Ocular Anatomy and Physiology Overview
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Anatomy
Science of body structures
Physiology
The science of body functions (ocular physiology)
Gross anatomy
Visible to the naked eye
Examples of gross anatomy of the eye
Iris, lens, palpebrae, sclera
Complementarity of structure and function
Function always reflects structure; what a structure can do depends on its form
Cornea
Curved, transparent. Allows to focus light
Iris and pupil
Contains muscle. Allows to adjust pupil size to control amount of light entering the eye
Lens
Lens is flexible and biconvex. Varying size of lens allows control of light being focused on the retina
Retina
Retina layout. Central cones allow that our best vision is focused on them
Optic nerve
Large bundle of optic nerves. Allows for efficient and rapid signal conduction
Microanatomy
Too small to be seen with naked eye
Anatomical position
A reference point. Universal shared method which allows healthcare professionals to pinpoint structures in an organism when communicating
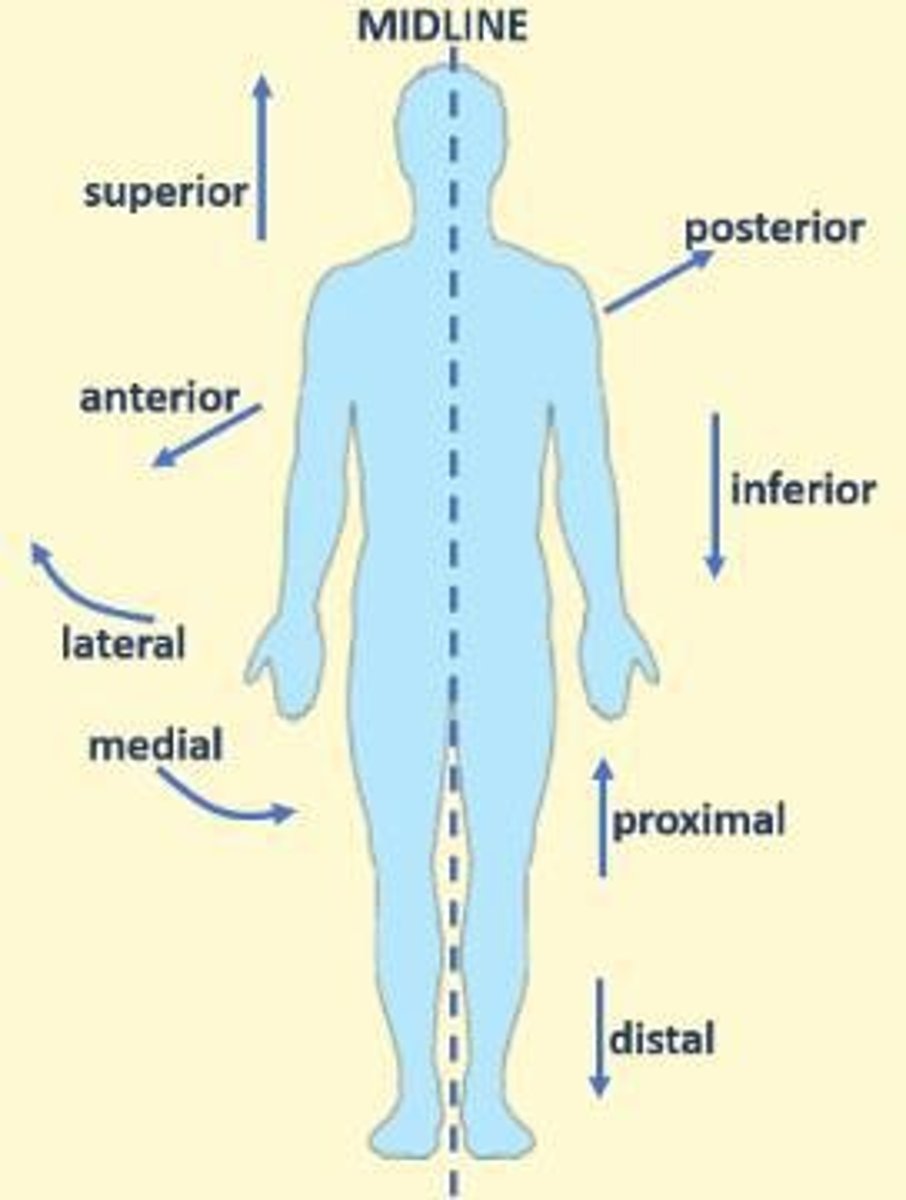
Anatomical terms
Terms: Anterior, posterior, lateral, medial, superior, inferior
Sagittal plane
