Test 3 Microeconomics
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Perfectly Competitive Market
A market with many buyers and sellers, homogeneous goods, and free entry and exit for firms.
Perfect Competition Characteristic
The actions of any single buyer or seller in the market have a negligible impact on the market price
Average Revenue (AR)
Total revenue divided by the quantity sold, indicating how much revenue a firm receives for a typical unit sold. AR = TR/Q = PQ/Q = P in perfectly competitive markets
Marginal Revenue (MR)
The change in total revenue from an additional unit sold. It's the slope of the total revenue function. MR = change in TR/change in Q
Marginal Revenue in Perfect Competition
For a perfectly competitive firm, marginal revenue equals the price of the good (MR = P).
Profit Maximization Rule
A firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR = MC).
Production in Perfect Competition
In perfect competition, a firm will produce where price equals marginal cost (P = MC).
Firm's Short-Run Supply Curve
The portion of the marginal cost (MC) curve that lies above the minimum average variable cost (AVC).
Short-Run Shutdown Decision
A firm will shut down in the short run if the price is less than the average variable cost (P < AVC).
Sunk Costs
Costs that have already been committed and cannot be recovered. They are irrelevant when deciding whether to shut down.
Demand Curve in Perfect Competition
The firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic
Perfect Competition Demand Curve
The individual firm's demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is precisely the price level! P = AR = MR = D
Positive Economic Profit
When price is greater than average total cost (P > ATC).
Negative Economic Profit (Loss)
When price is less than average total cost (P < ATC).
Zero Economic Profit (Normal Profit)
When price equals average total cost (P = ATC).
Breakeven Point
Occurs where price equals the minimum average total cost (P = min ATC).
Long-Run Exit Decision
A firm will exit an industry if price is less than the minimum average total cost (P < min ATC).
Long-Run Entry Decision
A firm will enter an industry if price is greater than the minimum average total cost (P > min ATC).
Long-Run Equilibrium
When there is no entry into or exit out of the industry.
Long-Run Equilibrium Conditions
Firms maximize SR profits such that P = SR MC, Profit = 0 so there’s no entry or exit, so P = min SR ATC, LRAC is at a minimum, so P = min LRAC, Firms produce at efficient scale.
Market Supply
Market supply equals the sum of the quantities supplied by the individual firms in the market.
Total Revenue
The total income a firm receives from selling its goods or services, calculated by multiplying the price per unit by the quantity sold. TR = P x Q
Profit (Perfectly Competitive Market)
The difference between total revenue and total costs. In a perfectly competitive market, profits are maximized when marginal cost equals marginal revenue, leading to zero economic profit in the long run.
Oligopoly
A market with 2-4 sellers, usually big firms, that have homogenous products.
Duopoly
An oligopoly with only two members
Collusion
An agreement among firms in a market about quantities to produce or prices to charge.
Cartel
A group of firms acting in unison.
Nash equilibrium
A situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the others have chosen. Always results in a suboptimal outcome.
Output effect
If P>MC, selling more output raises profits.
price effect
raising production increases market quantity, which reduces market price and reduces profits on all units sold.
game theory
the study of how people behave in strategic situations
Prisoner’s dilemma
2 criminals, the police have them on a weapons charge with a 1 year prison time. The police suspect they robbed a bank, but need a confession from one or both of them. They separate the criminals and offer each of them the same deal. If confess and your partner doesn’t, you go free and they get 20 years. If both confess, 8 years. If neither confess, 1 year. Both confess because either 0/8 years vs 1/20.
dominant strategy
the best strategy for a player to follow regardless of the strategies chosen by the other players.
tacit collusion
no paper trails, just “understanding” among firms.
Resale Price Maintenance
requiring a retailer to sell a good at a certain price determined by the wholesaler.pr
predatory pricing
charging too low prices, driving out competitors
tying
in order to buy a good, must purchase another good at the same time.
Monopolistic Competition
A market structure where producers have some control over prices due to product differentiation, leading to a scenario where firms face a downward sloping demand curve.
Monopolistic Competition in Short Run
In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm will produce where MC=MR and behave like a monopolist.
Monopolistic Competition in Long Run
In the long run, firms in monopolistic competition can enter or exit the market, leading to zero economic profits as firms adjust to the price equal to average total cost.
excess capacity
a situation where firms operate below their maximum efficiency, resulting in less output than a perfectly competitive market would produce.
monopolistic competition price vs marginal cost
P>MC
product variety externality
the introduction of a new product can add to consumer’s choices, so entry of a new firm is a positive externality for consumers.
business stealing externality
firms lose customers and profits from the entry of a new competitor so entry of a new firm is a negative externality for firms.
