Lectures 9-10 Emotions and Happiness
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is an emotion
How it differs from mood:
emotions: brief, response to a specific event or experience
mood: long lasting (hours to days), don’t know specific cause
components of an emotion
1. Appraisal process: refers to the cognitive evaluation or interpretation of a situation that leads to the generation of an emotional response.
fast automatic: is event consistent w goals? (leads to pleasant or unpleasant feelings)the
deliberate: What caused the event? who is responsible? is it fair? what can I do abt it?
2. Physiological responses: blushing, goosebumps out of frustration
3. Expressive behaviors: emotions expressed thru words, body gestures, facial- nonverbal
4. Subjective feelings: the personal, internal experience of emotion — what it feels like to be happy, sad, angry, afraid, etc
5. Action tendencies: refer to the urge or readiness to act in a particular way when experiencing a specific emotion (look at photo)
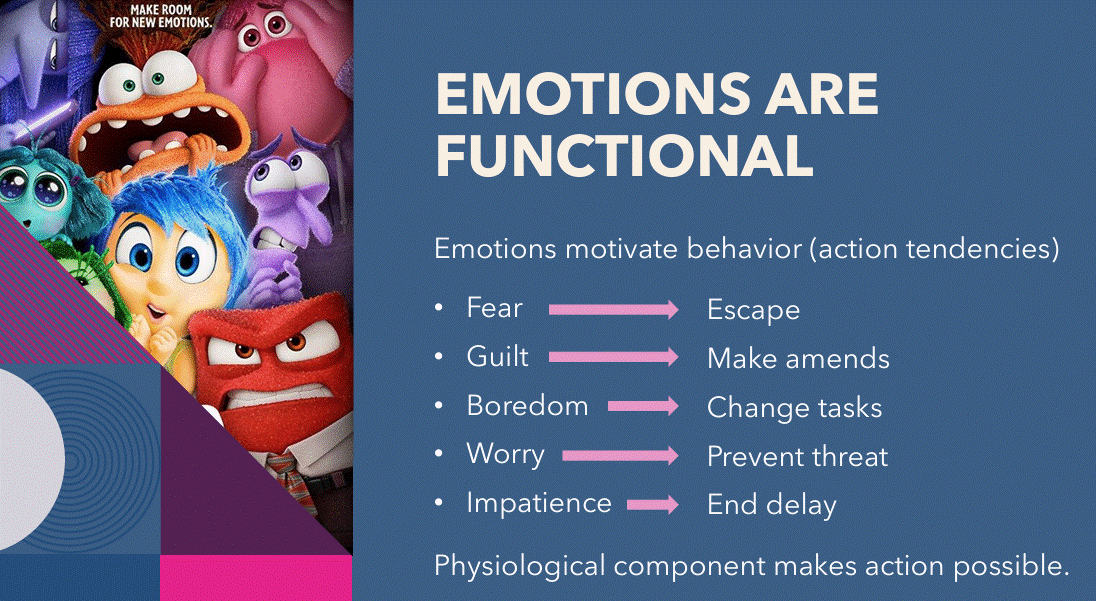
Why are emotions functional: action tendency example
the monkey example:
monkey wasnt given grape
started throwing stuff at researcher
Functionality: THEORY EVIDENCE: POSITIVE EMOTIONS AND CREATIVITY
Previous studies have found that positive emotions improve creative thinking (broaden)
1. Creativity and Word Association Tasks
• Design: Inducing positive emotions helped participants with creativity test of word associations
“How do these three words relate to each other: mower, atomic, and foreign”
Participants in a positive emotional state were more likely to solve these insight problems
2. Torrance Creativity Test
• Positive emotions also facilitated more creative responses from Torrance creativity test
“Name as many unusual uses as you can for the following object: a brick
Functionality: BROADEN-AND-BUILD THEORY (FREDRICKSON)
While negative emotions narrow and focus our behavior (thought-action repertoire), positive emotions broaden our behaviors by prompting us to pursue novel and creative thoughts and actions.
This broadening of behaviors also allows us to build personal resources over time.
Negative emotions (like fear or anger) narrow your focus.
→ Example: Fear = fight or flight.Positive emotions (like joy, love, interest) broaden your thought-action repertoire — meaning they open your mind to new ideas and actions.
→ Example: Joy might lead you to play, explore, or connect with others.
