NCLEX Questions
1/468
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
469 Terms
What are signs and symptoms of hemorrhagic shock?
Urinary output less than 30 cc/hr, dehydration, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, thirst
What are the side effects of external radiation?
- Dysgeusia (salty, rancid taste in mouth)
- Stomatitis
- Thrombocytopenia
Where is the spleen palpated on the abdomen?
RUQ "right upper quadrant"
What is the highest priority care for pyelonephritis?
-pyelonephritis: kidney infection
Increase the patient's fluid intake to 3 liters daily.
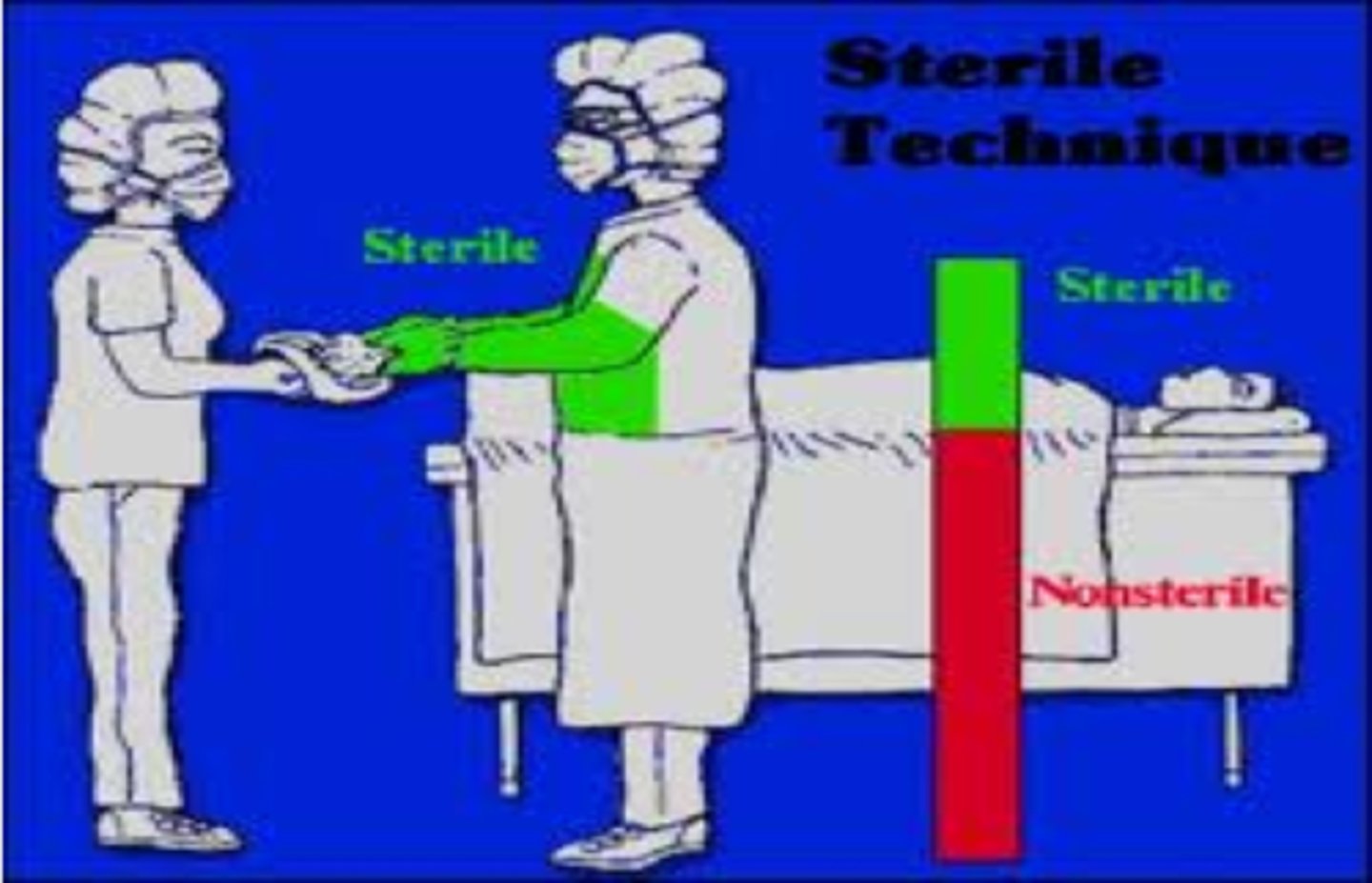
What is the difference between sterile and aseptic technique?
Sterile - absence and continued protection against all microorganisms.
Aseptic - used to prevent the SPREAD of microorganisms if a wound is already infected.
