micro lecture 2 - mycology
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
mycology
the study of yeast, molds, and mushrooms
are yeasts unicellular?
yes
are molds multicellular?
yes
are mushrooms multicellular?
yes
what kingdom do fungi belong to?
eukaryotes
where are fungi located?
air, soil, water
first characteristic of fungi
similar to algae; no chlorophyll
second characteristic of fungi
mainly aerobic or facultative
third characteristic of fungi
source of carbon + energy are organic compounds
fourth characteristic of fungi
absorption of food
what are some benefits of fungi?
food industry, antibiotics, decomposers of plant matter, medicinal, commercial, genetic engineering
is penicillium a fungi?
yes
trichoderma produces what enzyme?
cellulase
what are the medicinal benefits of fungi?
taxomyces sp.: taxol
aspergillus terreus: statins
tolypocladium sp.: cyclosporins
what are the commercial benefits of fungi?
trichoderma sp.: cellulase (clarify juice)
how are fungi used in genetic engineering?
yeast cells used to produce the hepatitis b vaccine; aspergillus sp. engineered with rennin gene
what are some undesirable effects of fungi?
food spoilage, plant disease, damage to buildings, animal diseases, human diseeases
what are examples of plant disease due to fungi
potato blight, dutch elm tree, chestnut tree disease
when damage is done to buildings by fungus, what is it called?
dry rot
what disease do bats get from fungal infections?
white-nose syndrome
what disease do humans get from fungal infections?
mycoses
what is the domain of bacteria?
bacteria
is bacteria prokaryotic?
yes
is bacteria unicellular?
yes
how does bacteria reproduce?
binary fission
are bacteria smaller or larger in size?
smaller
what is the cell wall of bacteria made of?
peptidoglycan
does the cell membrane of bacteria contain sterols?
no
what is the domain of fungi?
eukarya
are fungi prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
eukaryotes
are fungi unicellular or multicellular?
multicellular
how do fungi reproduce?
spores + budding
are fungi smaller or larger in size?
larger
what is found in the cell wall of fungi?
mannan, chitin, and glucan
does the cell membrane of fungi contain sterols?
yes
what areas do fungi prefer to grow in?
warm, moist areas (can also be dry)
at what rate do fungi grow?
slower than bacteria
what pH do fungi grow best at?
5
do fungi grow better in sugary or salty conditions?
both
what temperature do fungi grow best at?
room temperature
are fungi susceptible to heat?
yes
what do fungi metabolize best?
complex carbohydrates like lignin (wood)
why is yeast non-filamentous?
it is unicellular and reproduces by budding rather than hyphae
facultative
organisms that can grow with or without oxygen
is yeast facultative?
yes
what is the white, powdery coating on fruits and leaves?
yeast
how does yeast reproduce?
budding; can produce up to 24 new cells
psuedohypha
buds do not detach
dimorphic
cells are more pathogenic
how is dimorphism dependent on temperature?
at RT, yeast is mold-like. but at body temp, it is yeast-like
at what temperature is yeast mold-like?
25°C
at what temperature is yeast yeast-like?
37°C
vegetative structures of molds do what?
obtain nutrients
thallus
body of mold consisting of filaments
hyphae/hypha
filaments; can be very long; elongate at the tips
septa/septum
cross-walls
coenocytic hyphae
no cross-walls
mycelium
filamentous mass visible to the unaided eye
separate hyphae have what structures?
septum, pore, nuclei, cell wall
coenocytic hypha have what structures?
nuclei, cell wall
what grows from a spore?
growth of a hypha from a spore
molds are identified by what structures?
reproductive structures or spores
asexual spores
formed by hyphae of one organism (NO fusion of nuclei)
are asexual spores genetically identical to the parent?
yes
are asexual spores the product of mitosis or meiosis?
mitosis; occurs MORE often in nature
what is an example of asexual spores?
canidiospores (also known as conidia)
conidiosphore
supporting structure of a conidiospore
what two microbes are examples of conidiospores?
aspergillus sp. + penicillium sp.
aspergillus sp.
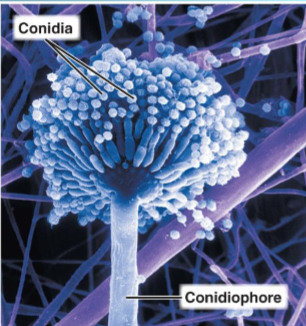
penicillium sp.
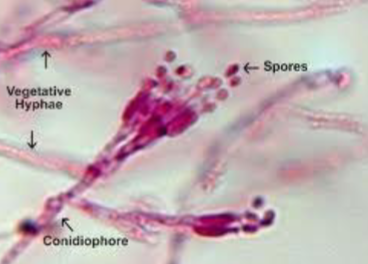
sporangiospores have what structures?
sporangium; sporangiophore
sporangium
sac
sporangiophore
supporting structure
what microbe is an example of a sporangiospore?
rhizopus sp. (mucor)
sexual spores
fusion of 2 nuclei from 2 opposite mating strains of the same species of fungi
sexual spores are made by mitosis or meiosis?
meiosis; occurs less often that asexual spores
medically important fungi will produce what types of spores in the lab?
asexual spores
medically important fungi will produce what types of spores in the body?
sexual spores
what are the types of sexual spores?
zygospores, ascospores, basidiospores
what is the first step in identifying fungi in the lab?
look for spores
cultures of fungi prefer what conditions?
sugary/salty; low pH; RT
mycotoxins
toxins/poisons produced by fungi; damage to kidneys, liver, nervous system
aflatoxin is produced by what microbe?
aspergillus sp.
where is aflatoxin found?
peanuts and corn fields
aflatoxin is dangerous to…?
humans + animals
aflatoxin causes damage to…?
the heart + liver
ergotism is caused by what microbe?
claviceps purpurea
where is ergotism (claviceps purpurea) found?
rye + cereal grains; crops; appears as a soot-like mass
ergotism was widespread during what time period?
middle ages; possible connection to the salem witch trials
ergot poisoning does what to the body?
restricts blood flow; causes hallucinogenic symptoms similar to LSD
mycoses (or mycosis)
fungal disease
mycoses can involve which 5 tissue groups?
superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, systemic, opportunistic
superficial mycoses
involves hair shaft + surface epidermal cells
piedra
superficial mycoses; found in tropical climates; causes cosmetic issues
what is a symptom of piedra?
hard black or white gritty nodules on hair shafts
what is the treatment for piedra?
shaving/cutting hair + miconazole (topical)
cutaneous mycoses
involves epidermis, hair, nails
dermamycoses
nail mycoses
tinea + ringworm infections colonize what parts of the body?
hair, nails, epidermis
keratinolytic fungi
fungi that target keratin (dermatophytes)