Week 9 Tutorial (Pets, Animal Welfare, and Livestock Production Systems)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What proportion of New Zealand households own at least one pet?
A significant majority, approximately 63%.
0 pets = 37%
1 pet = 31%
2 pets = 18%
3 pets = 7%
4 pets = 8%
List the top four (4) most common pets in NZ?
Cats(40%) ,Dogs (31%), Fowl(5.5%) and Fish(5.0%).
What is meant by the term anthropomorphism?
Attributing human characteristics and behavior to animals.
e.g. Birds giving hugs or dogs smiling.
List four (4) common reasons for owning a pet.
Companionship
Security
Relaxation
Giving younger children a responsibility.
Encouraged exercise.
Pest Control.
They needed a home.
Inherited it.
Is a working Animal.
To breed/ enter competitions/ as a hobby.
List four (4) common negative aspects of, or barriers to, pet ownership.
Allergies
Limited space/Unsuitable home.
Unsuitable Lifestyle
Large time commitment and responsibility.
Can be expensive.
Messy and potentially damage to house or belongings.
Could cause physical harm and disease.
Pet loss can be heartbreaking.
Property landlord does not allow animals.
TRUE or FALSE: In New Zealand, it is mandatory to desex (neuter/spay) your pet cat.
False.
It is dependent on your local councils legislations.
Thus, It is not mandatory to desex pet cats on a national level.
TRUE or FALSE: In New Zealand, pet dogs must be registered and microchipped.
True. In New Zealand, it is a legal requirement for pet dogs to be registered and microchipped.
Are animals used in research, testing and teaching covered under New Zealand’s Animal Welfare Act 1999?
Animals used in research, testing, and teaching are covered in the act, but by a separate section and are treated differently.
Why are sheep the most common animal used for research and teaching in New Zealand?
Sheep are the most commonly used because:
We have a massive agriculture sector and a lot of the research being done relates to animals in farming situation (Growth, behavior, breeding ect.)
Sheep also have similar physiology to other ruminants and thus can be used as proxies for these species. This is because in comparison to other ruminants, such as cattle, they are the cheapest and easiest to manage.
Sheep are also used in human pregnancy research due to the similar size of fetus, but are easier to operate on.
Why are live birds not allowed to be imported into New Zealand?
Live birds are not allowed to be imported into New Zealand due to concerns over biosecurity and the potential introduction of avian diseases, that we are currently free of, that could harm our unique population of rare and endangered birds, and poultry industries.
Define animal ethics.
A branch of ethics examining human-animal relationships and the moral consideration of animals, focusing on how nonhuman animals ought to be treated.
Define animal welfare.
Refers to the welfare of animals, specifically how they experience life and whether this experience is good or bad.
Define animal rights.
Primarily refers to the right of animals not to be used or exploited by humans.
List four (4) key points from New Zealand’s Animal Welfare Act 1999.
Recognizes animals as sentient.
Creation of regulations to make animal welfare more immediately enforceable.
Some animals are not protected under the act because they are classified as pests.
Animals used in research, testing, and teaching are covered in the act, but by a separate section and are treated differently.
Define what is meant by the 'physical, health, and behavioral needs' of animals as stated in the New Zealand’s Animal Welfare Act 1999.
The Act defines these needs as:
Proper and sufficient food and water
Adequate shelter
The opportunity to display normal patterns of behavior
Appropriate physical handling
Protection from, and rapid diagnosis of, injury and disease.
List the four areas of information provided in New Zealand’s Codes of Welfare in relation to provision of minimum animal welfare standards.
Details on minimum standards for specific species and situations are written into the various Codes of Welfare.
These codes cover:
Appropriate management of animals
Appropriate behavior of animal owners and handlers
Establishment of minimum standards
Identification and promotion of best practice
Who is the primary regulatory body responsible for the development of animal welfare policy in New Zealand?
The Ministry for Primary Industries (MPI) is responsible for the development of policy.
Policy formed by them on animal welfare standards are enforceable by law.
by RSPCA and MPI inspectors.
