Anatomy: Blood Flow and Renal Function
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
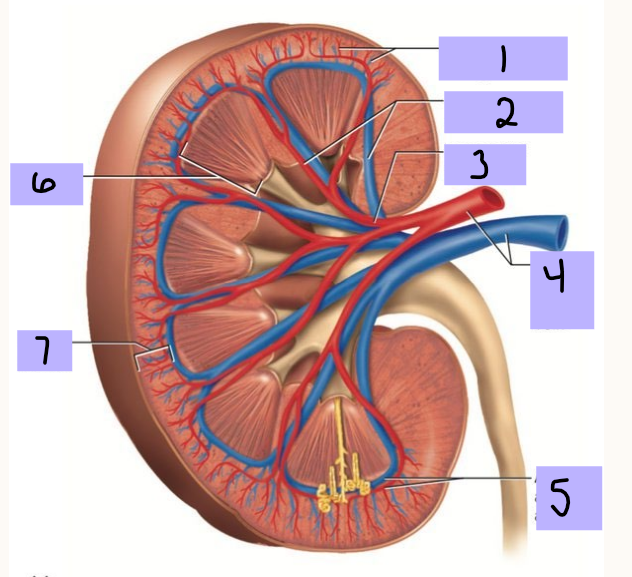
Cortical radiate artery (and vein)
#1
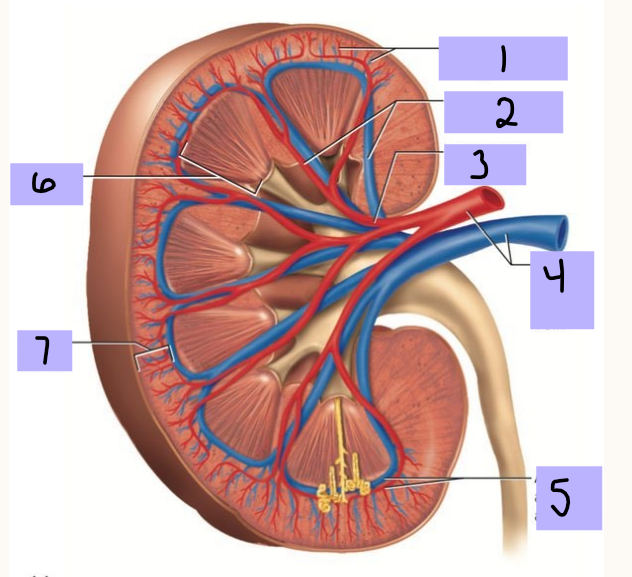
Interlobar artery (and vein)
#2
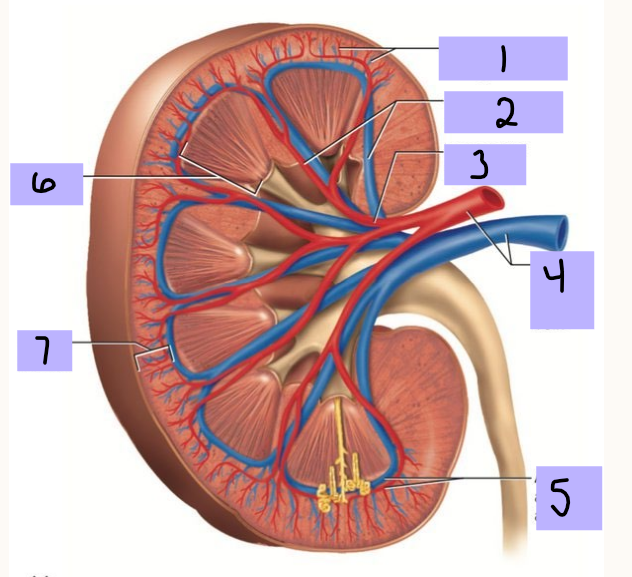
Segmental artery
#3
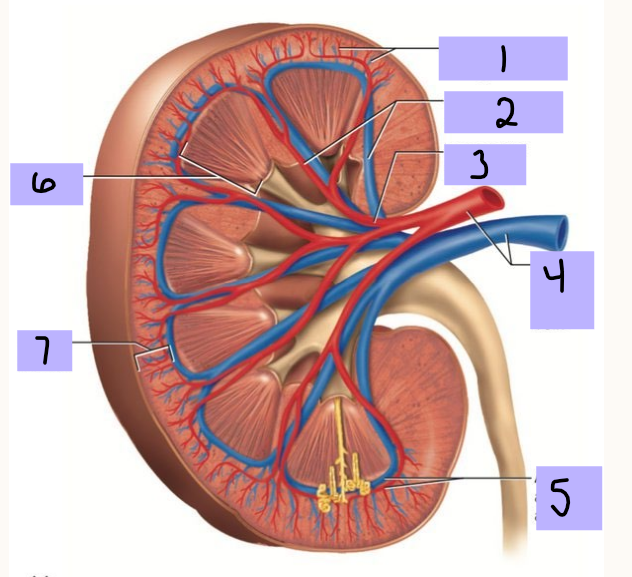
Renal artery (and vein)
#4
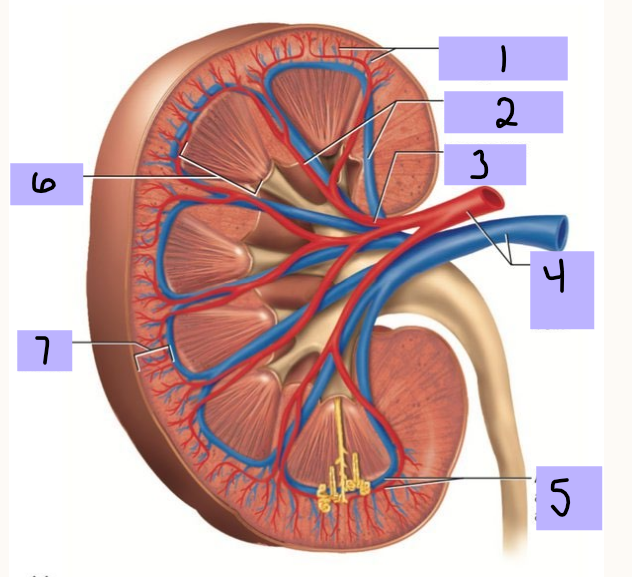
Arcuate artery (and vein)
#5
Renal medulla
#6
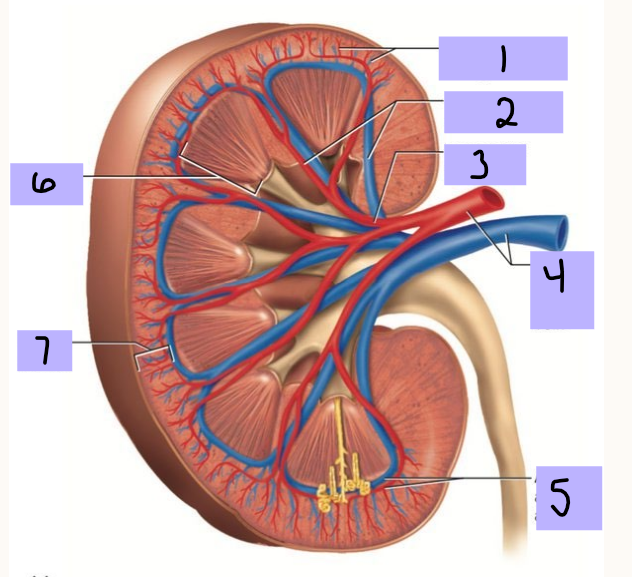
Renal cortex
#6
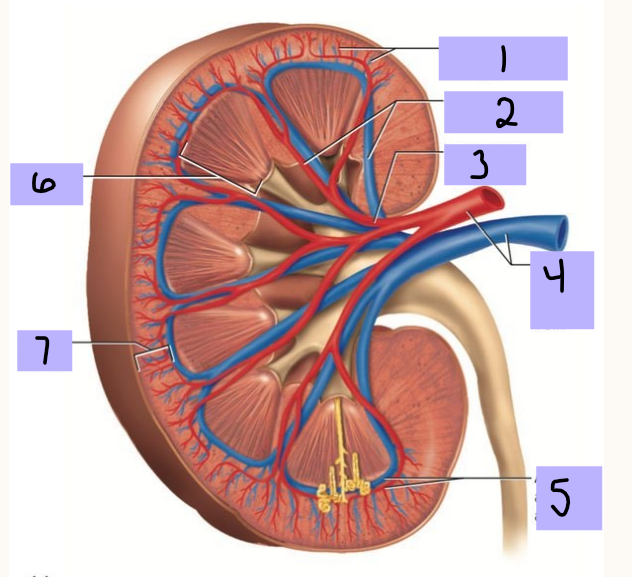
Vasa recta
The ______ _____ is the only blood supply to the medulla. Juxtamedullary nephrons have vasculature the whole way down the Loop of Henle
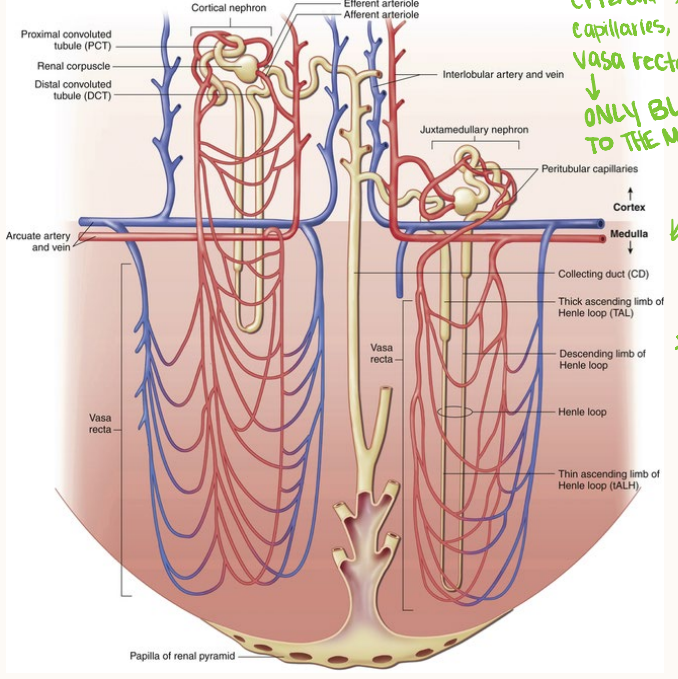
hematocrit, renal plasma flow, 20, glomerulus, Bowman
Renal Blood Flow
-Kidneys receive 20-25% of cardiac output, which is about 1000-1200 mL of blood per minute
-If normal __________ of 45%, about 600-700 mL blood flowing through the kidney per minute is plasma = _____ ______ _____
-__% of renal plasma flow is filtered at __________ and passes into _______ capsule
filtration, plasma, perfusion, capillaries
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
-The _________ of ______ per unit of time (usually minutes)
-Directly related to _________ pressure in the glomerular __________, happens in Bowman’s Capsule
filtration fraction, reabsorbed, capillaries
Renal Blood Flow
-80% of renal plasma flows through to efferent arterioles to the peritubular capillaries
-The ratio of glomerular filtrate to renal plasma flow is __________ _______
-Normally all but 1-2mL per minute of the glomerular filtrate is _________ and returned to circulation by the peritubular capillaries
GFR, hormonal, pressure, increases, output
Renal Blood Flow
-___ is directly related to renal blood flow, which is regulated by: intrinsic autoregulatory mechanisms, neural regulation, and ________
-Overall: blood flow to any organ is regulated by the arteriovenous __________ differences across the vascular bed
