Sociology Pt 1
5.0(7)
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
What is Sociology?
The systematic study of society and studies human interconnectedness
2
New cards
What is human interconnectedness?
assumes humans only live together in collective and must then study them in collective
3
New cards
Why is the object of study of sociology historical?
the level of complexity of the object of study depends on the part of society being studied
4
New cards
What is division of labour?
describes the phenomenon that different members are assigned different tasks to complete dependant on the role they have
5
New cards
How is the division of labour different for humans?
Depends on the society which is chosen by humans
6
New cards
Is social organization necessary for humans?
no. It only matters that there is social organization but the type can change
7
New cards
What parts of society do sociologists study?
Every single thing that leads to what is being studied (i.e orchestra example)
8
New cards
How does sociology contrast with other humanities?
Studies the humanity and its relationship to society
9
New cards
What is co-constitution?
Mills
the relationship between the individual and the society they are in (can’t understand one without the other)
the relationship between the individual and the society they are in (can’t understand one without the other)
10
New cards
How do individual decisions affect society?
Marx
Society is nothing without individual decision making capacity
Individuals are responsible for decisions in their own life but the decisions are made from circumstances they cannot control and thus limits the available decisions
Society is nothing without individual decision making capacity
Individuals are responsible for decisions in their own life but the decisions are made from circumstances they cannot control and thus limits the available decisions
11
New cards
Individual decision vs Circumstance?
Individual decision: whether to study
Circumstance: money, family support, responsibilities
Circumstance: money, family support, responsibilities
12
New cards
What is the sociological Imagination?
Emphasizes the co-constitution of individual people and the societies in which they are embedded (people create societies; societies create people)
Links biography and history
Links biography and history
13
New cards
What is biography / personal troubles?
the life trajectory and experience of an individual person
14
New cards
What is history / Public issues?
the trajectory of a society over a period of time
15
New cards
What is the nature of relationship between personal troubles and public issues?
Social forces
16
New cards
What are Social Forces?
societal level mechanisms that influence the character of individuals and their life trajectories
Two types: ideology/culture or social structure
Two types: ideology/culture or social structure
17
New cards
What is ideology/culture?
Systems of thought that influence choices about behaviour
behaviour is experienced as being unique to the individual, but exhibits observables patterns
Study the effect of ideology by observing those patterns
Example: marriage culture says need to be in love so may choose to divorce if not
behaviour is experienced as being unique to the individual, but exhibits observables patterns
Study the effect of ideology by observing those patterns
Example: marriage culture says need to be in love so may choose to divorce if not
18
New cards
What is social structure?
How the social world is organized to elicit particular patterns of practical activity
Example: anyone who petitions can divorce
Example: anyone who petitions can divorce
19
New cards
Objective vs Subjective?
Subjective: related to a subjectivity (mind/thought)
Objective: related to physical reality
Objective: related to physical reality
20
New cards
What is agency?
the capacity for indivdual decision making, always a part of societal reproduction
21
New cards
What influences society?
structure, culture and agency all influence each other which influence society
22
New cards
What is Societal Reproduction?
when individuals behave in a way that is consistent with the ideologies and structures they are embedded and thus reproduce the ideology and structure
Not behaving with them leads to social change
Not behaving with them leads to social change
23
New cards
What is empirical?
based on, concerned with or verifiable by observation or experience
24
New cards
How is sociology an empirical discipline?
sociologists rely on data and observation when we say things about the social world
25
New cards
Moral truth vs Empirical truth?
Moral: what’s right
Empirical: what it is
Empirical: what it is
26
New cards
What can be studied empirically?
Example: religion
Cannot: existence of god, truth of religion, moral claims
Can: network structure of a place of worship, degree of religious observance in a society, etc
Cannot: existence of god, truth of religion, moral claims
Can: network structure of a place of worship, degree of religious observance in a society, etc
27
New cards
How do sociologists separate their biases from their study?
Focus on what we actually observe
28
New cards
Anecdotes vs Systematic data?