List and briefly describe three NZ animal welfare issues.
Some Examples:
Methods of Egg production: caged versus barn.
Issues with overcrowding and living conditions.
Dairy farming: Concerns about treatment and living conditions of dairy cows.
Greyhound racing: Issues regarding the treatment of racing dogs and their retirement.
Methods of Euthanasia and Sexing/spaying.
Companion animals:
Nutrition and exercise.
The epidemic obesity in pets.
Designer breeds.
Cavalier King Charles Spaniels: Heart issues and a genetic condition called Syringomyelia.
British Bulldogs: Predisposition to bone and joint problems, particularly in the hip.
Poodles: Trouble with vision and patellar luxation.
Pugs: Brachycephalic Airway Obstruction Syndrome (BAOS).
Conservation:
Cats vs. wildlife.
Cats kill birds but restricting there outdoor movements infringes there rights under the animal welfare act.
Control of introduced species.
Captive breeding programs/zoos.
Define what is meant by “intensive livestock production”.
A productive system characterized by large amounts of labor and capital relative to land area.
Define what is meant by “extensive livestock production”.
A productive system characterized by small amounts of labor and capital relative to land area.
What type of climate does New Zealand have? ? Discuss the influence New Zealand’s climate has on its sheep and cattle production systems.
New Zealand has a temperate climate.
This provides suitable rainfall and pasture growth, allowing for a relatively cheap and renewable feed source.
Describe pig production systems currently used in New Zealand.
New Zealand has a relatively small pig industry:
Approximately 90 commercial pig farms in NZ.
Average herd size approximately 300 sows.
About 40-45% of these commercial pig operations are outdoor.
There are two types of these Outdoor Systems:
Free farmed (The majority):
Outdoor-based breeding herd.
Indoor-based housing system for growing pigs post-weaning.
Free range (2%):
Outdoor-based breeding herd.
Newly weaned pigs may be kept for a short period in a fenced outdoor pen with a shelter, before they are fully transitioned for rearing outdoors during the grower-finisher period.
Describe poultry production systems currently used in New Zealand.
There are two types of poultry; Broilers(meat production) and layer hens (egg production).
For Broiler Chickens:
Two housing systems:
97% of NZ Broiler chickens are raised in barns.
The remaining 3% in free-range system.
Birds housed in a barn but can roam freely outdoors for at least part of the day.
For Layer Hens:
Three housing systems:
Colony cages: 33%.
Free range: 34% - Access to an extensive outdoor area with an indoor shelter.
Barn: 33% - Deep litter system, similar to a broiler house.
New Zealand leads the world in poultry performance, in terms of growth, feed conversion and egg production. Why?
New Zealand leads the world in poultry performance because of its Biosecurity efforts.
These mean NZ is free of 2/3 major poultry diseases: exotic Newcastle disease and avian influenza.
Leading to the superior health of the New Zealand poultry flock.
Define stockmanship?
Stockmanship refers to the quality of care or management of animals as performed by the owner or caretaker.
Animal welfare is closely linked to stockmanship and is included in the codes of welfare.
True or false: Animals must be fit for transport; it is an offense under the Animal Welfare Act 1999 to transport unfit animals.
True
They have to be able to walk on the truck themselves.
Unfit animals should be treated on the farm or humanely slaughtered.
MPI governs national welfare standards using the 1999 Animal Welfare act. What about international organistations?
First OIE (World Organisation for Animal Health) global standards published in 2004.
182 member countries.
Massey University’s AWSBC is one of five partners of the world’s first OIE/WOAH Collaborating Centre for AWSBA.
What are the most common dairy cattle breeds in NZ?
Holstein-Friesian
Jersey
Kiwi Cross (Cross between Holstein-Friesian and Jersey)

What are the most common beef cattle breeds in NZ?
Angus
Hereford
What are the most common sheep breeds in NZ? (Also list what they are breed for)
Romney(Meat and course wool)
Merino (Fine wool)
What are the most common pig breeds in NZ?
