Genetics Exam 3
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rip
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Karyotes
An arrangement of condensed chromosomes.
What can karyotypes tell us about genetic abnormalities?
- Errors in meiosis:
- Non-disjunction: failure of homologous pairs of chromosomes/sister chromatids to separate in meiosis.
- Leads to loss or gain of additional copies of chromosomes in the process of meiosis = aneuploidy.
Trisomy
An extra copy of a chromosome.
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
A human genetic disorder resulting from the presence of an extra chromosome 21; characterized by heart and respiratory defects and varying degrees of intellectual disability.
Monosomy
Missing a chromosome.
Monosomy X (Turner Syndrome)
produces X0 females, who are sterile; it is the only known viable monosomy in humans.
Tetraploid
4 sets of chromosomes.
Deletions
Mutation involving the removal of one or more nucleotide pairs from a gene.
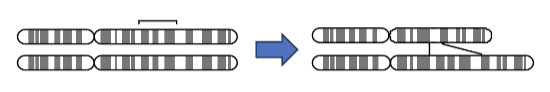
Pericentric Inversions
The centromere is included in the inversion, or when it is flipped.
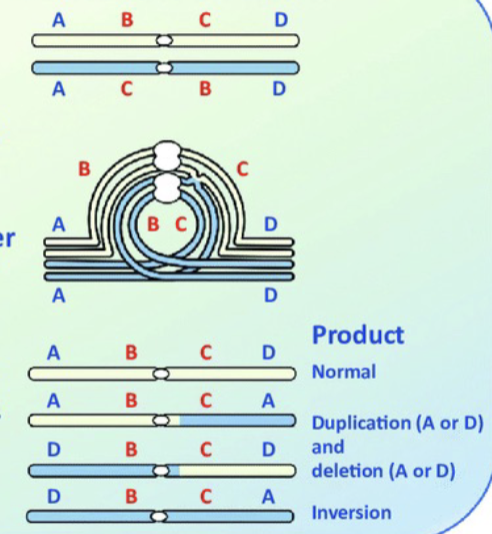
Paracentric Inversion
The centromere is NOT included in the inversion.$
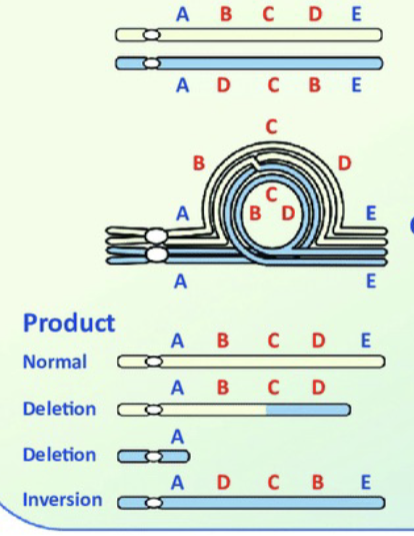
Duplications
Produces extra copies of the chromosomes.
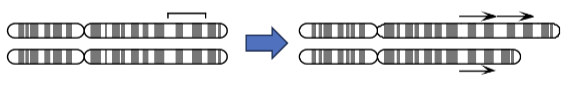
Translocations
Rearrangements of chromosomes due to the insertion of genetic material from one chromosome to another.
How do new alleles enter a population?
Mutations, natural selection, random genetic drift, migration/gene flow.
Inbreeding
Positive assortment mating, leads to increased homozygosity & decrease in heterozygosity, cannot change allele frequencies by itself.
Four Postulates of Natural Selection
Variation in phenotypes.
Heritability of phenotypes.
Differential survival and reproduction.
Survival and reproduction correlate with heritable phenotype.
Modern Synthesis
An overview of evolutionary processes that shape genetic variation. it unites different branches of evolutionary theory.
neo-Darwinism (modern synthesis)
Emphasized adaption via natural selection; it viewed natural selection as the primary evolutionary force governing patterns of variation.
Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution
Most new mutations are deleterious and removed by purifying selection.
Polymorphism and divergence overwhelmingly reflect neutral variation that drifts to fixation.
