A+P II Chp 27: Reproductive System
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
What are the 2 primary sex organs/gonads?
1) testes (males)
2) ovaries (females)
What are 2 functions of gonads?
1) produce gametes (sex cells)
2) secrete sex hormones
What are 3 types of accessory reproductive organs?
1) ducts
2) glands
3) external genitalia
What are the 3 sex hormones?
1) androgens (males)
2) estrogens and progesterone (females)
Sex hormones play roles in what 3 things?
1) development/function of reproductive organs
2) sexual behavior and drives
3) growth/development of other organs
The male gonads (testes) produce _______ and lie within the __________.
sperm; scrotum
Sperm are delivered to the exterior through a system of ducts. What is this pathway?
1) epididymis
2) ductus deferens
3) ejaculatory duct
4) urethra
What are the 3 male accessory sex glands?
1) seminal vesicles
2) prostate gland
3) bulbourethral glands
What do male accessory sex glands do?
empty their secretions into the ducts during ejaculation (accompanies sperm!)
The scrotum is a sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs __________ the abdominopelvic cacity.
outside
Why is the scrotum's external positioning important?
keeps testes 3°C lower than core body temp (needed for sperm production)
Intrascrotal temp is kept constant by which 2 sets of muscles?
1) dartos
2) cremaster
What type of muscle is each made up of and what does each do?
a) dartos
b) cremaster
a) smooth muscle that wrinkles scrotal skin
b) skeletal muscle that elevates the testes
Each testis is surrounded by 2 tunics. What are these 2 tunics?
1) tunica vaginalis: from peritoneum
2) tunica albuginea: fibrous capsule of testis
________ divide the testis into 250-300 ________, each containing 1-4 _____________________.
septa; lobules; seminiferous tubules
What is the function of seminiferous tubules?
produce sperm
What is the pathway of sperm from seminiferous tubules to the vas deferens?
1) seminiferous tubules
2) rete testis
3) efferent ductules
4) epididymis
5) vas deferens
Regarding the testes,
a) where does sperm enter
b) which part produces androgens
a) epididymis
b) interstitial or Leydig cells outside the seminiferous tubules
What is the blood supply to and from the testes?
1) testicular arteries: from abdominal aorta
2) testicular veins: arise from pampiniform plexus
What are the 3 parts of the epididymis?
1) head: caps superior aspect of testis
2) body
3) tail
Upon ejaculation the epididymis contracts, expelling sperm into the _________________.
ductus deferens
The ductus deferens runs from the epididymis through the _________________ into the ________________.
inguinal canal; pelvic cavity
Its terminus expands to form the _________ and then joins the duct of the ____________ to form the _______________.
ampulla; seminal vesicle; ejaculatory duct
What is a vasectomy?
- cutting/closing up the ductus deferens
- 100% effective birth control
What 4 things does the spermatic cord enclose?
1) ductus deferens
2) nerve fibers
3) blood vessels
4) lympathics that supply testes
What does the male urethra do?
conveys urine and semen (at different times)
What are the 3 regions of the male urethra? Where is each located?
1) prostatic: surrounded by prostate
2) membranous: lies in urogenital diaphragm
3) spongy/penile: through penis, opens at external urethral orifice
What is the penis? What does it do?
copulatory organ that delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract
What are the 3 parts of the penis?
1) root
2) shaft
3) glans penis
What is the prepuce (foreskin)?
cuff of skin covering the distal end of penis
What is circumcision?
surgical removal of the foreskin after birth
What is the internal penis made up of?
the urethra + erectile tissue
What is erectile tissue made up of?
spongy network of CT and smooth muscle with vascular spaces
What happens during an erection?
- erectile tissue fills with blood
- enlargment and stiffening of penis
What are the 2 types of erectile tissues?
1) corpus spongiosum
2) corpora cavernosa
Where is the corpus spongiosum located?
