22. bone pathology 3 (metabolic & inflammatory)
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
metabolic & inflammatory bone disease
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what is osteoporosis?
decreased bone with clinical disease
reduction in the quantity of bone mass, the quality of which is normal
cortical bone is reduced in thickness and increased in porosity → lacks strength and is easily fractured
osteoporosis causes
starvation
corticosteroids (hyperadrenocorticism)
disuse
aging
intestinal parasitism (chronic, severe)
trichostrongylus or ostertagia infections in lambs
calcium deficiency with normal levels of phosphorus and vitamin C
copper deficiency (various species) → brittle bone
what is the difference between rickets and osteomalacia?
rickets → disease of young, rapidly growing animals
osteomalacia → disease of mature animals
rickets/osteomalacia pathology
failure of mineralization of growth cartilage (rickets) and/or osteoid matrix (both rickets and osteomalacia)
rickets: abnormal endochondral ossification and defective bone formation with subsequent bone deformities and fractures
osteomalacia: similar to rickets but does not result in growth cartilage lesions
most common causes of rickets/osteomalacia
vitamin D deficiency
phosphorous deficiency
consequences of rickets/osteomalacia
bones break easily, marrow cavity enlarged, cortex thin and spongy
fractures on ribs, pelvis, and long bones of cattle; vertebral column of pigs
curving of keel bone with rib fractures common in laying hens
fibrous osteodystrophy pathology
increased osteoclastic resorption of bone, which is replaced by fibrous connective tissue
weak bones → lameness, pathologic fractures, and bone deformities
pathogenesis/causes of fibrous osteodystrophy
primary hyperparathyroidism (rare) → high PTH production
paraneoplastic
production of PTH-related protein (PTHrP)
secondary hyperparathyroidism
nutritional: low Ca:high P
renal: usually dog with renal disease → retain P, decreased 1,25 vitamin D (→ decreased Ca absorption)
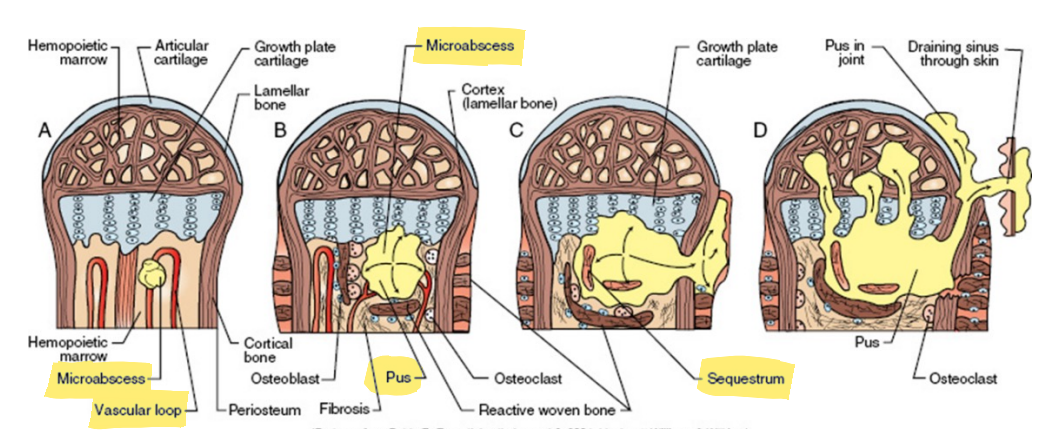
causes of bacterial/fungal osteomyelitis
direct trauma to bone
extension from infected soft tissue/wounds
actinomyces bovis
hematogenous → metaphysis
trueperella pyogenes, e. coli
staph aureus, mycobacterium avium
brucella sp.
coccidioides immitis, blastomyces dermatiditis
pathogenesis of bacterial/embolic osteomyeltitis
most common in young animals at metaphysis
capillaries make sharp turn to join medullary veins → slower and less turbulent blood flow → embolus gets trapped → abscess → sequestrum