Divides body into left and right side (line from front to back)
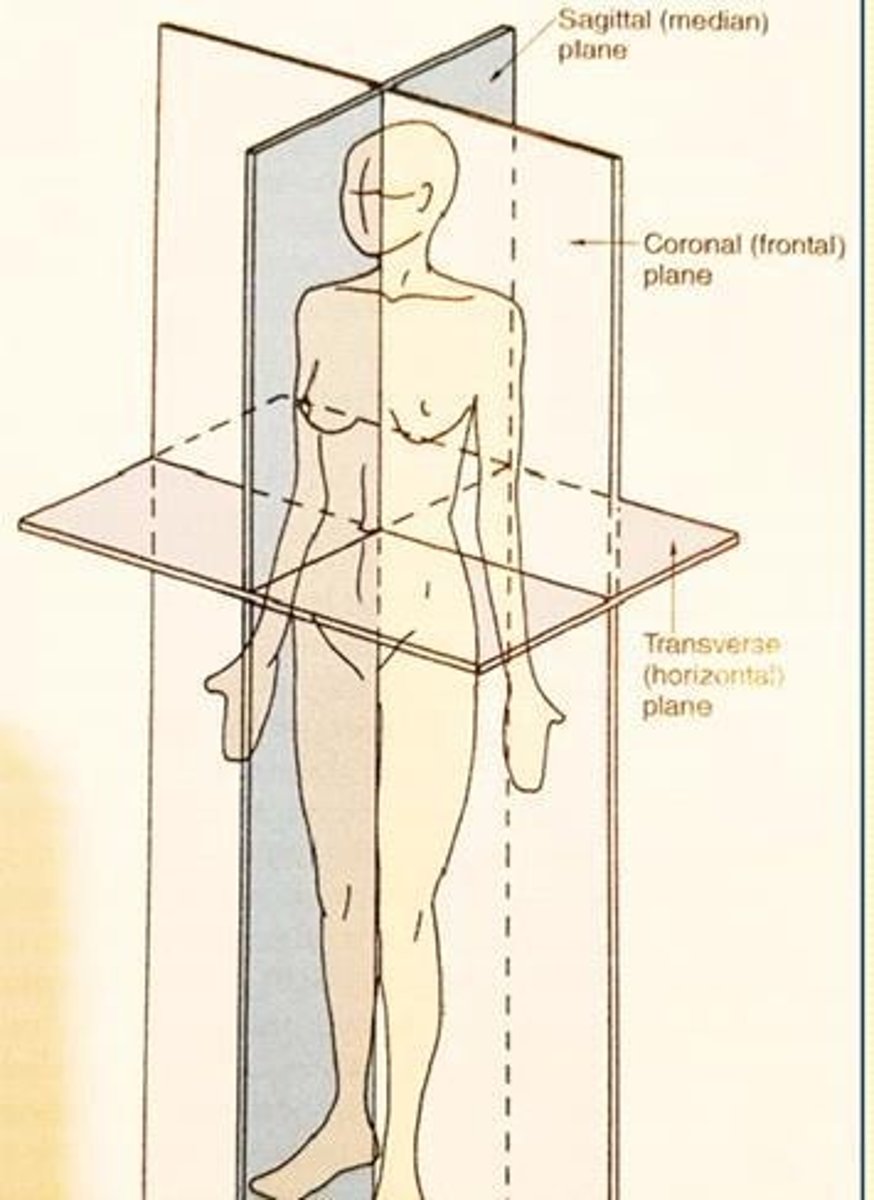
Coronal (frontal) plane
Divides body front and back (side to side line)
Transverse plane
Divides body into superior and inferior
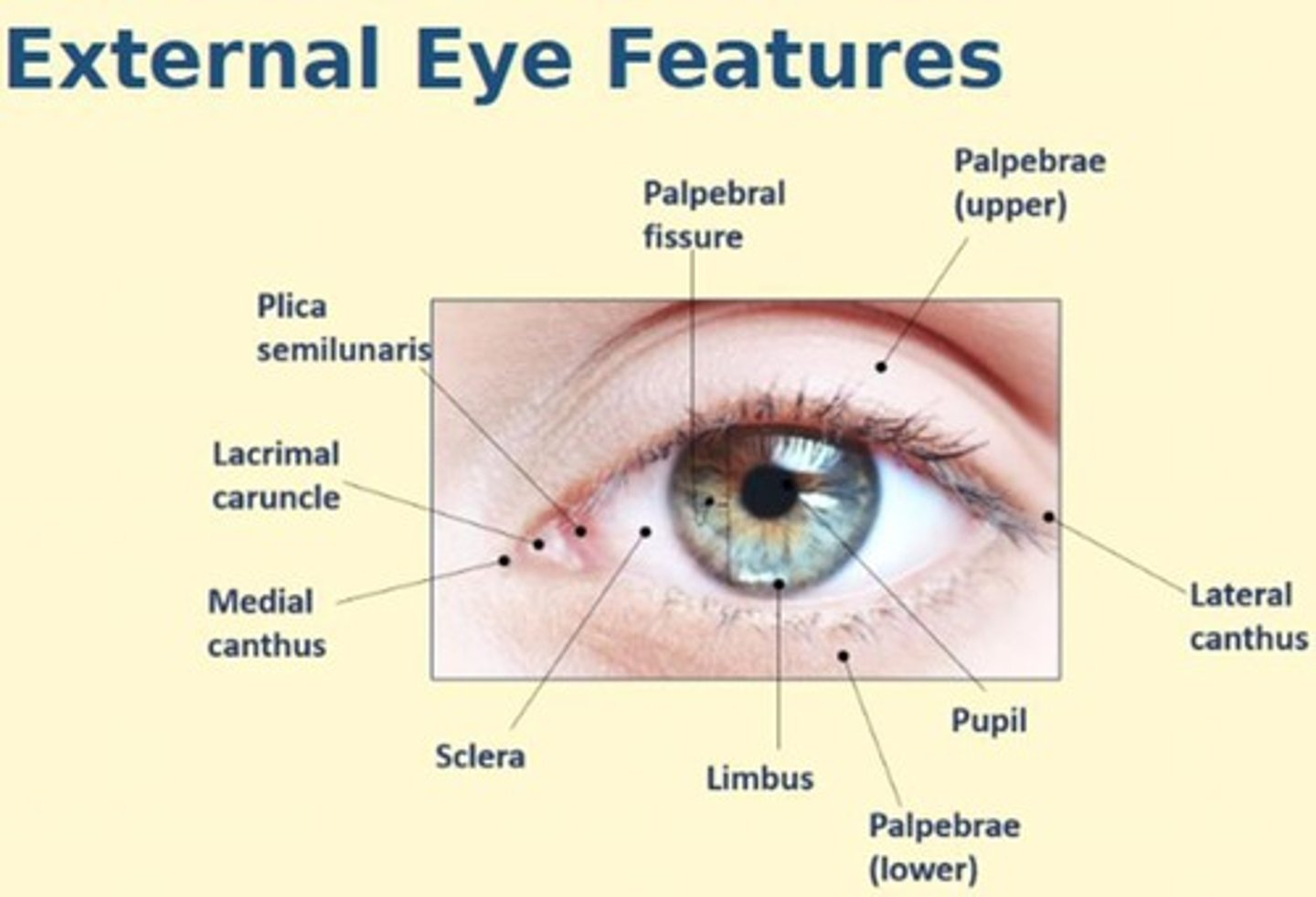
Principle structures of the eye (external features)
Limbus, sclera, iris, pupil, palpebrae, canthus, plica semilunaris, lacrimal caruncle + ocular adnexa
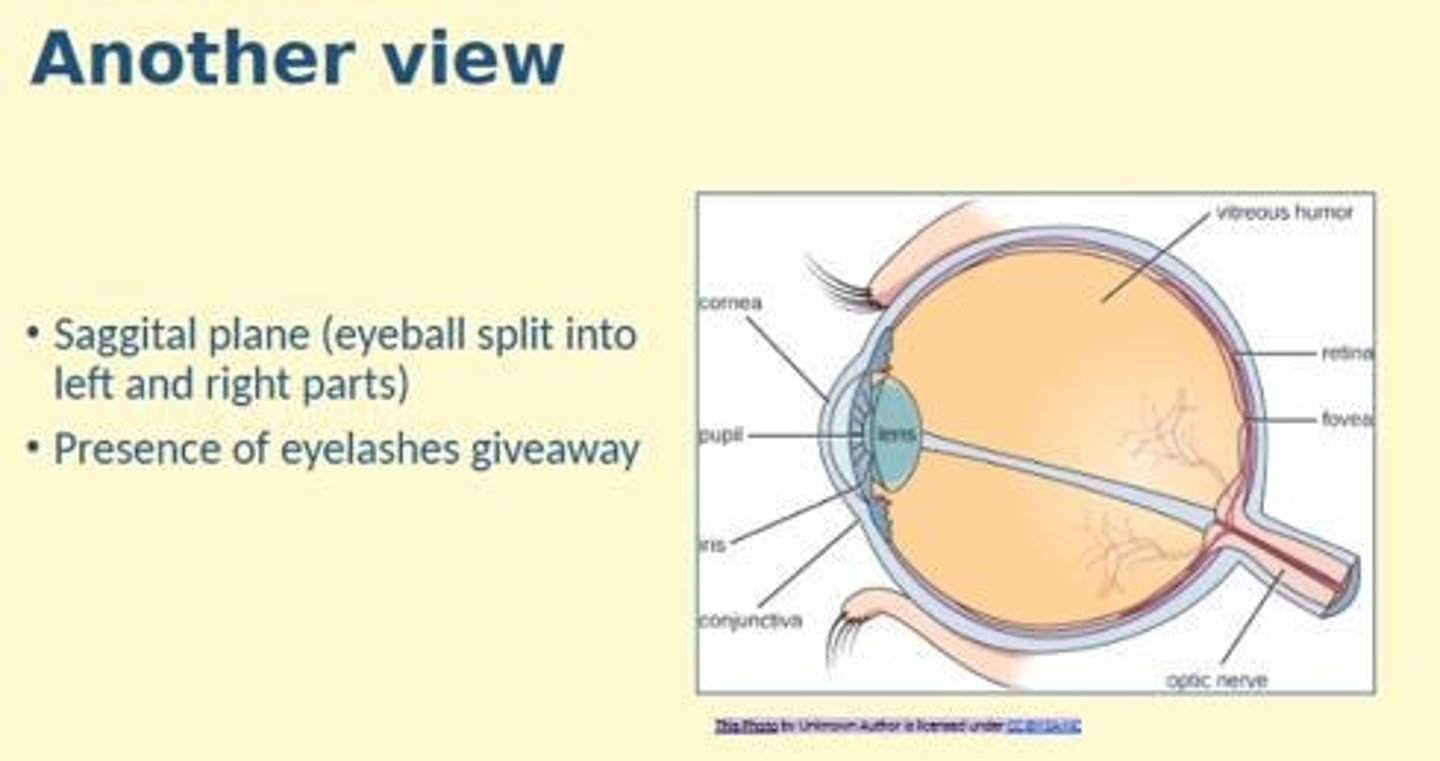
Principle structures of the eye (internal features)
Optic nerve, choroid, macular + fovea, vitreous humor, aqueous humor
Lesions
Can be described as being located inferio - medial, infero nasal. Use time as well e.g. 12 o'clock, size of lesion
Histology
The study of cells and tissues by microscopy
Epithelial tissue
Layers of cells that cover body surfaces. 2 main subtypes: covering or glandular
Role of epithelial tissue
Protection, absorption, secretion, filtration, excretion, sensory perception
Features of epithelial tissue
Good regeneration, sits on basal lamina, avascular, innervated, tightly joined together and polar
Naming epithelia
Based on two factors: Number of layers (simple, stratified, pseudostratified) and shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar, transitional)
