Topic 1 - scarcity and choice wjec/eduqas
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from topic 1 Made from Wjec/eduqas specification but should be the same for other specs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Market
A place where consumers and producers interact with each other to sell and buy goods/services
Market forces
determining the allocation of scarce resources and the relative price of goods/services
Total utility
total amount of happiness a consumer derives from a good at any particular level of consumption.
Marginal utility
the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service.
Normal good
a good that experiences an increase in demnd due to an increase in a consumers income.
Inferior goods
a good whose demand is indirectly proportional to consumers income > income^ -- demand⬇
A️ Giffen good
a good where the higher price means an increase in demand
Ostentatious good
a good whose main attraction is related to the image of being expensive/exclusive
Joint demand
when one good is directly related and positively related to a related good or service
Substitute good
next best alternative
Composite demand
when the good demanded has multiple uses
Complementary good
two or more goods typically consumed or used together such that a change in price/demand affects them both
Effective demand
the willingness and ability of a consumer to purchase goods at a different price
Derived demand
the demand that comes from the demand for something elsedemand for machinery is derived from the demand for the goods produced by the machinery
Needs
things that are essential for human survivalbasic food/shelter/water
Wants
things that are unessential for human survivalfast food, designer
Finite
a limited amount of somethingfossil fuels/minerals
Infinite
an unlimited amount of somethingoxygen
factors of production
resources or inputs that are used in the production of goods and services. CELLCapital, Enterprise, Land, Labour
Scarcity
limited resources, more demand than supply
Renewable energy
energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumedwind, solar
Non-renewable energy
comes from sources that will run out or will not be replenished in our lifetimesfossil fuels
Semi-renewable energy
can theoretically be renewed, but if they are over used then they could become extinctcod, tuna amazon r.f
Economic good
a good/service that has a benefit to society
Free good
a good available without limitstreet lights
Positive statement
is one that can be tested and verified and is not based on a value judgement
Normative statement
subjective statements that express value judgements, opinions or prescriptions about how things ought to be.
what’s allocative efficiency
an efficient market whereby all goods and services meet the needs and wants of society
Whats Pareto efficiency
If you increase good x then because of the opportunity cost you have to decrease good y
Whos theory was the “tragedy of the commons”
Victorian economist William Foster Lloyd in 1833
what is the tragedy of the commons
The tragedy of the commons is when there is an overconsumption of a particular product/service because rational individual decisions lead to an outcome that is damaging to the overall social welfare (people being selfish and thinking about the short term effects instead of the long run
what are the assumptions of the tragedy of the commons theory
when people make decisions, people take the course of action that maximises their own utilityan example of this would be free-riding, people slowly take more and more until there is nothing left
causes of the tragedy of the commons theory
People choosing short term needs instead of looking at the bigger pictureno formal control over the use of the resourceno barriers to entry
examples
Coffee consumption traffic congestionuse of the rainforest for agriculture
how to stop the tragedy of the commons theoretically
voluntary agreements along the lines suggestedGovernment regulationsClearly defined property rightsTaxes, fines, quotas
PPF curve
A graph that illustrates the possible quantities that can be produced of two products if both depend upon the same finite resources for their manufacture.
assumptions of a ppf curve
an economy chooses to produce these two productsthere are limited resourcestechnology and techniques remain constantall resources(FOP) are fully and efficiently used
Law of increasing opportunity cost
The concept that as an economy moves from one point on the PPF curve to another, the opportunity cost of producing one good increases as more resources are allocated to the production of the other good.
Scarcity
The condition of limited resources relative to unlimited wants, resulting in the need for choices to be made about how resources are allocated.
Opportunity cost
The cost of choosing one option over another, measured by the value of the next best alternative that is foregone.
Free market economics
An economic system characterized by no government intervention in the economic system, including no legislative control over employment, production, or pricing.
Command economics
An economic system characterized by government control, including authority, budget allocation, prioritization, mobilization of resources, and a unique vision, with no profit or private property.
Benefits of free market economics
Contributes to political and civil freedom, economic growth and transparency, and ensures competitive markets.
Benefits of command economics
Low or non-existent unemployment, speed in decision making, equality amongst citizens, and a focus on the workers as opposed to profits.
Problems of free market economics
Subject to manipulation, misinformation, asymmetries of power and knowledge, and fosters wealth inequality.
Problems of command economics
Lack of efficient resource allocation, lack of innovation, and the needs/preferences of society may be ignored due to poor planning.