surrounds urethra + forms glans and bulb of penis
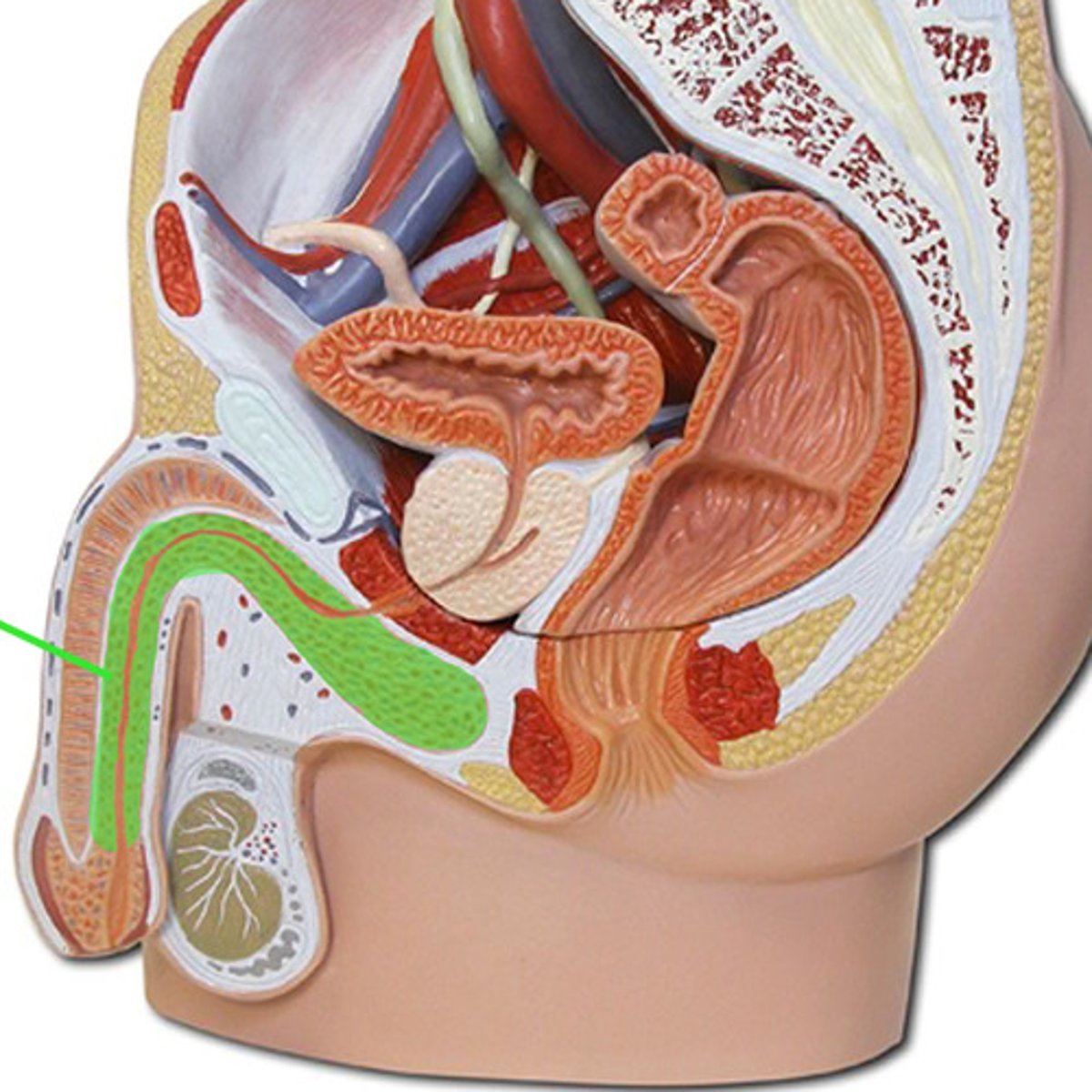
Where is the corpora cavernosa located?
