Nephron and Collecting Duct
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is uriniferous tubule?
The structural unit that includes the nephron and collecting duct
What are the 4 histological structures of the nephron?
Renal corpuscle #ff00d8
Proximal convoluted tubule #ff00a4
Loop of Henle #a700ff
Distal Convoluted tubule #6b00ff
What is the brief function of
Renal corpuscle
Proximal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal convoluted tubule
Collecting duct
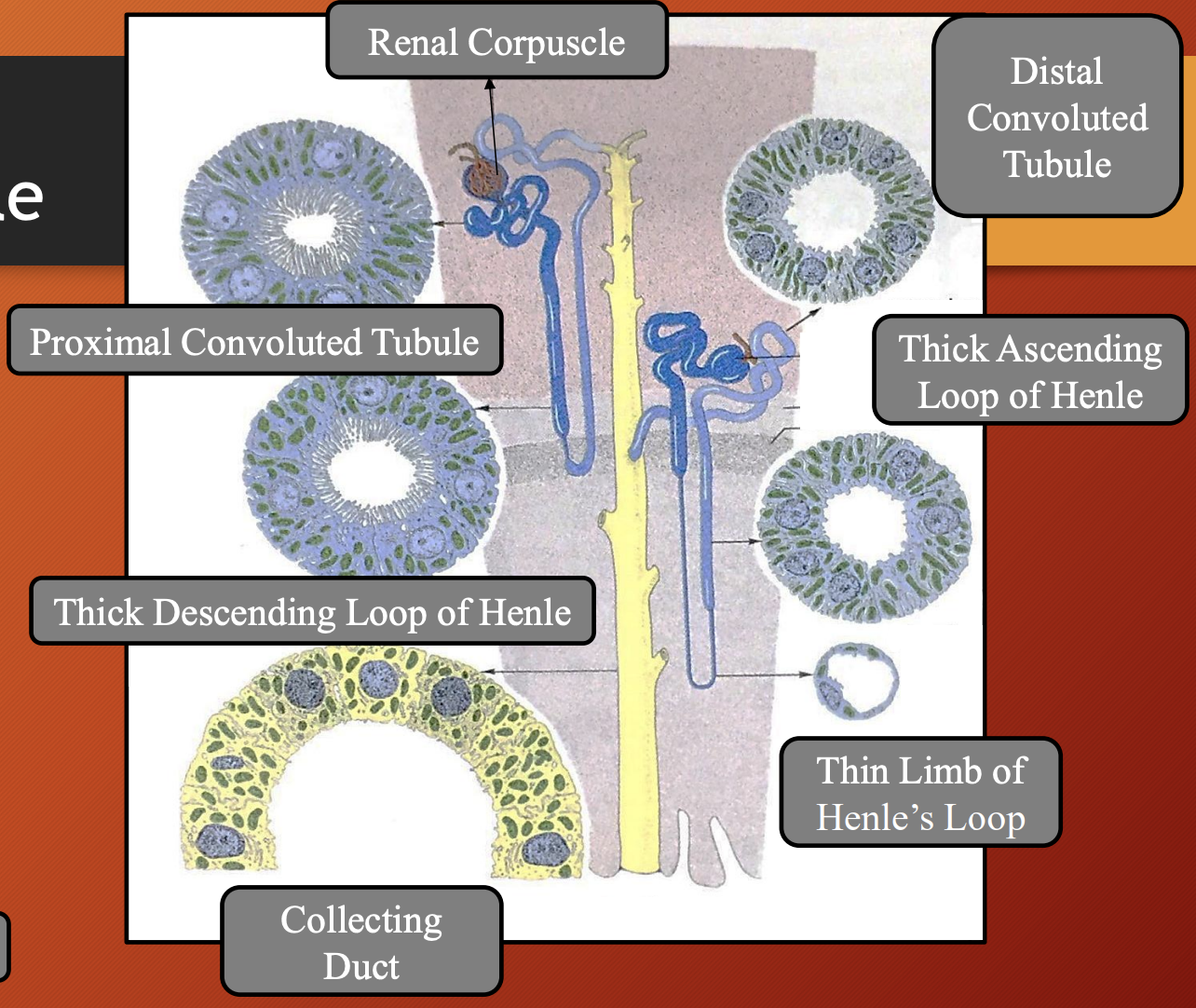
Renal corpuscle: Filtration
Proximal convoluted tubule: Reabsorption of water, ions and nutrients
Loop of Henle: Concentrates urine
Distal convoluted tubule: Selective secretion and absorption
Collecting duct: Receives urine from multiple nephrons, concentrating it and channels towards renal pelvis
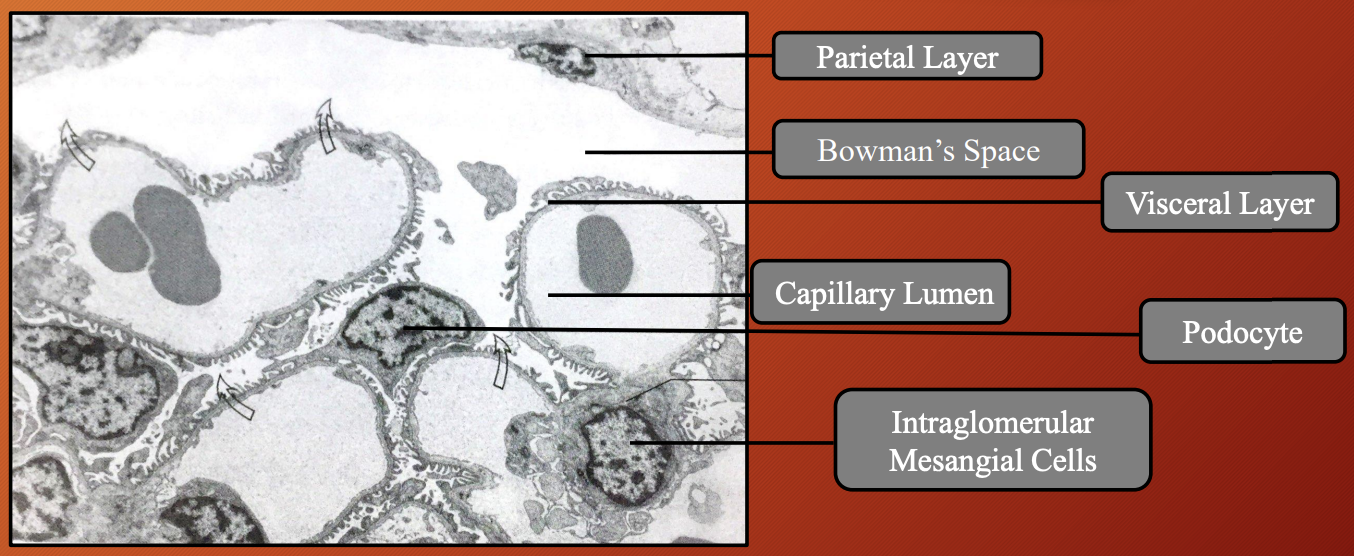
Nephron: Renal Corpuscles
Location
Consist of
Location: Cortical renal parenchyma
Consist of:
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule (consist of parietal layer, visceral layer and bowman’s space)
