carbohydrates 1+2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is glycolysis?
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid
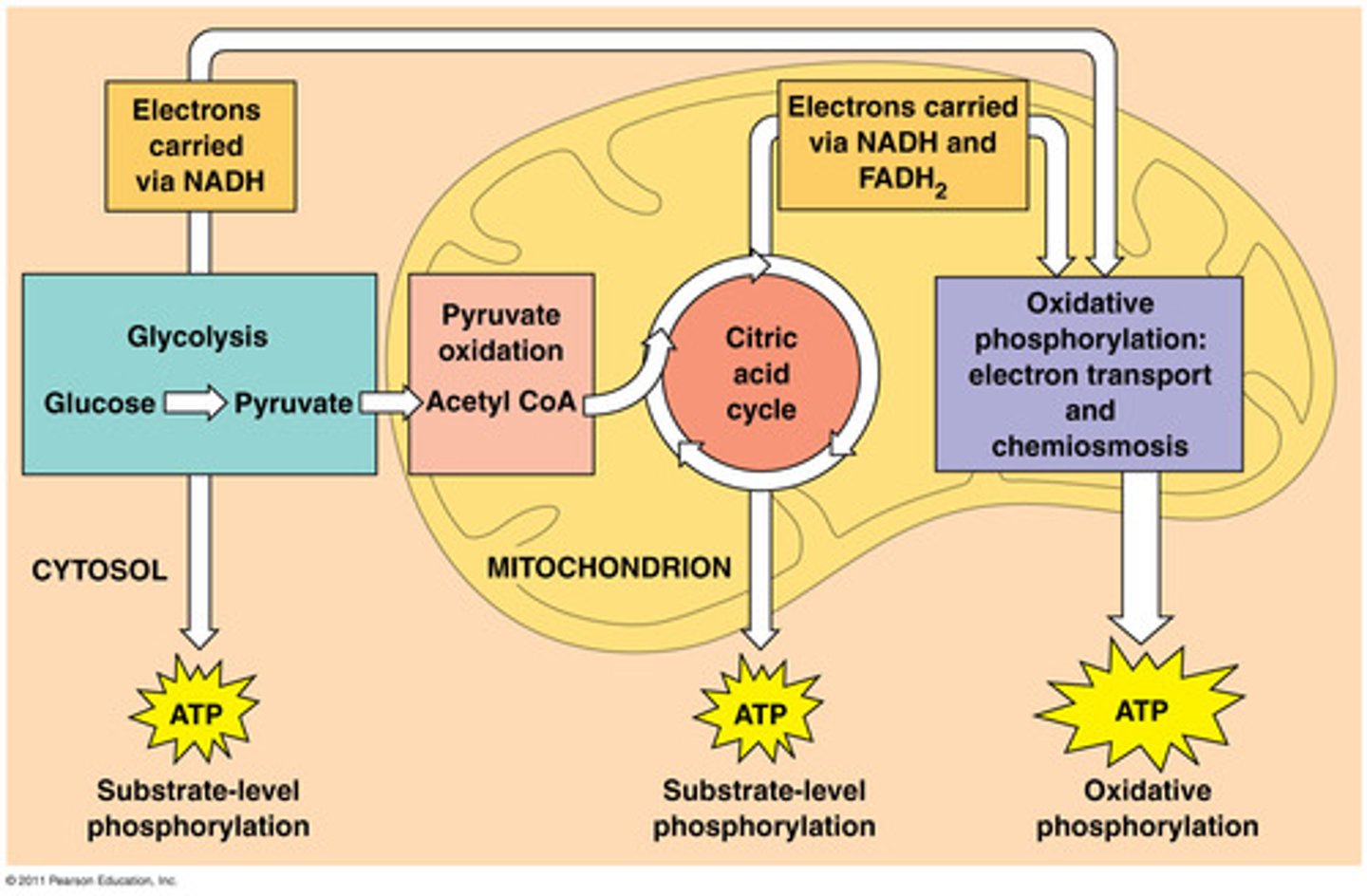
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytosol
2 phases of glycolysis
1. energy investment phase 2 ATP used
2. energy payoff phase - Net 2 ATP gain (4 gained altogether)
Step 1: Glycolysis
what is formed?
Enzyme used?
