OXYGEN-BINDING PROTEINS: HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Normal hemoglobin is?
α2β2
Fetal hemoglobin is
α2γ2
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is
α2β s 2
Hemoglobin that is desaturated with oxygen is deoxyhemoglobin (T, tense form), which has a ______________ oxygen affinity and a _________ degree of freedom.
Low
Hemoglobin that is saturated with oxygen is oxyhemoglobin (R, relaxed form), which has a ____________ oxygen affinity and a _________ degree of freedom.
High
The O2-binding curve shifts (left/ right) with increase in CO2, acidosis (low pH), increase in 2,3- BPG, exercise, and temperature.
Right
True or False
A leftward shift in the oxygen saturation curve occurs in the presence of a decrease in CO2, alkalosis (high pH, low hydrogen ion concentration), and decrease in 2,3-BPG
True
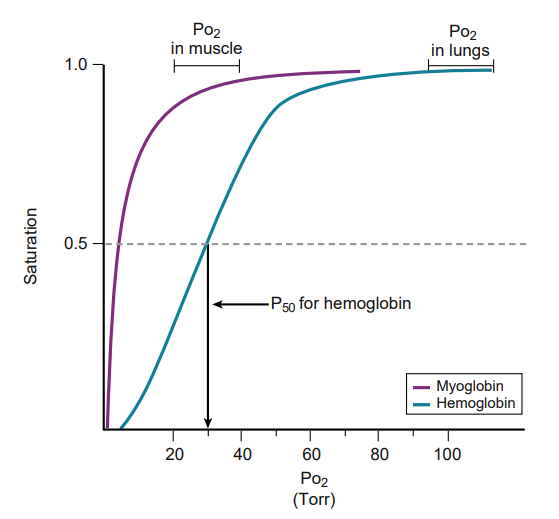
Comparison of oxygen-binding curves for hemoglobin and myoglobin. The P50 is the Po2 at half saturation. What does p50 signify?
Having a lower P50 means having a greater affinity for oxygen.
Myoglobin is present in?
Heart and skeletal muscle and acts as an oxygen carrier and location for storage of oxygen.
Myoglobin can only bind to one oxygen molecule; therefore the binding curve is
binding curve is hyperbolic
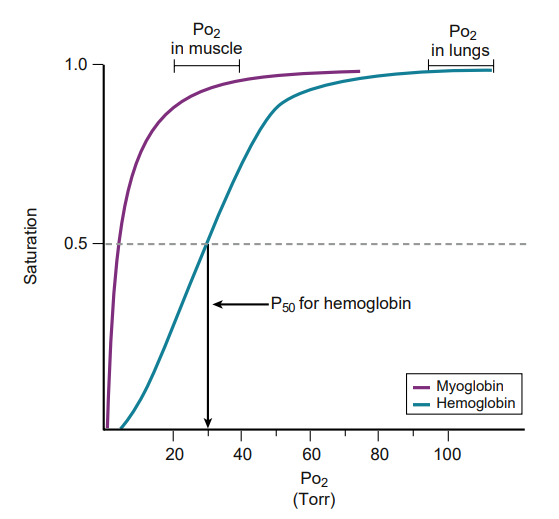
Carbon monoxide (CO) binds to hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin, which has a high affinity for CO and displaces O2. What happens to the curve in CO poisoning?
CO poisoning causes stabilization of the R state, a leftward shift in O2 saturation curve, and a saturation curve for hemoglobin that resembles the curve for myoglobin.
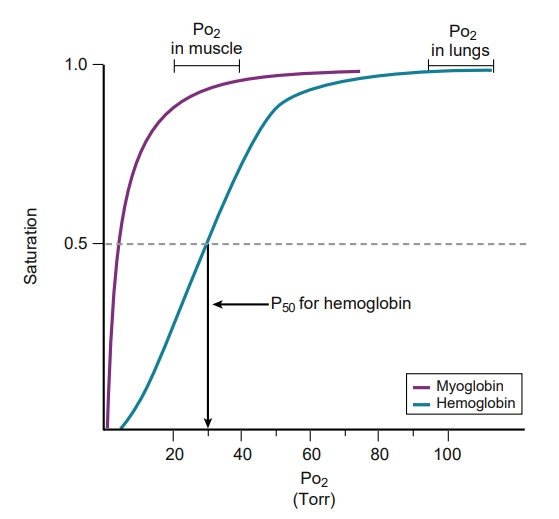
Myoglobin has a lower P50 than hemoglobin; therefore it has a greater affinity for O2. Thus O2 is bound to myoglobin in all cases except .
hypoxia
Hemoglobinopathies - Sickle cell characterization
homozygous recessive genetic disorder that
results from production of hemoglobin with an altered amino acid sequence,
caused by a single point mutation in the β-globin gene.
