Major concepts in The Origin of Species by Charles Darwin Natural Selection Inheritance Variation Survival of the Fittest PART 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:29 PM on 10/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
The Evolution Theory by Charles Darwin
- The evolution theory states that all forms of life started from simple forms and
transformed to complex ones. It refers to the physical transformation of modern
humans from hominids into thinking modern humans or Homo sapiens.
- Original research of Charles Darwin
- It was introduced by the naturalist and biologist known for his theory of evolution and the
process of natural selection - Charles Darwin who is called the Father of Evolution -
in his published work, On the Origins of Species by Means of Natural Selection.
- It refers to the physical transformation of modern humans from hominids into thinking modern humans or Homo sapiens.
- Lengthy process of change by which people originated from ape like ancestors
- Proponent: Charles Darwin
(naturalist and biologist)
transformed to complex ones. It refers to the physical transformation of modern
humans from hominids into thinking modern humans or Homo sapiens.
- Original research of Charles Darwin
- It was introduced by the naturalist and biologist known for his theory of evolution and the
process of natural selection - Charles Darwin who is called the Father of Evolution -
in his published work, On the Origins of Species by Means of Natural Selection.
- It refers to the physical transformation of modern humans from hominids into thinking modern humans or Homo sapiens.
- Lengthy process of change by which people originated from ape like ancestors
- Proponent: Charles Darwin
(naturalist and biologist)
2
New cards
Natural Selection
- Natural selection explains how species evolved and how they adapt to their environment.
3
New cards
Variation
- Every species is made up of a variety of individuals
with some better adapted to their environments compared to the others.
with some better adapted to their environments compared to the others.
4
New cards
Inheritance
- Organisms produce offspring with different sets of traits that can be inherited.
5
New cards
Survival of the Fittest
- Organisms that have traits most suitable to their environment will
survive and these variations are passed on to their offspring in subsequent generations.
- Cultural evolution, on the other hand, refers to the changes or development in cultures from a
simple form to a more complex form of human culture.
- A significant aspect of cultural evolution, by contrast, is that human populations may make large changes in their physical environment and thus create elaborate social environments into
which the young are enculturated and within which most human activities are carried on.
survive and these variations are passed on to their offspring in subsequent generations.
- Cultural evolution, on the other hand, refers to the changes or development in cultures from a
simple form to a more complex form of human culture.
- A significant aspect of cultural evolution, by contrast, is that human populations may make large changes in their physical environment and thus create elaborate social environments into
which the young are enculturated and within which most human activities are carried on.
6
New cards
The crux of Darwin's Theory of Evolution
- focuses on the elimination of inferior species gradually over time, through a process called
'Natural Selection'
'Natural Selection'
7
New cards
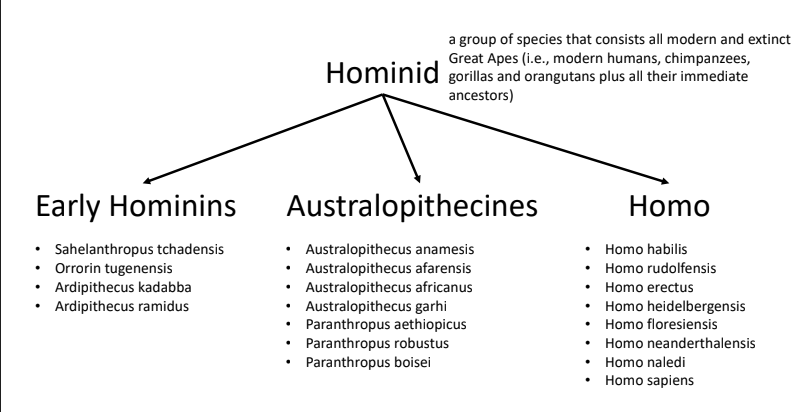
HOMINID
- Early hominins
- Australopithecines
- Homogenus
- Australopithecines
- Homogenus
8
New cards
The Prehistoric Man
The Prehistoric Man
9
New cards
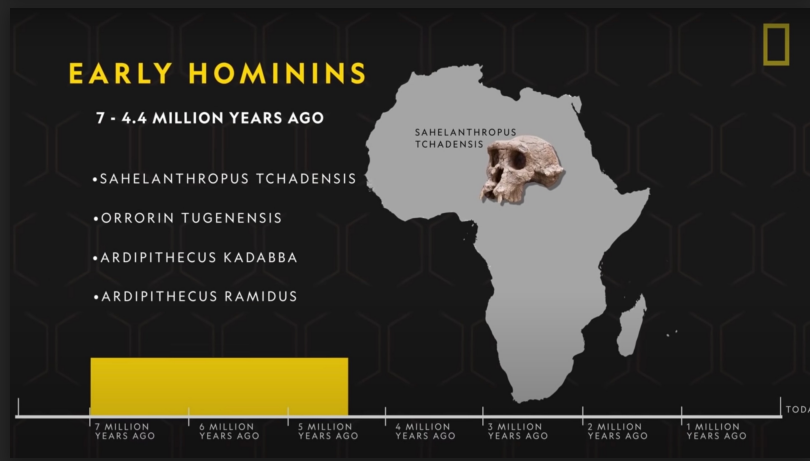
EARLY HOMININS
EARLY HOMININS
10
New cards
AUSTRALOPITHECINES
- Australopithecus afarensis -
“Lucy” - was one of the first
hominin fossils to become a
household name.