Large White
Landrace
Duroc
Hampshire
Popular for breeding with landrace and large white: to put some color in their skin for outdoor farming)
What are the most common chicken breeds in NZ?
Broiler: Meat chicken
Has two genetic strains: ross and cob
Layer Hen: for eggs
Two genetic strains: Highline and shaver
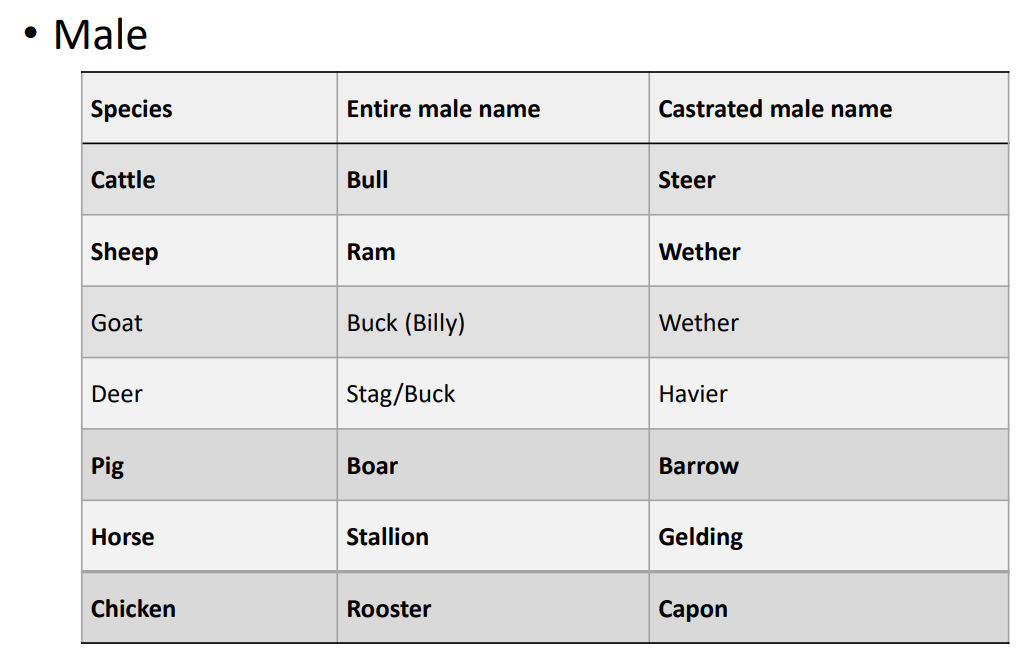
What is the term for a castrated and non-castrated male, of the following species:
Cattle
Sheep
Goat
Deer
Pig
Horse
Chicken
The term for a castrated male is "Steer" (cattle), "Wether" (sheep), "Wether" (goat), "Havier" (deer), "Barrow" (pig), "Gelding" (horse), and "Capon" (chicken). Non-castrated males are referred to as "Bull" (cattle), "Ram" (sheep), "Buck" (goat), "Stag" (deer), "Boar" (pig), "Stallion" (horse), and "Rooster" (chicken).