Intraglomerular mesangial cells
Vascular and urinary pole
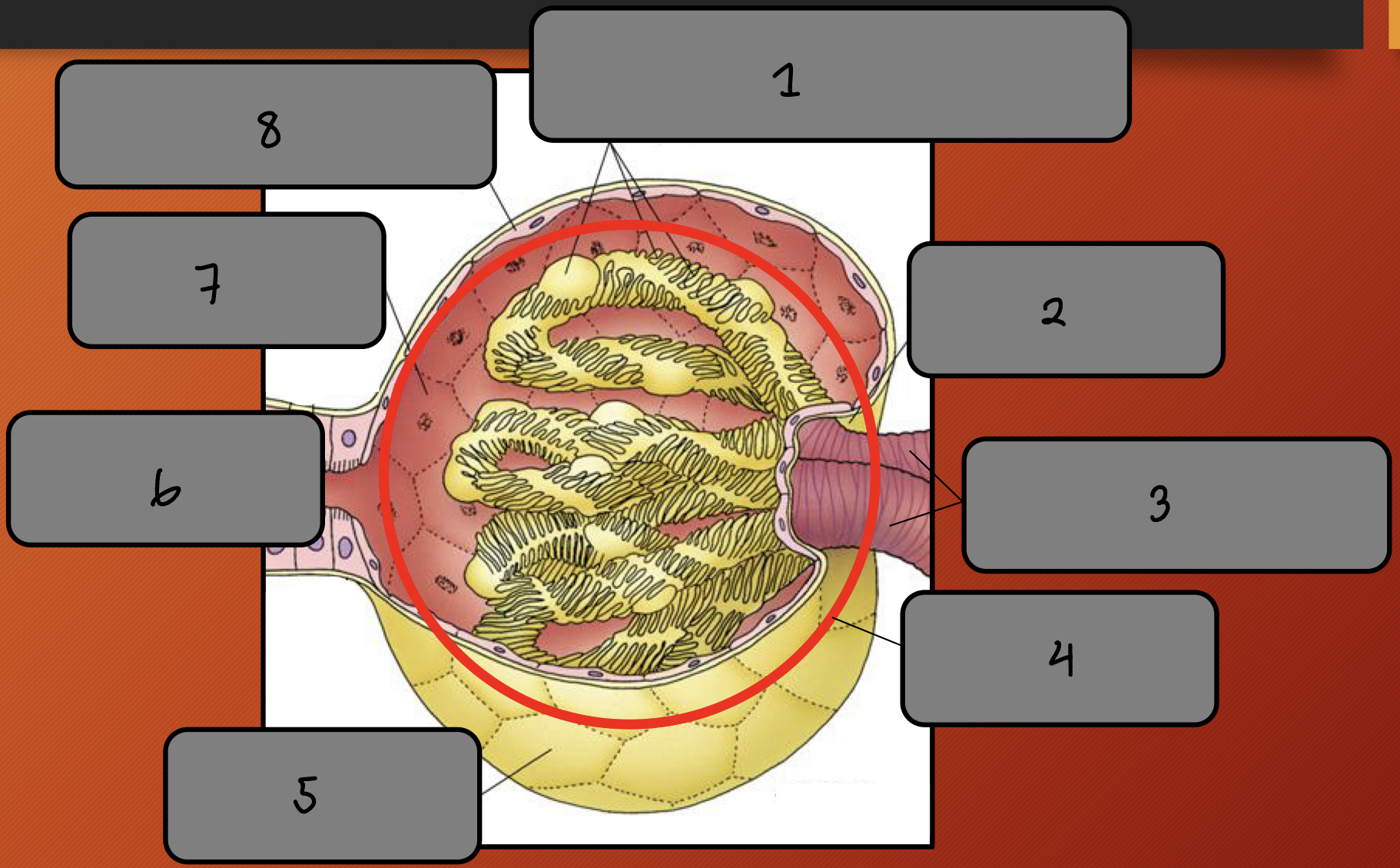
Label the image 1-8
Visceral layer of Bowman’s Capsule (podocytes)
Vascular pole
Afferent and efferent arteriole
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
Urinary pole
Bowman’s space
Parietal layer of Bowman’s Capsule
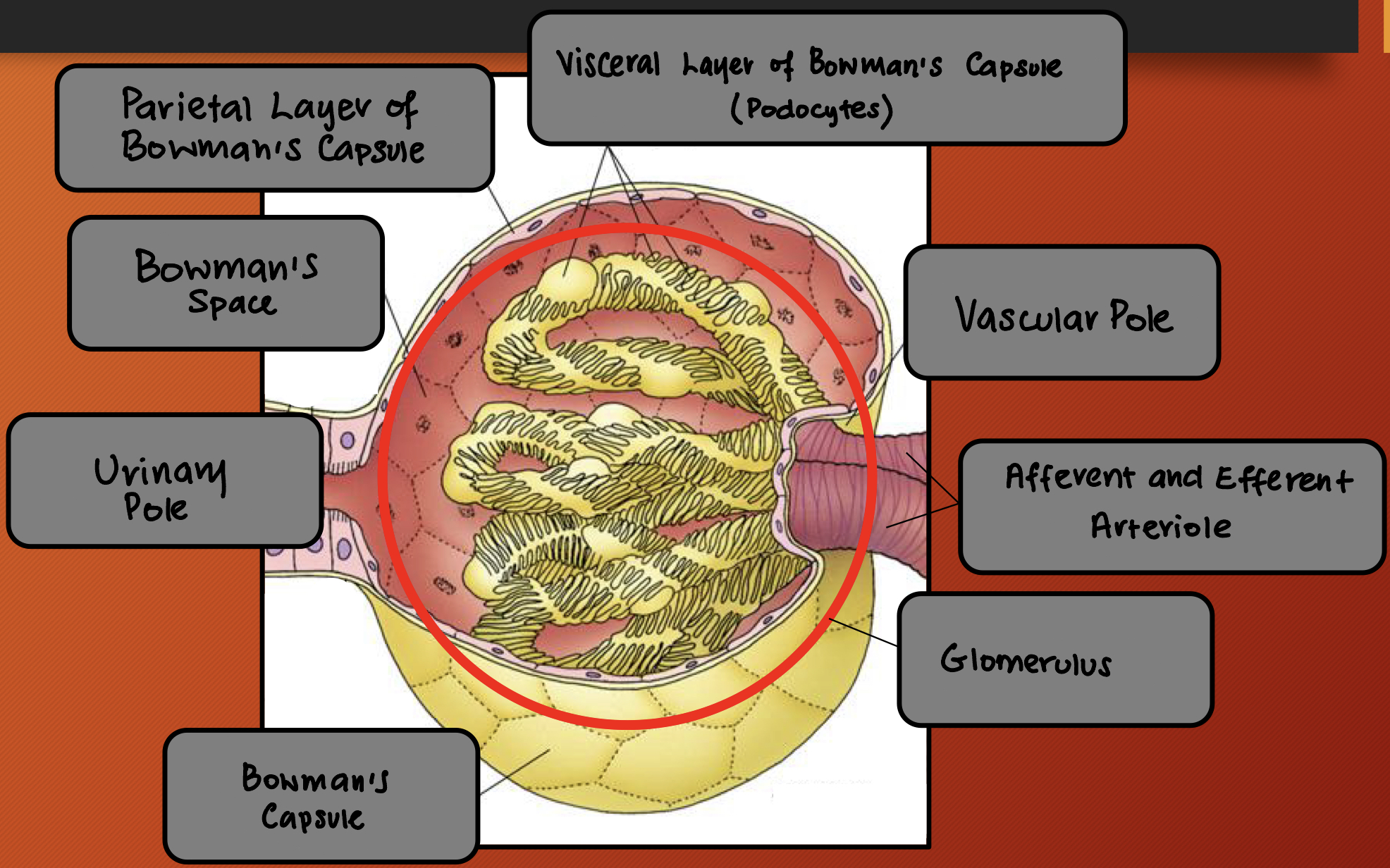
Nephron: Renal Corpuscles #ff00d8
What are the 3 components of the Bowman’s capsule
Parietal layer: Outerwall of Bowman’s capsule that is made of simple squamous epithelium
Visceral layer: Inner layer that lies directly on glomerular capillaries and podocytes
Bowman’s space: Gap between parietal and visceral layers
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles: Glomerulus
What
Location
Arises from
Pathway of blood
Composed of
What: Tuft of fenestrated capillaries
Location: Inside renal corpuscle
Arises from: Afferent arteriole
Pathway of blood: Enters through afferent arteriole —> filtered —> exits by efferent arteriole
Composed of:
Endothelial cell
Basement membrane
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles —> Glomerulus: Endothelial Cells
What
Function
Charge
Function
Produces
Function
What: Thin and fenestrated without diaphragms (no covering)
Function: Allows fluid to pass through
Charge: Anionic (negative)
Function: Repels negatively charged molecules
Produces: Endothelin
Function: Causes vasoconstriction to regulate glomerular pressure
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles —> Glomerulus: Basement Membrane
What
Location
Compose of
Function
Produced by
3 layers
What: Thin structural layer
Location: Between the capillary endothelium and podocytes
Compose of:
Type IV collagen
Sialic acids
Function: Gives negative charge
Produced by: Endothelial cells (but partly podocytes)
3 layers:
Lamina rara interna (closest to endothelium)
Lamina densa (middle dense layer)
Lamina rara externa (closest to podocytes)
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles: Glomerulus
How does the glomerulus have mechanical and chemical filtration?