Factors affecting the outwards shift of a PPF curve
anything to increase FOPinvestment in capital (plants and machinery)discovery of new materialsImmigration of skilled workersimproved education, training and healthcare to lift labour productivityinnovations that increase output per unit and reduce resource wastage
Factors affecting the inward shift of the PPF Curve
anything to decrease FOPDamaging effects of natural disasters such as droughts, tsunamis, floods and earthquakesdestruction of FOP caused by a civil war and other forms of conflict that last few many yearslarge scale of emigrationa trend decline in the productivity caused by a persistent economic recession
draw a specialisation curve and how it works
there has been an improvement in the quantity/quality of FOP that only benefits one of the goods meaning that they are specialised
specialisation factors
Improvements in technology new techniques better trained/skilled labour
Demand Curve
The graphical representation of the relationship between the price charged for a product and the quantity demanded, which is inversely proportionate.
Utility Theory
The theory that examines the satisfaction or benefit that a consumer gains from consuming a product.
Marginal Utility
The additional benefit or satisfaction gained by consuming an extra unit of a product.
Total Utility
The overall level of satisfaction that a consumer obtains from consuming all units of a product.
Plot a graph using the table
y axis = 300→-150x axis 0→7total utility curved marginal utility = demand curve
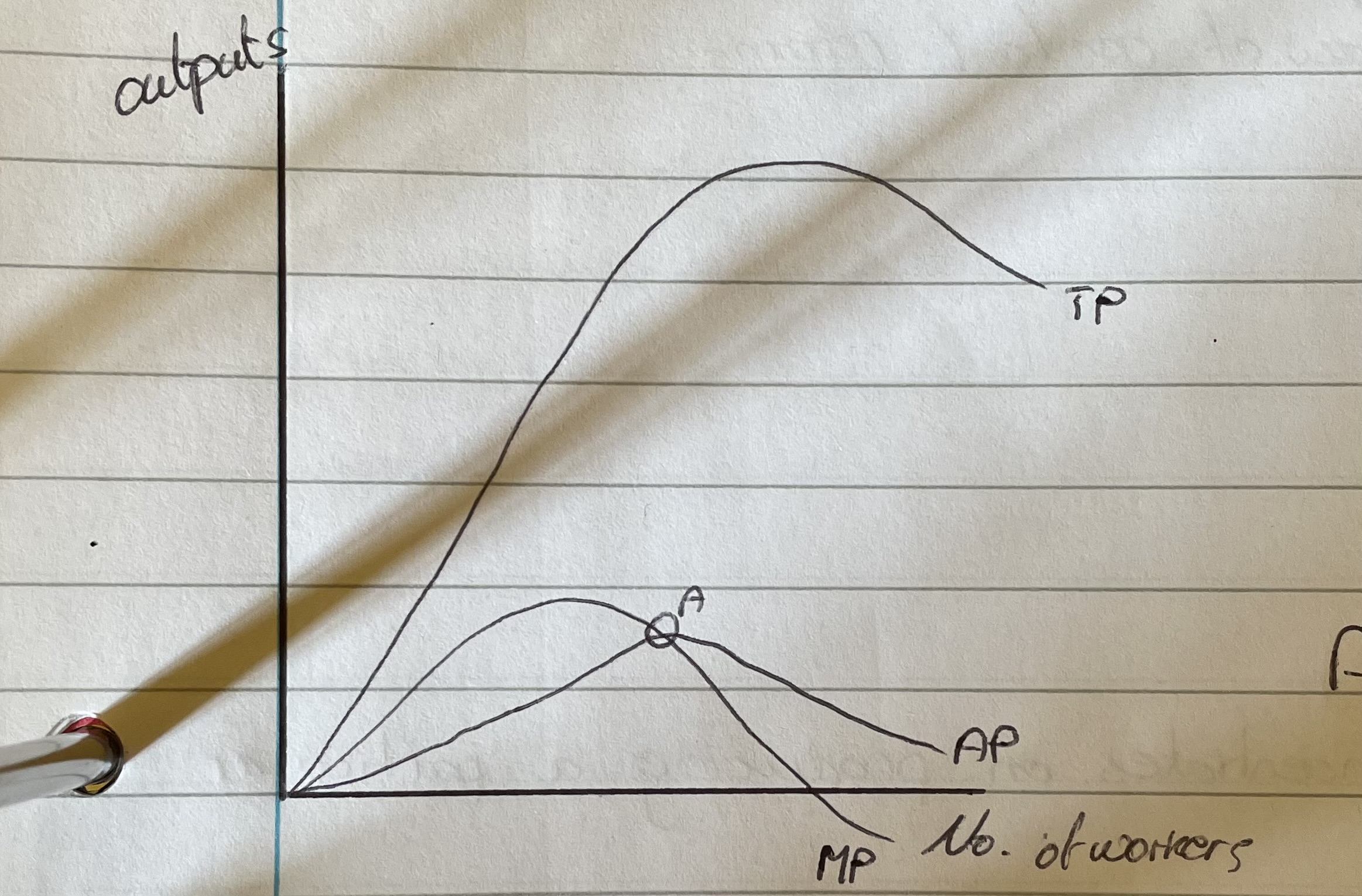
What happens to TP in this curve?
