (m)
Max distance from equilibrium
Energy displayed in the amplitude of the wave… more energy= larger amplitude
What’s 𝛌 (lambda)
Wave length (m) length of one COMPLETE wave
Basically crest→crest / trough→trough
THINK: length to complete a wwwaavveee (italize)
What’s v
Speed (m/s)
How fast wave travels
Depends on MEDIUM it travels thru, (density, thickness, stiffness etc)
PS. More energy CANT make wave travel faster→only makes bigger amplitude
Think: v=d/t, doesn’t care abt frequency, just abt cycles finished
What’s in phase and out of phase
In phase: Crests match
Out of phase: crests DONT match
What’s cursive f
Frequency
Hz OR cycles/s
How many waves pass/second
If wave’s travelling thru one medium→speed is constant
To change velocity of wave, must change MEDIUMS
Think: d/t doesn’t have anything abt frequency, no matter frequency its still same d and t
When incident wave hits fixed boundary,
It’ll be reflected→Opposite vertical (inverted)
Waves travel at speeds according to medium it’s in
If medium changes→speed+other behaviour of waves change
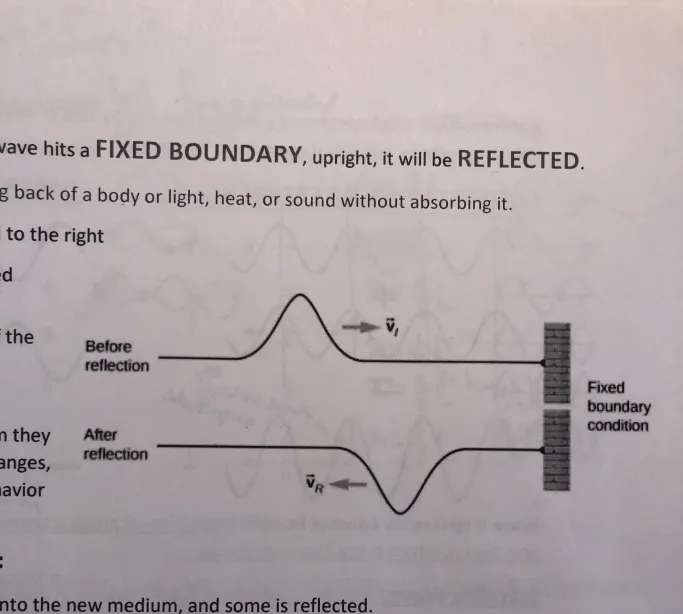
What’s reflection
Throwing back of body/light/, heat, sound w out absorbing it
If energy continues into new medium, some→reflected… In two these situation: new medium 1. more dense/2. less dense?
If new medium MORE dense, some energy goes onward into this new medium. The reflection is INVERTED
THINK: if the NEW person is more dense→ some energy goes onward into this new medium (we know) + reflection is INVERTED bc they have an INVERTED view on the world
If new medium=LESS dense, some energy goes onward into this new medium. The reflection is UPRIGHT
THINK: New person (medium) is less dense→ some energy goes onward into this new medium (we know) + reflection is upRIGHT

T or F:.. When frequency of wave is altered by crossing boundary
False pookie :(
When frequency of wave is NOT ALTERED by crossing boundary
But v might change if change in energy source
T or F: reflected pulse becomes INVERTED when wave less dense rope is heading toward boundary w more dense rope
YES!!!
Reflected pulse becomes INVERTED when wave less dense rope is heading toward boundary w more dense rope
T or F: Amplitude of incident pulse=always NEVER GREATER than amplitude of reflected pulsve
FALSE.