- Her skeleton is around 40% Complete
“Lucy” - was one of the first
hominin fossils to become a
household name.
- Her skeleton is around 40% Complete

11
New cards
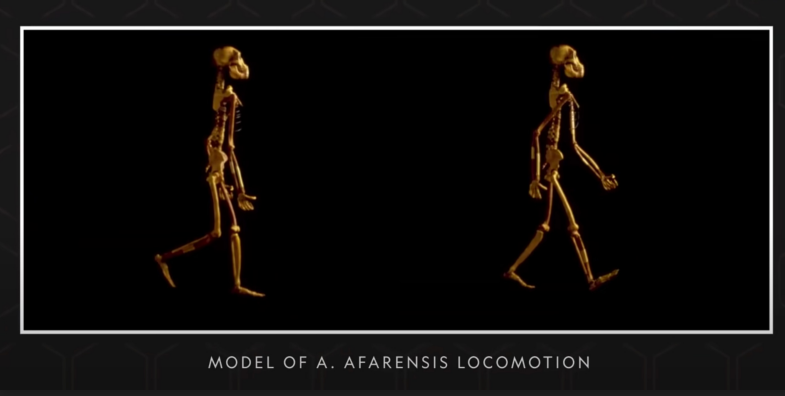
AFARENSIS LOCOMOTION MODEL
AFARENSIS LOCOMOTION MODEL
12
New cards
Homo habilis
“The Handy Man”
- first maker of stone tools as weapons and protection of
their enemies; skillfull in doing small tasks; usage of basic tools
- first maker of stone tools as weapons and protection of
their enemies; skillfull in doing small tasks; usage of basic tools

13
New cards
Homo erectus
“The Upright Man”
- manlike specie could walk
up straight (bipedalism)
- manlike specie could walk
up straight (bipedalism)

14
New cards
Homo sapiens
“The Thinking Man”
- first to develop and use oral language
- relative intelligence that
built today’s civilization
- first to develop and use oral language
- relative intelligence that
built today’s civilization

15
New cards
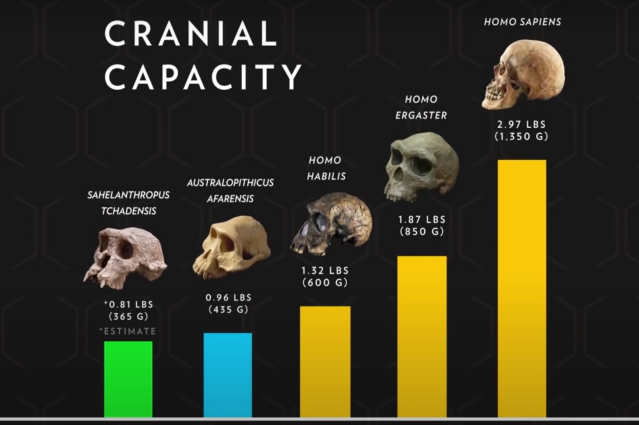
CRANIAL CAPACITY
CRANIAL CAPACITY
16
New cards
Australopithecines
- Bipedal
- Brain was 1/3
size of modern
humans.
- Lucy is part of
this group. 300
individual
fragments were
found in
Tanzania.
- Brain was 1/3
size of modern
humans.
- Lucy is part of
this group. 300
individual
fragments were
found in
Tanzania.
