Business - Chapter 2 - People in Business
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Motivated worker
– A hard working employee who works effectively for a business.
Why do people work?
● Money – People need money to buy food, water and other items they need to live.
● Social needs – People just like us likes to feel part of a team, socialise and make friends.
● Esteem needs – Feeling important, feeling that they are contributing to a business.
● Job satisfaction – enjoyment from the work and achievements they have accomplished.
● Security – Feeling of having a secure job with a stable income. (not likely to lose job etc...)
Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
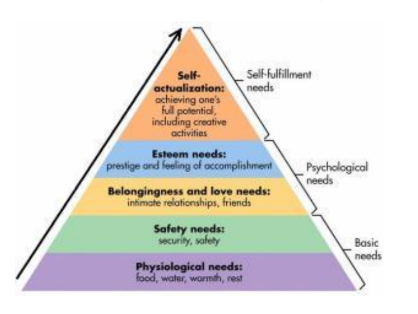
what does Abraham Maslow’s theory states
that the more levels of needs achieved by the worker = the higher motivated they will become. This also means that each level of motivation must be achieved before an employee can move to the next level of motivation.
Criticisms of Abraham Maslow’s theory
● These needs to not apply to all employees (all humans are different)
● Difficult for managers to determine which needs their employees need
what does F.W. Taylor’s theory state
Employees are motivated by money.
More money = employees become more motivated
criticisms of F.W. Taylor’s theory
● Employees can be motivated by other factors not just money
● There is no guarantee that all employees will work harder if they are paid more
● There are many jobs where output cannot be measured easily (difficult to determine if employee actually works hard)
what Federick Herzberg’s theory states
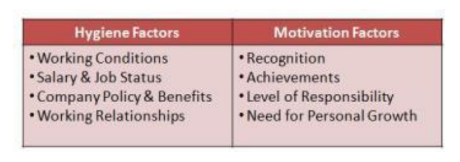
2 factors Hygiene & Motivation factors
Workers expect hygiene factors to be available to them otherwise they will become demotivated. Hygiene factors will not motivate the workers only motivation factors will make the employees work harder.
3 Ways to motivate employees
● Financial rewards
● Non-financial rewards
● Job satisfaction
Wages (time rate) - financial reward
Payment for a period of time such as amount per hour e.g. $10 per hour.
cons of wages (time rate)
Good & bad workers get paid the same, Recording every employee’s working hours may be complicated, costs business to hire an employee to calculate each workers’ wage.
Wages (piece rate) - financial reward
Workers paid depending on quantity of product produced e.g. $2 for every bicycle assembled.
cons of Wages (piece rate)
Workers may rush and produced bad quality products, Workers that make slow high-quality products will get paid less.
Salaries - financial reward
Employees paid monthly, often used to pay office workers. Managers only need to calculate salaries once a month which uses less time.
types of Additional Payments (Money added to salaries)
● Commission – Sales staff are often paid a small percentage of the selling price of the product they are selling e.g. If a car salesman sells a car, the salesman might get 20% of the selling price of the car which is added to his salary.
● Profit sharing – Employees receive share of the company’s profit. This benefits the company because employees will want the company to have a higher profit.
● Bonus – Money paid to workers when they work well usually at the end of the year.
● Performance related pay – Employee’s pay is linked to the effectiveness of their work. This is often used with jobs where output cannot be easily measured.
● Share ownership – Employees are given some of the company’s shares. This makes them work hard as prices of shares may increase if the business is doing well. + This also makes the employee feel that they are part of the company.
Non-Financial Rewards
● Health care paid by company
● Company cars
● Free trips / company holidays
● Employee of the month
● Free meals
● Discount on company’s products
● Free housing
● Children’s education fees paid by company
Job Satisfaction consists of
● Pay
● Promotion
● Working conditions
● The work itself
● Status of the job
Ways to improve job satisfaction
● Job Rotation – Workers swap roles to do different tasks. This stops the employee from getting bored.
● Job Enlargement – More extra tasks are given to the worker so they have a variety of things to do. However, these tasks should not be more difficult. e.g. supermarket cashier now adds price label on items.
● Job Enrichment – Adding tasks that require more skill and responsibility. e.g. receptionists employed to greet clients now deal with telephone enquiries.
● Autonomous work groups & team working – Working in teams make employees more interested in the tasks since they can organize themselves.
Organisation Structure
how responsibility and authority is shared in a business organisation.
2 common type of organisation charts
● Tall organisational charts – These have a long chain of command and a small span of control
● Flat organisational charts – Short chain of command, wide span of control
Advantages of an organisational chart
● Shows how everybody is linked together in a business
● Lines of communication are clear
● Motivational as employees can see where they belong and can plan their career paths
Chain of Command
how the power and authority is passed down from the top of the organisation (managers) to lower employees
Span of Control
The number of employees working directly under a manager.