Anecdotes: unreliable
Systematic data: reliable
Systematic data: reliable
29
New cards
What are research questions?
what a research project sets out to answer. Generally deals with concepts
30
New cards
What are the levels of analysis?
Micro, mezzo, macro
31
New cards
What is the micro research scope
social interactions between individual people
Example: family members
Example: family members
32
New cards
What is the mezzo research scope?
One organization and its structure
Example: students at u of m
Example: students at u of m
33
New cards
What is the macro research scope?
multiple sites. governmental / national
Example: Canadian uni students
Example: Canadian uni students
34
New cards
What two categories does social data fall into?
Quantitative and qualitative
35
New cards
What is quantitative data?
data that is numerical or can be represented using mathematics or statistics. involves translating social reality into measurable variables
Example: income, major, age, etc
Example: income, major, age, etc
36
New cards
What is a variable?
Some characteristics that differs from subject to subject or from time to time
Example: university major
Example: university major
37
New cards
What is qualitative data?
Data that is represented in prose. Often a part of the social world that cannot be translated into a numerical representation
38
New cards
What are the quantitative methods?
two steps. 1. Data collection 2. Data analysis
39
New cards
What is operationalization?
involves researchers specifying precisely how concepts are translated into variables. Each variable has faults and excludes information
process of turning abstract concepts into variables
process of turning abstract concepts into variables
40
New cards
What is an independent variable?
the variable that is hypothesized to have some effect. The cause
41
New cards
What is a dependent variable?
the variable hypothesized to be influenced by the independent variable. thing that is caused
42
New cards
What is sample?
a subset of the population that is actually empirically studied
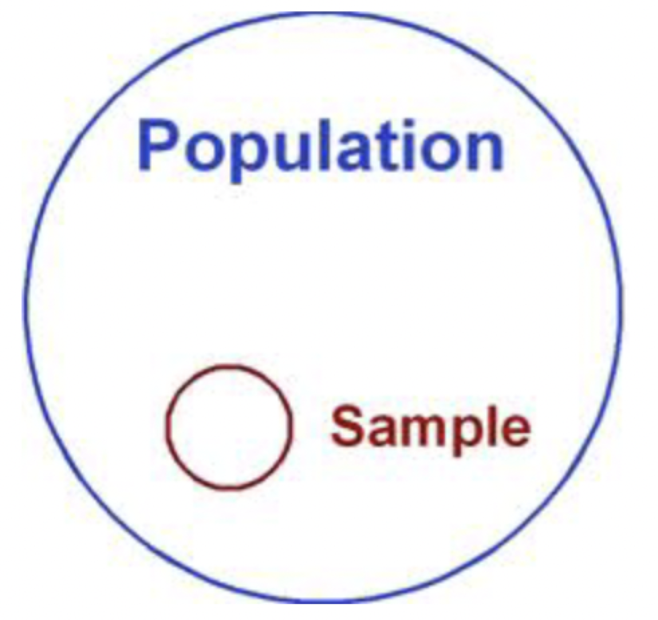
43
New cards
What is the population?
The universe of cases that the research question is relevant to
44
New cards
What is generalizability?
the extent to which observations about a sample can be reasonably assumed to represent a population
45
New cards
What are the four types of sampling procedure?
random, representative, convenient, snowball sampling
46
New cards
What are the sampling procedures in relation to generalizability?
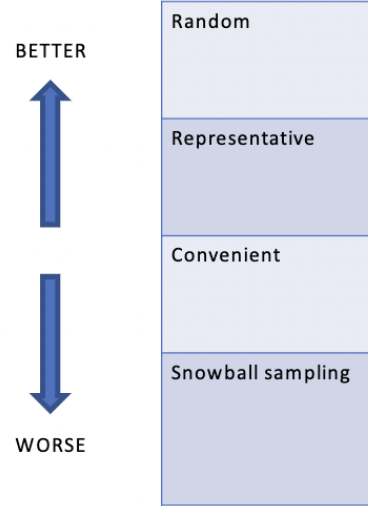
47
New cards
What is random sampling procedure?