Mechanical filtration: Because the blood passes through 3 layers so only small molecules (water, glucose, urea, electrolytes) pass through
Fenestrated endothelium
Basement membrane
Filtration slits between podocytes
Chemical filtration:
Basement membrane and podocyte surfaces are negatively charged
BM also secretes protelycans which are negative
So it repels negatively charged proteins
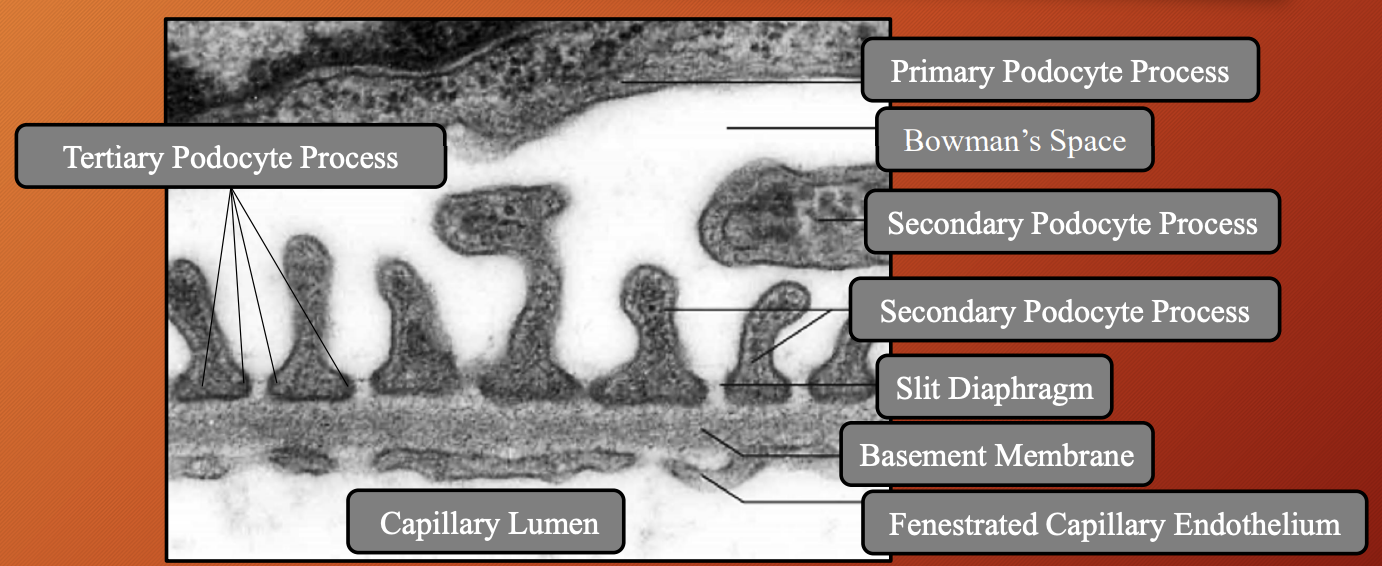
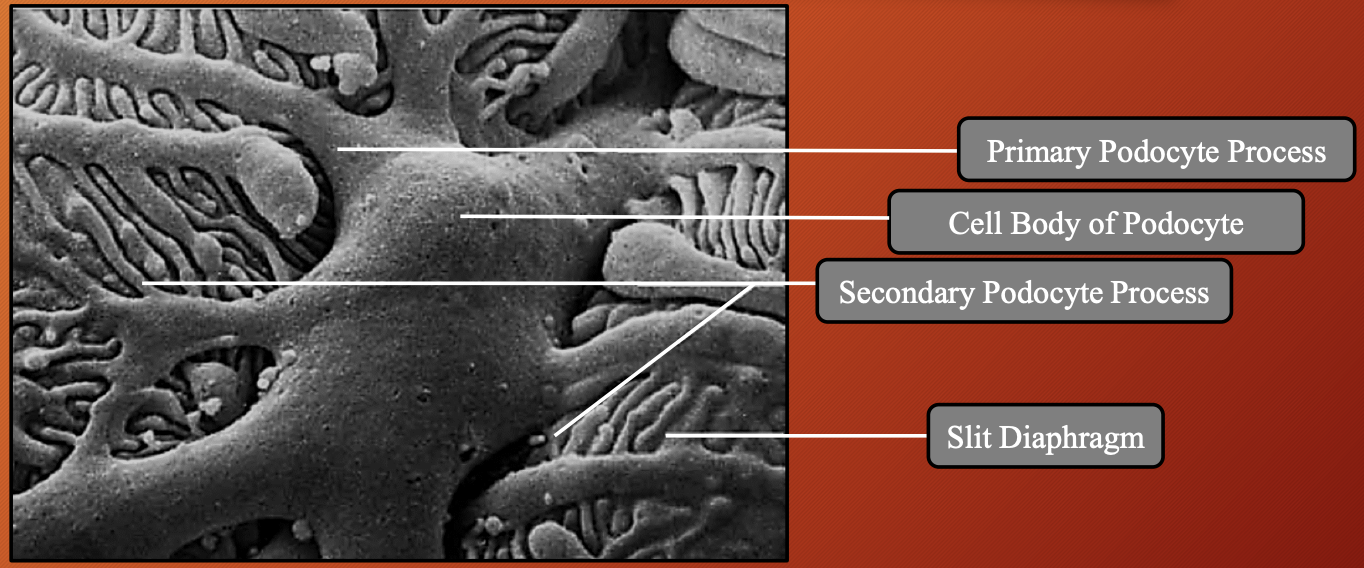
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles —> Bowman’s Capsule: Visceral Layer
What
Made up of
How does it allow for filtration
Which part bulges into Bowman’s space
Primary process
What
Rich in
Function
Secondary process
What
Function
Tertiary process
What
What is slit diaphragm
Function
What: Inner layer that sits directly on glomerular capillaries
Made up of: Podocytes (speacilased flattened cells that wrap around outside glomerular capillaries)
How does it allow for filtration: Don’t touch each other completely
Which part bulges into Bowman’s space: Nuclei and cell bodies
Primary process:
What: Long arm like extensions from podocyte cell body
Rich in: Actin
Function: Help with shape and support
Secondary process:
What: Branches that come off primary processes
Function: Increase SA
Tertiary process:
What: Final, tiny extensions that in direct contact with basement membrane
What is slit diaphragm: Interdigital space between tertiary process
Function: Acts like tiny filtration barrier
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles —> Bowman’s Capsule: Parietal Layer
What
Made of
Covering from
Underneath has
What: External part of Bowman’s capsule
Made of: Flattened, simple squamous epithelium
Covering from: Vascular pole to urinary pole
Underneath has: Basal lamina and loose CT
