Understanding Placenta Previa and Related Conditions
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
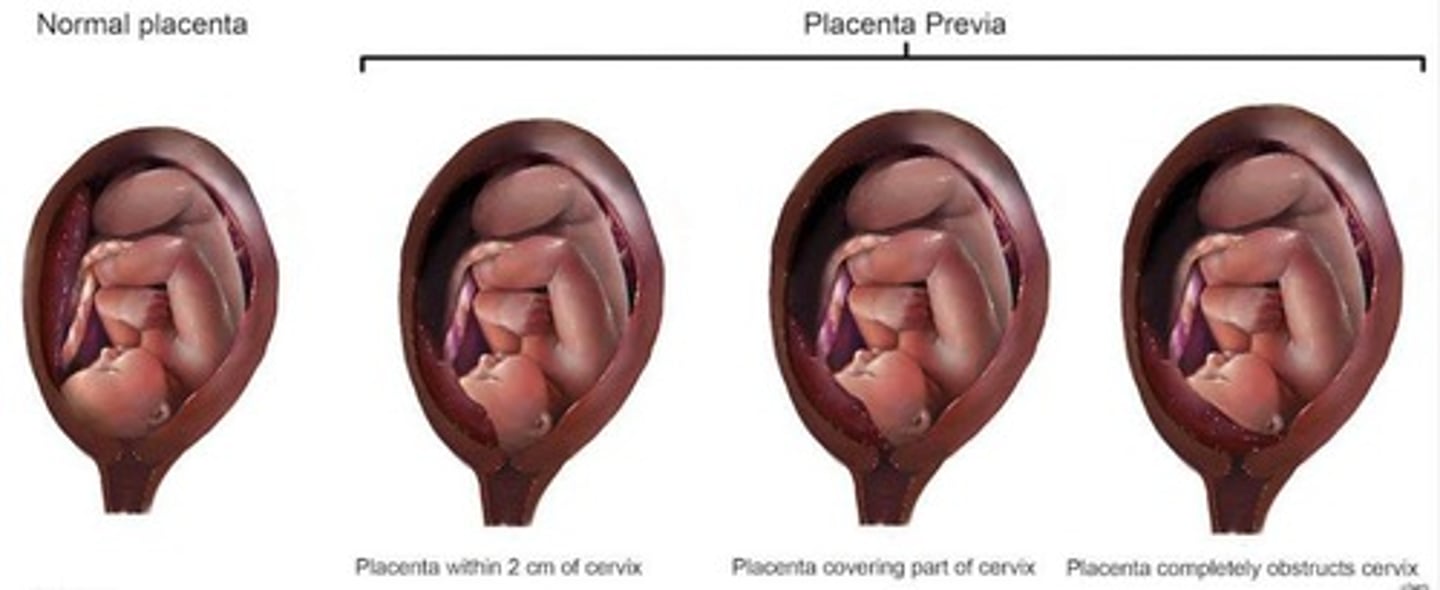
Placenta Previa
Placenta attaches near or over cervical opening.
Placental Migration
Self-resolution of placenta previa during pregnancy.
Hemorrhagic Bleeding
Life-threatening bleeding in third trimester.
Incidence of Placenta Previa
Affects approximately 0.5% of pregnancies.
Cesarean Section Risk
10% incidence after four cesarean deliveries.
Low Egg Implantation
Fertilized egg implants low in the uterus.
Uterine Fibroids
Noncancerous growths in or on the uterus.
Uterine Scarring
Damage to uterine lining affecting implantation.
Previous Placenta Previa
Recurrence rate of 4-8% in subsequent pregnancies.
Myomectomy
Surgical removal of fibroids preserving the uterus.
Cocaine Use Risk
Increases likelihood of placenta previa.
Multiple Gestations
Pregnancy involving twins or more.
Multiparity
Having multiple previous pregnancies.
Advanced Maternal Age
Increased risk for women over 35 years.
Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Anemia from fetal red blood cell destruction.
