Cell Structure- Chapter 2
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms

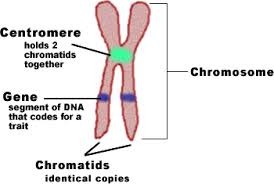
What do these proteins determine?
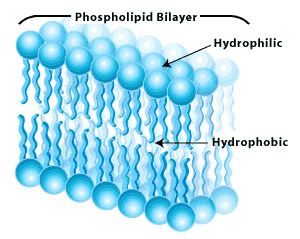
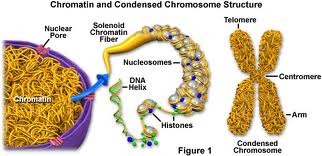
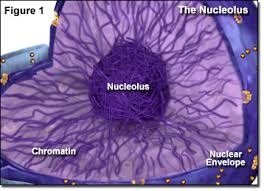
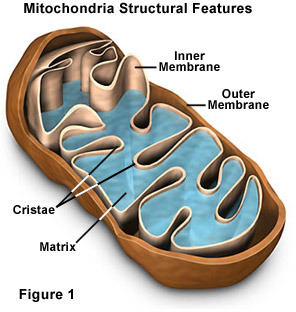
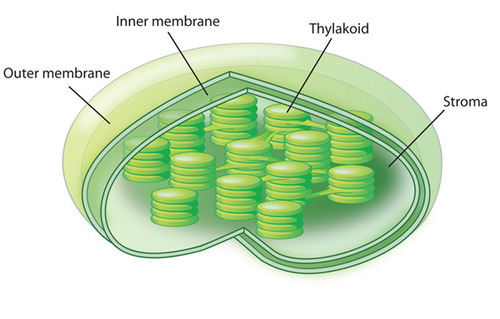
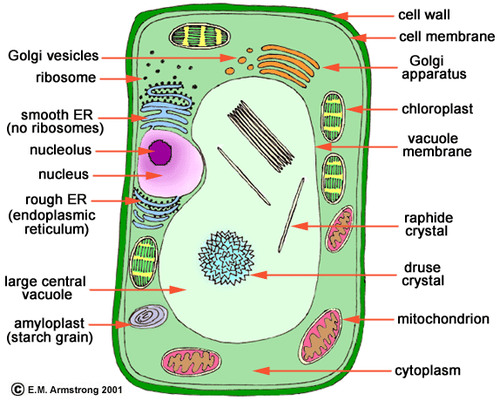
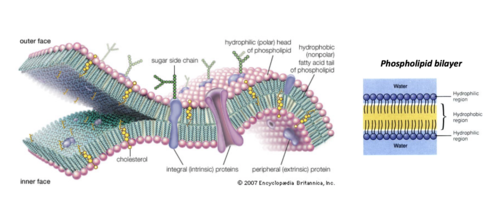
-membranes are said to be fluid
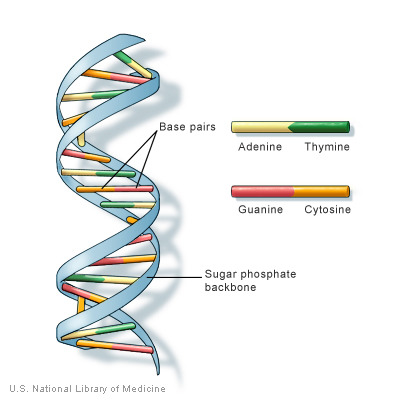
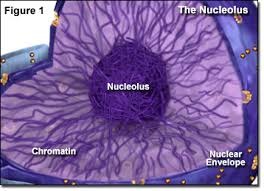
-makes ribosomes
-contains RNA, DNA and proteins
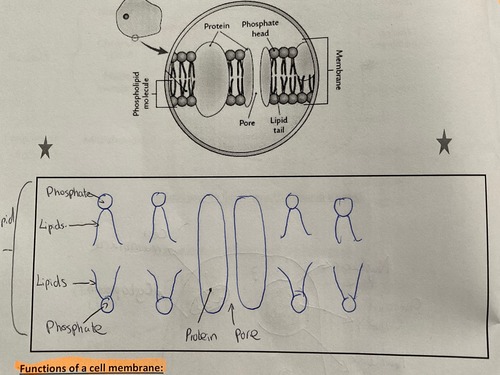
* __prevents__ it from bursting at it fills with water
* It is __fully permeable__ and has no control over the entry of substances into the cell.