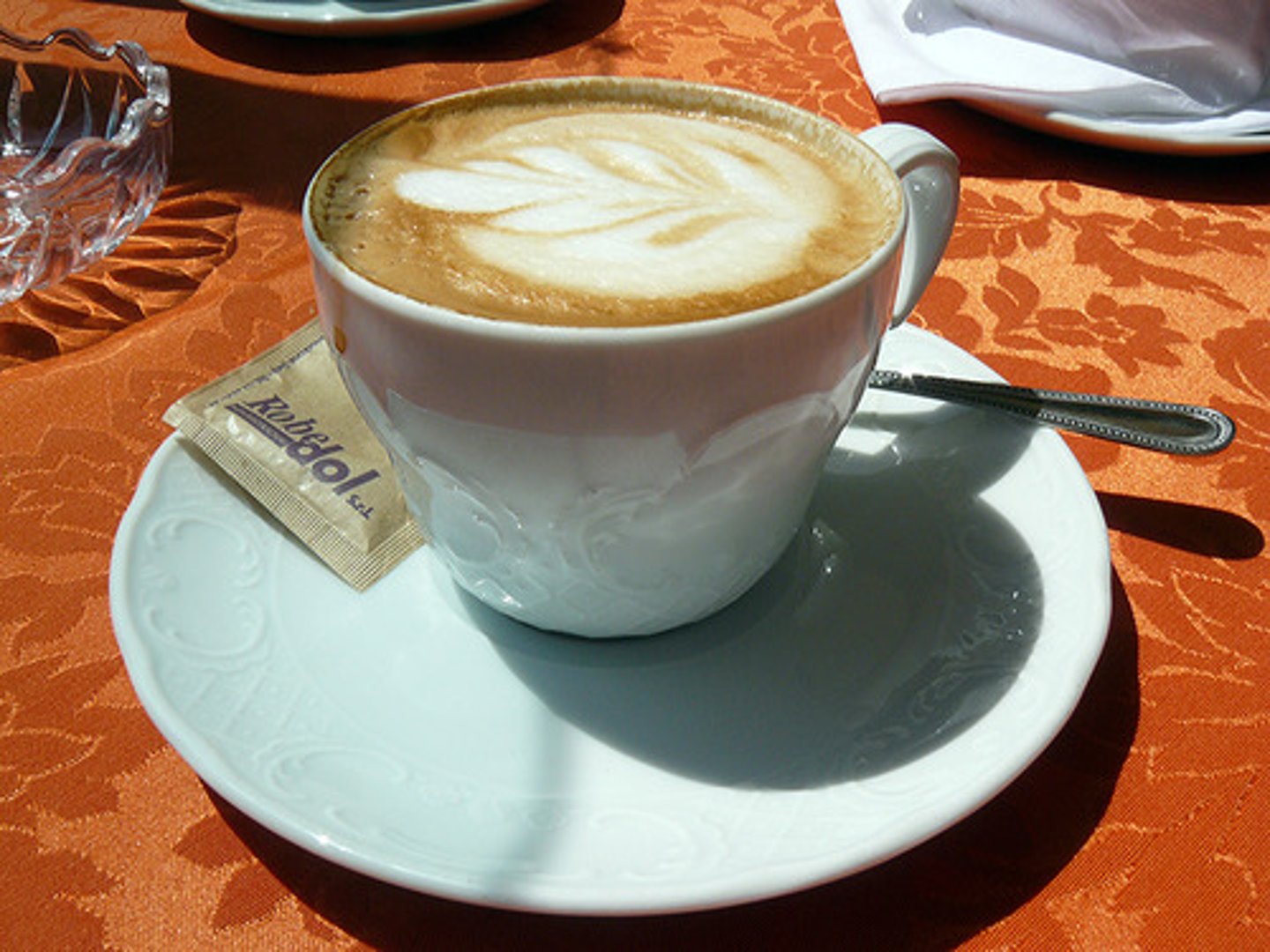
Up to how many milligrams of caffeine can a pregnant women consume?
300 mg

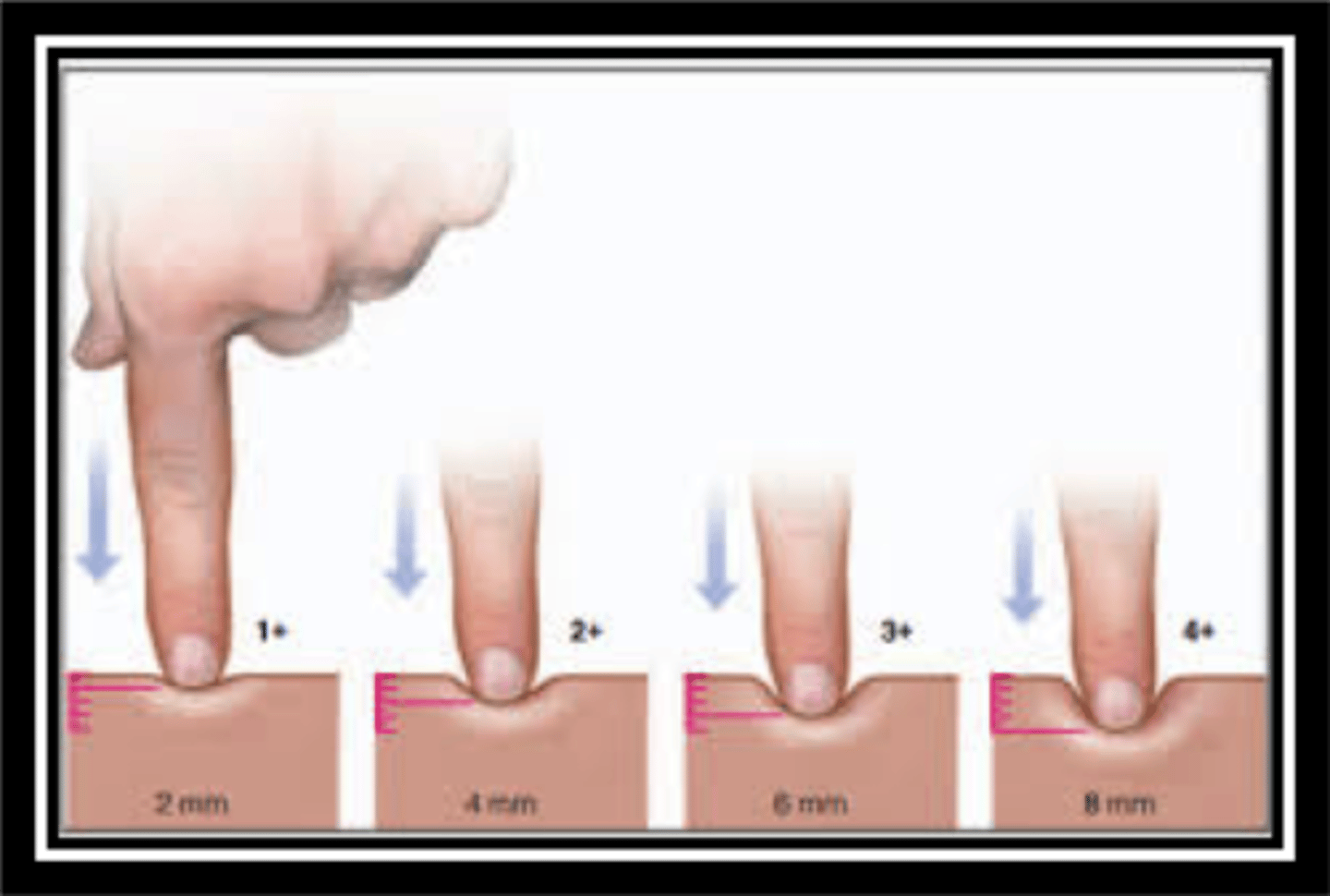
What is the edema scale? (1-4)
1 - 2cm
2 - 4cm
3 - 6cm
4 - 8 cm
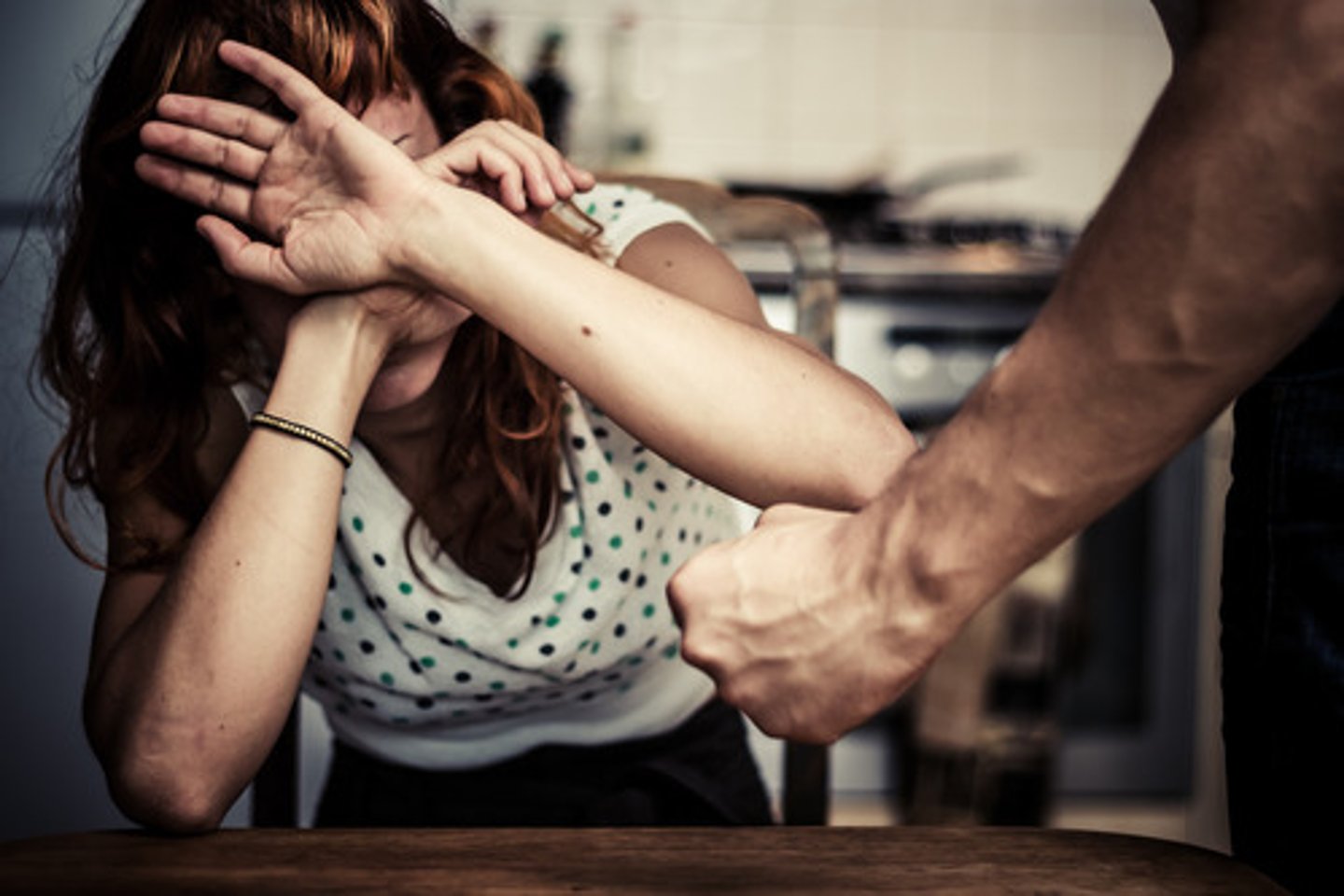
What screening tool is used for domestic violence?
HITS "hurt, insult, threaten, scream"

Where on an infants lips should they be latched on for proper sucking?
areola

What diet should a patient maintain for colorectal cancer screening?
"colorectal cancer screening for colon or rectum"
Avoid fish, cantaloupe, turnips, and red meats 48-72 hrs before the procedure.
What are signs and symptoms of pernicious anemia?
