Endocrine Body system Organiser Unit 2.2
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is glucagon and where does it travel?-hormone
It raises glucose levels by signaling the liver to release glucose after being sent to the pancreas. Pancrea→Liver
What is Insulin and where does it travel?-hormone
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by traveling through the blood and alerting cells to intake glucose. Pancreas→Liver,Pancreas→Skeletal Muscle
What is GnRH and where does it travel?-hormone
It stimulates the pituitary gland to release FSH and LH. Hypothalamus→Pituitary gland
What is FSH and where does it travel?-hormone
It stimulates the development of gametes. Pituitary gland→ovaries,Pituitary gland →testes
What is testosterone and where does it travel?-hormone
It stimulates sperm production and growth. Testes→skeletal muscle
What is estrogen and where does it travel?-hormone-hormone
Stimulates the management of the menstrual cycle. Ovaries→Uterus
What is progesterone and where does it travel?-hormone
Maintains the uterine lining for potential pregnancy. Ovaries→uterus
What is the function of the ovaries?
Produces female gametes and secretes sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone,which regulates reproductive cycles.
What is the function of the testes?
Production of sperm cells and secretion of testosterone.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
Acts as a link between the nervous and endocrine system. Controls the pituitary gland by secreting hormones.
What is the function of the pituitary gland?
Receives the signal and releases hormones that regulate hormones that regulate the activity of the the ovaries and testes.Controls other bodily functions like growth as well.
What is the function of LH and where does it travel?
Triggers ovulation in the ovaries and testosterone production in the testes. Pituitary gland→ovaries,Pituitary gland→testes
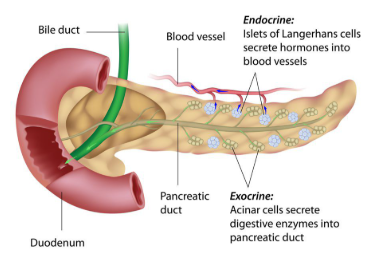
How is the pancreas an exocrine and endocrine gland?
The pancreas acts as an exocrine gland by secreting digestive enzymes and bicarbonate through ducts into the small intestine to break down food. Simultaneously, it functions as an endocrine gland by releasing insulin and glucagon directly into the bloodstream to maintain blood glucose homeostasis.
-Mention that the exocrine part uses ducts while the endocrine part is ductless (it goes straight into the blood). This is a common "trick" question on PLTW assessments.
What is the function of the uterus?
The uterus uses ovarian estrogen and progesterone to build its lining, then acts as an endocrine structure by secreting prostaglandins or prolactin to either trigger menstruation or maintain pregnancy.