* Stores sugars and salts that are dissolved in water.
* When water moves into the vacuole, it pushes the cytoplasm against the cell membrane and cell wall giving the cell turgor (turgidity)
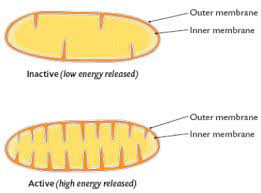
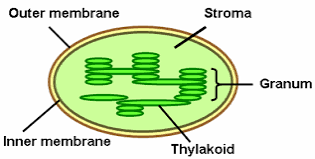
* Grana are the stacks of these thylakoid disks formed inside the chloroplast.
This is the key difference between grana and thylakoids
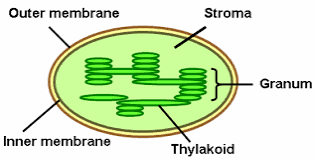
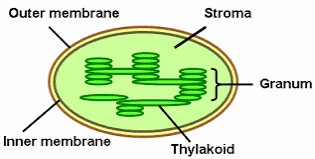
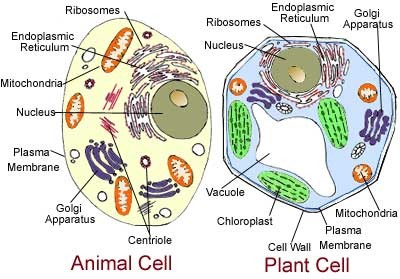
* Cell wall (shape is rigid)
* Large vacuoles
* Chloroplasts
\
__Animal Cell__
* No cell wall (shape can change)
* Small vacuoles
* No chloroplasts
1. retains organelles in the cell
2. acts as a selectively-permeable barrier
3. contains receptor sites (for matching molecules such as hormones)
4. displays antigens (molecules that stimulate the formation of anitbodies
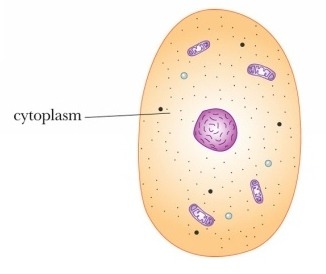
1. separates organelles
2. acts as a storage area for food, salts
3. chemical reactions occur there
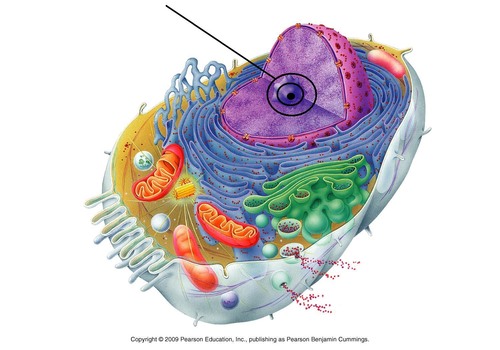
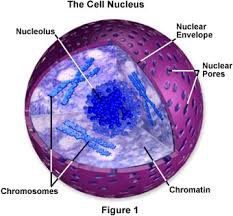
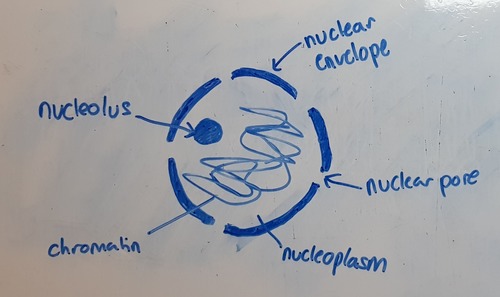
1. controls cell structures and function
2. DNA replication and nuclear division
3. controls the formation of mRNA
* retains the nuclear contents
* has pores to allow materials in and out of the nucleus
(ii)to prevent plant cells from bursting when water is taken in by osmosis (It allows the development of turgor.)