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles —> Bowman’s Capsule: Bowman’s Space
Location
Function
Location: Between visceral and parietal layer
Function: Collect ultra-filtrate before leaving renal corpuscle by urinary pole
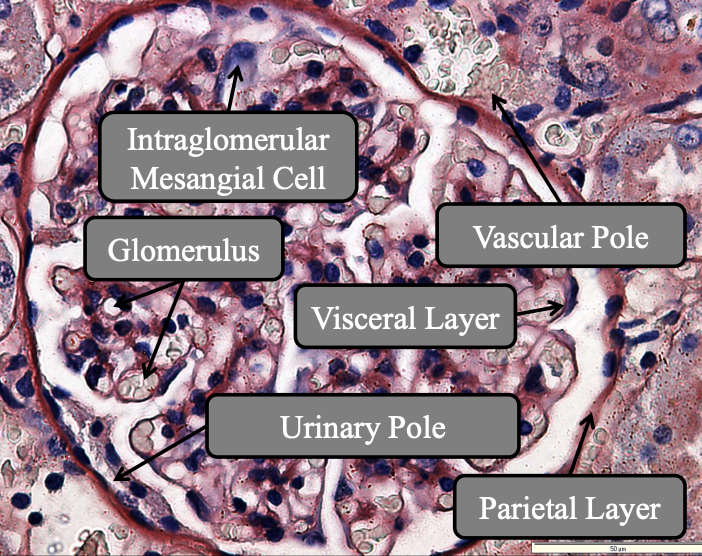
Nephron —> Renal Corpuscles: Intraglomerular Mesangial Cells
Location
Shape
Nucleus
Processes
What located in mesangial matrix
Function
Expresses
Function
Function
Location: Between glomeruli and vascular pole
Shape: Spindle/Star
Nucleus: Heterochromatic nuclues
Processes: Long cytoplasmic processes that penetrate basement membrane and endothelial glomerulus
What located in mesangial matrix: Scatted fibril bundle
Function: Allow contraction
Expresses: Angiotensin II receptor
Function: Regulation of blood pressure
Function: Structural support, phagocytosis, regulates blood flow

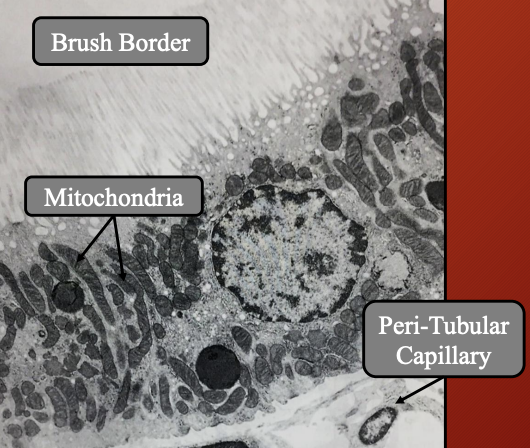
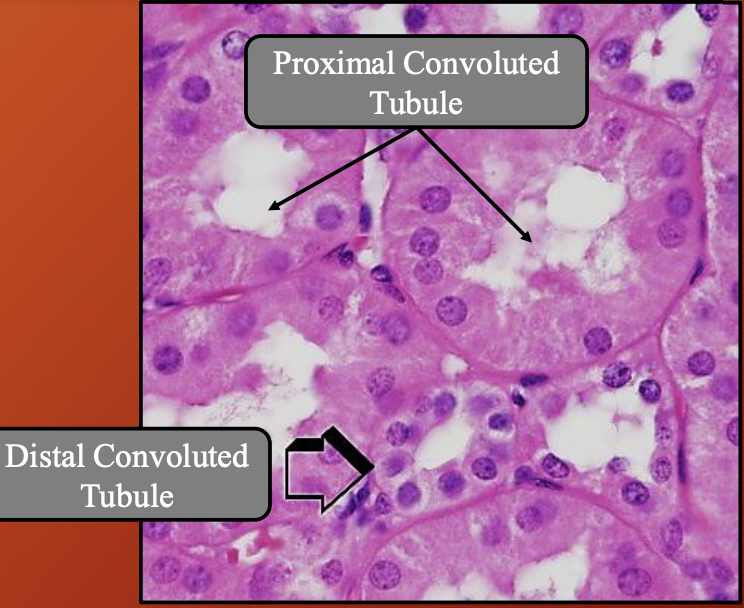
Nephron: Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) #ff00a4
Location
What type of epithelium lines PCT
Function
Function of apical brush border (microvili)
What organelles are abundant in apical cytoplasm
Which species have lipid droplet in apical cytoplasm
Importance of infolded basal membrane and elongated mitochondria
What is basal labryinth in PCT
How is PCT supported by blood supply
Location: Cortical renal parenchya (renal cortex)
What type of epithelium lines PCT: Tall cubodial or low columnar epithelium (acidophilic)
Funciton: Reabsorption and secretion of toxins
Function of apical brush border (microvili): Increase SA for reabsorption
What organelles are abundant in apical cytoplasm:
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Resorption vacuoles
