Scale of the Universe - Lecture Flashcards
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from the lecture notes on the scale of the universe and solar system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the Astronomical Unit (AU) defined as?
The average distance between the Earth and the Sun.
The most common element in the universe is
Hydrogen.
What is a light year?
The distance that light travels in one year.
For scientists, an element is defined by
the number of protons in its nucleus.
The location of the Earth in the Milky Way Galaxy is
a little less than 30,000 LY from the center.
Sort the celestial objects in order of size (largest to smallest).
Universe > Galaxy > Solar System > Star > Planet.
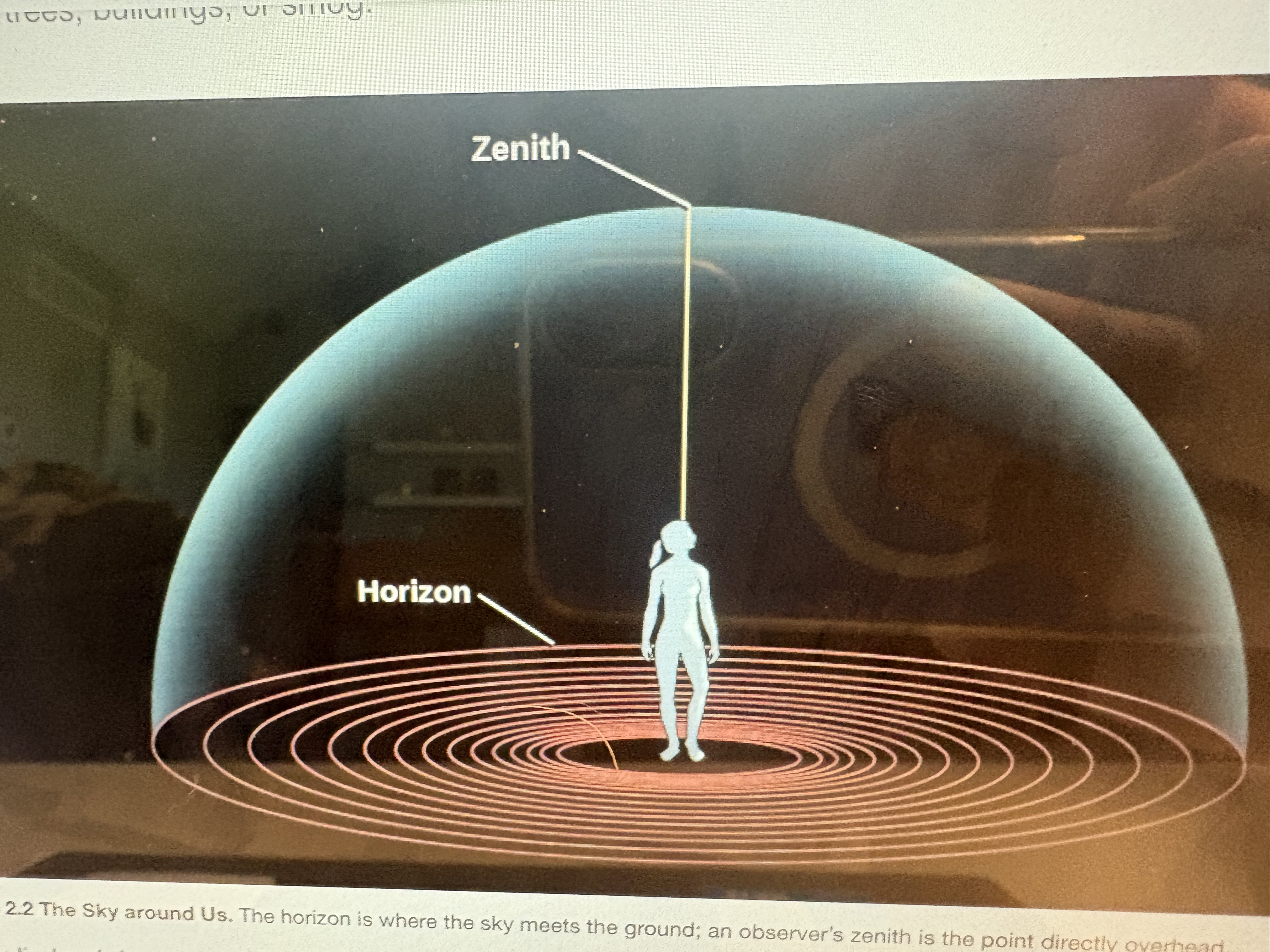
What is the name of the point directly above your head?
Zenith
Retrograde motion
When a planet appear to move backwards in the sky from Earths perspective
Prograde motion
Motion in the same direction as the dominant orbital direction of a system
Classical astronomers, like Ptolemy, could or could not explain Retrograde motion with their models
Could explain
{who} observed gibbous phases of {what} as evidence for the heliocentrism of our solar system
Galileo, Venus
Parallax
The apparent shift in the direction of an object as a result of the motion of the observer
Apparent magnitude
A measure of how bright a star looks in the sky; the larger the number, the dimmer the star appears to us
Celestial equator
A great circle on the celestial sphere 90 degrees from the celestial poles; where the celestial sphere intersects the plane of Earths equator
Which of the following was not done by Hipparchus, the great ancient astronomer
Explained retrograde motion
A satellite in a circular orbit and then burns thrusters to increase speed slightly, what happens
Its orbit would become more elliptical
A rocket blasts its engines long enough to reach escape velocity from the surface of earth. What is its orbital shape?
None, will fly away from earth
What is the semi-major axis it the orbital period is 2 years?
1.59AU