paired dorsal erectile bodies bound by fibrous tunica albuginea
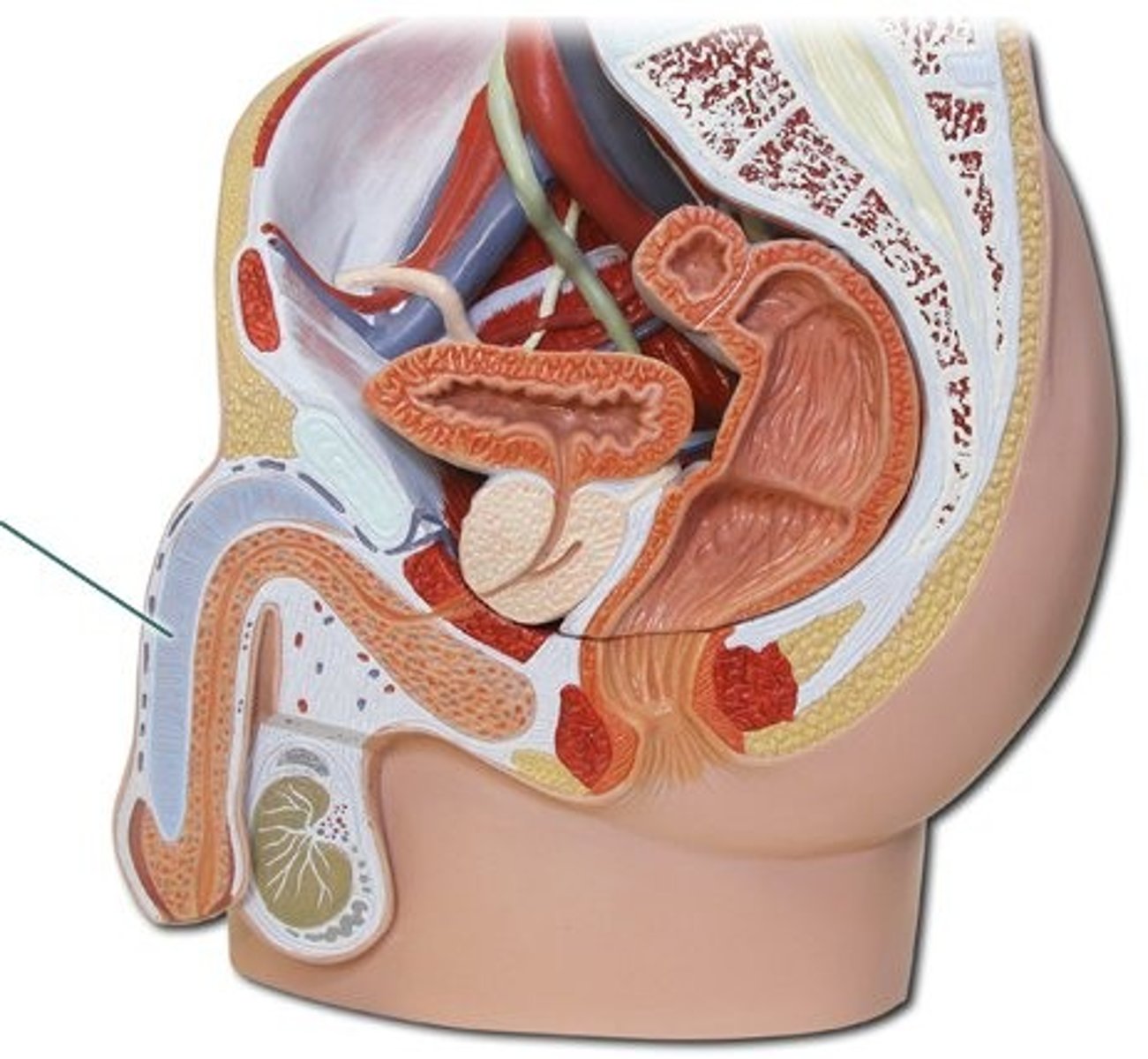
What do seminal vesicles do?
secrete 60% of the volume of semen
What is semen? What does it contain
- viscous alkaline fluid
- contains fructose, ascorbic acid, coagulating enzyme, prostaglandins
The seminal vesicles join the _________________ to form the ejaculatory duct.
ductus deferens
What happens to the sperm from the ductus deferens and the seminal fluid from the seminal vesicles?
- mix in ejaculatory duct
- enter the prostatic urethra during ejaculation
What are 2 roles of the prostate gland?
1) accounts for 1/3 of semen volume
2) plays a role in the activation of sperm
What are 4 characteristics of the prostate gland's fluid?
1) milky
2) slightly acidic
3) contains citrate and enzymes
4) has prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
Where does fluid from the prostate gland enter?
it directly enters the prostatic urethra during ejaculation
What do the bulbourethral glands do?
produce thick, clear mucus prior to ejaculation (lubricates the urethra)
Where is each located?
a) seminal vesicles
b) prostate gland
c) bulbourethral glands
a) posterior wall of bladder
b) encircles part of urethra; inferior to bladder
c) inferior to prostate
_________ are the primary female reproductive organs.
ovaries
What are 2 functions of ovaries?
1) make female gametes (ova)
2) secrete female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
What are 3 female accessory ducts?
1) uterine tubes
2) uterus
3) vagina
What does each include?
a) internal genitalia
b) external genitalia
a) ovaries and the internal ducts
b) external sex organs
The ovaries are paired organs on each side of the uterus held in place by several ligaments. What are these 3 ligaments?