"Addison's anemia" - condition in which the body can't make enough healthy red blood cells because it doesn't have enough vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is a nutrient found in some foods. The body needs this nutrient to make healthy red blood cells and to keep its nervous system working properly.
Neuropathy of lower extremities, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, lack of energy, light-headedness with exertion, swollen or red tongue, bleeding gums
neuropathy - disease or dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves "outside brain/spinal cord", typically causing numbness or weakness.
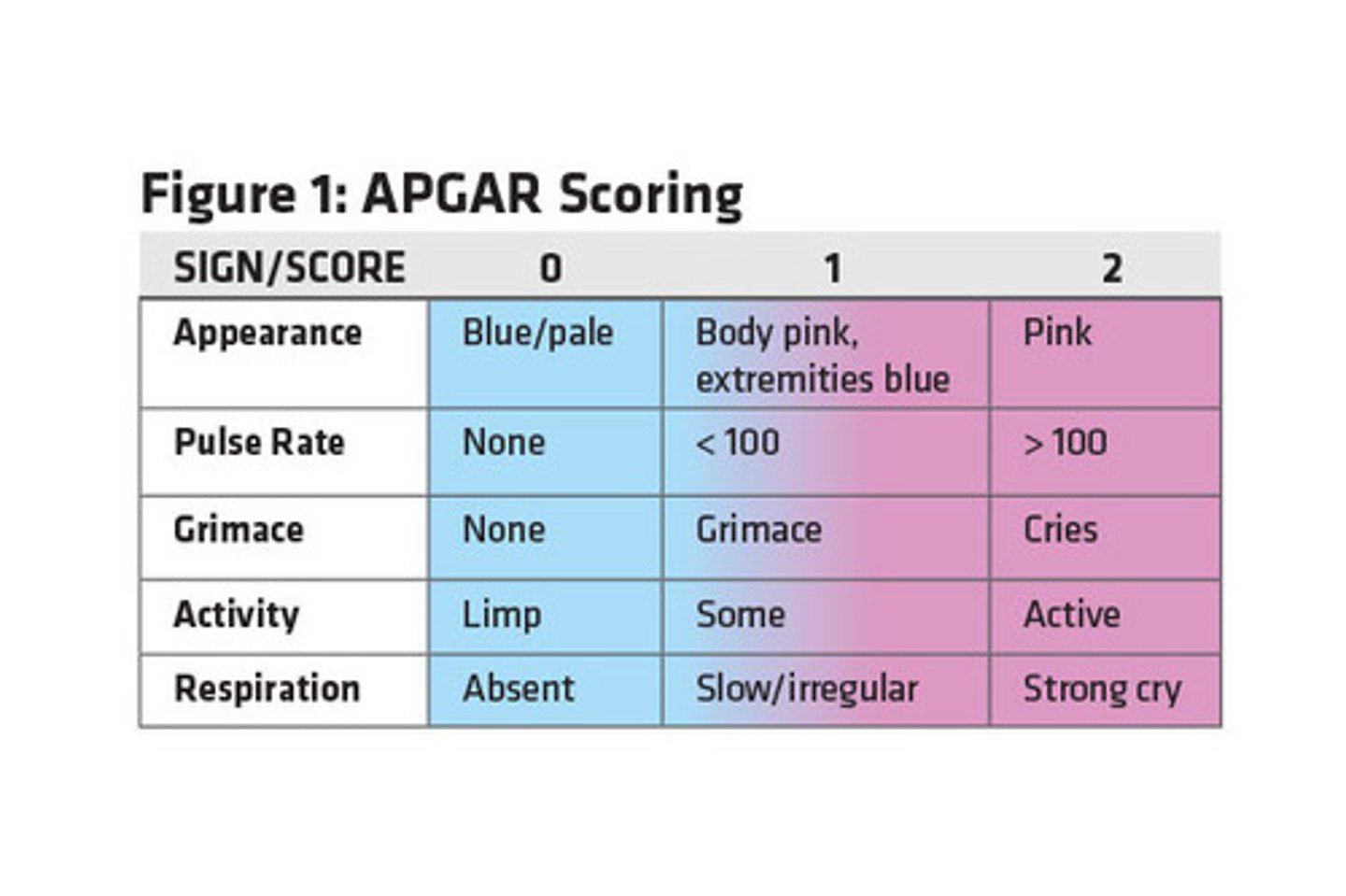
What does the APGAR score assess?