Situation Selection (emotion and regulation)
deciding when to engage or disengage in a specific situation to pre-regulate emotions (I know this environment will stress me out so I am purposely avoiding this environment)

Situation modification (emotion and regulation)
changing aspects of env that influence our emotional experience (when ppl are being loud in lib so you wear headphones)
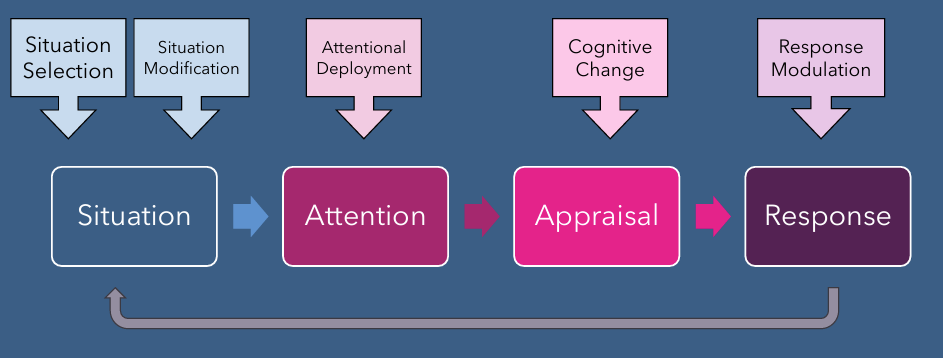
Attention deployment (emotion and regulation)
changing where u are direction attention (towards or away from situation that is eliciting emotional response)
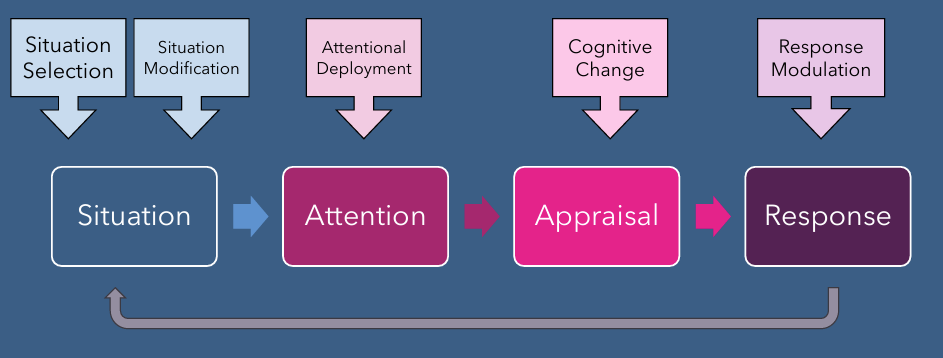
Cognitive change (emotion and regulation)
involves changing how we think about situation to alter emotional impact it has on us
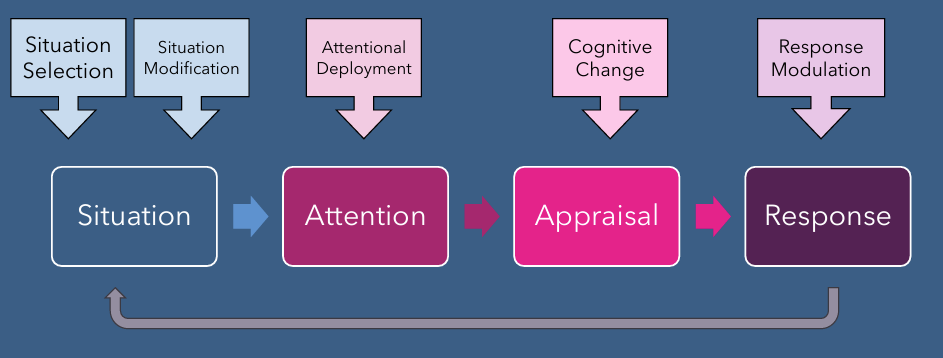
Response modulation (emotion and regulation)
changing physiological responses or outward expressions of responses (hiding behaviors, breathing, social sharing
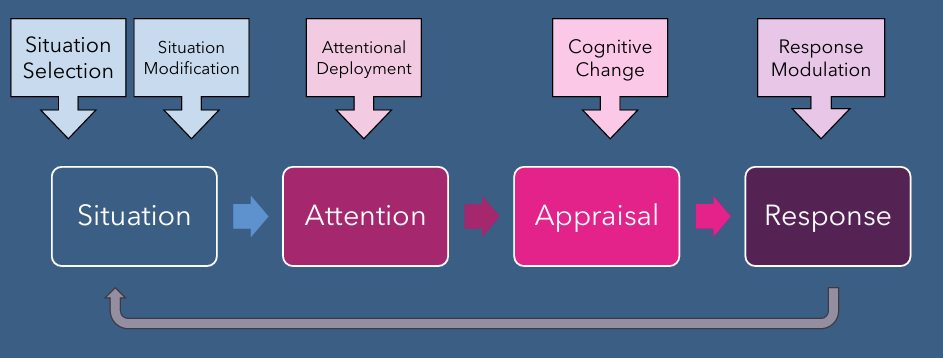
emotional regulation strats
1. Situation Selection
Choose the situation to influence emotions.