1) ovarian
2) suspensory
3) mesovarium
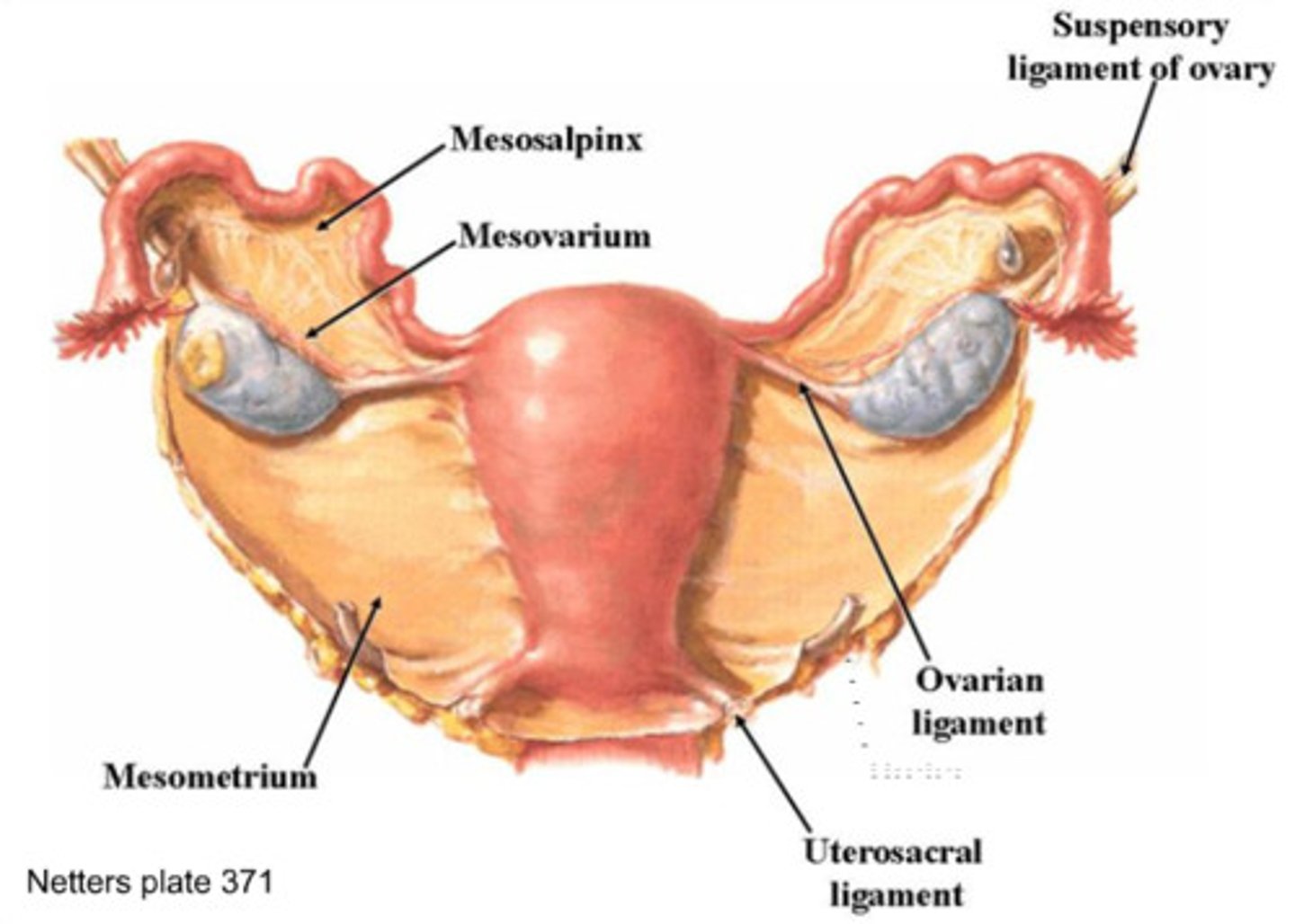
How does each ligament support the ovary?
a) ovarian
b) suspensory
b) mesovarium
a) anchors ovary medially to uterus
b) anchors ovary laterally to pelvic wall
c) suspends ovary in between
Regarding the broad ligament,
a) what does it support
b) what does it also contain
a) uterine tubes, uterus, vagina
b) suspensory ligament, mesovarium
Regarding the ovaries,
a) what are they surrounded by
b) what is embedded in its cortex
a) a fibrous tunica albuginea
b) ovarian follicles
What is a follicle?
an immature egg (oocyte) surrounded by cell layer(s)
What type of cells is the oocyte surrounded by if its...
a) one cell layer thick
b) more than one cell layer
a) follicle cells
b) granulosa cells
What are the 4 stages of ovarian follicle development?
