RTE 1021 - Unit 3
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
What are the three cardinal rules of radiation protection. Which is the most effective in reducing occupational dose?
Time, Distance, Sheilding
Briefly describe each radiation safety method:
Bucky Slot Cover
Lead Gloves
Lead Apron
Fluoro Timer
Bucky slot cover - Reduces scatter from the fluoro table
Lead Gloves - Protect hands from radiation (compton scatter)
Lead Apron - Protect body and organs from radiation (compton scatter)
Fluoro Timer - 5 minute timer. Only counts when fluoro is active.
Where is the best place for the technologist to stand during fluroroscopy?
Side of the table behind the RPA or doctor.
Never stand at the foot or head of the table
What tools may be used to help visualize GERD?
Esophagram is the exam that visualizes this.
Tools are breathing exercises, water tests, compression paddle, and toe-touch
What is the Valsalva maneuver?
Deep breath in, hold it, and bear down as though trying to move bowels
What type of breathing instructions should be given to the patient during an esophagogram using a thin barium mixture?
Valsalva Maneuver and Mueller Maneuver
When must the technologist inform the radiologist during the samll bowel timed imaging?
When the contrast passes through the ileocecal valve.
To make the patient as comfortable as possible during a single-contrast barium enema, the radiographer should:
Communicate with the patient as much as possible throughout the exam. Warm the contrast to 85-90 degrees.
The barium enema bad should be placed:
No higher than 24” above the table
If the patient has a SBS, UGI, and BE scheduled in one day, what order should they be competed in?
BE, UGI, SBS
Ingestion of barium sulfate is contraindicated in which of the following situation(s)?