Avoidance – Stay away from stress.
Approach – Go toward positive or growth opportunities.
2. Situation Modification
Change the situation itself.
Problem solving – Fix the issue.
Seek social support – Ask for help.
Conflict resolution – Work out disagreements.
3. Attentional Deployment
Shift your focus.
Distraction – Focus elsewhere.
Rumination – Stuck thinking (not helpful).
Focus on positive – Look for the good.
Thought suppression – Try not to think about it (often fails).
4. Cognitive Change
Change your thoughts.
Self-efficacy – “I can handle this.”
Challenge appraisal – View as challenge, not threat.
Acceptance – Allow emotions.
Distancing – Think like an outsider.
Positive appraisal – Find meaning/growth.
5. Response Modulation
Manage emotional responses.
Suppression – Hide emotion.
Social sharing – Talk it out.
Breathing – Calm your body.
emotions as social info
Emotions tend to be elicited by other people, expressed toward other people, and regulated to influence other people or to comply with social norms
💁 Individual Level
Emotions are influenced by others but felt within the person.
You may feel emotions because of what someone else did.
You might regulate your emotion to fit social expectations.
🧠 Example: You feel embarrassed when you trip in public and hide it to avoid judgment.
🤝 Dyadic Level (Two-Person Interaction)
Emotions are expressed toward another person and used as social signals.
Emotions help guide how two people respond to each other.
Includes emotional influence, like empathy, guilt, or anger.
🧠 Example: If you see a friend crying, you might comfort them—your behavior changes based on their emotion.
👥 Group Level
Emotions can be shared across groups, creating group moods or norms.
People may regulate their emotions to match the group or follow group rules.
Emotional expression can influence group cohesion or conflict.
🧠 Example: At a funeral, people remain solemn to respect group expectations, even if they feel differently inside.
individual level (emotions as social info)
motivates social actions, eferring to how your own emotions (even when felt privately) help guide your thinking and behavior in social contexts.
ex: gratitude can lead us to act towards other, form of award of being generous, reward to keep us social
even when you don’t outwardly express an emotion, feeling it helps you understand your social world.
dyadic level (emotions as social info)
When you express an emotion, the other person uses that information to understand you and decide how to respond.
(expressions of regret lead people to to think the expressor is responsible-the problem)
if angry they are the victim
group level (emotions as social info)
Group emotional patterns shape norms, cohesion, differentiation, and individual behaviors, how we know who are outsiders (people seek to conform to group so ppl don’t feel left out )
universal nature of emotions
darwin thot we share similar emotional expressions with other animals Darwin
More recent findings:
• Ekman’s work on facial expressions – 80-90% agreement, even in a remote tribal group.
• Tracy’s pride studies – Posture of pride recognized across cultures, expressed by the blind, similar to animals.
CULTURAL VARIATION IN EMOTIONS: affect valuation theory and display rules
• Affect valuation theory : how people’s cultural values and personal goals shape the emotions they want to feel
western culture values that high feeling —music before game
• Display rules : How, when, and to whom it’s appropriate to express emotions.
HISTORY OF POSITIVE PSYCHOLOGY
Post World War II
• Focus of psychology on human problems and how to remedy them
• Led to the development of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
Led to field embracing a “disease model of human nature”
Diagnosing and treating mental illness
Identifying what is wrong with people (e.g., depression, anxiety, trauma)
Fixing psychological deficits or dysfunctions
People seen as flawed and fragile
Casualties of cruel environments or bad genetics
Focus on fixing weaknesses
POSITIVE PSYCHOLOGY
The scientific study of human flourishing, or of what goes right in life
Challenges disease model, arguing that human goodness and excellence are just as authentic as disorders and distress
“THE GOOD LIFE”
Well-being researchers currently study 3 types of well-being, or as Shige Oishi describes it “ways to pursue the good life”
happy life
meaningful life
psychological rich life
Subjective Well-Being
scientific way to measure happiness, based on how people experience and evaluate their lives.