-given newborns after birth, given twice: once at 1 minute after birth, and again at 5 minutes after birth.
Breathing effort, heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, skin color
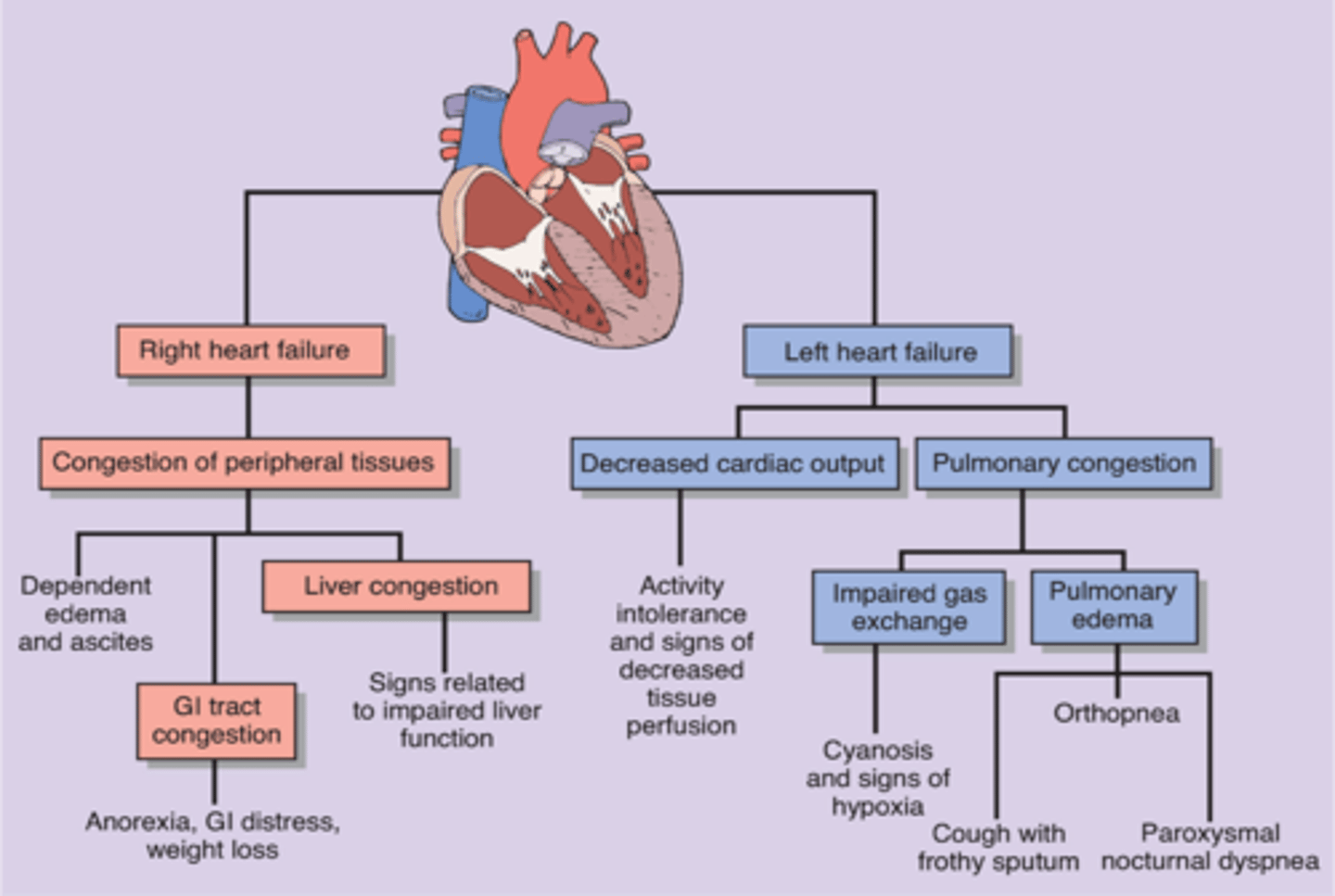
What are symptoms of left sided heart failure?
Cough - pink or frothy sputum, oliguria, fatigue, SOB, palpitations
- Frothy sputum: Foamy white mucus "sometime signs of COPD/GERD"
- Oliguria: Low urine output
- SOB: shortness of breath "dyspnea"
- Palpitations: noticeably rapid, strong, or irregular heartbeat due to agitation, exertion, or illness.