Esophageal or bowl perforation, bowel obstruction, recent or soon GI tract surgery, allergy to barium
What is a potential risk associated with the use of water-soluble contrast agents, especially for geriatric patients?
Dehydration
List side effects that may occur with injected iodinated contrast:
Sensation of warmth, metallic taste, nausea, headache, dizziness
Largest solid organ in the body, is located in the _____________ quadrant.
Right upper
Where is the gallbladder located in relation to the liver?
Posterior and inferior
There are ___ major lobes and ___ minor lobes.
2
2
What separates the right and left lobe?
Falciform ligament
Bile is manufactured in the __________ and stored in the ___________.
Liver
Gallbladder
What are the major functions of bile?
Aid in the digestion of fats by emulsifying fat globules and in the absoportion of fat following its digestion.
The ________ is the main organ involved in metabolism.
Liver
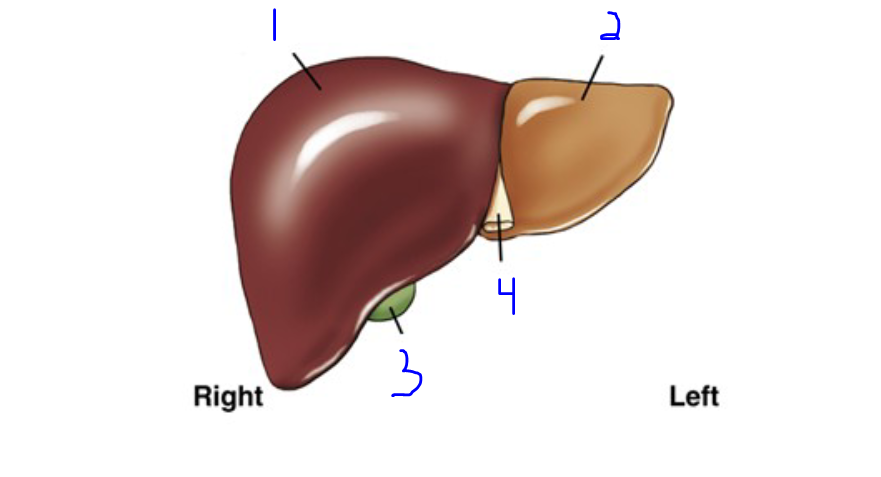
Label
Right lobe
Left lobe
Gallbladder
Falciform ligament
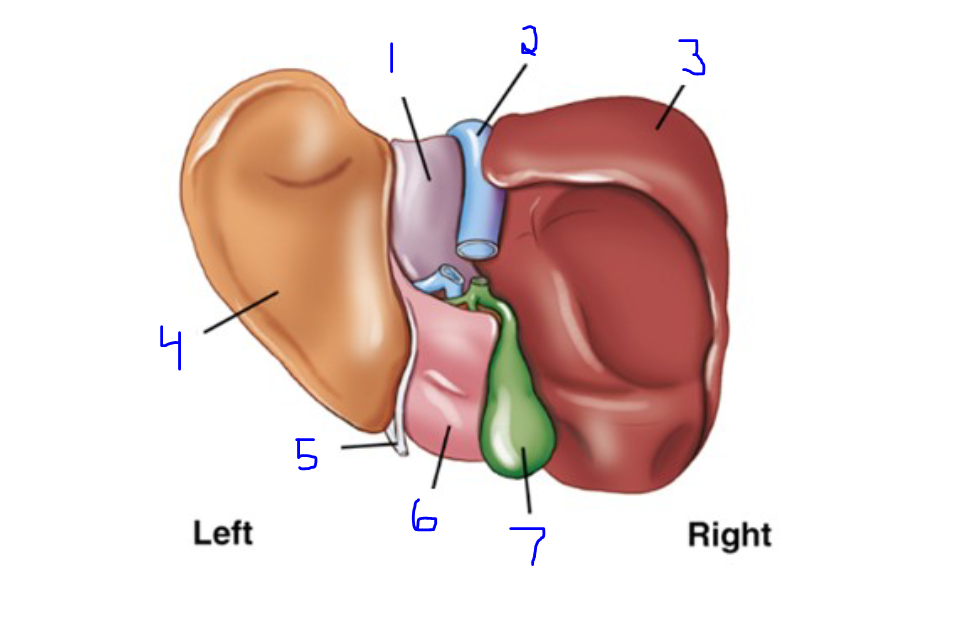
Label
Caudate lobe
Inferior Vena Cava
Right lobe
Left lobe
Falciform ligament
Quadrate lobe
Gallbladder
Bile is carried to the gallbladder via the _____________ or into the duodenum via the ________________.
Cystic duct
Common bile duct
What are the 3 parts of the gallbladder?
Fundus, Body, and Neck
List the 3 primary functions of the gallbladder:
Store bile
Concentrate bile
Contract when stimulated
The hormone secreted when fatty acids are in the duodenum:
Cholecystokinin
The terminal end of the common bile duct is closely associated with the terminal end of the _____________ duct or duct of _______________.
Pancreatic
Wirsung
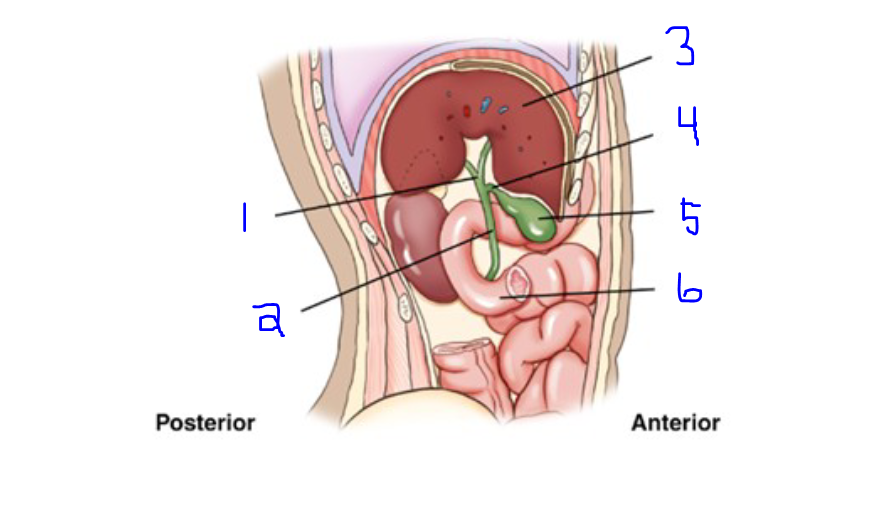
Label
Common Hepatic Duct
Common Bile Duct
Liver
Cystic Duct
Gallbladder
Duodenum