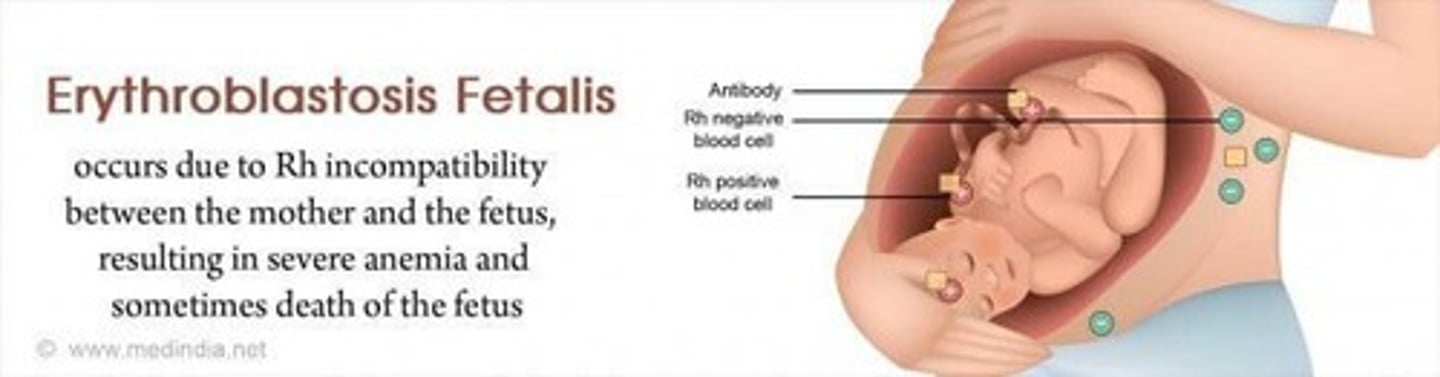
Rh Factor
Inherited protein on red blood cells.
Rh Positive
Blood type with Rh factor present.
Rh Negative
Blood type lacking Rh factor.
RhoGAM
Medication preventing Rh-positive blood cell attack.
Direct Coombs Test
Confirms antibody-induced hemolytic anemia diagnosis.
Sensitization
Immune response to Rh-positive blood exposure.
Yellow Amniotic Fluid
Indicates bilirubin presence from blood breakdown.
ABO Incompatibility
Blood group incompatibility causing fetal anemia.
Maternal Immune Reaction
Mother's immune system attacks fetal red blood cells.
Symptoms of Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Range from mild anemia to fetal death.
Fetal Blood Group Inheritance
Fetus inherits blood factor from father.
Uterine Structural Abnormality
Physical abnormalities affecting uterine function.
Anti-D Immunoglobulin
Injection preventing RhD sensitization.
Bilirubin
Substance causing yellow amniotic fluid.
Cigarette smoking
Causes carbon monoxide hypoxemia in pregnancy.
Hyperplacentosis
Increased placental weight and hCG levels.
Jaundice
Yellowing of skin and eyes in infants.
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD)
Tumors from abnormal trophoblastic proliferation.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone produced by trophoblast cells.
Hydatidiform moles
GTD with villi present in placenta.
Trophoblastic neoplasms
GTD lacking villi in the placenta.
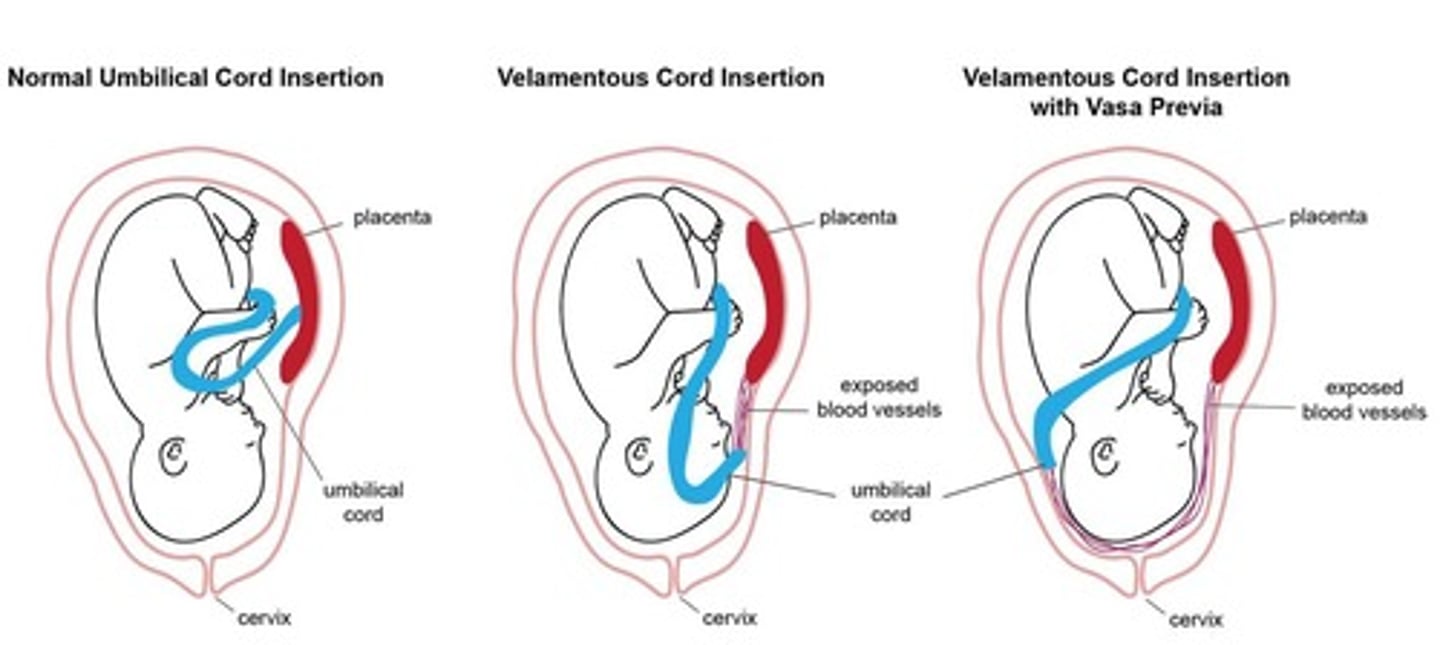
Velamentous cord insertion
Abnormal cord insertion with diverging vessels.