17
New cards
homo habilis
- handy man
- first maker of stone tools
- increased cranial capacity
- smaller molar and premolar teeth
- human- like foot slightly larger brain
- first maker of stone tools
- increased cranial capacity
- smaller molar and premolar teeth
- human- like foot slightly larger brain
18
New cards
Homo erectus
- prominent brow ridges, retreating forehead
- angled rear skull
- a larger brain
- angled rear skull
- a larger brain
19
New cards
Homo sapiens
- large brain size (1400cc)
- lived in shelters
- food gatherers
- ate plants and fruits
- hunted animals
- made more sophisticated and smoothened tools.
- first to develop and use oral language
- robust cranial vault with a massive arched brow ridge
- limb bones were
- robustly built
- front teeth were larger than those of modern humans
- flattened cranial base
- Mousterian Industry
- lived in shelters
- food gatherers
- ate plants and fruits
- hunted animals
- made more sophisticated and smoothened tools.
- first to develop and use oral language
- robust cranial vault with a massive arched brow ridge
- limb bones were
- robustly built
- front teeth were larger than those of modern humans
- flattened cranial base
- Mousterian Industry
20
New cards
The Means of Cultural
Adaptations of Early Humans
Adaptations of Early Humans
- Brain
- Teeth
- Bipedal
- Teeth
- Bipedal
21
New cards
Philippine Prehistoric Man
Philippine Prehistoric Man
22
New cards
Tabon man
- Lipuun Point Reservation of the
Tabon Caves Complex in the
southern part of Palawan Island
- Dr. Robert Fox (1918-1985)
Tabon Caves Complex in the
southern part of Palawan Island
- Dr. Robert Fox (1918-1985)

23
New cards
Homo luzonesis
• It was excavated in 2007 in Callao
Cave, Peñablanca, Cagayan Valley, Philippines
• Dr. Armand Salvador Mijares.
Cave, Peñablanca, Cagayan Valley, Philippines
• Dr. Armand Salvador Mijares.

24
New cards
Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution

25
New cards
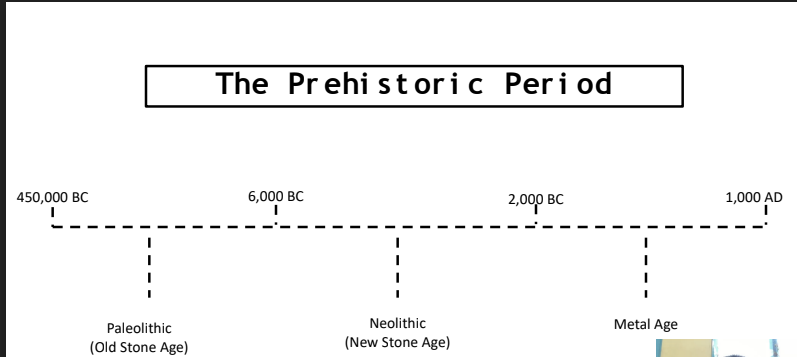
The Prehistoric Period Timeline
The Prehistoric Period Timeline
26
New cards
Paleolithic-Old Stone Age
(450,00 - 6,000 B.C.)
(450,00 - 6,000 B.C.)
- Produced fire by rubbing two
stones together.
- Produced basic stone tools
and stone art (self-expression)
- Nomads
stones together.
- Produced basic stone tools
and stone art (self-expression)
- Nomads
27
New cards
Neolithic-New Stone Age
(6,000 - 2,000 B.C.)
(6,000 - 2,000 B.C.)
-Stone tools were shaped by
polishing or grinding.
-Settlement in permanent
villages.
polishing or grinding.
-Settlement in permanent
villages.
28
New cards
Metal Age
(2,000 B.C - 1000 A.D.)
(2,000 B.C - 1000 A.D.)
-The used of metal such as bronze, copper, and iron produced
- Changes in settlement organization, ritual life, and interaction between the societies were evident.
- The civilization which defines to a more developed social, cultural, political and economic system.
- Changes in settlement organization, ritual life, and interaction between the societies were evident.
- The civilization which defines to a more developed social, cultural, political and economic system.
29
New cards
The Prehistoric Period
The most important thing to remember regarding this
period is that stone tools provide evidence about
the technologies particularly the mental skills and
innovations that were within the grasp of early
human toolmakers.
period is that stone tools provide evidence about
the technologies particularly the mental skills and
innovations that were within the grasp of early
human toolmakers.