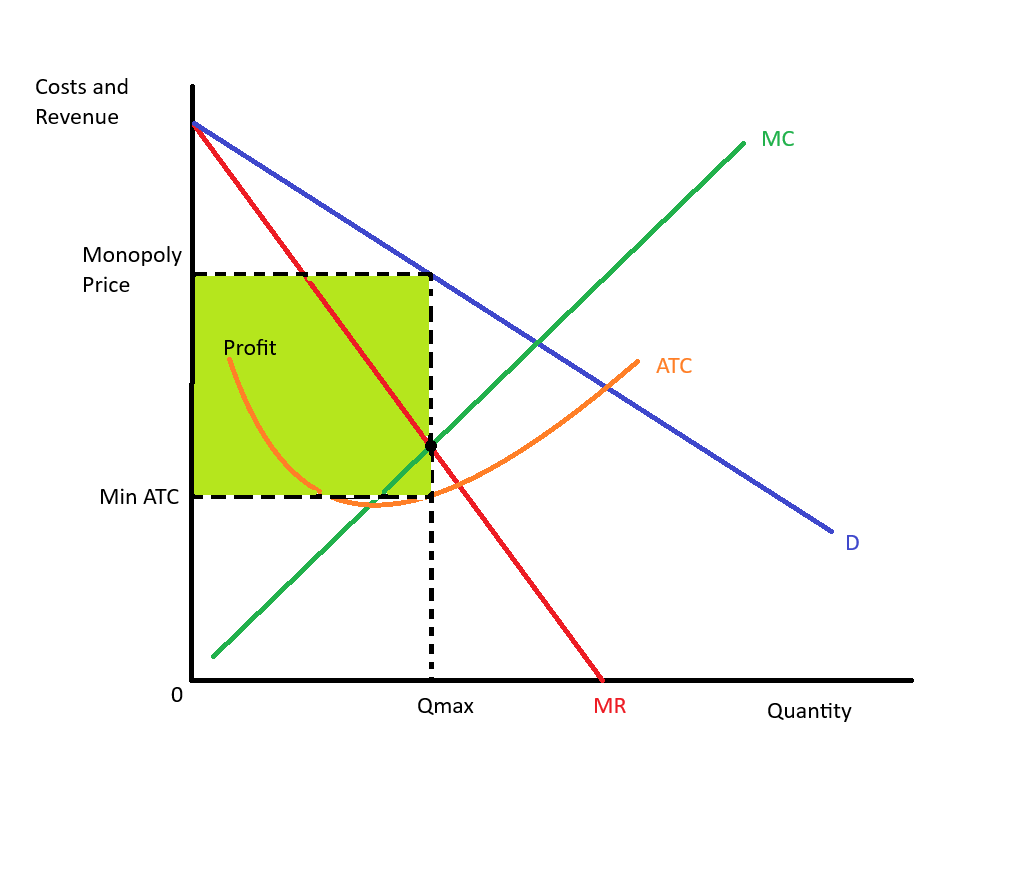
Short Run Monopolistic Competition (profit)
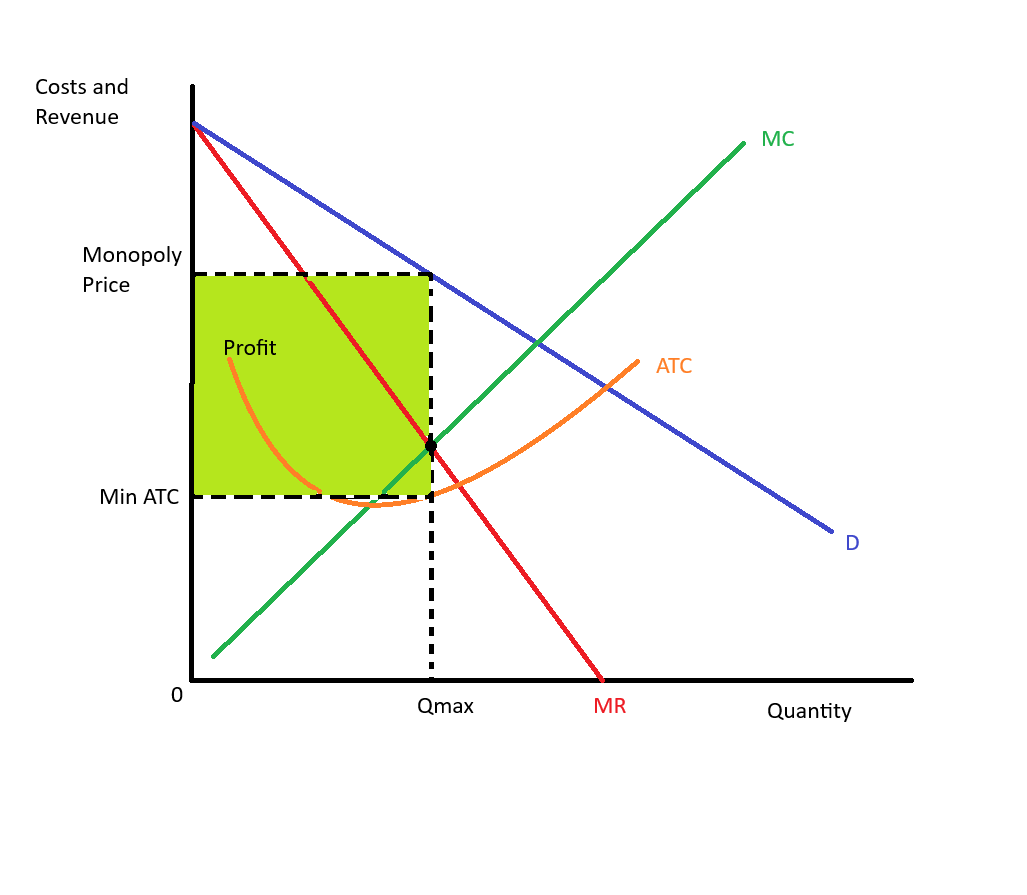
Long Run Monopolistic Competition
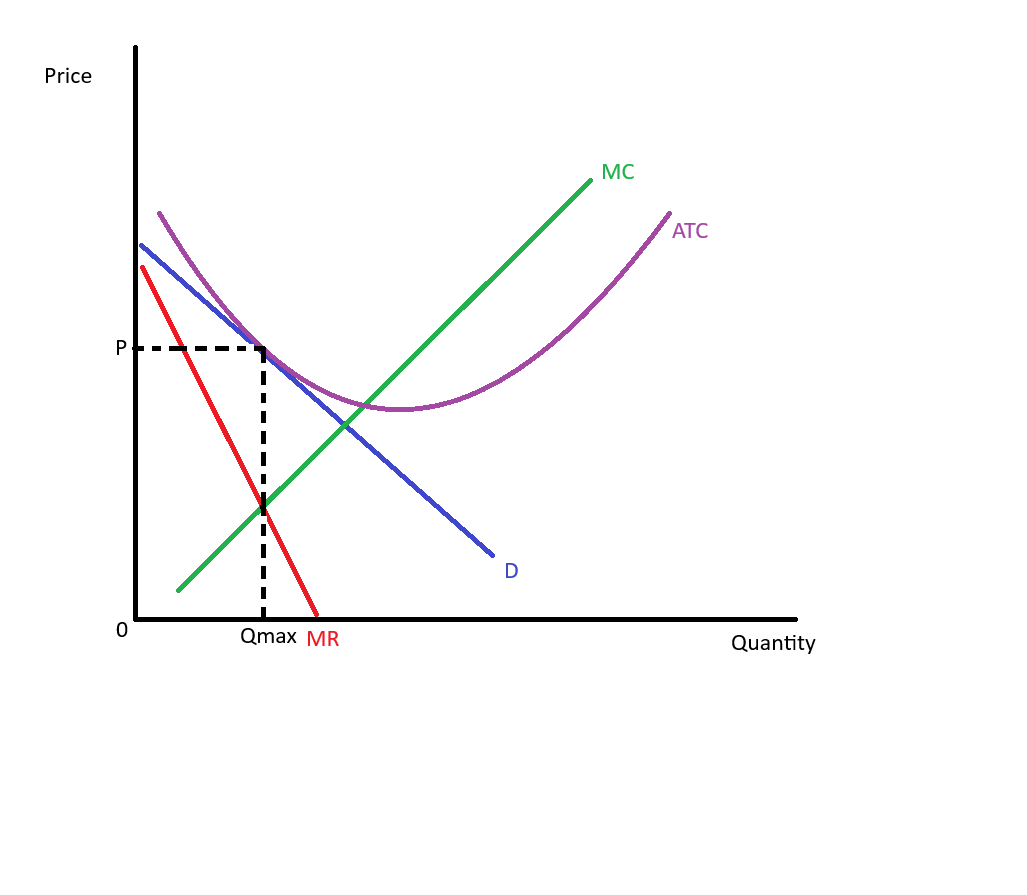
Monopoly
A market structure characterized by a single seller or producer who controls the entire supply of a product or service without close substitutes and has significant pricing power (price setter).
Why monopolies arise
Monopolies can arise due to high barriers to entry for other firms, control over essential resources, government regulation granting exclusive rights, or significant economies of scale that make it inefficient for competitors to enter the market.
monopoly demand curve
typically downward sloping, indicating that a monopolist can set prices above marginal cost.
Marginal Revenue for a monopoly
The additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of a good or service, which declines as output increases due to the downward sloping demand curve. MR<P
Profit-maximizing for monopoly
occurs where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, allowing the monopolist to maximize its total profit.
Competition Law
Regulations that promote competition and prevent monopolistic practices in markets, ensuring fair trade and protection against anti-competitive behavior.
Government Regulation of Monopolies
Government agencies regulate the price a monopoly may charge, usually P = MC to ensure fair pricing and promote consumer welfare.
Public Ownership
A situation where the government or collective owns and manages a resource or service, aiming to provide equitable access and prevent market monopolies.
Price Discrimination
A pricing strategy where different prices are charged to different customers for the same product or service, often based on willingness to pay.
perfect price discrimination
A type of price discrimination where a seller charges each customer the maximum they are willing to pay, capturing all consumer surplus.
second degree price discrimination
A pricing strategy where customers are charged based on the quantity purchased or the form of the product, often through discounts for bulk buying or product versions. Also called multi-part or block pricing.
third degree price discrimination
A pricing strategy where different prices are charged to different consumer groups based on identifiable characteristics, such as age or location.
Monopoly supply curve
A monopolist does not have a supply curve due to the price-setting nature of its market power.
Monopoly price/quantity diagram