Each individual of the population has an equal opportunity of being chosen
48
New cards
What is representative sampling procedure?
The sample is a reproduction of the population along particular demographic characteristics
49
New cards
What is convenient sampling procedure?
People are sampled based on their availability
50
New cards
What is snowball sampling procedure?
People that have been sampled introduce the researcher to other possible research participants
51
New cards
What are three other quantitative methods in sociology?
Secondary analysis, data scraping, quantitative content analysis
52
New cards
What is secondary analysis?
when researchers analyze existing data in a novel way
53
New cards
What are the pros of secondary anlysis?
Sample size, sampling technique, cost
54
New cards
What are the cons of secondary analysis?
limited existing questions, cannot go back and ask for more
55
New cards
What is data scraping?
using computer algorithms to generate data about peoples online behaviour
56
New cards
What is quantitative content analysis?
the analysis of the content of some media. a study of what people produce.
Ex
Ex
57
New cards
What are the variables for quantitative analysis?
nominal/categorical, ordinal, ratio
58
New cards
What are nominal / categorical variables?
Numbers are used to represent different conditions but the phenomenon is not quantitative
Example: race. marital status
Example: race. marital status
59
New cards
What are ordinal variables?
different values of the variable can be ranked but there is no way to measure the precise difference between ranker values
Example: class, pain, likert scale
Example: class, pain, likert scale
60
New cards
What are ratio variables?
Differences between values are measurable, and there exists a real zero (limit)
Example: income, number of siblings
Example: income, number of siblings
61
New cards
62
New cards
What is central tendency?
the average? measures of central tendency attempt to give a quick pic of the content of one variable
63
New cards
What is mode?
the variable value that is the most common or has the highest count.
For nominal variables: the measure of central tendency.
calculated for numerical, ordinal, ratio
For nominal variables: the measure of central tendency.
calculated for numerical, ordinal, ratio
64
New cards
What is median?
the value that separates the sample number into two equal halves.
Calculated for ordinal and ratio variables.
Calculated for ordinal and ratio variables.
65
New cards
What is mean?
the average value. Sum of variables / number of cases. Calculated for ratio variable
66
New cards
What is proportion?
tells us the percentage of a variable that falls into one particular variable value. Between 0 and 1
67
New cards
What is the normal curve?
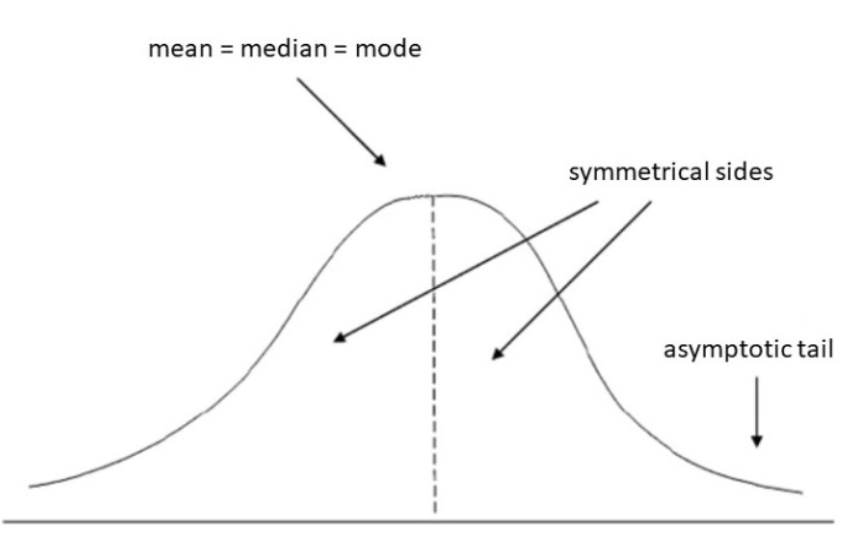
68
New cards
What is kurtosis?