30
New cards
Types of Society
• Hunting and Gathering Stage
• Pastoral Stage
• Horticultural Stage
• Agricultural Stage
• Industrial Stage
• Post-Industrial Stage
• Pastoral Stage
• Horticultural Stage
• Agricultural Stage
• Industrial Stage
• Post-Industrial Stage

31
New cards
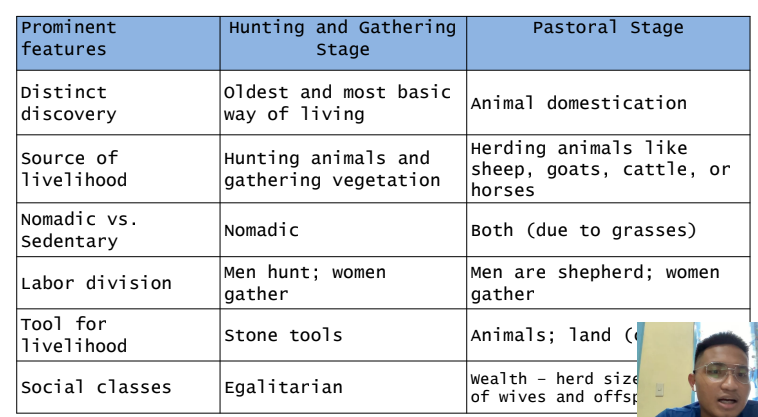
Hunting and Gathering Stage
This refers to the early nomads who transfer from
one place to another to get food for their survival.
This stage is the oldest and most basic way of living.
Equality in duties between men and
women is seen. Men are tasked to hunt
animals available in their area. The women,
on the other hand, are responsible for
gathering vegetation.
- Because they depend on nature in terms of
food, they frequently transfer from one place
to another and do not have permanent
settlements.
- Survival of people is through hunting animals
and gathering of edible plants.
- The primary institution is the family,
which decides how food is to be shared, how children are to be socialized, and
who provides for the protection of its members.
- Population size is few which is usually less than 50.
- They are nomadic because they need to transfer to where food is available.
- High level of interdependence is evident in the members of this society.
- Labor division is based on sex: men hunt, and women gather.
one place to another to get food for their survival.
This stage is the oldest and most basic way of living.
Equality in duties between men and
women is seen. Men are tasked to hunt
animals available in their area. The women,
on the other hand, are responsible for
gathering vegetation.
- Because they depend on nature in terms of
food, they frequently transfer from one place
to another and do not have permanent
settlements.
- Survival of people is through hunting animals
and gathering of edible plants.
- The primary institution is the family,
which decides how food is to be shared, how children are to be socialized, and
who provides for the protection of its members.
- Population size is few which is usually less than 50.
- They are nomadic because they need to transfer to where food is available.
- High level of interdependence is evident in the members of this society.
- Labor division is based on sex: men hunt, and women gather.
32
New cards
Pastoral Stage
Pastoral comes from the root word “pastor,” a Latin word which means
“shepherd.” This period is between 8500-6500 BC.
- One of principal livelihoods is animal domestication. They are animal
herders and subsist in the resources provided by the animals.
- They have settlements but they don’t stay in one place permanently.
Pastoralists are merely farmers who specialize in herding animals like sheep,
goats, cattle, or horses.
- Production is for more than meat and milk. Some animals are used as beasts
of burden, while others are used for their fur. Animal products are for both
personal use and trade.
- Extensive land use is evident in this society in which animals are moved to
grasslands.
- To serve their duties in the society, the pastoralists together with their
extended families help each other in caring for and domesticating animals.
- Division of labor is gender based.
- Most pastoralists are monotheistic (but not all of them); usually the belief is
tied closely to their animals.
- The concept of ownership is restricted to animals, housing, and some
domestic goods. Land is communal.
- Many pastoralists contend that they have travel rights over lands because of
centuries-old migratory patterns that supersede modern land ownership.
- Wealth is determined by herd size and, often, by the number of wives and
offspring a man has.
- Decisions about when to move are made communally.
“shepherd.” This period is between 8500-6500 BC.
- One of principal livelihoods is animal domestication. They are animal
herders and subsist in the resources provided by the animals.
- They have settlements but they don’t stay in one place permanently.
Pastoralists are merely farmers who specialize in herding animals like sheep,
goats, cattle, or horses.