Which species have lipid droplet in apical cytoplasm: Feline and canine (ruminants and equines lack)
Importance of infolded basal membrane and elongated mitochondria: Support active ion transport by increasing SA and energy supply
What is basal labryinth in PCT: Network of membrane folds that allows connection between adjacent cells
How is PCT supported by blood supply: Enwrapped by peri-tubular capillary network for reabsorption
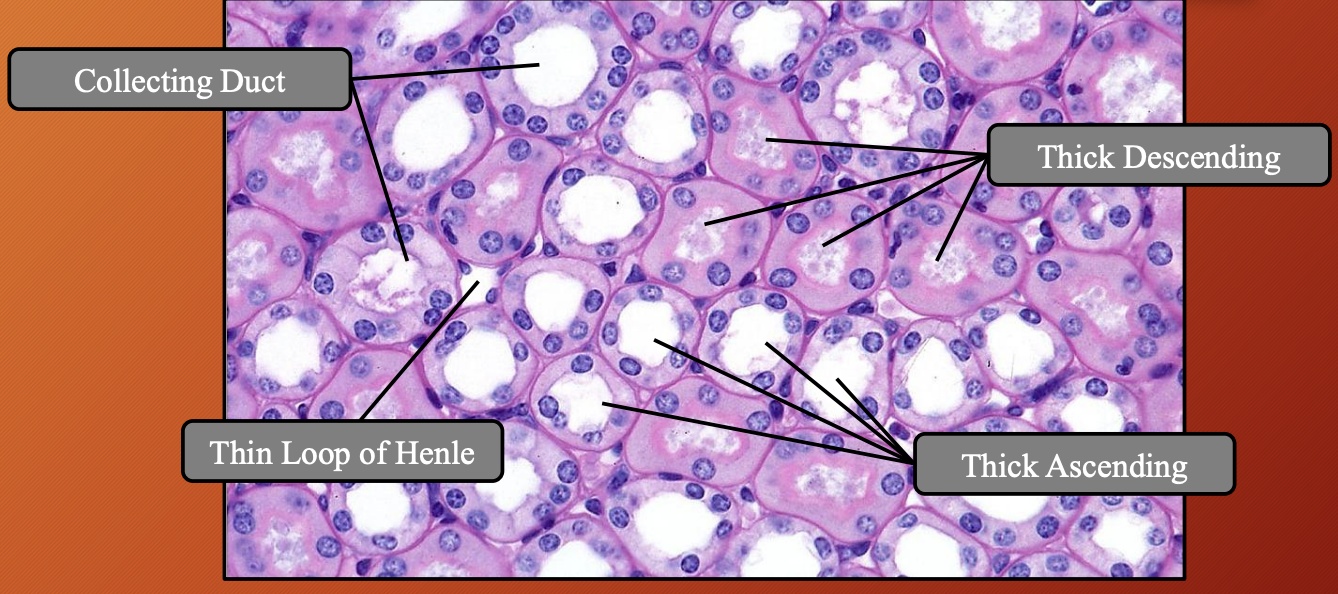
Nephron: Loop of Henle (LoH) #a700ff
Location
Shape
Types of segments
Thick segment lined with
Thin segment lined with
Which segment has brush boarder and why
Lacks
Nuclei
Location:
Starts in cortex (as continuation of PCT)
Dips into medulla (descending limb —> ascending limb)
Returns to cortex (to connect with distal convoluted tubule)
Shape: Hairpin like bend
Types of segments: Thick and thin descending and ascending segment
Thick segment lined with: Cubodial epithelium
Thin segment lined with: Squamous epithelium
Which segment has brush boarder and why: Thick descending has brush boarder because it relies on passive transport so it needs an increased SA
While thick ascending relies on active transport so increased SA not needed
Lacks: Brush boarder
Nuclei: Slightly protruding into lumen
Nephron —> Loop of Henle (LoH): Counter Current System
What
How
Creating
Established by
What species lacks this
What: When filtrate flows in opposite directions in the descending limb and ascending limb
How:
Descending limb: Water out, salt in —> concentrated filtrate
Permeable to water but not to solutes (Na+, Cl-)
So water leaves tubule into surrounding salty medulla
Resulting in the filtrate to be more concentrated as it descends
Ascending limb: Salt out, water in —> dilute filtrate
Impermeable to water but actively pumps out Na+ and Cl-