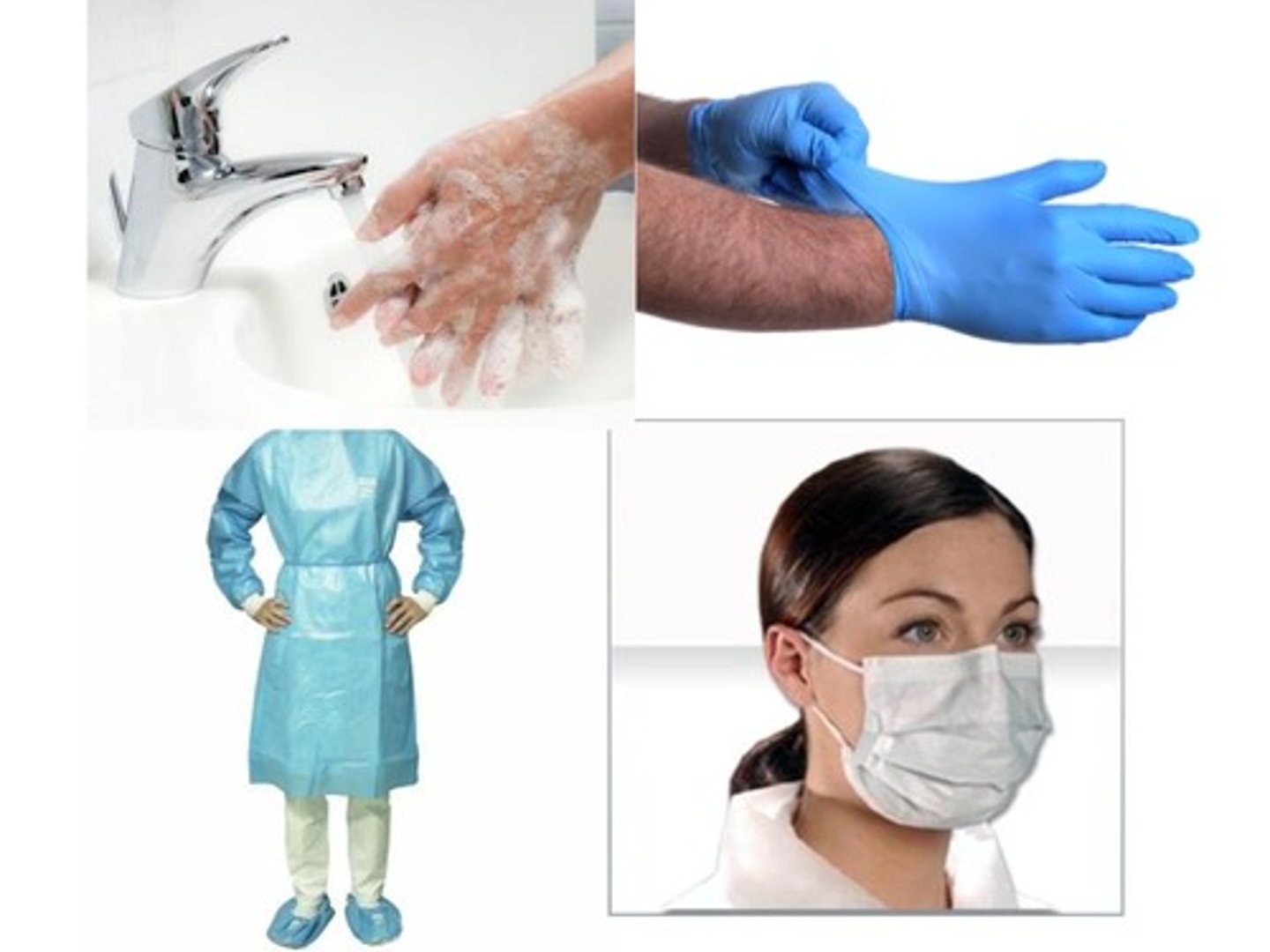
What is worn for droplet precautions?
Glove, gown, and mask

What is a healthy total cholesterol to maintain? LDL? HDL?
Total - <200 mg/dl
HDL - >60 mg/dl "good"
LDL - <130 mg/dl "bad"
What is pulsation between the pubis and umbilicus indicative of?
An aortic aneurysm - medical emergency
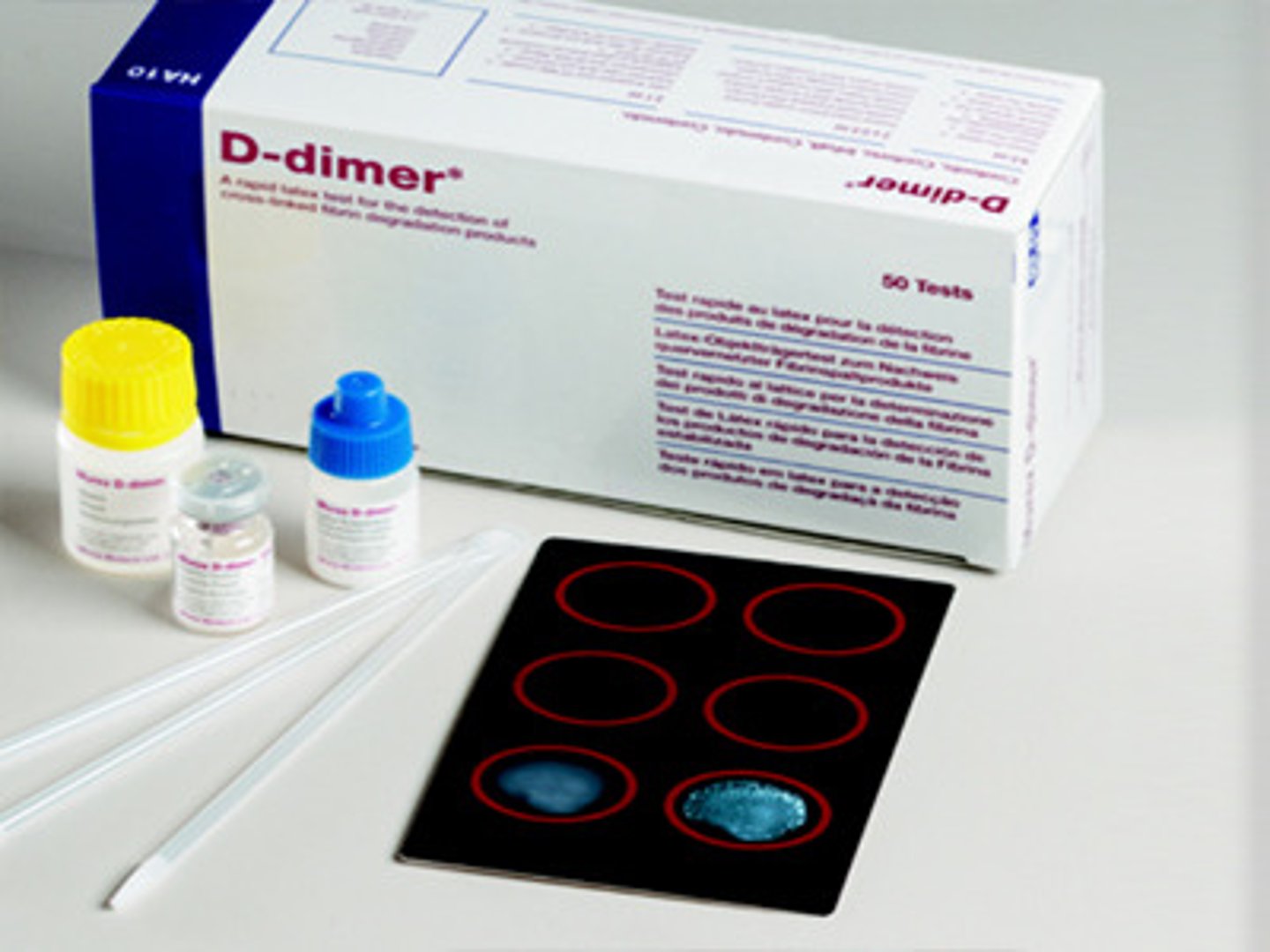
What is a D-Dimer test used for/indicative of?
blood test that can be used to help rule out the presence of a serious blood clot.