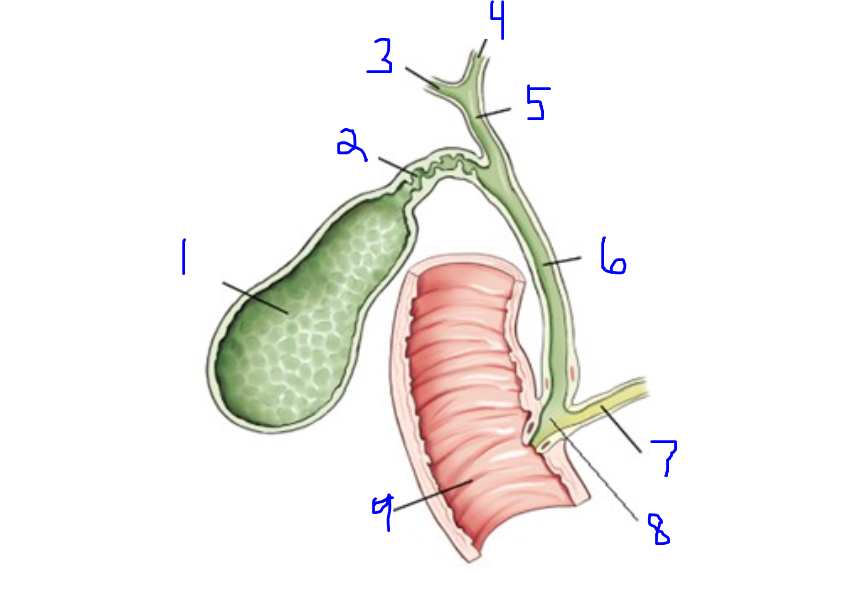
Label
Gallbladder
Cystic Duct
Right Hepatic Duct
Left Hepatic Duct
Common Hepatic Duct
Common Bile Duct
Pancreatic Duct (Duct of Wirsung)
Hepatopancreatic Ampulla (Ampulla of Vater)
Descending Duodenum
List the 3 primary function of the digestive system:
Intake and Digestion
Absorption
Elimination
Mastication
Act of chewing
Deglutition
Act of swallowing
Peristalsis
Wave-like involuntary muscle contractions that propel solid materials
List and describe the 3 salivary glands:
Parotid
Submandibular
Sublingual
This covers the opening of the larynx during swallowing:
Epiglottis
List the 3 parts of the pharynx (superiorly to inferiorly):
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
The esophagus is about ___ inches in length and ___ in diameter.
10 inches
½ inch
Where is the esophagus located in relation to the trachea? To the C-Spine?
Posterior to the trachea
Anterior to the C-Spine
The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is the:
Also referred to as the:
Esophagogastric junction
Cardiac orifice
Vertebral level of Upper margin of larynx
C3
Vertebral level of Cricoid cartilage of larynx
C5-C6
Vertebral level of Larynx-Trachea junction
C6
Vertebral level of Carina
T4-T5
Vertebral level of Esophagogastric junction
T11
Vertebral level of Iliac Crest
L4-L5
Vertebral level of Thryoid cartilage
C4-C5
Vertebral level T6 can be found by palpating ___ inches _________ inferior to the jugular notch.
2”
Inferior
The stomach has 3 main subdivisions:
Fundus, Body, Pylorus
The gastric air bubble is typcially found in this subdivision:
Fundus
Rugae
Stomach is empty and internal lining is thrown into muscosal folds.
Where is rugae most evident?
Lower body of the stomach alond the greater curvature.
The head of the pancreas is located where?