Mutation is a glutamate-to-valine mutation at position 6 in the β-globin chain.
Sickling is increased by anything that increases the proportion of HbS in the deoxygenated state such as
decreased O2 tension,
increased Pco2,
decreased pH,
dehydration,
increased concentration of 2,3-BPG in erythrocytes.
An infant does not begin to show symptoms of the disease until sufficient HbF has been replaced by HbS so that sickling can occur. What is the treatment of sickle cell disease?
Hydroxyurea
Because it increases circulating levels of HbF, which decreases RBC sickling. Sickle cell disease is tested for at birth to allow prophylactic antibiotic therapy to begin soon after because these children are at risk for sepsis.
Hemoglobin C disease (HbC disease) results from production of hemoglobin with an altered amino acid sequence as a result of ?
Glutamate-to-lysine substitution at position 6 in the β-globin gene.
Homozygous patients have a mild, chronic hemolytic anemia.
Hemoglobin SC
occurs when some β-globin genes have the sickle cell mutation,
Thalassemias are caused by
decreased production of normal hemoglobin as a result of defective synthesis of either the α- or the β-globin chain
β-thalassemia the synthesis of Beta - globin chains is?
is decreased or absent, but the α-globin chain synthesis is normal.
e β-globin is not expressed until late in gestation, symptoms of β-thalassemia appear?
only after birth.
There are _______copies of the α-globin gene
Four
In Alpha - globin,
If one copy of the α-globin is absent or defective, the person is a _______
Two defective genes lead to_____________
Three defective genes lead to _________
If all four α-globin genes are defective it leads to _________
Silent carrier
α-thalassemia trait
Hemoglobin H (HbH) disease.
Hydrops fetalis and fetal death result because α-globin chains are required for the synthesis of HbF
Collagen is composed of a__________
Triple helix of three α-chains held together by hydrogen bonds
Collagen has a large amount of
proline and glycine
Proline helps in the formation of the α-chain,
Glycine is found in every third amino acid
The sequence is –Gly–X–Y–, where X is often proline and Y is often hydroxyproline or hydroxylysine.
The biosynthesis of collagen
mRNA transcription in the nucleus of a fibroblast
mRNA is translated into pre-procollagen on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and these peptide chains are directed into the lumen of the RER and become pro-α-chains
Proline and lysine residues are next hydroxylated by prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase
Some hydroxylysine residues are glycosylated with glucose and galactose.
Pro-α-chains form procollagen, which has a central triple helix with N- and C-terminal propeptide extensions; these prevent premature assembly of collagen within the endoplasmic reticulum.
Procollagen is transported to the Golgi apparatus, where it is released into the extracellular space.
After release of procollagen, peptidases remove the terminal propeptides, forming tropocollagen.
Tropocollagen then spontaneously assembles into collagen fibrils.
The collagen fibers are crosslinked by lysyl oxidase, which oxidatively deaminates lysyl and hydroxylysyl residues in collagen, forming covalent cross-linked, mature collagen fibers
In collagen synthesis, The hydroxylation reaction requires both
Oxygen and the reducing agent vitamin C (ascorbic acid) for the hydroxylating enzymes prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase to function.
Vitamin C deficiency leads to a lack of prolyl and lysyl hydroxylation, making collagen fibers unable to be cross-linked, which decreases the tensile strength of the assembled collagen fiber. This disease is called?
Scurvy
Clinical signs of Scurvy include
Because of the weak collagen structure, patients often have bruises, corkscrew hairs, and perifollicular hemorrhage caused by capillary fragility.