Levels of Hierarchy
Number of layers in an organisation structure
Advantages of short chain of command
● Faster communication – Communication is quicker and more accurate since it is passed on by fewer people.
● Stronger relationship between high-level managers and employees – This is because there are fewer levels between managers and employees.
● Each manager is responsible for more employees – This encourages them to delegate (pass down) more work to employees.
De-layering
removing an entire row of management
Roles of managers in a business
1. Planning
● Set goals for the future of the organisation.
● Give the business a sense of direction and purpose (e.g. we will aim to increase sales by 10% by next year.)
2. Organising
● Organising of people and resources so that the business operates efficiently (Managers can’t do everything, they must delegate tasks to other employees)
3. Coordinating
● Making sure all departments are working together to achieve the overall objectives and plans of the organisation. (e.g. Manager makes sure marketing and operations department work together to plan for a new product launch)
4. Commanding
● Guiding, leading and supervising of employees in the organisation. (Managers need to make sure that employees are doing their work!)
5. Controlling
● This involves monitoring performance to ensure that objectives will be met.
Delegation
Passing down authority and responsibility to a subordinate (employee)
Advantages of delegation
● More time for manager to do other tasks
● More interesting and rewarding work for employee (motivational)
● Employee feels trusted (motivational)
● Trains employee to do important tasks.
3 main leadership styles
Autocratic, democratic and laissez-faire
Autocratic
Leader is in charge and gives orders to employees
● Makes decision alone
● Everything depends on the leader
● May de-motivate employees
● May be an advantage for some businesses where decision needs to be made quickly
Democratic
Other employees involved in decision making
● Communication between managers and employees
● Future plans are discusssed with other employees
● Motivates employees because they are involved in making decisions.
● Sharing of ideas within the business.
● Can delay decision making
Laissez-Faire
“let it be” Leader sets objectives and employees makes decision and organise their own work.
● Can be useful when creative ideas are needed
● Highly motivational for employees as they control their own working life
● Poor coordination and decision making
● Relies on good team work
factors Leadership style may be dependent on
● Type of business (creative or supply driven)
● Nature of task (requires cooperation?)
Trade union
Group of workers who have joined together to ensure their interest are protected.
Why join a trade union?
● Improved conditions of employment
● Improved work environment
● Improved benefits
● Improved job satisfaction
● Advice/financial support
● Strength in number (many employees will join)
Disadvantages of a trade union
● Cost money to be a member
● May be forced to take action e.g. strike even if you don’t agree
Why do businesses recruit?
● To replace staff who have left or been promoted
● Bring in staff with new skills
● Recruit more staff as business expands
Job Analysis
A study of the tasks and activities to be carried out by the new employee
Job Description
This describes the main duties and responsibilities of the job
Job Specifications
The qualifications and qualities necessary to perform the job (e.g. educational requirements, experience needed)
Internal Recruitment
Promoting staff or moving workers from one job to another within the company.
Advantages of internal recruitment
● Saves time and money – Don’t need to spend money on advertising the job vacancy
● Applicants ‘know’ the firm
● Motivates other workers (chance for them to get promoted)
disadvantages of internal recruitment
● Applicants may not bring in new ideas
● Promoting an employee may make other employees jealous and demotivated
External Recruitment
Recruiting someone who is not an existing employee and will be new to the business.
Advantages of External Recruitment
● New ideas from new workers
● More likely to hire someone who matches job specification
disadvantages of External Recruitment
● Expensive – need to advertise job
● Demotivating for internal candidates
types of Recruiting channels
Internal
● Noticeboards
● Company Newsletters
External
● Local newspaper
● National newspaper
● Recruitment agencies
● Job centres
ways to Select staff
Application forms and CVs – To see if applicant matches the job specification
Interviews – Find out information about candidate’s abilities and personal qualities
Purpose of interview
1. Find out if applicant has the ability to do the job
2. Personal qualities about the applicant
3. To see if the candidate will ‘fit in’ with the culture of the business
Testing
Applicants may be required to undertake tests to check their ability to do the job.
Type of tests
1. Skill test – to observe the candidate’s skills
2. Aptitude test – to see how quickly candidate can learn new skills
3. Personality test – to see if their personality has the characteristic that the job may require
4. Group situation test – to see how candidate(s) works as a team
Part-time worker
employee that works fewer hours than a full-time worker.