Microvilli
Membrane projections that increase the surface area of plasma membrane (for absorption)
Cilia
Tiny hair-like structures that are motile and sweep debris and mucus
Keratin
A protein that helps protect the skin from heat, microbes and chemicals
Connective tissue
The most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body. Space filling tissue.
Fibroblasts
Produces extracellular matrix (and cells) which provides support and elasticity to tissues.
Adipocytes
Cells that store fat.
White blood cells
Cells of the immune system that help the body fight infection.
Extracellular matrix
Made up of fibres (collagen, elastic and reticular) and ground substances which binds everything together.
Loose connective tissue
Loose arrangement of fibres (collagen) with lots of ground substances, providing support and flexibility.
Dense connective tissue
Closely packed collagen fibres with little ground substances, providing support and resistance to stretching.
Ground substances
Combination of water, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and adhesion proteins that fills space between cells and acts as a medium for exchange in nutrients and waste.
Collagen fibres
A protein (most abundant protein in the body) which is very strong but also flexible.
Types of cell junctions
Includes tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions, each with specific functions.
Tight junctions
Integral membrane proteins from neighbouring cells fuse together to form impermeable junctions which prevent molecules from passing.
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that prevent adjacent cells from separating but still allow molecules to pass.
Gap junctions
Hollow channels (connexins) from both plasma membranes of adjacent cells connect with each other, allowing molecules to transport from cell to cell.
Bone shapes
Four different bone shapes: long, short, irregular, and flat bones.
Mineral composition of bone
Made up of majority calcium at 39%, phosphate, carbonate, potassium, sodium, magnesium, and organic compounds (cells & extracellular matrix).
Osteogenic progenitor cells
Stem cells that can differentiate into osteoblasts.
Osteoblasts
Cells that secrete collagen.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells.
Osteoclasts
Created by fusion of many white blood cells and involved in phagocytosis and repair of bone.
Compact bone
Found on external surface, dense, strong, and heavy.
Spongy bone
Found internal to compact bone, light and loose.
Periosteum
A thin dense layer of connective tissue that surrounds compact bone.
Osteons
Arranged units in compact bone.
Lacunae
Empty spaces where osteocytes reside in compact bone.
Trabeculae
An irregular latticework of thin bone found in spongy bone.
Function of bone tissue
Supportive for movement and protection, mineral homeostasis, blood cell production (red bone marrow), and triglyceride storage (yellow bone marrow).
Cranial bones
Include Parietal (x2), Temporal (x2), Occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid.
Facial bones
Include Nasal (x2), Maxillary (x2), Zygomatic (x2), Mandible, Lacrimal (x2), Palatine (x2), Inferior nasal conchae (x2), and Vomer.
Sutures
Joints that unite the bones of the skull, forming immovable joints except for the mandible.
Cavities
Spaces within the skull, including the orbital cavity, cranial cavity, and nasal cavity.
Paranasal sinuses
Mucosa lined, air-filled cavities located in four orbital bones: frontal sinus, maxillary sinus, ethmoid sinus, and sphenoid sinus.