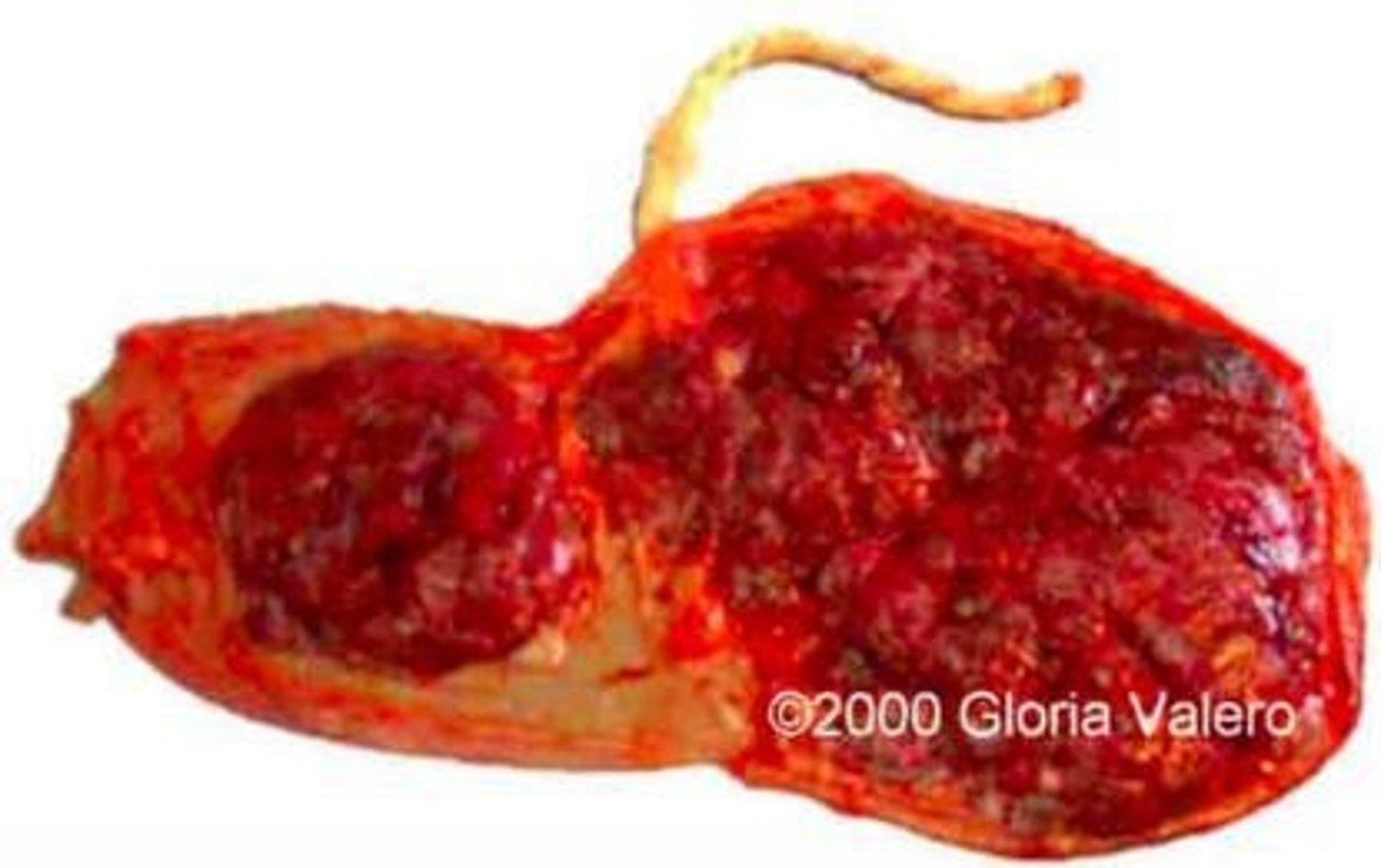
Succenturiate lobe
Accessory placental lobe smaller than main lobe.