TP increases as workers are added and then it peaks and starts decreasing as overmanning starts to become a problem.Law of diminishing returns
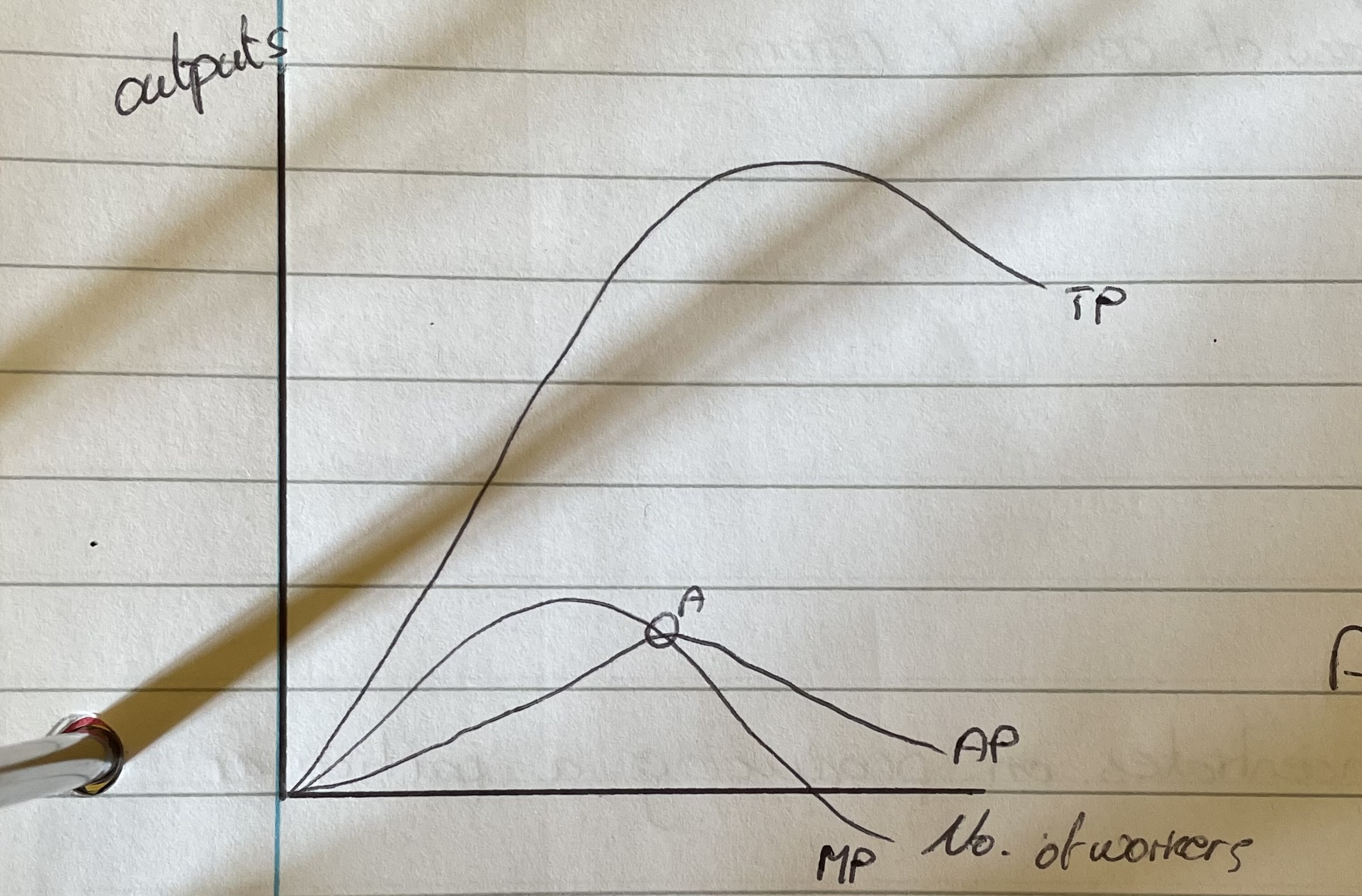
What happens to AP?