C-loop of the duodenum
The only portion of the duodenum considered intraperitoneal is:
Duodenal bulb (first portion)
The longest portion of the duodenum where the opening for the common bile and pancreatic ducts is located:
Second portion (duodenal papilla)
The duodenum and jejunum join at the:
Duodenojejunal flexure
The small intestine has three main sections (list in order):
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
Haustral churining primarily takes place in the:
Large intestine
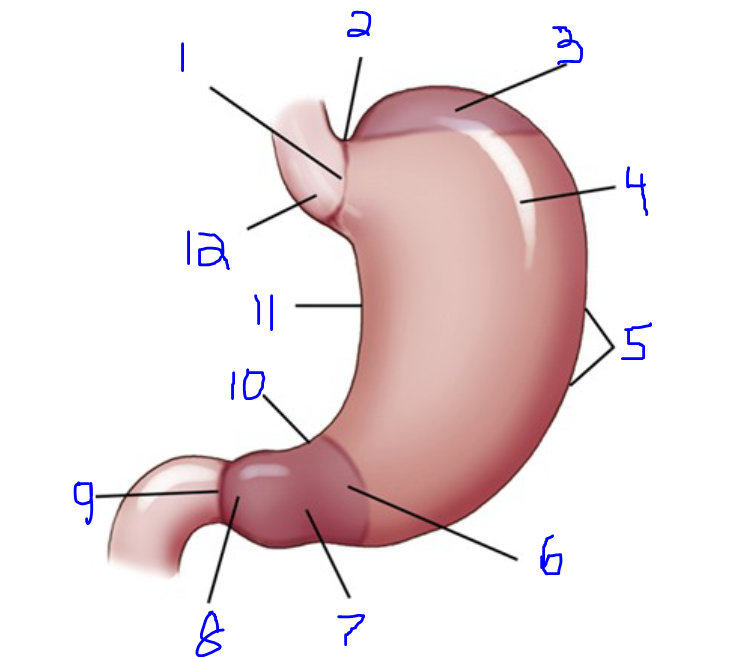
Label
Esophagogastric junction
Cardiac notch
Fundus
Body
Greater curvature
Pyloric portion
Pyloric antrum
Pyloric canal
Pyloric orifice
Angular notch
Lesser curvature
Cardiac antrum
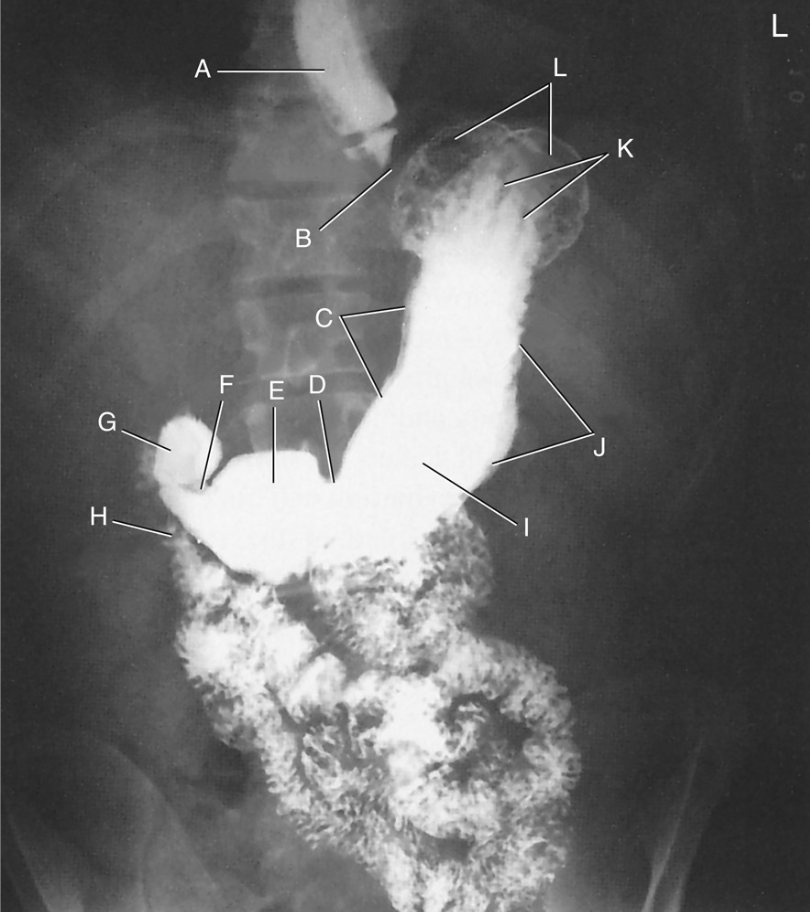
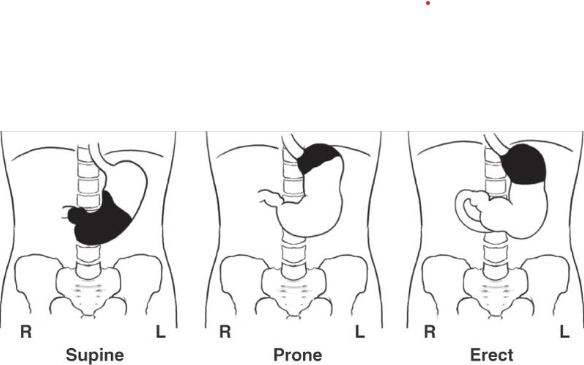
What position is the patient in?