If mean arterial pressure decreases or vascular resistance _________, renal blood flow declines and urinary _________ decreases
stretched, reducing, constant, pressure, barotrauma
Autoregulation of Renal Blood Flow: Intrinsic Autoregulatory Mechanism
-Intrinsic autoregulatory myogenic mechanism of contraction when blood vessels are __________ due to increased renal blood flow → reduces renal blood flow, _________ GFR and vice versa for decreased blood flow
-Keeps RBF and GFR ________ despite changes in systemic blood _______
-Solute and water excretion regulated despite arterial pressure changes
-Prevents __________ in states of higher BP
individual, macula densa, vasoconstriction, juxtaglomerular, renin, decreased, increases, water, sodium
Autoregulation of Renal Blood Flow: Tubuloglomerular Feedback
-When GFR in an _________ tubule changes with arterial pressure, the ______ ______ senses the change and stimulates afferent arteriolar vasodilation or ___________, thus improving GFR
-At the same time, the _____________ cells can secrete ______ when GFR is _________ → angiotensin II → vasoconstriction of efferent arterioles, thus increasing glomerular hydrostatic pressure → _________ GFR
-This mechanism prevents large fluctuations of body ______ and ________ levels
sympathetic, afferent, catecholamines, vasoconstriction, GFR, reabsorption, opposite
Neural Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
-Renal blood vessels are innervated by __________ nerve fibers located on ________ arterioles
-When systemic arterial pressure decreases → increase renal sympathetic nerve activity → sympathetic nerves release ____________ → stimulates afferent renal arteriolar _____________ → decreasing RBF and ___ → increases renal sodium and water _____________ → increases blood pressure
-Systemic arterial pressure increases → the ________ occurs
hormone, metabolize, BP, angiotensin II, parasympathetic
Renalase
-Renalase is a _________ secreted by heart and kidney that helps __________ catecholamines, helping regulate __
-SNS also participates in some in hormonal regulation of blood flow with __________ __