Fibrin degradation product, indicative of DVT
- Fibrin degradation product: substances that remain in your bloodstream after your body dissolves a blood clot
- DVT: Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein located deep inside your body.
At what ages do different teeth begin to appear?
Primary - have all 20 by age 3
Wisdom - age 6
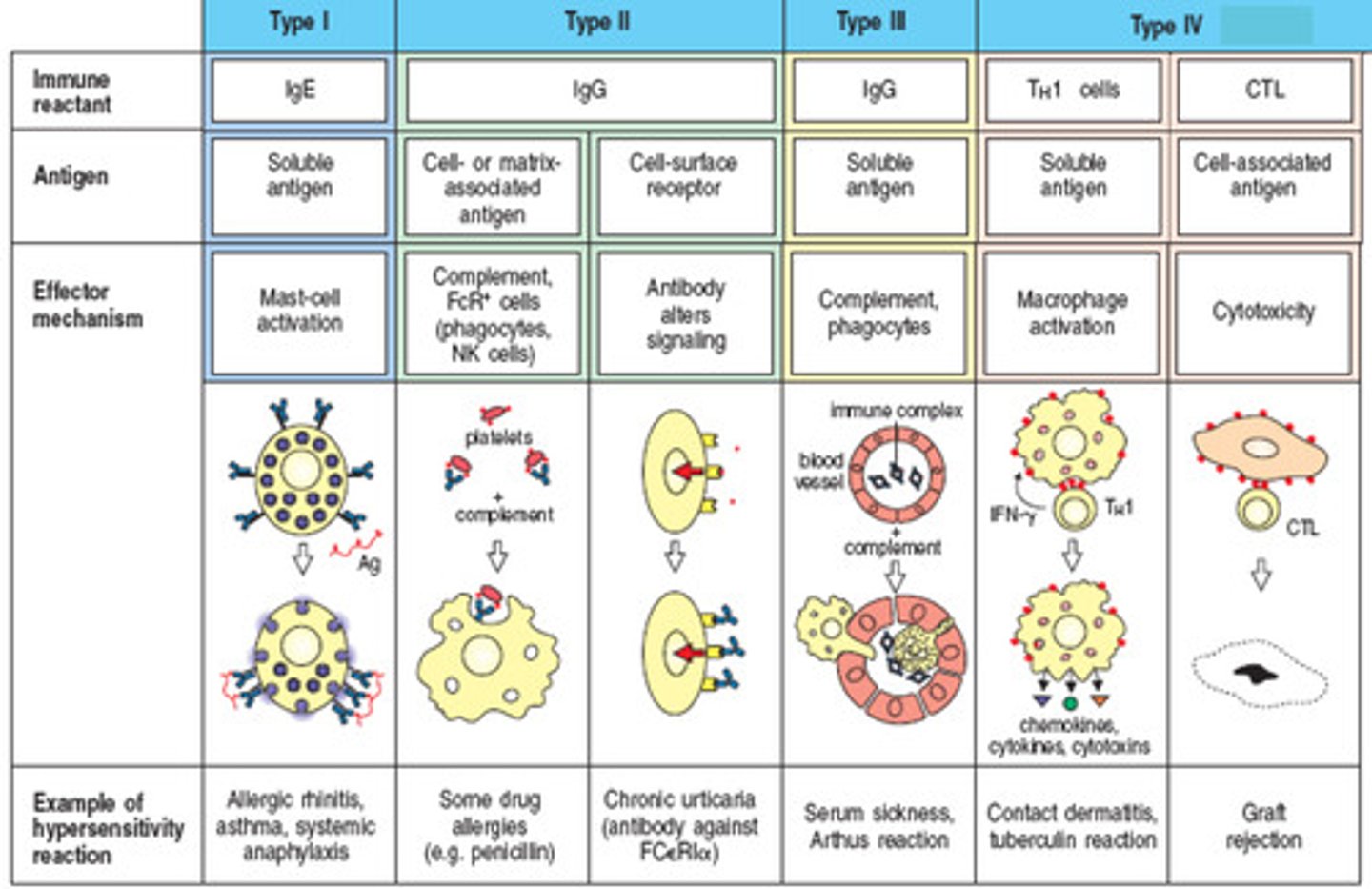
How are the different types of hypersensitivity reactions classified?
Type 1 - immediate allergic reaction involving IgE "anaphylaxis"
Type 2 - involves IgM and IgG, leads to cell lysis "ABO incompatibility, hemolytic anemia"
Type 3 - involves antigen-antibody complexes, leads to an inflammatory response "lupus: an inflammatory disease caused when the immune system attacks its own tissues."
Type 4 - delayed hypersensitivity reaction involving T-cells - takes several days to develop "transplant rejection"
Immunoglobulin (Ig)
What is Chlordiapoxide used for?
-It is used for alcohol withdrawal
-Ativan also might be used

What is Pantoprazole used for?
Proton pump inhibitor used to reduce gastric acid secretion in the prevention and treatment of gastric ulcers.