(ii) stores food (sugar, salt, protein, amino acids, etc.)
(iii) holds gases (02 , CO2)
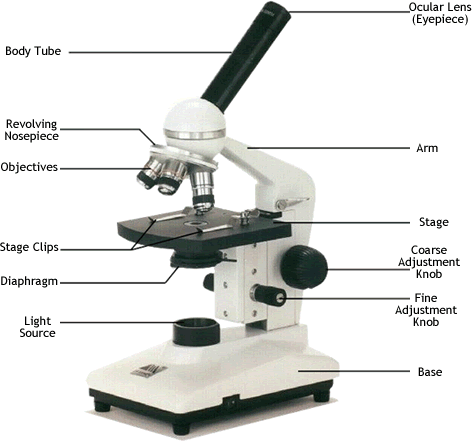
When looking at animal cells under the microscope, describe how you obtained a sample of the cells
Rubbed the inside cheek with a swab
Why is a coverslip used?
to protect the lens
to protect the sample from drying out
Describe how you examined cells using the microscope
Focus using coarse focus
Focus using fine focus
(Marking scheme 3+3)
State the precise location of the cell membrane in plant cells
immediately inside the cell wall
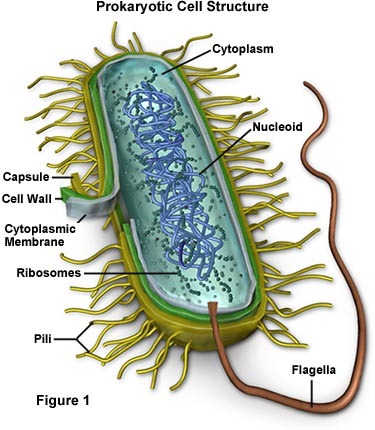
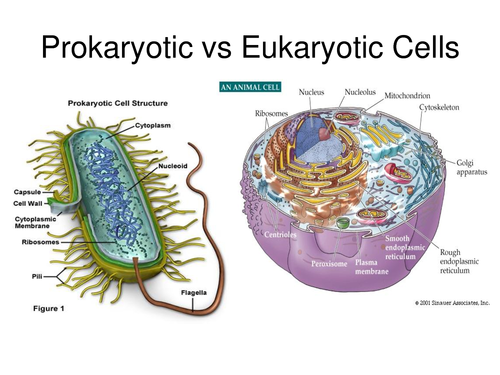
With what type of cell do you associate membrane-bound organelles?
What corresponding term is used to describe bacterial cells?
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic
The cell membrane is described as being selectively permeable, what does this mean?
Only some substances allowed through
Why is diffusion alternatively known as passive transport?
No (or little) energy (ATP) required
Osmosis is described as a ‘special case of diffusion’ Explain why.
The movement of water or (osmosis) requires a membrane
Name the structure by which Amoeba gets rid of excess water that has entered by osmosis
Contractile vacuole
Give two locations in a cell at which there is a selectively permeable membrane
nucleus, vacuole or chloroplast, mitochondrion
Explain the biological basis for the use of high sugar or high salt concentrations in the preservation of food.
bacteria loses water by osmosis and this causes death
In the human diet zinc, iron and copper are examples of…
In the human diet zinc, iron and copper are examples of trace elements.
The walls of xylem vessels are reinforced with…
lignin
Where in the cell would you expect to find phospholipids?
cell membrane
Vitamin … is an example of a water soluble vitamin.
Vitamin C is an example of a water soluble vitamin.
Name a disorder associated with the deficiency of vitamin D
rickets
What are the final products of digestion of a protein?
amino acids