-No ____________ stimulation
vasodilation, RAAS
Hormonal and Other Mediator Regulation
-Can simulate ___________ or vasoconstriction → altering vascular resistance
-_______ system → stimulated and increases systemic arterial pressure, changing RBF
renin
Juxtaglomerular cells form and store _______
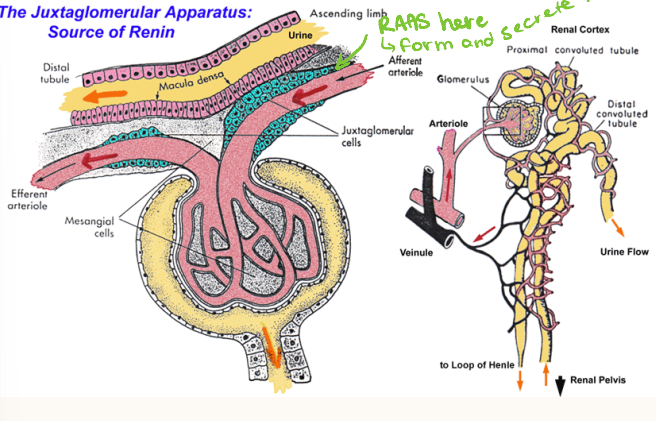
RAAS, renin, decreased, sympathetic, prostaglandins
Hormonal and Other Mediator Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
-Can stimulate vasodilation or vasoconstriction → altering vascular resistance
-______ system → stimulated and increases systemic arterial pressure, changing RBF
-Renin release is triggered by→ _________ blood pressure in afferent arterioles, decreased sodium chloride concentrations in distal convoluted tubules, ___________ nerve stimulation of B-adrenergic receptors on juxtaglomerular cells, and release of ____________
angiotensinogen, ACE, aldosterone, ADH
Hormonal and Other Mediator Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
-Renin is released → cleaves ___________ in the plasma to form angiotensin I → if ____ is present, then converted to angiotensin II → stimulates vasoconstriction, stimulates ___________ secretion from adrenal cortex → stimulates ___ and thirst
antagonist, volume expansion, inhibit, afferent, efferent, urine, decreased
Hormonal and Other Mediator Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
-Natriuretic peptides: natural __________ to RAAS system
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) = myocardial cells from atria
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) = myocardial cells from ventricles
When the heart dilates due to ______ ________ → ANP and BNP _____ sodium and water absorption by kidney tubules → inhibiting renin and aldosterone → vasodilation the _______ arterioles and vasoconstrict the ________ arterioles → increased _____ formation and __________ blood pressure
endothelium, nephron, distal, ducts
Other Hormones