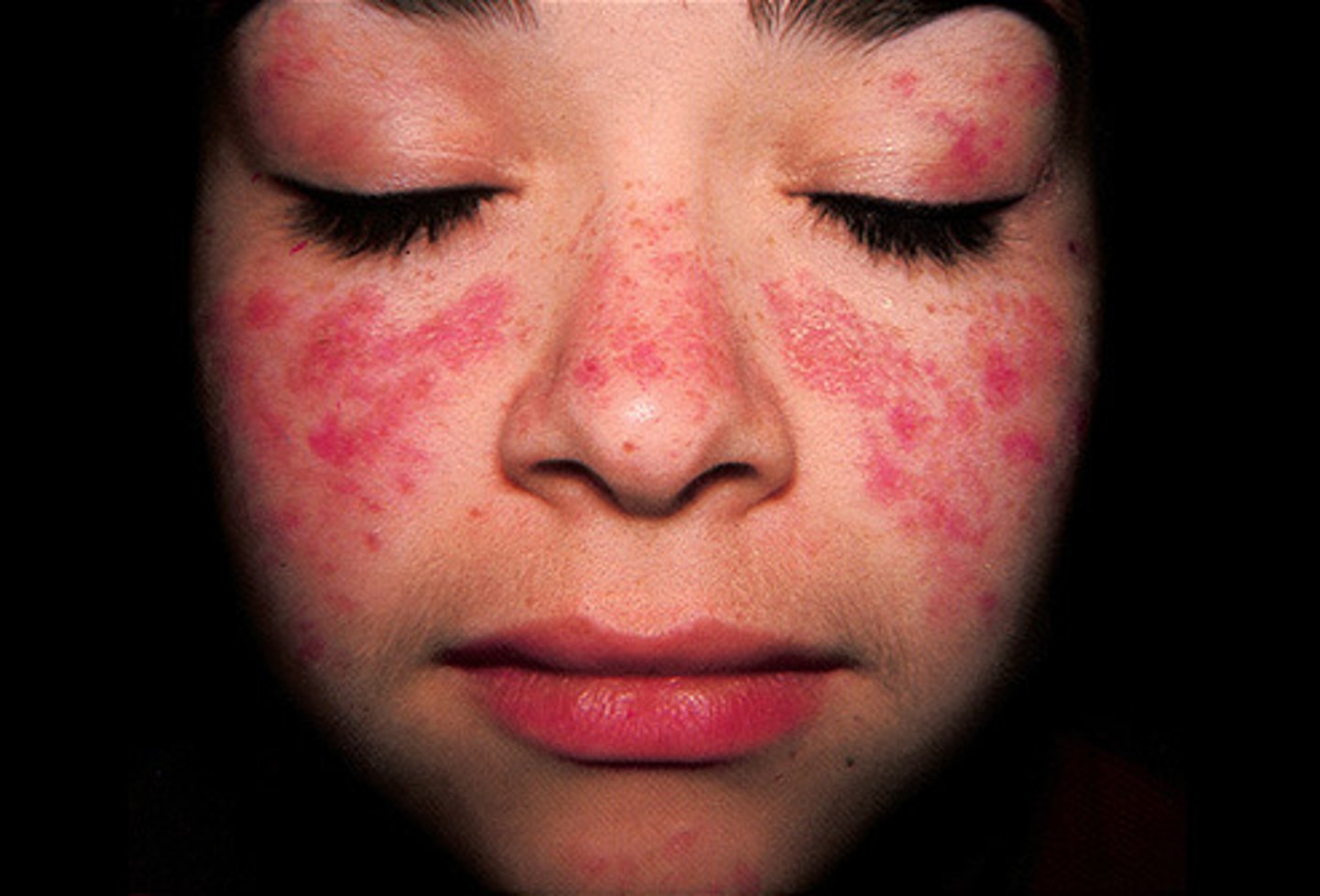
What are symptoms of SLE? "Systemic lupus erythematosus"
Autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. It can affect the joints, skin, brain, lungs, kidneys, and blood vessels.
-proteinuria
-butterfly rash
-chest pain with inspiration
-fatigue
-fever
-general discomfort
-hair loss
-mouth sores
-photosensitivity
-weakness.
What are ways to reduce allergic reaction to dust mites in the home?
-Use impermeable covers on pillows and mattresses
-keep floors and surfaces bare and avoid carpeting wash and rinse linens in hot water.
What is done for clients in ketoacidosis?
Administer sodium bicarbonate, administer IV insulin, add potassium to replacement fluid therapy, and have IV of normal saline running.

What do basophils do? Normal %?
Release histamine during an ALLERGIC or ANAPHYLACTIC reaction, leads to vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, and bronchospasm
Normal % - 0.5-1%

What do neutrophils do? Normal %?
Defend against BACTERIA and FUNGI and produce a small inflammatory response
Normal % - 55-70%

What do lymphocytes do? Normal %?
Defend against VIRAL infections
Normal % - 20-40%
What do eosinophils do? Normal %?
Primarily defend against PARASITIC infections and are important in ALLERGIC responses - release interleukin, not histamine.
Normal % - 1-4%
What do monocytes do? Normal %?
Differentiate into macrophages to defend against infection.
Normal % -2-8%
What valvular disorder are syncope and dyspnea on exertion hallmark for?
Aortic stenosis
What does a spacer device do?
May eventually lead to a decreased need in dosage or frequency of a medication
What is a hepatobiliary scan used for?
Used to evaluate the function of the gallbladder
What is a erythrocyte sedimentation rate used for?
Used to measure a non-specific measure of inflammation in the body - used to help diagnosed SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, and Kawasaki's disease
What is a CBC used for?
Used to detect anemia and thrombocytopenia
What is an antinuclear antibody test for?
To diagnose SLE
What is Diltizazem used for?
Used to treat arrhythimias and hypertension
What is a normal range for lactate?
0.5-2.2mmol/L - it is a sign of spesis or tissue ischemia
What causes an oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curse to shift left? (oxygen uptake)
Increased pH, decreased 2, 3-DPG, low temperature, increased CO, pCO2 decreased
What causes an oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to shift right? (oxygen release)
Decreased pH, increased 2, 3-DPG, increased temperature, decreased CO, pCO2 increased
What are Erikson's stages of psychosocial development?
* Basic trust vs mistrust (0-2 yrs)
*Autonomy vs shame and doubt (2-4 yrs)
*Initiative vs guilt (4-5 yrs)
*Industry vs inferiority (5-12 yrs)
*Identity vs role confusion (13-19 yrs)
*Intimacy vs isolation (20 - 24 yrs)
*Generativity vs Stagnation (24-64 yrs)
*Ego integrity vs despair (65-death)
What are characteristic of autism?
Over responsiveness to sensory stimuli (light or sound), impairment in communication, inability to name objects, and echolalia common
What classifies a full thickness burn?
3rd degree - white/brown, dry, leathery, painless, no blanching
What classifies a superficial burn?
1st degree - red, dry, painful
What classifies a superficial partial thickness burn?
2nd degree - red, clear blisters, moist, painful, blanches
What classifies a deep partial thickness burn?
2nd degree - red and white, bloody blisters, moist, painful, less blanching
What classifies a 4th degree burn?
Black, eschar, dry, painless, no blanching
What is Kawasaki disease?
An autoimmune disease involving the inflammation of blood vessels, lymph nodes, skin, and mucosa - initial symptom is a high fever, later symptoms include conjunctivitis, rash, peeling, and edema
How far should an enema be inserted?