What are the terms for the offspring, of the following species:
Cattle
Sheep
Goat
Deer
Pig
Horse
Chicken
Calf (Cattle)
Lamb (Sheep)
Kid (Goat)
Fawn (Deer)
Piglet (Pig)
Foal (Horse)
Chick (Chicken)
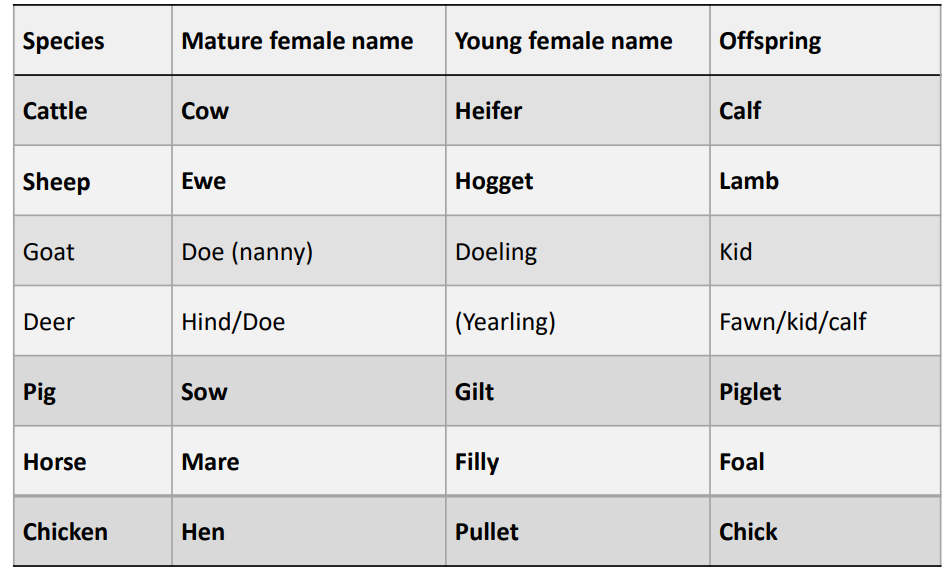
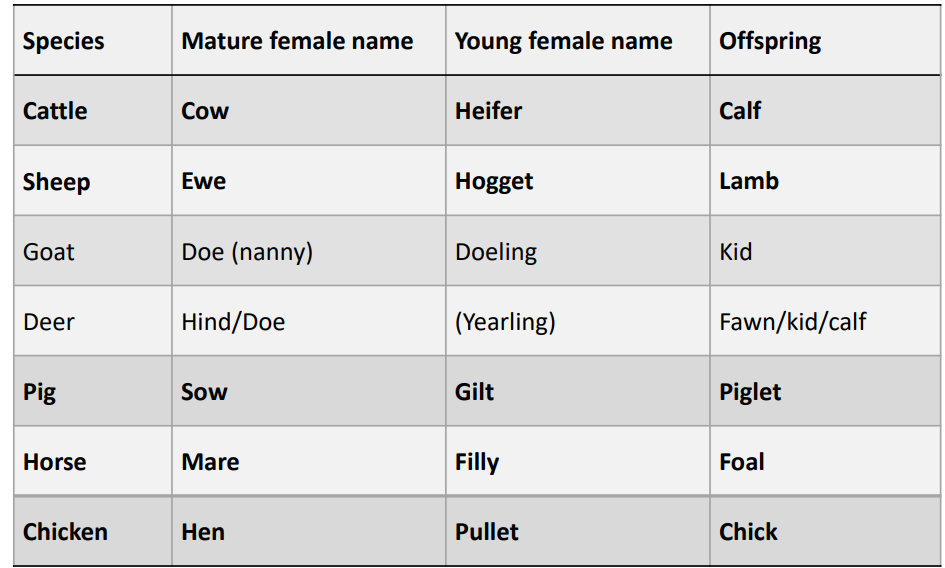
What are the terms for young and mature females, of the following species:
Cattle
Sheep
Goat
Deer
Pig
Horse
Chicken
Mature
Cattle = cow
Sheep = ewe
Goat = doe (nanny)
Deer = hind/doe
Pig = sow
Horse = mare
Chicken = hen
Young
Cattle = heifer
Sheep = Hogget
Goat = Doeling
Dear=Yearling
Pig= gilt
Horse = filly
Chicken = pullet
How many types of farm classes are there for beef and lamb production? How are they classed?
8 farm classes
Based on land type and/or farming activity
How many types of farm classes are there for diary production? How are they classed?
5 production systems
Based on feed inputs.
A reprint of the New Zealand Animal Welfare Act stating that animals are 'sentient' happened in what year?
The reprint of the 1999 Animal Welfare Act was in 2015.
New Zealand has strict pet import regulations to protect the local flora and fauna from exotic diseases.
Which of the following is the most significant import ban from a biosecurity perspective?
Live birds, because NZ is currently free of 2/3 major avian diseases. A serious risk to our native bird species and poultry industries.