Initially rises with the increase in TP but as diminishing returns sets in it’ll fallIf MP>AP then AP will decreaseIf MP<AP then AP will rise
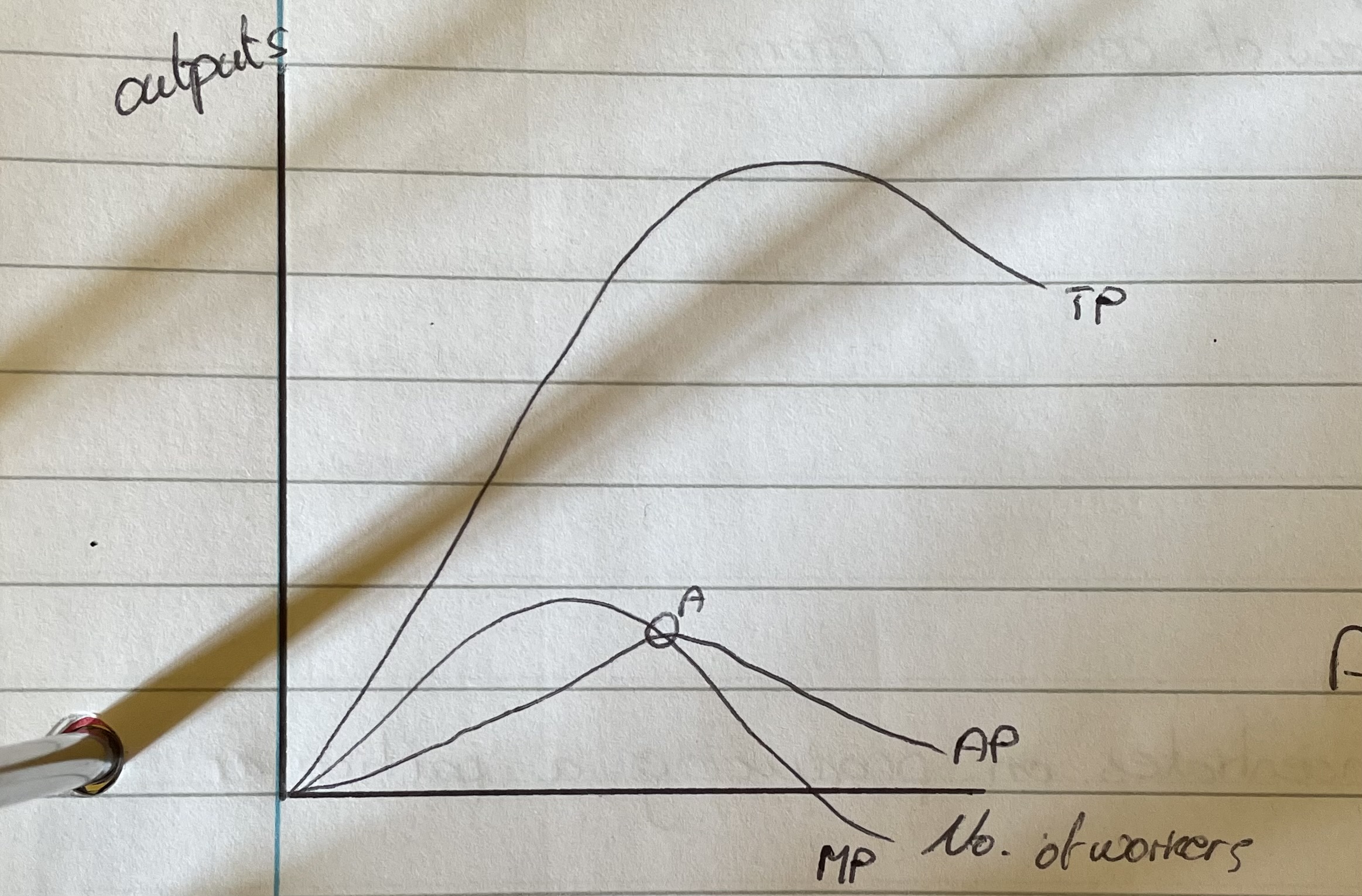
What happens to MP?What is MP?
MP rises and falls due to the law of diminishing returns, but when MP=0 this will cause TP to peak because the increase in workers no longer means and increase in product. when MP<0 then TP will fallMarginal product is the product that each new worker adds.
What makes the PPF curve curved and not straight?
Its curved because when changing what products they’re producing their skills aren’t 100% interchangeable which causes the graph to curve.
How can a PPF curve be straight?
If all the skills are interchangeable then a straight line can be drawnlaw of contact returns
what does PINTSWC mean
Productivity, indirect tax, number of firms, technology, subsidy, weather, cost of production
What does PASIFIC mean
Price, advertisement, substitutes, income, fashion and trends, interest( subsidies and taxes), complementary
Economics of scale-
Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies
risk-bearing, financial, managerial, technical, marketing, purchasing