Amplitude of incident pulse=ALWAYS. GREATER than amplitude of reflected pulse
BC transfer of some energy into wall
What’s superposition
Displacement of medium caused by 2/+ waves = sum of displacement by individual waves (interference)
→Constructive OR destructive interference
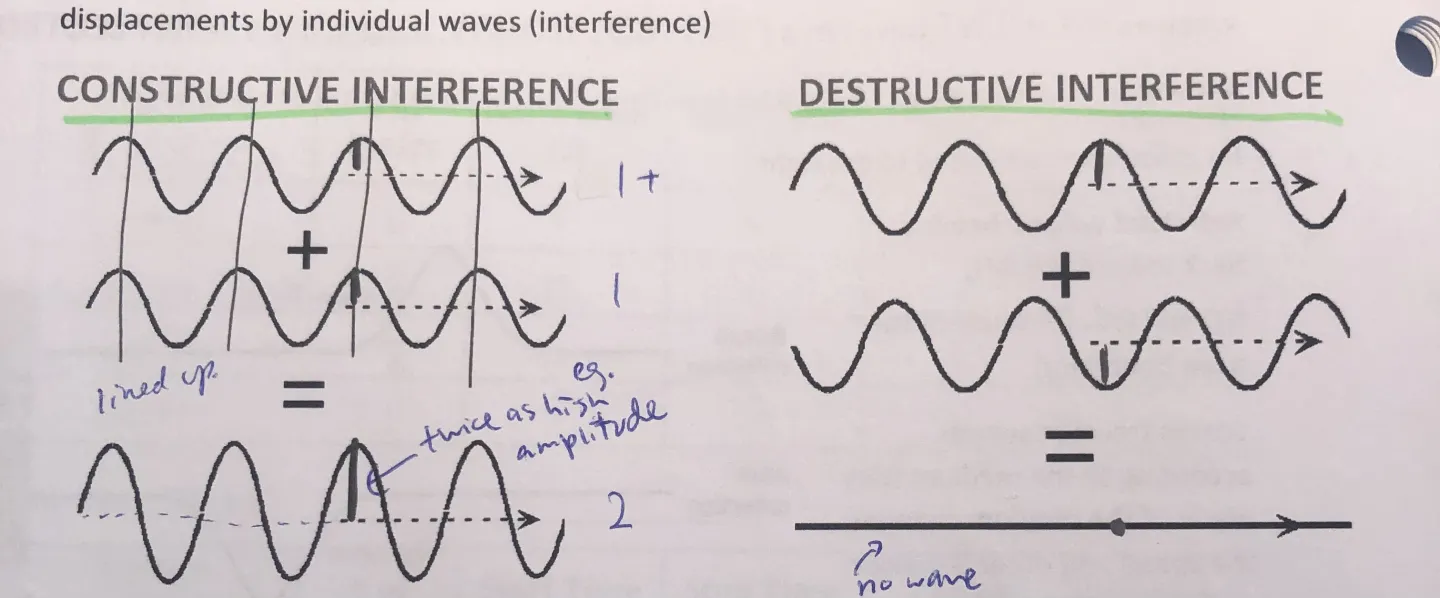

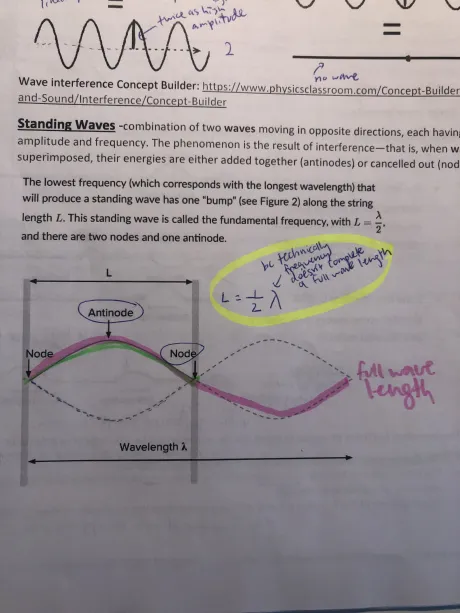
What’s standing waves
Combo of 2 waves moving in opp directions, each having same amplitude +frequency
This cool thing is result of interference (when waves r superimposed), energies either added together (antinodes) or cancel out (nodes)
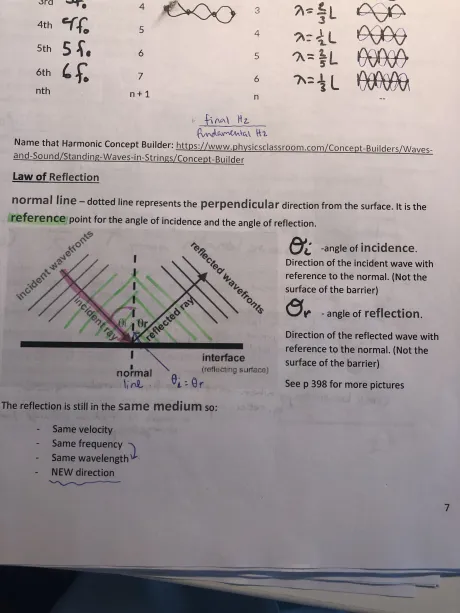
What’s the law of reflection
NORMAL LINE= dotted line=perpendicular direction from surface. Ref point for angle of incidence+ angle of reflection
𝛳i =angle of incidence
𝛳r=angle of reflection
→Direction of reflected wave w ref to normal (not surface of barrier)
→reflection is still in same medium so .. same velocity, Hz, wavelength, but NEW DIRECTION POOKEH!!
How would echo from insect flying TOWARD BAT differ from insect flying away from bat???
Think: car nyoom
Insect flying to bat: higher Hz from bat
Flying away from bat: lower Hz from bat
What’s the law of refraction
Bending of path of light wave that passes from one material to another
Occurs at boundary
Caused by change in speed of light wave upon crossing of boundary
Hz doesn’t change as usual