When variable is more skinny or more spread out
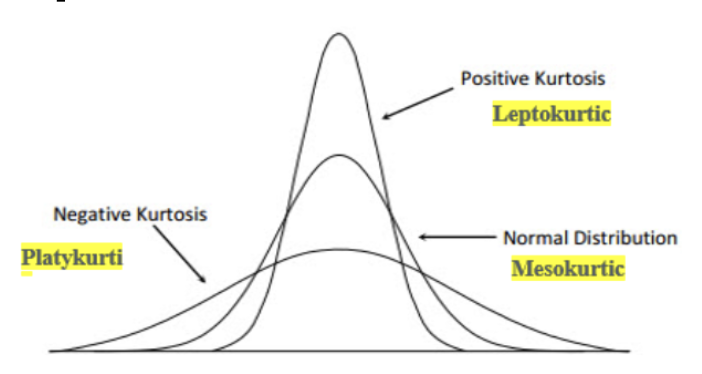
69
New cards
What is deviation from normality: skew?
Positive: mode < median < mean (ex: income)
Negative: mode > median > mean
Negative: mode > median > mean
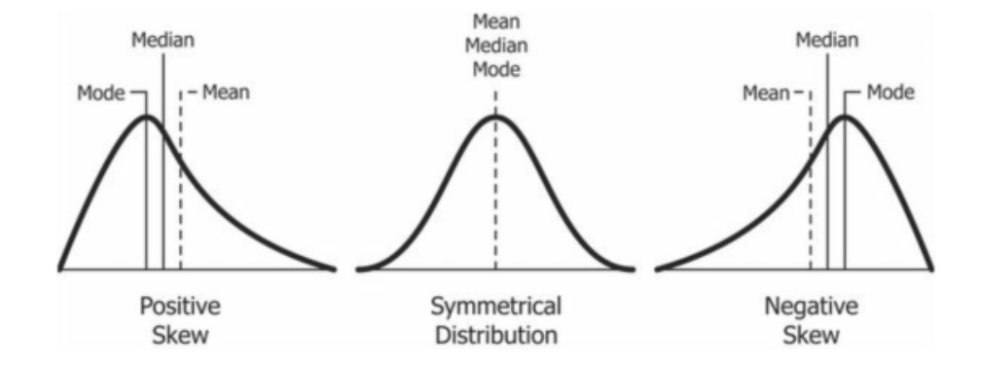
70
New cards
What is an outlier?
extreme cases that over influence the median and the mean.
Sometimes appropriate to exclude
Sometimes appropriate to exclude
71
New cards
What is bi-modal distribution
Two humps with a flat point in the middle
72
New cards
What is inferential statisictics?
Measures the relationship between two or more variables. Knowing the value of one lets us make an inference about another variable
73
New cards
What is bivariate statistics: cross tab
Measure the relationship between two variables. Cross tab is useful for calculating the relationship between two variables when at least one is nominal/categorical
74
New cards
What is bivariate statistics: correlation coefficient?
measures the relationship between two ratio-level variables. -1 to 1. 0 is no relationship. The closer to 1 the more the values correspond to one another
75
New cards
What is negative correlation?