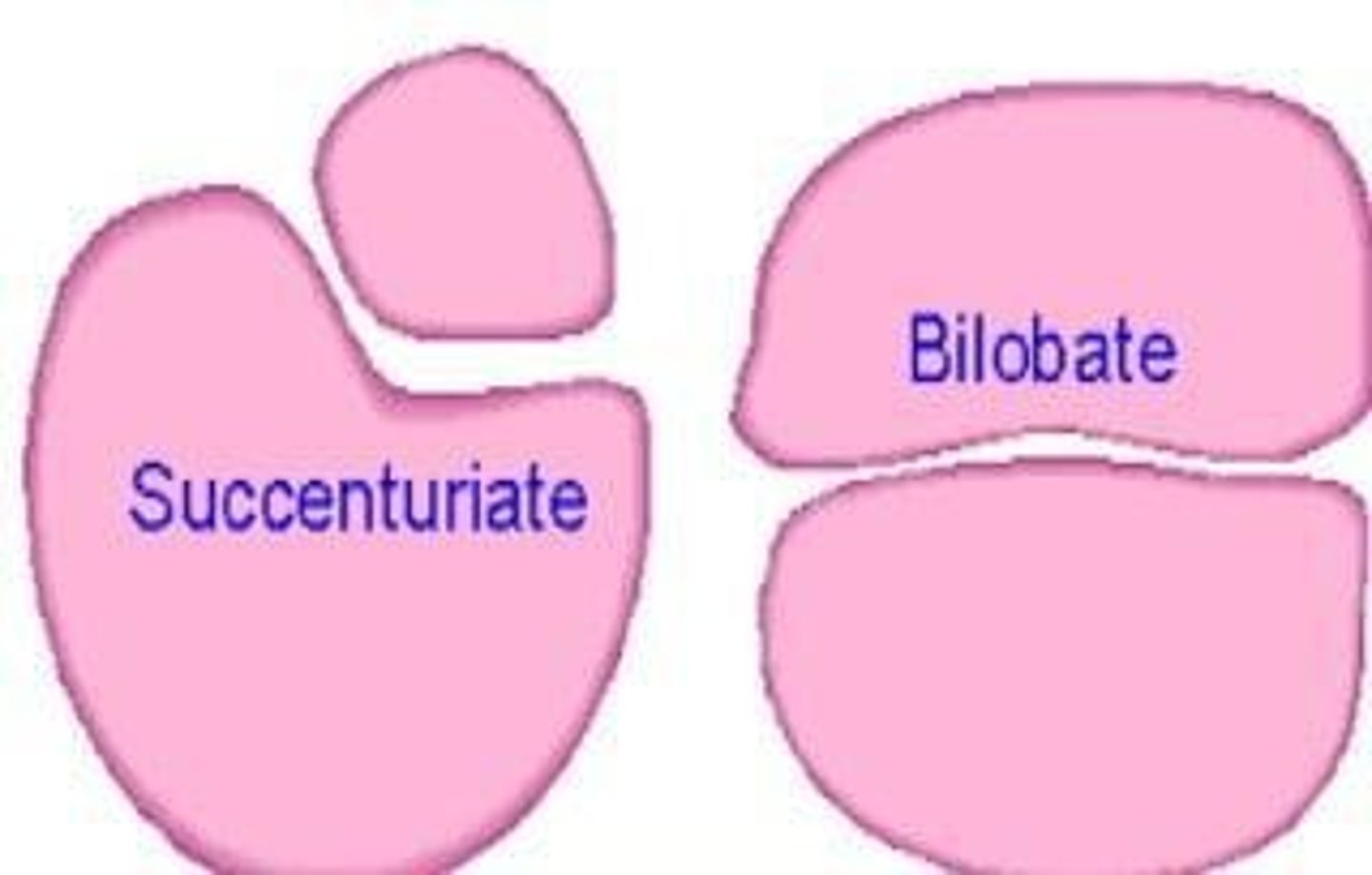
Bipartite placenta
Placenta divided into two nearly equal lobes.
Placenta accreta
Placenta grows too deeply into uterine wall.