Articulations
The region where adjacent bones contact each other, forming a joint.
Foramina
A small opening that allows the passage of structures from one region to another.
Fissures
Similar to foramina, these are small openings that allow the passage of structures, shaped more like a crack or cleft.
Fossa
A shallow depression in the bone.
Blowout fracture
A medical condition where high external pressure on the eye causes the maxillary sinus bone to break, leading to immediate swelling, bleeding, and limited ocular movement.
Weak points of the orbit
The floor and medial aspects are the weak points that can lead to fractures.
Osteoporosis
A condition that leads to weak bones, making them prone to breaking, which can increase the risk of orbital cellulitis.
Orbital cellulitis
A bacterial infection of the skin around the eye, common in children under 7, characterized by inflammation, redness, swelling, and fever.
Total volume of the orbit
30ml, which includes 6.5ml for the eyeball and 23.6ml for the optic nerve, connective tissue, muscles, and adipose.
Retina
The innermost layer of the eye, sandwiched between the choroid and the vitreous, with light-sensitive and non-light-sensitive parts.
Optic disc
A pale-colored area that lies medially, where branching blood vessels extend from.
Macula
A central part of the retina that includes the fovea and is crucial for high-acuity vision.
Functions of the retina
Converts light into neural signals and sends these signals to the brain for visual recognition.
Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
The outer layer of the retina that supports photoreceptors.
Photoreceptors
Cells in the retina that detect light and convert it into neural signals.
Outer nuclear layer
Layer in the retina containing the cell bodies of photoreceptors.
Inner nuclear layer
Layer in the retina containing the cell bodies of bipolar, horizontal, and amacrine cells.
Outer plexiform layer
Layer in the retina where synapses occur between photoreceptors and ganglion cells.
Inner nuclear layer
Cell bodies of bipolar, horizontal and amacrine cells
Inner plexiform layer
Synapse with ganglion cells
Ganglion cell layer
Layer containing retinal ganglion cells
Nerve fibre layer
Layer made up of axons of ganglion neurons, unmyelinated until they penetrate the sclera at the optic disc
Internal limiting membrane
Basal lamina which forms the boundary between retina and vitreous body
Neuroglial cells
Support cells in the retina that don't transfer neural signals, including Muller cells, microglia, and astrocytes
Muller cells
Cells that extend throughout the retina, enclosing dendritic processes within the synaptic layer and maintaining pH by absorbing waste products and regulating ion concentration
Microglia
Wandering phagocytic cells found in the retina that become active during infection or injury
Astrocytes
Star-shaped fibrous cells found in the inner retina that provide support to nerve fibres and retinal capillaries
Photoreceptor layer
Layer made up of rods and cones segment
External limiting membrane
Made up of tight junctions between Muller and photoreceptor cells
Outer nuclear layer
Layer made up of rod and cone cell bodies
Outer plexiform layer
Layer made up of neural synapses of photoreceptors, horizontal and bipolar cells
Inner plexiform layer
Layer made up of nuclear synapses between bipolar cells and amacrine cells with retinal ganglion cells
Ganglion layer
Layer consisting of retinal ganglion cells and displaced amacrine cells
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Non-invasive imaging tool to observe changes in the retina, allowing visualization and evaluation of distinctive layers and nerve fibre layers
Rods
Photoreceptors with discs that are separate from the outer membrane
Cones
Photoreceptors with discs that are continuous with the outer membrane
Outer segment of photoreceptors
Contains discs, functions to contain photopigment and initiates phototransduction cascade
Inner segment of photoreceptors
Contains mitochondria and resides in the photoreceptor layer of the retina, serving as the metabolic centre
Connecting cilium
Joins the inner and outer segments of photoreceptors
Fovea
Region where cones are elongated and longer, providing high acuity vision
Isomerisation
Chemical process where one molecule is transformed into another molecule with the same composition but different order
Hyperpolarisation
Condition where the cell becomes more negative inside