Prone
Describe the orientation of the stomach on an average patient:
J shaped and extends from T11 down to L2
Where would the barium be located (use fundus, body, and pylorus)?
Supine
RAO
Prone
Erect
Supine - Fundus
RAO - Body and Pylorus
Prone - Body and Pylorus
Erect - Body and Pylorus
Hypersthenic Body Type
Transverse colon
Large Intestine
Gallbladder
Stomach
Duodenal Bulb
Transverse colon - High
Large Intestine - Extends to the periphery of the abdominal cavity
Gallbladder - High and almost transverse
Stomach - High and assumes a transverse position
Duodenal Bulb - T11 or T12, right of midline
Hyposthenic/Asthenic Body Type
Transverse colon
Large Intestine
Gallbladder
Stomach
Duodenal Bulb
Large Intestine - Down into the low abdominal and pelvic cavities
Stomach - J shaped and low in the abdominal cavity
Gallbladder - Near midline a lvl of iliac crests
Duodenal Bulb - Near midline at lvl L3-L4
Sthenic Body Type
Stomach - J shaped and lower than the hypersthenic
Gallbaldder - Less transverse and lies midway b/w lateral abdominal wall and midline
Large Intestine - High, under the left diaphragm
Duodenal Bulb - lvl of L1-L2, right of midline
List additional factors that may affect the position of the stomach:
Stomach contents, respiration, body position, previous abdominal surgeries, and age.
All abdominal organs tend to drop ____ inches in an ______ erect position.
1-2”
Erect
List the quadrant(s) each of the three parts of the small intestine is located in:
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Duodenum - RUQ and LUQ
Jejunum - LUQ and LLQ
Ileum - RUQ, RLQ, and LLQ
The jejunum contains numerus plicae circulars, which are:
Mucosal folds which increase the surface area to aid in the absorption of nutrients
The terminal ileum joins the large intestine at the __________ valve.
Ileocecal
What causes teh feather-like appearance of the duodenum when it is filled with barium?
Tight circular folds formed by the mucosa that contain villi.
Most digestion and absorption take place within the:
Small intestine
List and describe the two digestive movements of the small intestine:
Peristalsis - wave like contraction that proplels food through the digestive tract
Rhythmic segmentation - localized contractions in area that contain food
The primary function of the large intestine is to:
Eliminate feces
List and describe the four digestive movements of the small intestine:
Peristalsis - wave like contraction that propels food through digestive tract
Haustral churning - produces movement of material within the large intestine
Mass peristalsis - moves the entire large bowel contents into the sigmoid colon and rectum
Defecation - emptying of the bowel
The large intestine beings in the ______ quandrant.