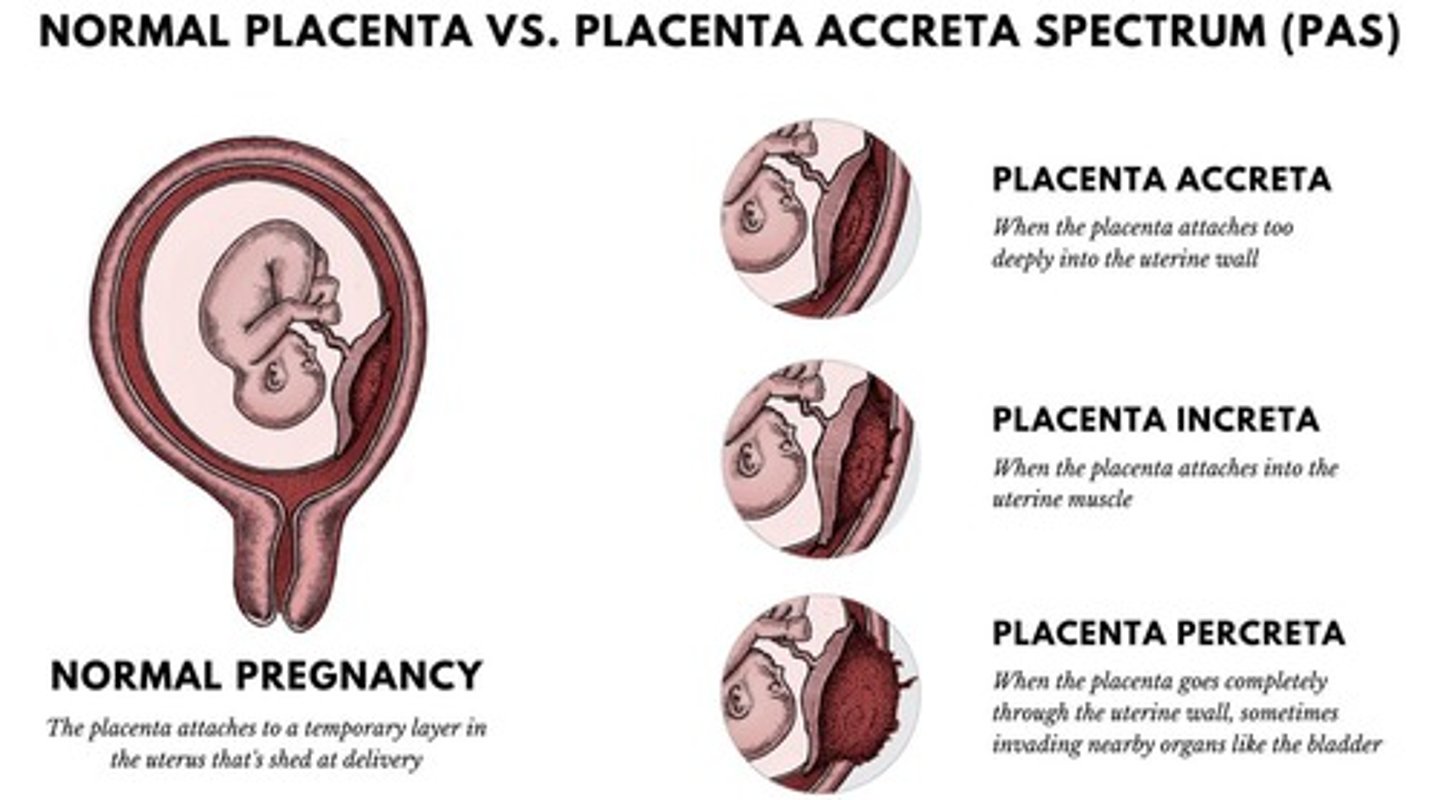
Placenta increta
Placenta invades muscle wall of uterus.
Placenta percreta
Placenta grows through uterus to nearby organs.
Vaginal bleeding
Common symptom in second half of pregnancy.
Bright red bleeding
Characteristic of placenta previa complications.
Low implantation
Fertilized egg implants too low in uterus.
Uterine fibroids
Abnormal growths affecting uterine lining.
Placenta previa
Placenta partially or completely covers cervix.