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
Glucose → G6P (phosphorylation)
hexokinase enzyme
ATP used
IRREVERISBLE
step 2 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
G6P→F6P (conversion)
phosphohexase isomerase
REVERSIBLE due to free energy
step 3 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
F6P →F1,6BP (phosphorylation)
phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
ATP
IRREVERSIBLE - first committed step of glycolysis - cannot go back after this
step 4 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
cleavage of F1,6BP → DHAP + G3P (splitting part of glycolysis - 1 Glc into 2 triose sugars)
F1,6BP aldoase (aldoase for short)
none
REVERSIBLE
step 5 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
interconversion of triose sugars to form 2 G3P
triose phosphate isomerase
none
REVERSIBLE
what triose can only participate in glycolysis
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
step 6 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
oxidation of G3P to 1,3-biphosphate
dehydrogenase
2 NADH produced
REVERSIBLE
first energy payoff phase
step 7 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
transfer from 1,3-BiPG to ADP forms 3-phosphoglycerate
phosphoglycerate kinase
2 ATP produced
spontaneous
REVERSIBLE
substrate level phosphorylation
step 8 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
conversion of 3-PG to 2-PG
phosphoglycerate mutase
REVERSIBLE
step 9 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
dehydration of 2-PG to PEP
enolase
none
REVERISBLE
step 10 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
transfer of PEP to ADP
pyruvate kinase
2 ATP produced
IRREVERSIBLE
final step - produces pyruvate
No NAD+ has what effect on glycolysis?
Inhibits it, NAD+ is required for glycolysis.
Fate of Pyruvate
Depends on oxygen availability.
- oxygen is present, pyruvate oxidised to acetyl-CoA, enters the citric acid cycle
- Without oxygen, pyruvate reduced in order to oxidise NADH back to NAD+ (2 lactate or 2 ethanol + CO2)
function of pyruvate dehydrogenase
converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA so it can enter citric acid cycle
Function of lactate dehydrogenase
changes pyruvate to lactate to regenerate NAD+
Fate of blood lactate
cori cycle
- ATP made via substrate level phosphorylation producing lactate - converted to glucose in liver via gluconeogenesis
- liver repays O2 debt
What is gluconeogenesis?
production of glucose from pyruvate
is glycolysis irreversible or reversible
three steps are irreversible
bypass reactions A + B of gluconeogenesis
pyruvate --> into mitochondria --> oxaloacetate --> malate --> out of mitochondria --> oxaloacetate --> PEP
pyruvate carboxylase
malate dehydrogenase
PEP carboxykinase
reaction C of gluconeogenesis
F-1,6-BiP + H2O --> fructose-6-phosphate + Pi
checkpoint
irreversible
enzyme - fructose-1,6-phosphatase
bypass reaction D of gluconeogenesis
glucose-6-phosphatase + H2O --> glucose + Pi
dephosphorylation
PEP --> pyruvate generates how many ATP
1 but in glycolysis there are two PEP molecules for one glucose
where is fructose metabolised
liver
What are carbohydrates?
sugars and starches
functions of carbohydrates
quick energy
energy storage
structure
cell-cell communication
3 important monosaccharides
glucose, galactose, fructose
How are disaccharides formed?
condensation reaction
bonds found in disaccharides
glycosidic bonds
3 important disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
What are polysaccharides?
large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides
glycogen
Storage form of glucose
alpha 1-4 linked subunits with alpha 1-6 branches
glycogen in liver
replenishes blood sugar when fasting
Glycogen in skeletal muscle
catabolism of glycogen produces ATP for contraction
what carbohydrates are in our diets (9)
starch - cereals potatoes rice
glycogen - meat
cellulose - plant cell walls
oligosaccharides - short - peas, beans, lentils - not digested
lactose - milk
sucrose - sugar
maltose - beer
glucose - fruit
fructose - honey
how are carbohydrates digested - describe the process (4)
mouth - amylase breaks down starch
stomach - no carbohydrate digestion here but need to bypass to get to intestines
duodenum - pancreatic amylase breaks down starch - same as salivary amylase
jejunum - final digestion by mucosal cell surface enzymes
what enzymes digest carbohydrates in jejunum
isomaltase - hydrolyses alpha 1-6 bonds
glucoamylase - removes glucose sequentially from non-reducing ends
sucrase - hydrolyses sucrose
lactase - hydrolyses lactose
How is glucose absorbed?
Na+ glucose symporter into epithelial cell
GLUT2 uniporter into blood
meanwhile ATPase is always pumping Na out of cell so symporter works
fate of absorbed glucose
glucose diffuses through epithelial cells into portal blood and to the liver
glucose immediately phosphorylated into glucose-6-phosphate by hepatocytes
G-6-P cannot diffuse out of cell as GLUT transporters will not recognise it
enzyme catalysts - glucokinase (liver) and hexokinase (other tissues)
glucokinase Km and Vmax
High Km and high Vmax
hexokinase Km and Vmax
Low Km and low Vmax
synthesis of glycogen step 1
glycogenin begins process - covalently binds glucose from uracil diphosphate (UDP)
glycogenin forms chains of around 8 glucose residues
glycogen synthase takes over
synthesis of glycogen step 2
chains formed by glycogen synthase are broken by glycogen branching enzyme and reattached via alpha 1-6 bonds to give branch points
degradation of glycogen
this process produces glucose 1-6 phosphate from breaking alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glycosidic bonds