-C-Type Natriuretic Peptide = secreted from vascular __________ → vasodilation in the ______
-Urodilatin = secreted by ______ convoluted tubules and collecting _______ → vasodilation, increased renal blood flow, diuretic effects
glomerulus, filtrate, volume, pH
Renal Function
-Filters plasma at __________
-Reabsorbs and secretes different substances along tubular structures
-Forms a ______ of protein-free liquid
-Regulates the filtrate to maintain body fluid ______, electrolyte composition, and __ within narrow limits
Glomerular Filtration
movement of fluid and solutes across glomerular capillary membrane into Bowman space
Tubular reabsorption
movement of fluid and solutes from the tubular lumen to the peritubular capillary plasma (tubes → blood)
Tubular secretion
transfer of substances from the plasma of peritubular capillary to the tubular lumen (blood → lumen)
Excretion
elimination of a substance in the final urine
water, proteins, filtration slits, negatively, capillary, Bowman Capsule
Glomerular Filtration
-Glomerulus = freely permeable to ______ and relatively impermeable to large colloids, plasma ________
Restricted by small size of ________ _____ in glomerular epithelium
Restricts ________ charged macromolecules by negative charge along filtration membrane
-_________ pressure moves water and solutes across filtration membrane into ________ _______, also affecting filtration
Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman Space
Effective oncotic pressure of the glomerular capillary blood
out, back, back, net
Glomerular Filtration
-Hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries = pushes fluid ___
-Oncotic pressure of plasma proteins = pulls fluid ____
-Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s Space = pushes fluid _____
-___ filtration pressure = favoring filtration - opposing forces
rise, fall, capillary, declines, stopping, low, high, reabsorption
Glomerular Filtration
-Protein free filtrate enters Bowman’s capsule, which leads to a ____ in plasma oncotic pressure and a ____ in hydrostatic pressure along the glomerular capillary.