Positive selection and adaptation is extremely rare.
Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL)
Identifies genomic regions that affect quantitative traits using controlled crosses.
Take 2 genotypes, cross them, cross them, cross the F1 generation, and look for associations between trait variation and genotype variation.
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
Identifies associations between genetic variants and traits in natural populations; NO CROSSING IS INVOLVED.
A trait is measured in many individuals, their genomes are sequenced, and then look for associations in trait variation and genotype variation.
What is the main difference between QTL and GWAS?
QTL cannot be done on humans. You cannot choose humans to cross, it is unethical. Additionally, it is time consuming to wait for two generations to form.
McDonald-Kreitman Test
An assay for neutral molecular evolution that compares polymorphism within species and divergence between species.
When molecular evolution is neutral:
Silent: Replacement Polymorphism = Silent: Replacement Divergence
A/C = B/D in the McDonald-Kreitman Test
Indicates that we cannot reject neutrality in molecular evolution.
A/C > B/D in the McDonald-Kreitman Test
Excess replacement divergence.
Indicates a positive selection elevated protein evolution beyond neutrality: ADAPTATION!
A/C < B/D in the McDonald-Kreitman Test
Reduced replacement divergence.
Purify selection has slowed protein evolution below neutral expectations.
Can genetic variation be used to define racial groups?
No, genetic variation cannot be used to divide humans into racial groups; there is more variation within racial groups than between them.
What is the myth regarding the genetic basis of race?
There are specific genes or traits that define racial groups, which is not supported by genetic evidence.
Founder Effect
Occurs when a small group from a larger population establishes a new population, leading to reduced genetic diversity.
What is the genetic relationship between genetic diversity and geographic location?
Genetic diversity is generally greater in population that have lived in a region longer, such as African populations.
Traits associated with populations in high-altitudes
Hight altitude hypoxia tolerance.
Admixture
Refers to the mixing of different populations, resulting in a mosaic of genomes.
% in which humans are genetically similar
99.9% similar, only a 0.1% variation.
What is the role of environmental factors in genentic variation?
They can drive allele frequency changes, influencing traits like skin pigmentation and disease resistance.
Synonymous mutations
Do not change the amino acid sequence.
Nonsynonymous mutations
Do change the amino acid sequence.
Polymorphism
The presence of two or more variants in a population, contributing to genetic diversity.
How does genetic variation in Africa compare to other regions?
Africa has much greater genetic variation due to its longer history of human habitation and the migration patterns of populations.
Bottleneck Effect
The bottleneck effect occurs when a population’s size is significantly reduced, leading to a loss of genetic diversity.
What is sickle cell trait and where is it commonly found?
Sickle cell trait is common among Black Americans, as well as in populations from India, Turkey, Greece, Italy, and the Arabian Peninsula.
What is the significance of sickle-cell trait in relation to malaria?
Carriers of the sickle-cell trait have a selective advantage due to increased resistance to malaria.
What is high altitude hypoxia?
The ability to survive in high elevation, with different genetic variants found in Tibetans and Andeans.
Genomics
Studying genetics at the scale of entire genomes.
Highlights of Genomics
Personalized genomics and medicine
Increased productivity in agriculture.
Genetic ancestry and unknown relatives
Technology is constantly developing.
Potential Pitfall of Genomics
Your genetic information can be acessable public or private organizations.
Short Reads
A single sequencing reaction only yields 50-800 bases. It necessitates building consensus sequence from overlapping reads.
How are short reads used?
Cut many genome copies into random fragments.
Sequence each fragment.
Overlap sequence reads: overlapping sequencing reads are merged to generate a contiguous consensus sequence (contigs).
Overlap contigs for the complete sequence.
WGS: Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing
Taking genomic DNA, cutting it into a lot of tiny pieces, sequencing those, aligning them up to form a contiguous sequence.
Next-generation WGS
Uses “next generation” sequencing techniques:
DNA prepared for sequencing without cloning.
Advanced fluidics and cameras allow sequencing reactions in microscopic volumes.