CH 13: Reactions at The Alpha Carbon of Carbonyl Compounds
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is a carbon acid and who is it bonded to?
A compound that has sp3 hybridized carbon bonded to α-hydrogens that are relatively acidic.
Why is the α-hydrogen usually attacked by a base?
It is relatively acidic. Since the α-carbon is bonded to a carbonyl group (C=O), it stabilizes the resulting enolate ion after deprotonation, making the hydrogen atom more easily removed.
What mechanism uses a catalyst?
keto-enol interconversion in acidic and basic conditions
halogenation in acidic condition
intra/intermolecular adol addition in basic condition
Which compounds have the most acidic α-hydrogens?
The α-hydrogens of aldehydes are the most acidic.
Which compounds have the least acidic α-hydrogens?
The α-hydrogens of amides are the least acidic.
What is the more stable (enol or keto) form for aldehydes and ketones?
The ketone form is the more stable form.
What stabilizes the enol tautomer in aldehydes and ketones?
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
What is the more stable (enol or keto) form for phenol? Why?
Enol tautomer predominates because it is aromatic.
What type of reactions uses the α-carbon bonded to carbonyl compounds to form enols?
Substitution reactions
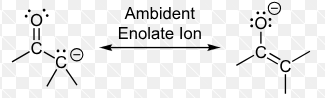
How many nucleophilic sites does an enolate have?
Two nucleophilic sites
Which (oxygen or carbon) nucleophilic site does protonation preferentially occur on?
Oxygen site
What is likely the nucleophile if the oxygen site is not involved?
The carbon site is likely the nucleophile.
Under acid condition, what reagents reacts with carbonyl compounds to replace one α-hydrogen with a halogen?
X2, H3O+
Under basic conditions, what reagents react with carbonyl compounds to replace ALL α-hydrogens with halogens?
(excess) X2, X+ -OH
Who does the alkylation method work on?
Ketones, esters, and nitriles at the α-carbon.
Why do aldehydes give poor yields in alkylation?
They react with themselves under basic conditions.
In an aldol addition, how does one carbonyl compound act?
acts as a nucleophile
What is the role of the other carbonyl compound in an aldol addition?
It acts as an electrophile which is the carbonyl carbon.
Are ketones more or less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than aldehydes? Why?
Less susceptible due to steric hindrance.
What can an aldol addition product lose to form an aldol condensation product?
Water (H2O)
What does mixed aldol addition produce?
A mixture of products.
What do intramolecular aldol additions require?
A compound containing two carbonyl groups.
What type of rings do 1,4-diketones afford in intramolecular aldol additions?
Five-membered rings.
What reaction can esters undergo due to containing both α-hydrogens and a carbonyl bond?
Substitution reaction.
In a Claisen condensation, what acts as the nucleophile?
One ester who becomes the enolate.
What bond is formed during the Claisen condensation?
A new carbon-carbon bond.
What is the function of the base used in Claisen condensation? Why?
To be the alkoxy of the ester to avoid trans-esterification.
What is a similar mechanism to the Claisen condensation?
Aldol condensation.
What mechanism(s) use up their reagents? In other words, what mechanism(s) do not replenish their reagents?
Halogenation in basic condition
Claisen condensation
What reagents react with carbonyl compound to replace α-hydrogen with an alkyl substituent?
1) Strong, bulky base in polar aprotic solvent (LDA/THF)
2) alkyl halide/haloalkane
What reagents react with carbonyl compound to replace the α-hydrogen with an alcohol chain?
1) X+ -OH, H2O
2) carbonyl compound (acts as the E+)
What reagents react with carbonyl compound (aldehyde) to replace the two α-hydrogen with a double (or pi) bond?
1) X+ -OH, H2O
2) carbonyl compound (acts as the E+)
3) H3O+, heat
What reagents react with carbonyl compound (ketone) to replace the two α-hydrogen with a double (or pi) bond?
1) X+ -OH, H2O
2) carbonyl compound (acts as the E+)
3) -OH, heat
In a mixed adol addition, how many possible enolates can be made? How many possible products can be made?
2 enolates, 4 products
What ring can 1,5 and 1,7-diketones afford?
6-membered ring
What ring can 1,6-diketones afford?
5-membered ring
What reagents react with carbonyl compound to replace α-hydrogen with a ß-ketone?
1) X+ -OR
2) H3O+
What is an enolate ion?
negatively charged carbonyl compound