closer to -1
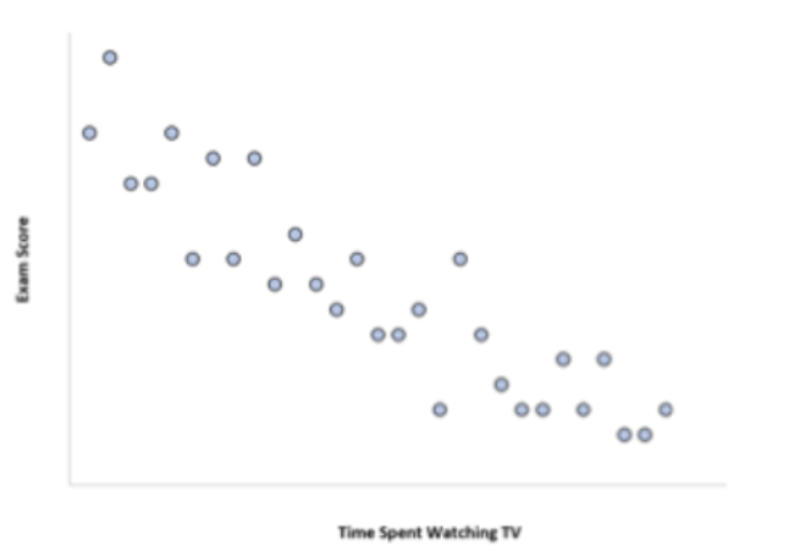
76
New cards
What is positive correlation
closer to 1
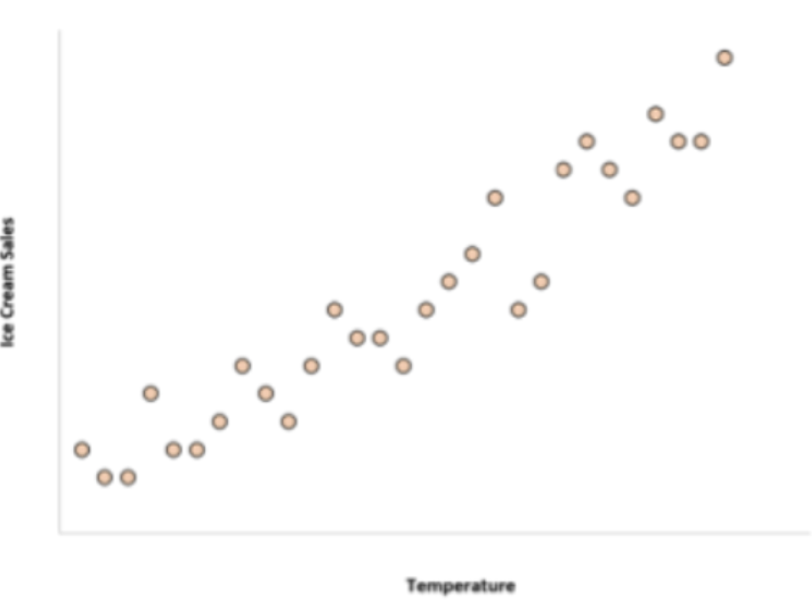
77
New cards
What is multivariate statistics?
describe the effect of several independent variables at once on some dependent variable. Needed because we dont use experiments. Has multiple independent variables
Ex. measure the time spent watching tv and the effect and parental income and
Ex. measure the time spent watching tv and the effect and parental income and
78
New cards
What are the weaknesses of qualitative research?
not generalizable
79
New cards
What are the pros of qualitative research?
limit of what you can observe is not imposed by the limits of the data collection (asks more than just the question)
80
New cards
What are the steps of qualitative interviews?
design interview schedule, sample and conduct interviews, transcribe interviews, analyze transcripts
81
New cards
What is saturation
when a researcher determines that further data collection is unlikely to yield new information
Happens for qualitative research
Happens for qualitative research
82
New cards
How do you analyze a qualitative interview?
coding.
Transcribe into a document, search for salient themes of codes.
Transcribe into a document, search for salient themes of codes.
83
New cards
What is inductive coding?
Codes are generated from the data. When research question is exploratory. Example: what are the most important parts of the pandemic?
84
New cards
What is deductive coding?
Codes are developed in advance. When a research question is specific
85
New cards
What is ethnography?
the researcher embeds themself in the social milieu they wish to study.
Can range from complete participant to complete observer
Can range from complete participant to complete observer
86
New cards
What are the steps of Ethnography?
select research site and gain access, observe for min of 1 year, data is field notes
87
New cards
What is the role of the researcher in Ethnography?
the researchers social position has a huge impact on the quality of the data they are able to generate. ie outsider is an advantage or you must be demographically linked to the research site
88
New cards
What is qualitative content analysis?
the researcher analyzes the data using thematic codes