- Production is for more than meat and milk. Some animals are used as beasts
of burden, while others are used for their fur. Animal products are for both
personal use and trade.
- Extensive land use is evident in this society in which animals are moved to
grasslands.
- To serve their duties in the society, the pastoralists together with their
extended families help each other in caring for and domesticating animals.
- Division of labor is gender based.
- Most pastoralists are monotheistic (but not all of them); usually the belief is
tied closely to their animals.
- The concept of ownership is restricted to animals, housing, and some
domestic goods. Land is communal.
- Many pastoralists contend that they have travel rights over lands because of
centuries-old migratory patterns that supersede modern land ownership.
- Wealth is determined by herd size and, often, by the number of wives and
offspring a man has.
- Decisions about when to move are made communally.
33
New cards
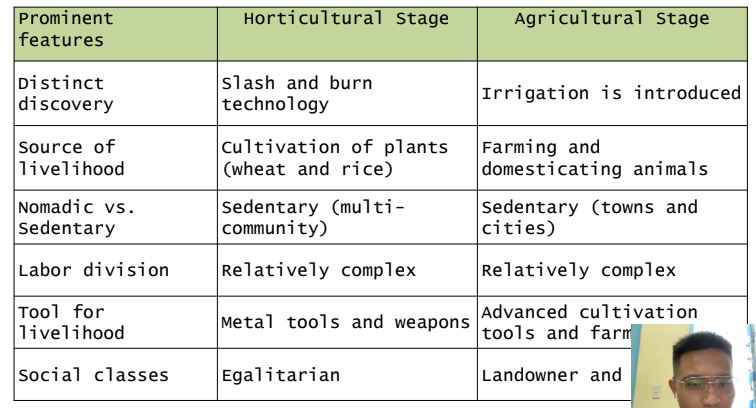
Horticultural Stage
Simple cultivation as a supplementary to
hunting and gathering.
- Communities are formed in areas where rainfall
and other conditions allow them to grow stable
crops.
- Cultivation of plants such as wheat and rice are
practiced.
- They used metal tools and weapons.
- Slash and burn technology is developed.
- They use hand tools to cultivate plants.
- They place more emphasis on providing for the
needs of their family and less on other members of society.
- They establish permanent settlements.
- They can an create more elaborate cultural artifacts like house, thrones,
and large stone sculptures.
- They have a relatively more complex division of labor.
- They are a multi-community society.
hunting and gathering.
- Communities are formed in areas where rainfall
and other conditions allow them to grow stable
crops.
- Cultivation of plants such as wheat and rice are
practiced.
- They used metal tools and weapons.
- Slash and burn technology is developed.
- They use hand tools to cultivate plants.
- They place more emphasis on providing for the
needs of their family and less on other members of society.
- They establish permanent settlements.
- They can an create more elaborate cultural artifacts like house, thrones,
and large stone sculptures.
- They have a relatively more complex division of labor.
- They are a multi-community society.
34
New cards
Agricultural Stage
It began 5,000 years ago during the Neolithic Period when their population
increased into millions.
- They start to cultivate cereals such as wheat, barley, peas, rice, and millet.
- They begin farming and domesticating animals such as sheep, goats, and
pigs.
- A more advanced cultivation tools are produced and farming skills that
can support and sustain a town with over a thousand population are developed.
- They settle permanently and improve technology in farming.
- Money becomes a form of exchange replacing the barter system.
- There is reliance on permanent tools for survival.
- Distinct social classes evolve.
increased into millions.
- They start to cultivate cereals such as wheat, barley, peas, rice, and millet.
- They begin farming and domesticating animals such as sheep, goats, and
pigs.
- A more advanced cultivation tools are produced and farming skills that
can support and sustain a town with over a thousand population are developed.
- They settle permanently and improve technology in farming.
- Money becomes a form of exchange replacing the barter system.
- There is reliance on permanent tools for survival.
- Distinct social classes evolve.