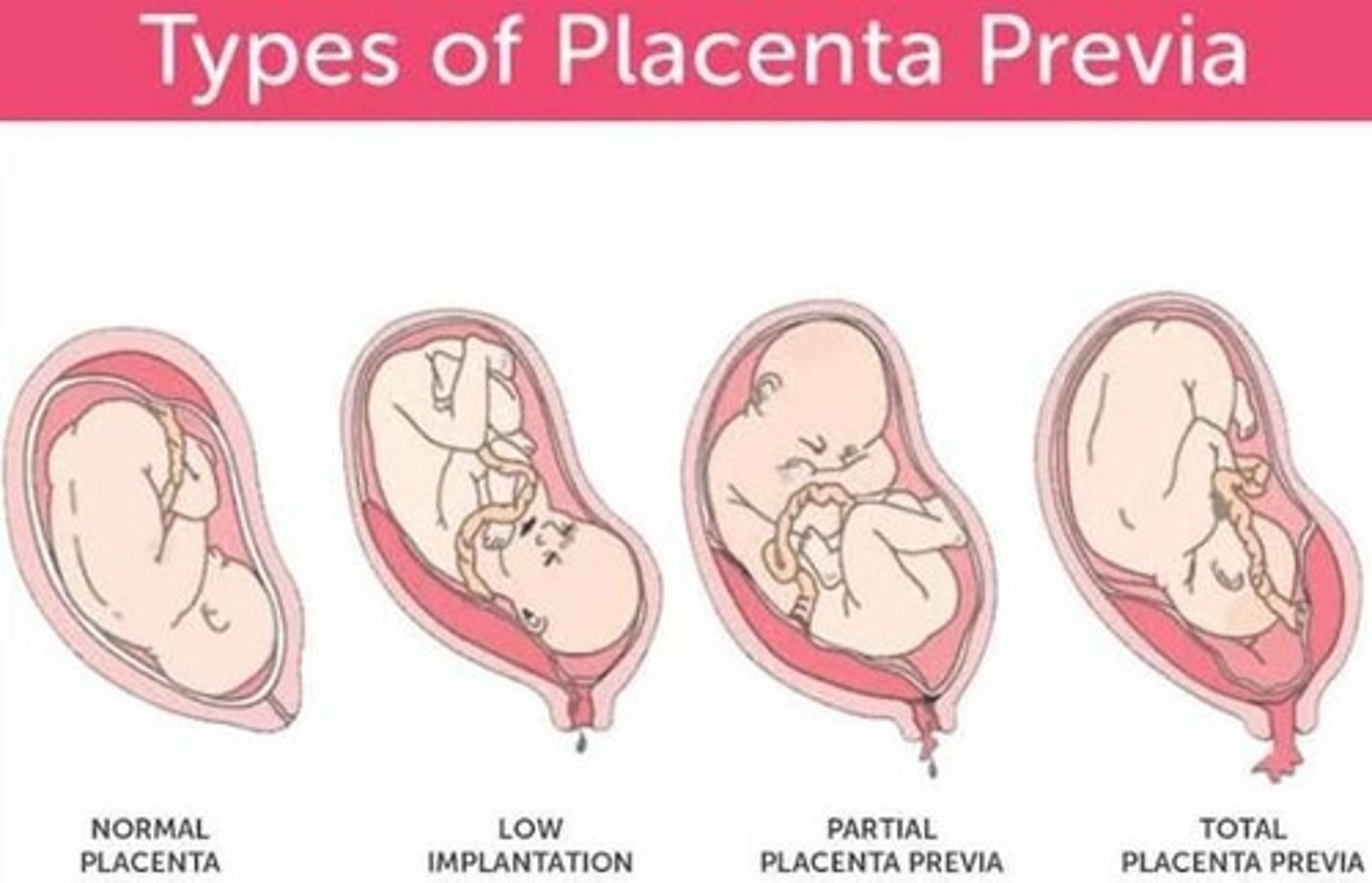
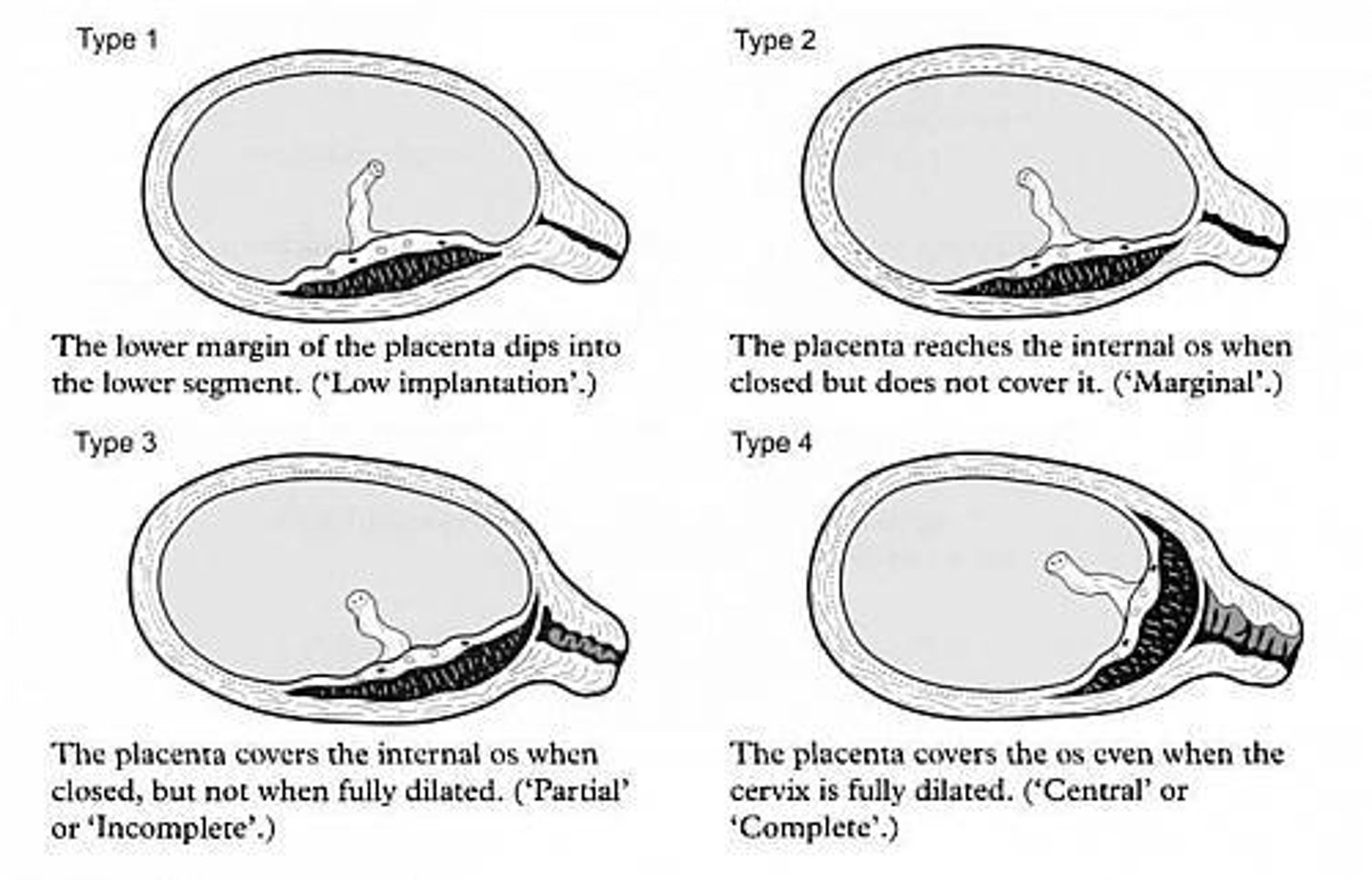
Type I placenta previa
Low-lying placenta not reaching internal os.
Type II placenta previa
Placenta reaches but does not cover cervix.
Type IIA placenta previa
Marginal anterior placenta near cervix.
Type IIB placenta previa
Marginal posterior placenta near cervix.
Corticosteroids in pregnancy
Given to accelerate fetal lung development.
Cesarean section recommendation
Surgical delivery for significant bleeding cases.
Fetal growth restriction
Complication due to placental issues.
Abnormal fetal position
Fetus in breech or transverse position.
Management of placenta previa
Initial assessment of mother and fetus required.
Placenta Previa
Condition where placenta covers cervical os.
Marginalis Posterior
Worse prognosis due to encroaching on true conjugate.
Marginalis Anterior
Less severe than marginalis posterior type.
Fetal Engagement
Head compresses placenta, risking fetal asphyxia.
Outpatient Treatment
Safe for placenta previa under 30 weeks gestation.
Immediate Delivery
Indicated if fetus or mother is in distress.
Incomplete Centralis
Placenta partially covers cervical os.
Complete Centralis
Placenta fully covers cervical os even when dilated.
Blood Volume Replacement
Maintains blood pressure during placenta previa.
Blood Plasma Replacement
Maintains fibrinogen levels in the mother.
Corticosteroids
Given at 24-34 weeks to reduce premature birth risk.
Major Degrees
Includes traditional grades III and IV.
Minor Degrees
Includes traditional grades I and II.
Vaginal Delivery
Possible if placenta is 2 cm from internal os.
Caesarean Section
Indicated for major degrees of placenta previa.
DIC
Disseminated intravascular coagulation, contraindicates caesarean.
Hysterectomy
May be required in severe bleeding cases.
Abruptio Placenta
Placenta separates from uterus before birth.