So salt leaves, water stays
Resulting in more dilute filtrate as it goes up
Makes medulla salty helping pull water out of DL of LoH
Creating: High osmolarity gradient in medulla
Established by: Having both DL and AL close with vasa recta
Species lacks this: Avian
Nephron: Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) #6b00ff
Location
Close contact with
Forms
Type of cells
Cytoplasm
Why
Lumen
Apical membrane
Labyrinth
Which organelle numerous
Epithelium regulated by
Location: Cortical renal parenchyma
Close contact with: Glomeruli
Forms: Partly form juxtaglomerular apparatus
Type of cells: Cuboidal epithelial cells
Cytoplasm: Light acidophilic
Why: Lots of water in cytoplasm
Lumen: Wider tubular
Apical membrane: Irregular small microvilli present
Labyrinth: Prominent basal
Which organelle numerous: Mitochondria
Epithelium regulated by: Hormones (aldosterone, AD, calcitonin, parathyroid)
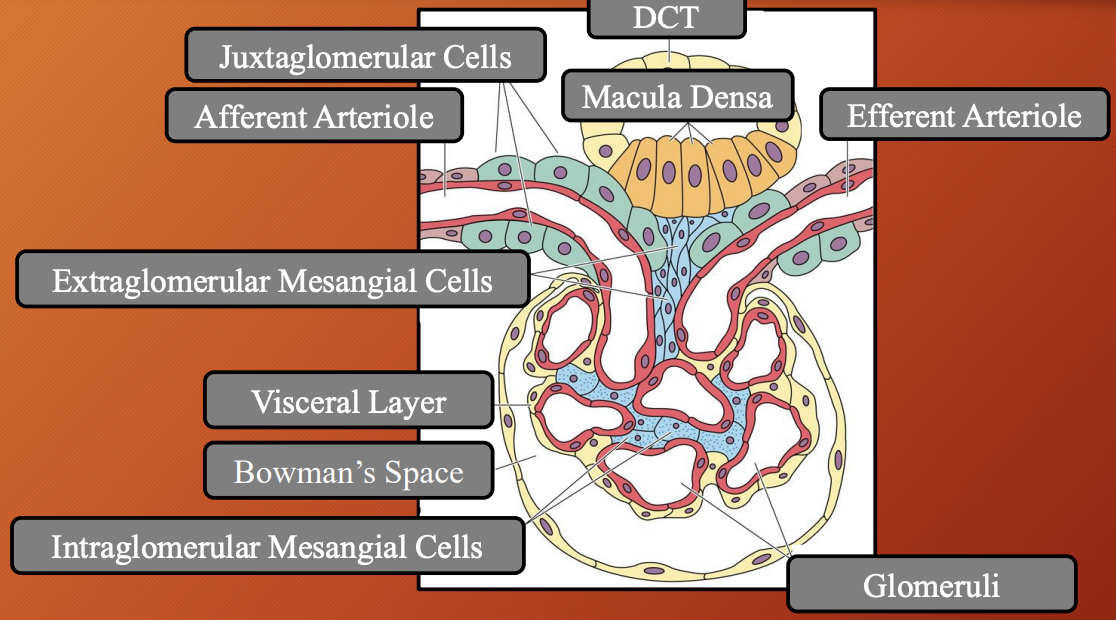
Nephron —> Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) #6b00ff
Location
What
Consist of
Location: Dorsal to the renal corpuscle (cortical renal parenchyma)
What: Specialised structure where the DCT is close contact with glomerulus of the same nephron
Consist of:
Macula Dense
Juxtaglomerular cells
Extraglomerular mesangial cells
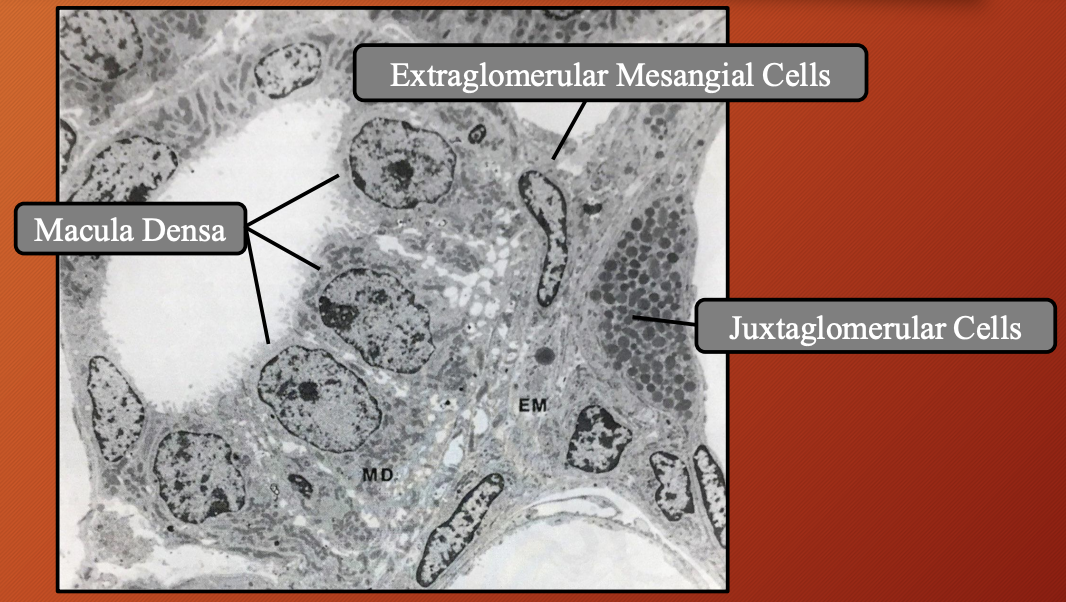
Nephron —> Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) —> Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA): Macula Densa
Location
Part of
Type of cells
Cytoplasm
Microvilli
Lack of
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Function
Location: Adjacent to vasular pole between afferent and efferent arteriole
Part of: DCT
Type of cells: Tall, narrow and pale modified columnar epithelial cells
Cytoplasm: Dense
Microvilli: Short