35
New cards
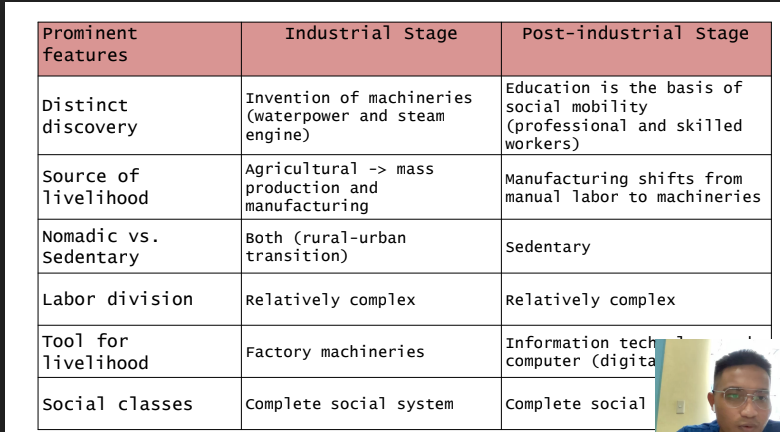
Industrial Stage
It started when the Industrial Revolution occurred in Europe during the 18th
century and half of the 19th century.
- Agricultural society is transformed to production and manufacturing.
- Advanced form of energy is used to operate factory machineries.
- Creation of centralized workplaces, economic interdependence, formal education, and complete social systems.
- People leave their farms and transfer in urban areas to work in factories.
- Mass production is introduced.
century and half of the 19th century.
- Agricultural society is transformed to production and manufacturing.
- Advanced form of energy is used to operate factory machineries.
- Creation of centralized workplaces, economic interdependence, formal education, and complete social systems.
- People leave their farms and transfer in urban areas to work in factories.
- Mass production is introduced.
36
New cards
Post-Industrial Stage
With the development of information technology and computers, many
societies become digital
There is a significant increase in the number of professionals and technical
workers employed and a decline in the number of skilled and semi-skilled
workers.
- Education is the basis of social mobility.
- The strength of the society is identified through human capital.
- The focus is on communication infrastructure.
- Knowledge becomes a source of invention and innovation.
- The period is characterized by a service-based economy.
- Workers are mostly technical and professionals.
- Greater attention is paid to the theoretical and ethical implications of
new technologies which help society avoid some of the negative features of
introducing new technologies, such as environmental accidents and massive
widespread power outages.
- Newer scientific disciplines
- stronger emphasis on the university and polytechnic institutes
societies become digital
There is a significant increase in the number of professionals and technical
workers employed and a decline in the number of skilled and semi-skilled
workers.
- Education is the basis of social mobility.
- The strength of the society is identified through human capital.
- The focus is on communication infrastructure.
- Knowledge becomes a source of invention and innovation.
- The period is characterized by a service-based economy.
- Workers are mostly technical and professionals.
- Greater attention is paid to the theoretical and ethical implications of
new technologies which help society avoid some of the negative features of
introducing new technologies, such as environmental accidents and massive
widespread power outages.
- Newer scientific disciplines
- stronger emphasis on the university and polytechnic institutes
37
New cards
Prominent features
Hunting and Gathering Stage
Pastoral Stage
Hunting and Gathering Stage
Pastoral Stage
Hunting and Gathering Stage
Pastoral Stage
Pastoral Stage
38
New cards
Prominent features
Horticultural Stage
Agricultural Stage
Horticultural Stage
Agricultural Stage
Horticultural Stage
Agricultural Stage
Agricultural Stage
39
New cards
Prominent features
Industrial Stage
Post-industrial Stage
Industrial Stage
Post-industrial Stage
Industrial Stage
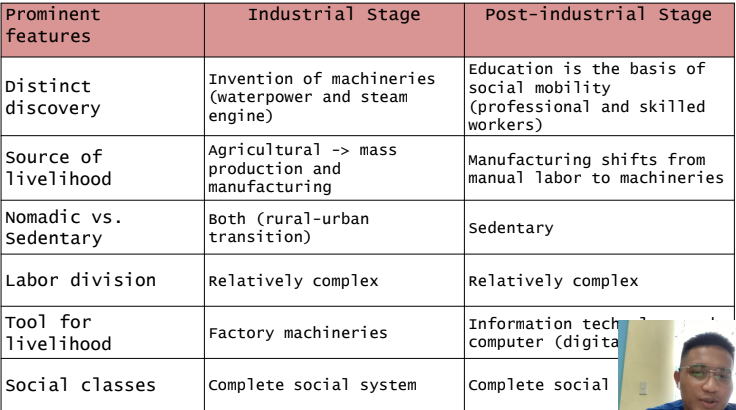
40
New cards
Prominent features
Industrial Stage
Post-industrial Stage
Industrial Stage
Post-industrial Stage
Post-industrial Stage