Right lower
List the 4 major parts of the large intestine:
Cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal
List the 4 sections of the colon:
Ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid
The right colic flexure is also called:
Hepatic
The left colic flexure is also called:
Splenic
The appendix is attached to this part of the large intestine:
Cecum
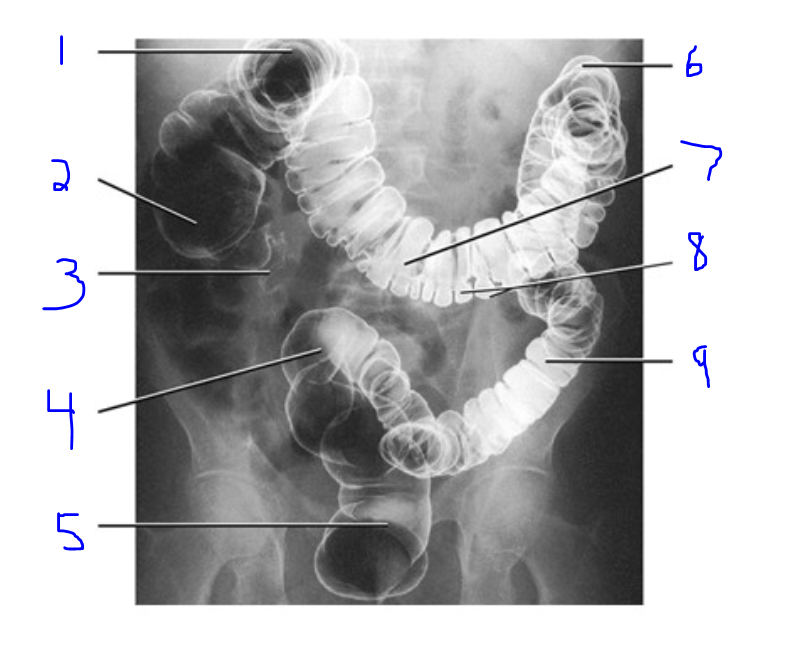
Label
Right Colic Flexure
Cecum
Vermiform appendix
Sigmoid colon
Rectum
Left Colic Flexure
Transverse Colon
Haustra of Colon
Descending Colon
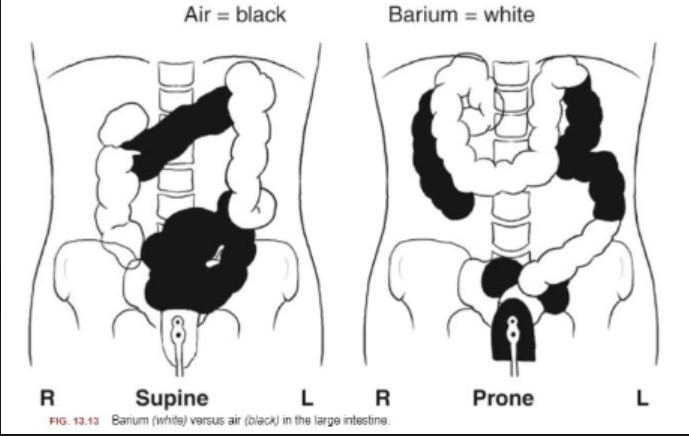
Describe which contain air and barium.
Supine
Barium (ascending/descending/rectum)
Air (transverse/sigmoid)
Prone
Barium (transverse/sigmoid)
Air (ascending/descending/rectum)
Define bolus injection:
Entire volume of contrast medium is injected at one time.
Define drip infusion:
Specified amount of contrast is given over a specified period
Which veins are most suitable for IV urograms?
Veins found within the antecubital fossa
The needle bevel must be:
Facing up
The injection angle for an IV is:
25 degrees or less (15-25)
What type of contrast must be used for urinary imaging?
Omnipaque, non-ionic (Water-soluble, iodinated)
What is one major downfall of ionic contrast agents?
More likely to experience a reaction
What is one major downfall of non-ionic contrast agents?
High cost
List common side effects of injected iodinated contrast media:
Temporary hot flash and metallic taste in mouth
Normal level of Creatinine
0.6-1.2 mg/dL
Normal level of BUN
7-20 mg/dL
Normal level of GFR
Over 90 ml/min/1.73 m2
What is the common drug given during a severe allergic reaction?
Epinephrine
What might patients be premedicated with to reduce the chances of an allergic reaction?
Benadryl/Antihistamine and may include prednisone (decreases inflammation)
Which kidney is slightly lower?
Right
The average kidney is ____ inches long.
4-5
A normal kidney is rotated about ____ to the midline and forms a vertical angle of about ____ to the MSP.
30 degress
20 degrees
Kidneys lie about halfway between the _____________ and the ____________.
Xiphoid process
Iliac crest