Lack of: Basal lamina
Mitochondria: Small
Nucleus: Pushed to apex and infranuclear Golgi apparatus
Function: Chemoreceptor (Na+)
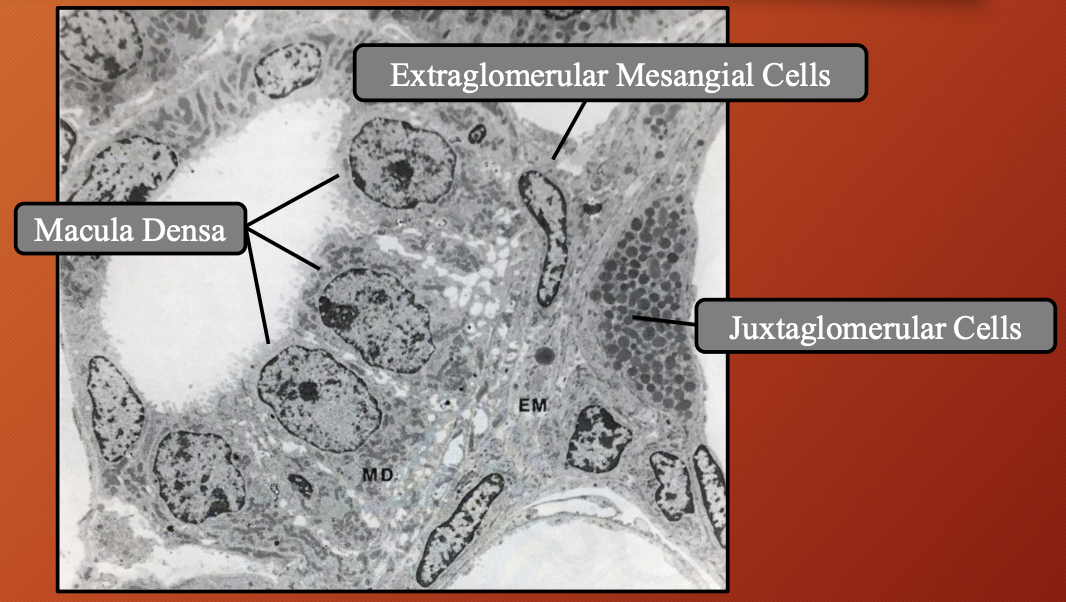
Nephron —> Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) —> Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA): Juxtaglomerular Cells #6b00ff
What
Location
Has
Innervated by
What: Granular modified smooth muscle cells
Location: Tunica media of afferent and efferent arteriole
Has: Myosin filament and dense renin granules
Innervated by: Sympathetic nerve fibers
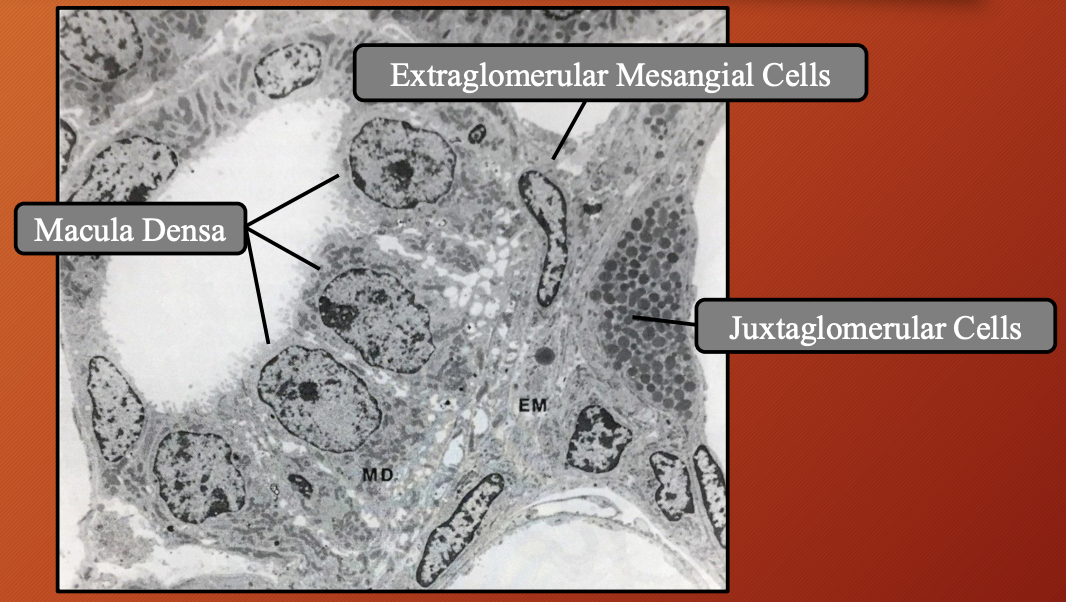
Nephron —> Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) —> Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA): Extraglomerular Mesangial Cells #6b00ff
What type of cells
Location
Continuous from
Function
What type of cells: Polissen and lacis cells
Location: Between macula densa and arterioles
Continuous from: Intraglomerular mesangial cells
Function: Reserve cells for juxagloemerular cells
Collecting Duct
Location
What merges with CD
One CD drained from
Grouped in
Forms
CD merge to
CD emptys into
Epithelium in cortex
Epithelium in medulla
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Structures located in older animals
Organelle located in equine
Expresses
Location: Cortical and medullary renal parenchyma
What merges with CD: Short, arched collecting tubules
One CD drained from: 10 nephrons
Grouped in: Parallel straight
Forms: Medullary rays
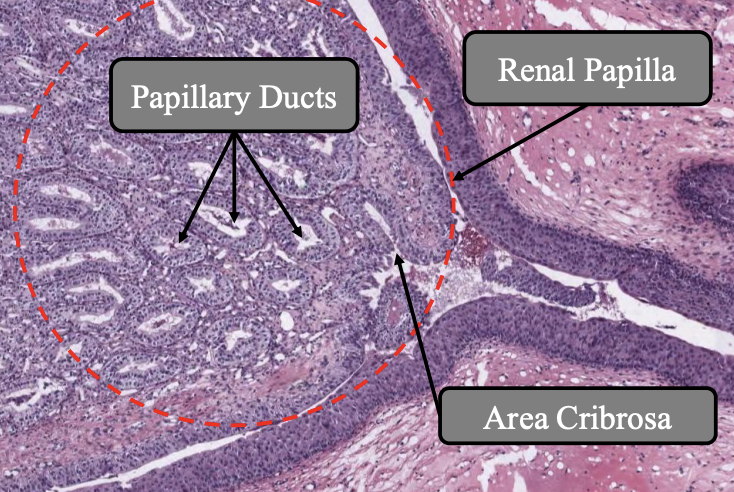
CD merge to: Papillary ducts
CD empty into: Renal papilla
Epithelium in cortex: Cubodial
Epithelium in medulla: Columnar
Nucleus: Centrally located
Cytoplasm: Pale
Structures located in older animals: Lipid droplets
Organelle located in equine: Goblet cells
Expresses: ADH receptors