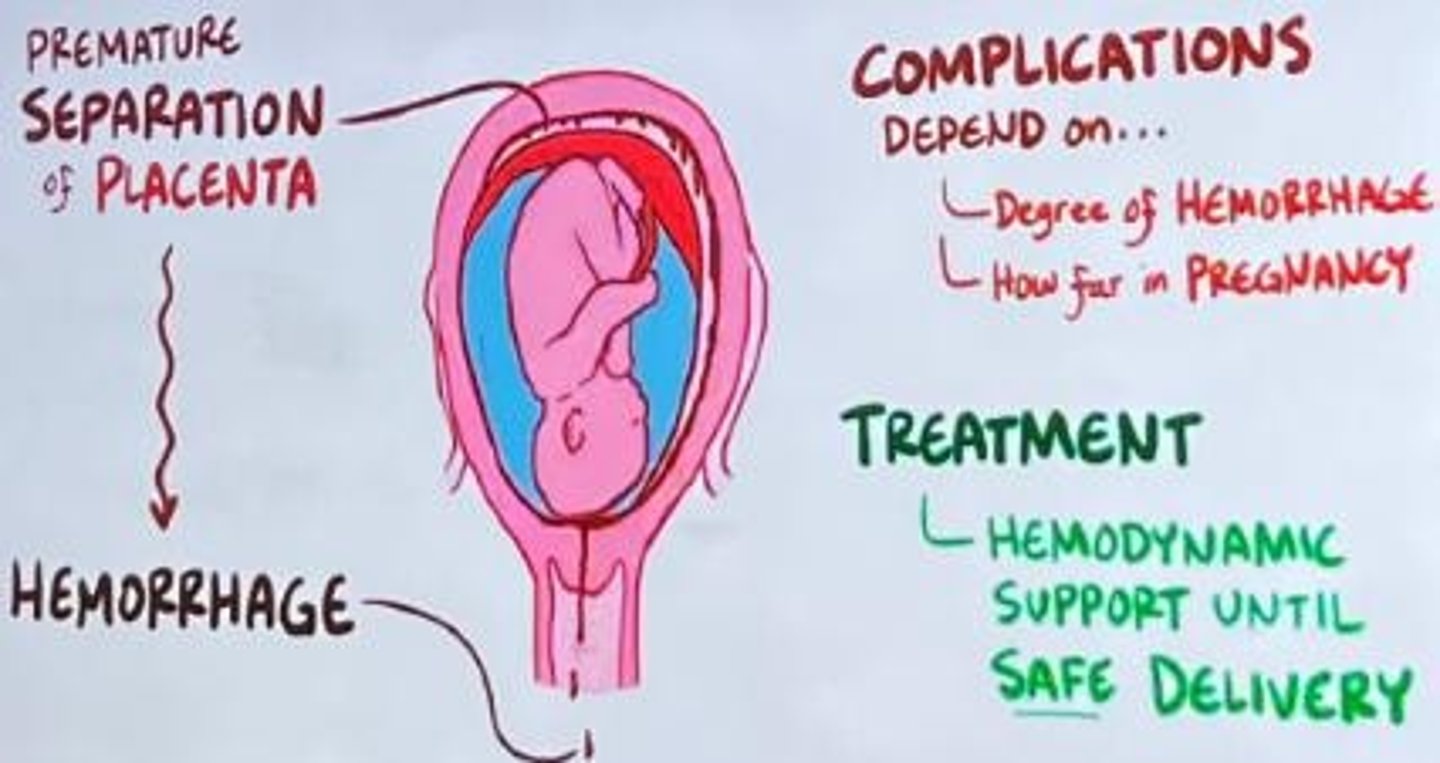
Oxygen Deprivation
Can occur due to placental abruption.
Risk Factors
Includes blunt trauma, drugs, multiparity, maternal age.
McAfee Regimen
Management protocol for placenta previa patients.
Strict Bed Rest
Improves placental blood flow during treatment.
Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
Monitored to prevent low blood levels.
Fetal Kick Chart (FKC)
Tracks fetal well-being during pregnancy.
Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
Regular checks of fetal health during treatment.
Steroids for Lung Maturation
Administered if gestational age is under 34 weeks.
Emergency Cesarean Section
Prepared for in case of torrential bleeding.
Blunt Trauma Causes
Includes car crashes, falls, domestic violence.
Cocaine and Methamphetamine
Drugs causing vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure.
Maternal Age Risk
Age over 35 increases risk of complications.
Previous Abruption
History of placental abruption raises future risk.
Gestational Age
Duration of pregnancy measured in weeks.
Steroids
Medications given for lung maturation in preterm infants.
Dexamethasone
12 mg steroid administered intramuscularly for lung development.
Emergency Delivery
Delivery procedure initiated due to urgent medical need.
Neonatal Anesthesia
Anesthesia prepared for newborns during delivery.
Caesarean Section Facility
Surgical facility for performing C-sections.
Blood Transfusion Facility
Facility equipped for administering blood transfusions.
Intranasal Oxygen
Oxygen delivered through the nasal passages.
Intravenous Fluid
Fluids administered directly into the bloodstream.
Wide-bore Cannula
Large diameter cannula for fluid administration.
IV Giving Set
Equipment used to deliver intravenous fluids.
Ultrasound at 36 Weeks
Imaging procedure to assess fetal development.
Longitudinal Muscle
Muscle layer aiding in uterine contractions.