According to psychologist Ed Diener, SWB has two main components:
1. Affective Component 😄😞
This is about emotions — how people feel on a daily basis.
Positive affect: Feeling joy, excitement, love, etc.
Negative affect: Feeling anger, sadness, anxiety, etc.
Happiness = experiencing more positive than negative emotions over time.
2. Cognitive Component 🧠
This is about life satisfaction — how people think about their lives overall.
It’s a reflective judgment: "Am I satisfied with my life?"
Based on your personal values, goals, and comparisons.
CORRELATES OF HAPPINESS
Genetic heritability
Ex: Personality traits, such as high extraversion or low neuroticism
Income and wealth (to an extent)
Close relationships
Relationship between social support and well-being
Married people report being happier and more satisfied with life (compared to single and divorced people) 6
Faith and Religion
HEDONIC ADAPTATION
After positive (or negative) events (i.e., something good or bad happening to someone), and a subsequent increase in positive (or negative) feelings, people return to a relatively stable, baseline level of affect 8
Also referred to as the “Hedonic Treadmill”
Sustainable happiness model
Can u pursue happiness
proposes our subjective well-being is influenced by three factors:
1. Our Set Point/Genetics: 50%
2. Life Circumstances: 10% External factors like income, age, health, relationship status
3. Intentional Activity: 40% The part you control! Gratitude, acts of kindness
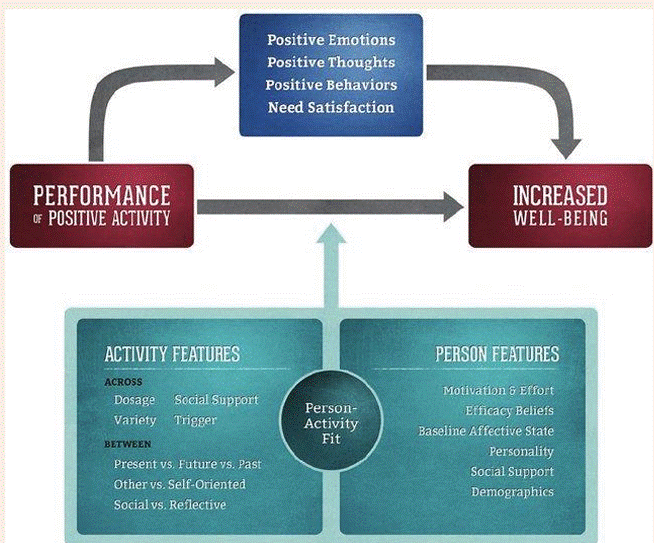
Sustainable happiness model: positive activity model
Goal: Explains how and why positive activities boost well-being.
Flow:
Do a Positive Activity
(e.g., gratitude, kindness, savoring)Leads to:
Positive emotions
Positive thoughts
Positive behaviors
Psychological need satisfaction
Result:
→ Increased well-being (happiness, life satisfaction, less depression)
What Affects the Outcome?
Person-Activity Fit — how well the activity matches the person.
🔹 Activity Features:
Dosage & variety
Social support
Self vs. other-oriented
Present vs. future focus
🔹 Person Features:
Motivation & effort
Beliefs about effectiveness
Personality & mood
Social support & demographics
The better the fit, the greater the boost to well-being.
Why pursue happiness: how does it lead to sucess
💡 Slide 1: Why Pursue Happiness?
Happiness isn’t just a result of success — it can also be a cause of success.
Relationships: Happier people are more likely to get married and have strong marriages.
Career: Happiness predicts getting hired, performing better at work, and earning more.
Health: Positive emotions are linked to better physical health, including a stronger immune system.
💡 Slide 2: How Does Happiness Lead to Success?
🔬 Based on Fredrickson’s Broaden-and-Build Theory:
Positive emotions broaden attention and thinking.
This helps people:
Approach others and new opportunities
Build resources (like social connections, skills, and knowledge)