3-4 inches
What foods have tyramine in them?
Caffeine, dairy products, alcohol, ginseng, and aged meat,
What are signs and symptoms of psoriasis?
It is a chronic inflammatory diseased caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system - symptoms include lesions with red and white scales that appear on the extensor surfaces of joints (elbows and knees)
What is a safe Troponin-1 level?
<0.01 ng/ml
What is, and what are signs and symptoms of systemic scleroderma?
it is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and sclerosis of the skin, muscles, joints, kidneys, and heart - others, weakness, pruritus, Raynaud's phenomenon, difficulty swallowing, edema, tight skin, shortness of breath, fatigue, and hypertension
How is idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura treated?
First line of treatment is corticosteroids to dampen immune response and increase platelet count - will raise BG levels, need to be monitored.
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
Blood test - not reliable until 6-8 weeks after exposure - treated with antibiotics (Doxycycline)
What are signs and symptoms of Lyme disease?
Bullseye rash, fever, malaise, muscle soreness, and headache
What do lesions in Kaposi's sarcoma look like?
They are papular, nonpruritic, bilater, and pink, brown, or violet.
What factors increase the risk of prostate cancer?
*African american race
*Folic acid supplementation
*Increased levels of dihydrotestosterone
*Hormones
*Age
What is Sjogren's syndrome?
A systemic autoimmune disease that affects exocrine galnds - causes a deficiency in saliva, tears, skin lubrication, and other exocrine secretions - moisture replace usually the is treatment of choice.
How does Theophylline work?
Relaxes bronchial smooth muscles and stimulates the CNS and skeletal muscles
What is the onset, peak, and duration of rapid-acting insulin? (insulin aspart, lispro)
*Onset - 15 min
*Peak 1-3 hours
*Duration 3-5 hours
What test is used to diagnose SLE?
Antinuclear antibody
What are risk factors for endocarditis?
*History of mechanical valve replacement
*Dental procedures
*IV drug use
*immunosuppression
What is Cyclosporine used for?
It is an immunosuppressant used to prevent rejection in organ transplants
When is the trough of a medication measure?
It is the measurement of a drug's lowest level - commonly done immediately before the next administered dose.
What level should Fi02 remain below?
<50%
What hormone abnormalities would be present in a patient with Grave's disease?
Elevated T4, diminished TSH
What does hypoparathyroidism cause?
A decrease in calcium and an increase in serum phosphorus?
What is the normal range for phosphorus?
3-4.5 mg/dl
What is the normal range for calcium?
9-10.5 mg/dl.
What is a stage 2 pressure ulcer?
Skin is not intact, loss of the dermis occurs, pink/red, open wound, shallow
What is a stage 1 pressure ulcer?
Skin intact, red, non-blanching, warm, painful
What is a stage 3 pressure ulcer?
Full thickness skin loss, extends into the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Slough and tunneling may be present
What is a stage 4 pressure ulcer?
Full thickness skin loss, exposed bone, tendon, or muscle, slough or eschar, and tunneling
What is the best position for a dyspneic patient to enhance respiration?
Leaning forward against a steady surface.
What should a nurse do when preparing an I.V medication from an ampule?
Nurse should place a gauze around the neck to protect hand from broken glass.
What are several ways E.Coli can be spread?
It originates in the intestinal tract of animals - avoid swimming in standing water, and cook all meat thoroughly
What is angina pectoris and when is it caused?
It is caused by increased oxygen demand and decreased oxygen supply to the heart - occurs during activity, stops when rest occurs, and pain spreads to arms and back.
Where should a nurse assess for jaundice in a patient with dark skin?
Hard palate of the mouth.
What is the rooting reflex?
Brushing an infant's cheek will cause the baby to turn in that direction.
What is the tonic neck reflex?
Occurs when newborn's head is turned to the side, the arm on that side will extend while the opposite arm will contract - prepares the infant for voluntary reaching and may be a precursor to hand/eye coordination.
What is the extrusion reflex?
Occurs when an object is placed on the anterior portion of the tongue - protective reflex that prevents the swallowing of inedible substances.
How can a nurse reduce friction and sheer in Buck's traction?
Elevating the food of the bed.
What position should a person be placed in after a ventriculoperitoneal shun is placed?
Flat - to avoid a rapid decrease in ICP.
What is a normal neutrophil level?
2,500 - 8000 cells/mm3
What is a normal hemoglobin level?
14-18 g/dl (male) 12-16g/dl (female)
What are physical features of fetal alcohol syndrome?
Small head and brain, sunken nasal bridge, thin upper lip, small teach, and an upturned nose - it can also cause vision difficulties, intellectual disability, short attention span, delayed mental development, and poor impulse control
What are symptoms of Down's syndrome?
Short stature, short wide neck, slanted eyes, low set ears, hypotonia, intellectual disability, and learning disabilties
What are symptoms of Klinefelter's syndrome?
Present in males - less facial and body hair, reduced muscle mass, and strength, broad hips, gynecomastia, and hypogonadism
What are signs and symptoms of mercury posions?
Peripheral neuropathy, skin discoloration (pink), swelling, shredding of the skin, tremors, visual changes, hearing impairment, and fatigue.
What are appropriate nursing interventions for a patient with emphysema?
Postural drainage, chest physiotherapy, low-flow oxygen, high fowlers position, and increased fluid intake.
What is a unit a measure of?
A measure of effect.
What is pertussis?
A highly contagious bacterial infection - it causes whooping cough, and vomiting that can last 6 weeks - can be prevented with Dtap, once contracted, it is treated with antibiotics.
What are a few blood transfusions that would work?
Rh negative blood can donate to Rh positive of same type.
O negative is universal donar
AB patients can recieve both A and B, as long as there is Rh compatibility.
What is involved with Thromboangitis obliterans (buerger's disease)?
It is inflammation and thrombosis of the vessels of the hands and feet, strongly associated with smoking. - patient should inspect skin regularly for signs of tissue ulceration and necrosis.
When should levothyroxine be taken?
In the morning, before breakfast.
What increases a patients risk of digitalis toxicity?
*Hypothyroidism
*Hypomagnesemia
*Hypokalemia
*Hypoxemia
*Advanced heart disease
What is a patient at risk for after parathyroidectomy?
Hypocalcemia
What is a Myxedema coma?
it occurs from a low thyroid production - occurs after acute illness, rapid discontinuation of thyroid medication, or hypothermia
What are signs and symptoms of Myxedema coma?
Hypotension, coma, hypoglycemia, edema, bradycardia, and respiratory failure.