The Endocrine System and Fight or Flight Response
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
soz for memees it was 9pm and i was feeling cheeky x
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Describe the function of the endocrine system
Communicates chemical messages (i.e. hormones) to the organs of the body
Hormones regulate body’s growth, metabolisms and sexual development
Name the major glands of the endocrine system (PPART)
Pituitary gland
Pineal gland
Adrenal glands
Reproductive organs (testes & ovaries)
Thyroid
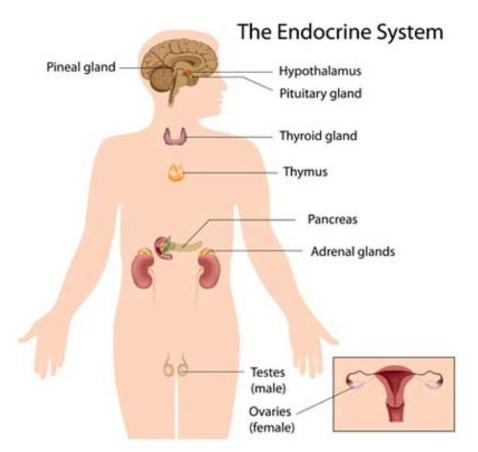
Describe the function of glands in the endocrine system
Organs that produce and secrete hormones to regulate many bodily functions
Major gland = pituitary gland since it controls the release of hormones from all other endocrine glands in the body
Describe the function of hormones in the endocrine system
Chemicals that circulate the bloodstream
Influence target organs that have a receptors for that hormone in order to regulate bodily activites
Produced in large amounts but disappear quickly
Very powerful effects
Describe adrenaline
Gland
Location
General effects
Behavioural effects
Gland: Adrenal medulla (part of the adrenal glands)
Location: Adrenal glands above the kidneys
General effects:
Involved in body’s fight or flight response
Increases heart rate and expands airways etc.
Behavioural effects:
Heightens alertness and increases focus
Prolonged exposure to high levels due to chronic stress can lead to anxiety and difficulty sleeping

Describe testosterone
Gland
Location
General effects
Behavioural effects
Glands:
Testes in males
Ovaries in females
Adrenal glands in both
Location:
Testes (scrotum)
Ovaries (pelvic cavity)
Adrenal glands (above kidneys)
General effects:
Promotes muscle and bone growth
Leads to development of male secondary sexual characteristics
Females - helps to maintain bone density
Behavioural effects:
Increases aggression and competitiveness
Associated with risk-taking behaviours and dominance in social contexts

Describe melatonin
Gland
Location
General effects
Behavioural effects
Gland: Pineal gland
Location: Centre of the brain
General effects:
Regulates sleep-wake cycle
Induces sleepiness and lowers body temperature
Behavioural effects:
Induces sleep patterns and can contribute to mood changes
May affect cognitive performance and alertness
Lack of melatonin is associated with insomnia and mood disorders
Describe progesterone and oestrogen
Gland
Location
General effects
Behavioural effects
Glands:
Ovaries
Adrenal glands
Placenta (during pregnancy)
Location:
Ovaries (pelvic cavity)
Adrenal glands (above the kidneys)
Placenta (uterus)
General effects:
Prepares uterus for implantation and maintains pregnancy
Regulates menstrual cycle
Behavioural effects:
May promote calmness and relaxation
Affects mood and contributes to mood swings and irritability - especially during PMS

Describe cortisol
Gland
Location
General effects
Behavioural effects
Glands:
Adrenal glands
Location:
Above the kidneys
General effects:
Plays key role in stress response by increasing blood sugar and suppressing immune system
Helps the body respond to danger by providing quick source of energy
Behavioural effects:
High levels of cortisol are associated with anxiety and irritability
Chronic stress can lead to depression and fatigue

Draw flow chart of fight or flight response
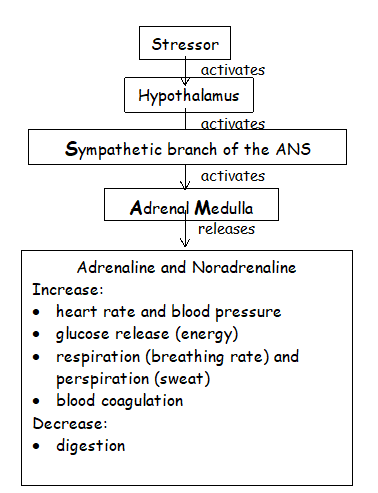
Give examples of what happens to the body during sympathetic state
Increased heart rate
Dilates pupils
Increased breathing rate
Inhibits saliva production
Inhibits digestion

Describe the fight or flight response
Hypothalamus directs the sympathetic branch of the ANS to send neurotransmitters to the adrenal medulla
Results in release of adrenaline into bloodstream and causes a ‘fight or flight’ response
This leads to activation of emergency functions such as increased heart rate and blood pressure
Non-emergency body processes such as digestion are suppressed here
Parasympathetic branch of the ANS kicks in when threat has passed