-As a result, the net filtration pressure progressively _______ to zero by the efferent arteriole, effectively __________ filtration at that point. The efferent arteriole then carries blood with ___ hydrostatic pressure and _______ oncotic pressure into the peritubular capillaries, promoting the ____________ of fluid from the proximal convoluted tubule
reabsorbed, blood, tumors, loss, oncotic, malnutrition, liver
Glomerular Filtration
-Glomeruli filters around 180L of fluid per day, and 99% of that is _________ into peritubular capillaries and returned to the ______
-Decreases GFR
Urinary strictures, stones, _______ cause retrograde increase in Bowman Capsule Pressure
Excessive ____ of protein-free fluid increases glomerular capillary ________ pressure
-Increases GFR
___________ or severe ____ disease with low levels of plasma protein cause decreased oncotic glomerular capillary blood pressure because there is no protein available to slow it down
chloride, acids, urea, lumen, passive
Tubular Transport: Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Reabsorption:
-Sodium (Na+) actively reabsorbed via the Na/K ATPase pump, which is the main job of the PCT
-______ passively follows sodium
Water follows osmotically
Glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed via cotransporters
Secretion:
-Organic _____/bases (drugs, creatinine, etc.)
-Leaves increased concentration of ____ within the tubular _____, creating gradient for _______ diffusion into peritubular plasma
water, hypertonic, reabsorption, hypotonic
Tubular Transport: Loop of Henle
Descending Limb:
-Highly permeable to _______, which is reabsorbed
-Impermeable to solutes
-Filtrate becomes ___________
Ascending Limb:
-Impermeable to water
-Active __________ of Na+, K+, Cl-
-Dilutes the filtrate (__________ solution)
opposite, parallel, gradient, medulla, longer, vasa recta
Tubular Transport: More on Loop of Henle
-Countercurrent exchange system → fluid flows in ________ directions through the _______ tubes of loop of henle by concentration ________ in the ______
-The ______ the Loop of Henle → greater their extension into the concentration gradient
-____ ______ acts as countercurrent exchange for maintaining gradient
urea, glomerulus, uromodulin, thick ascending
Tubular Transport: Loop of Henle pt 3
-_____ → major constituent of urine along with water
Filtered by __________
Tubular reabsorption depends on urine flow rate
50% excreted in urine and 50% recycled in the kidney
-_________ → protection against infection, kidney stones, CKD
Protein produced in ____ __________ Loop of Henle and binds to uropathogens
reabsorbs, ADH, calcium
Tubular Transport: Distal Convoluted Tubule
-________ Na+ and Cl- (NaCl transporter)
-Impermeable to water unless ___ present
-Reabsorbs __________ (regulated by parathyroid hormone)
aldosterone, ADH, K+, hydration
Tubular Transport: Collecting Duct
-Final adjustment of urine
__________ increases Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion
___ (vasopressin) increases water reabsorption via aquaporins
H+ and __ secretion for acid-base balance
-Concentrates or dilutes urine depending on ___________
acidic, no, protein
Urine
-Clear or yellow color
-pH 4.6-8.0, typically more ______
-__ glucose, blood cells
-Can have trace ________, especially with exercise
posterior, permeability, vasa recta, glomerulus
ADH
-Secreted from _______ pituitary
-Increases water ___________ in the last segment of DCT and along lengths of collecting ducts
-Water diffuses into ascending limb of the ____ _____, then returns to systemic circulation
-Urine output decreases to 1% of what was filtered by the ________
excess, reabsorption, plasma, water, urine
ADH Related Disorders
-SIADH: ________ ADH → increased water ___________ and excess water in the _____
-Diabetes Insipidus: inadequate ADH → distal tubules and collecting ducts become impermeable to _____ → excess diluted _____
kidney, parathyroid, calcitriol, Vitamin D
Hormones Made by Renal System: Vitamin D
-2-step process to utilize in body: second hydroxylation occurs in ________ and stimulated by ___________ hormone → active form in body is calcitriol
-___________ required to absorbs calcium and phosphate in small intestine
-Feedback system where low calcium stimulates parathyroid hormone stimulating synthesis of active __________ _
liver, kidney, cortex, bone marrow, increase
Hormones Made by Renal System: Erythropoietin
-Produced by fetal ______ and adult ________
Essential for erythropoiesis
If decreased oxygen in kidney → fibroblasts in juxtamedullary _______ releases erythropoietin → stimulating _____ ________ to ________ RBC production