Copper is also a cofactor for lysyl oxidase
EDS arises from;
lysyl hydroxylase deficiency,
Procollagen peptidase deficiency,
Mutations in collagen amino acid sequences, most importantly collagen type III.
Skin hyperextensibility and joint hypermobility are seen in patients with EDS.
Osteogenesis imperfecta is from a defect of type what collagen?
Type 1 collagen causing brittle bones and blue sclera.
Decreased production of collagen α-chains, leading to bones that are prone to bending and fracture.
Elastin is synthesized from ____________ a precursor protein.
Tropoelastin
After secretion from the cell, tropoelastin deposits onto fibrillin
In the alveoli, elastin is broken down by elastase from activated neutrophils. __________, an enzyme produced in the liver, usually blocks elastase and protects the lungs.
α1-Antitrypsin
Genetic defects in α1-Antitrypsin can lead to ______________at a young age because of increased breakdown of lung connective tissue.
pulmonary emphysema
A higher Km means a (lower/Higher) affinity of the substrate for the enzyme.
Lower
zero-order kinetics.
When [S] > > than Km, the rate of the reaction is independent of [S]
When [S] = Km, then the initial velocity (v) =
Vmax/2
First-order kinetics.
When [S] < Km, the reaction rate is proportional to [S].
Competitive inhibitors
Km is increased, Vmax is unchanged
Noncompetitive inhibitors
Km is unchanged, Vmax is decreased
What is the rate limiting step in the Urea Cycle?
Draw the cycle & name the enzymes in the urea cycle and where the belong. eg mitochondria vs cytosol
What happens with OTC deficiency?
Carbamoyl phosphatase 1
Carbamoyl phosphatase synthetase 1 —→ Ornithine Transcarbamoylase —→ arginine synthetase ——> Agininesuccinase ——> arginase
Increase in Carbamoyl phosphatase and a decrease in citrulline production leading to a impaired urea cycle. Carbamoyl phoaspatsse then creates orotic acid which is toxic
Aminotransferases require ______________ for function
Pyridoxal phosphate (a derivative of vitamin B6)
Amino groups are removed from amino acids by two sequential reactions
Transaminases - alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), transfer amino groups to α-ketoglutarate, producing an α-keto acid and glutamate. The α-keto acid can enter the citric acid cycle.
Glutamate dehydrogenase - oxidatively deaminates glutamate to α-ketoglutarate and free ammonia (NH3)
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is activated by
N - acetylglutamate
N-acetylglutamate is synthesized from
acetyl coenzyme A (CoA).
Neomycin and rifaximin orally administered can reduce the number of urease-producing bacteria. They are used to treat what?
Hepatic encephalopathy
Symptoms of hyperammonemia are
Ammonia has a toxic effect on the central nervous system (CNS), causing tremors, cerebral edema, and blurring of vision.
In neonate hyperammonemia during the first weeks after birth. ——————— is common.
Mental retardation
________ can be used to assists in clearance of nitrogen from the blood.
Phenylbutyrate - a prodrug that is metabolized to phenylacetate, combines with glutamine to form phenylacetyl-glutamine
What are the non essential amino acids?
Arginine
Alanine
Asparagine
Aspartic acid
Cysteine
Glutamic Acid
Glutamine
Glycine
Proline
Serine
Tyrosine
Aspartate, alanine, and glutamate are synthesized from transamination of α-keto acids. What are they?
Aspartate is derived from oxaloacetate,
Glutamate from α-ketoglutarate,
Alanine from pyruvate.
Glutamine and asparagine are synthesized by amidation.
Glutamine synthetase forms glutamine from glutamate. This reaction also helps to reduce ammonia levels.
Asparagine synthetase forms asparagine from aspartate
Serine is synthesized from _______________
Glycine, in turn, can be synthesized from_____________
Proline is synthesized from ___________.
Arginine is synthesized from ___________________
3-phosphoglycerate
Serine.
Glutamate
Citrulline
Cysteine is synthesized from ______ and _____
Homocysteine is derived from ______________.
Tyrosine is synthesized from __________ by phenylalanine hydroxylase and BH4 cofactor
homocysteine and Serine
Methionine
Phenylalanine