Advantages of part time working
● Have more employees during busy periods
● Flexible working hours
● Less expensive than hiring full-time employees
disadvantages of part time working
● Workers are less trained than full-time employees (because their job is temporary)
● Less committed to the business (temporary job)
● More difficult to communicate with part-time workers when they are not at work
Why train employees?
● Trained workers are more productive
● decrease the amount supervision required
● may lead to job satisfaction
● reduce accidents and injuries
● improve chances for internal promotion
Induction training
Introduction given to a new employee explaining the company’s activities and procedures and introducing them to other employees.
Advantages of induction training
● Helps new employee settle in
● Health and safety training may be required
disadvantages of induction training
● Time consuming (delays the start of employee’s work)
● Wages are paid but no work has been done by the employee
On the job training
Experienced worker teaches new worker how to do the job.
Advantages of on the job training
● Training is cheap
● Training is specific for their job
● Work can be done while training
Disadvantages of on the job training
● The trainer will not be getting work done.
● Training won’t be effective if the trainer is bad
Off the job training
Training taking place off the job (not being trained while doing job)
Advantages of off the job training
● Trainers are experts (Skills can be taught)
● Training can be done outside of working hours (in employee’s own time)
disadvantages of off the job training
● Off the job training is expensive
● Worker may receive training paid by business and leave
● Training may not be specific for the job
Why might a business need to reduce the number of employees?
● automation (machines replace humans)
● factory/shop closure
● business relocating
● demand for goods/services falling
● business merging
Dismissal
– Employee is told to leave because of bad behavior
Redundancy
– Employee told to leave because the business doesn’t need a worker for that job anymore (not employees fault)
How to decide who is made redundant?
● Some workers may volunteer because they might have planned to leaveanyways.
● Length of time worked (employees who have worked there for a long time can stay)
● Workers with good skills remain
● Worker’s employment history (e.g. behavior / performance of employee)
what do employees need to be protected from
● Unfair discrimination at work and when applying for job
● Wage protection (e.g. minimum wage)
● Health and safety standards
● Unfair dismissal
Communication
– Process by which information or instruction is exchanged between one group or person to another.
Internal communication
(Communication from and to people within the business)
what does Poor internal communication leads to
● Workers don’t understand what they have to do
● Poor motivation
● Wastage (e.g. 2 employees do the wrong task because of wrong instructions)
External communication
(Communication from people inside the business to people outside the business)
What does Poor external communication leads to –
● Unhappy customers (leads to fewer sales)
● Bad business reputation (lower sales)
● Problems with suppliers/customers due to incorrect information (e.g. wrong supplies being delivered)
Formal communication
Recognised and approved by business (e.g. formal emails, official meetings, reports)
Informal communication
– Information is sent and received casually (e.g. employee talking during lunch break)
One way communication
Communication that does not allow for a response
Two-way communication
Communication where the receiver sends feedback to the sender about the topic.
Advantages of two way communications
● Receiver can tell the sender that they have understood the information/instruction
● Chance to ask for more information
● Allows the receiver to contribute ideas
Methods of communication
● Verbal
● Visual
● Written
types of Verbal (oral) communication
● Discussions
● Telephone calls
● Meetings
Advantages of verbal comm
● Fast
● Opportunity for receiver to reply (2 way comm)
● Body language
Disadvantages of verbal comm
● Feedback from receiver slows process down
● No permanent record of the discussion
Types of Written communication
● Emails
● Reports
● Newsletters
● Notices
Advantages of written comm
● permanent record of message
● May be required by law (e.g. legal information or safety notices)
● Can be easily sent to many people (e.g. emails to all employees)
Disadvantages of written comm
● Readers may find long letters boring and hard to read
● No feedback from receiver unless they reply
● No body language
Types of Visual communication
● Posters
● Images
● Videos
● Graphs / Charts / Diagrams
Advantages of visual communication
● Interesting (Readers may pay more attention to posters / videos than boring letters)
● Information can be clearer than other methods (e.g. Video instructions can be clearer than letter instructions)
Disadvantages of visual communication
● No feedback
● Some people may find charts / graphs difficult to read
Types of Problems with the sender (communication barriers)
● Difficult/technical language is used – The sender needs to use language that could be understandable by the sender
● The sender speaks too quickly or not clear enough – The sender should ensure that the message is clear
● The sender sends the wrong message or sends it to the wrong receiver – The sender must make sure that the right person is being sent the correct message
Problems with the communication channel
● The wrong communication channel was used (e.g. important letter placed on board that does not get seen) – The appropriate communication method must be selected
● No opportunity for feedback – Sender uses a one-way communication channel which does not allow receiver to contribute ideas
● Long chain of command – Message needs to be sent through a long chain of command where the message could be changed