1) primordial follicle
2) primary follicle
3) secondary follicle
4) Graafian follicle
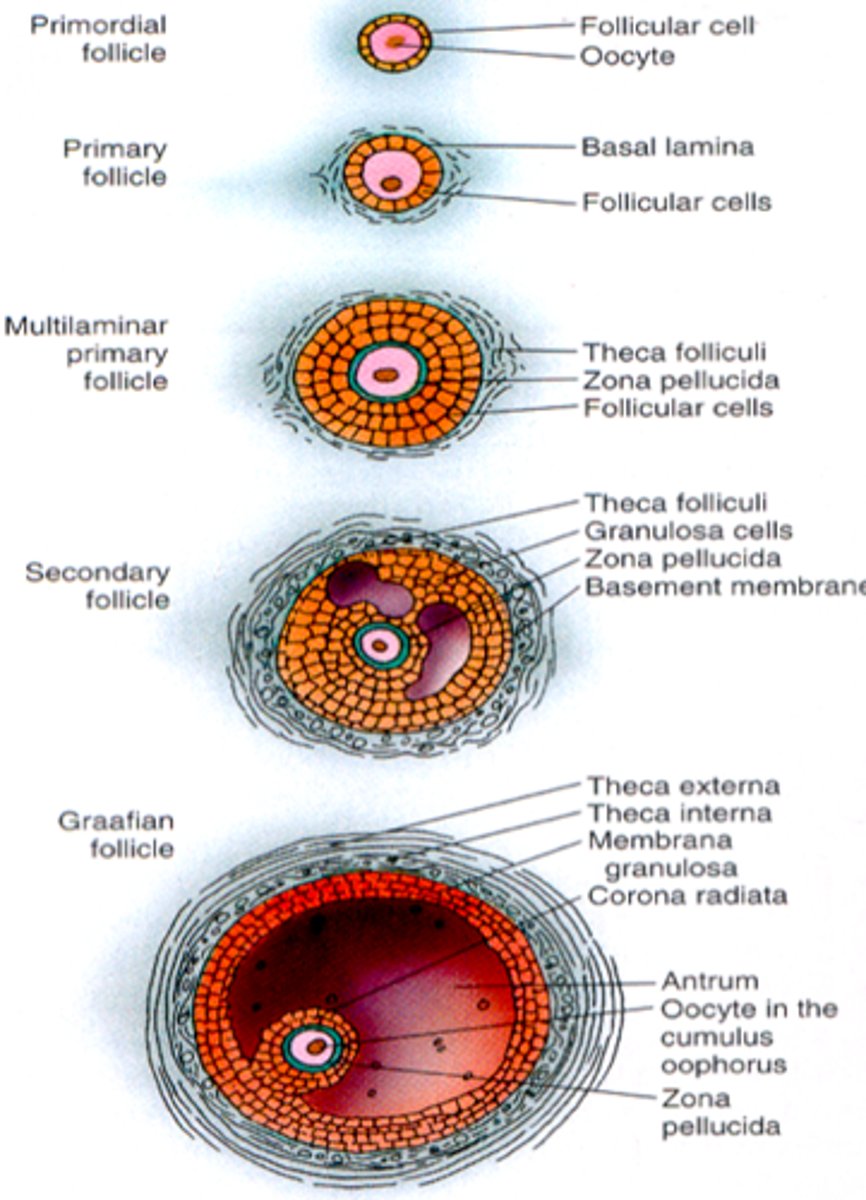
What surrounds the oocyte in...
a) primordial follicle
b) primary follicle
a) one layer of squamous like follicle cells
b) two or more layers of cuboidal granulosa cells
What does the secondary follicle have?
a fluid-filled space btwn granulosa cells, which forms a central antrum
What is the Graafian follicle?
- secondary follicle at its most mature stage
- bulges from surface of ovary
What is ovulation?
ejection of oocyte from ripening follicle
What is corpus luteum?
ruptured follicle after ovulation
What do the uterine tubes do?
- receive ovulated oocyte
- site of fertilization
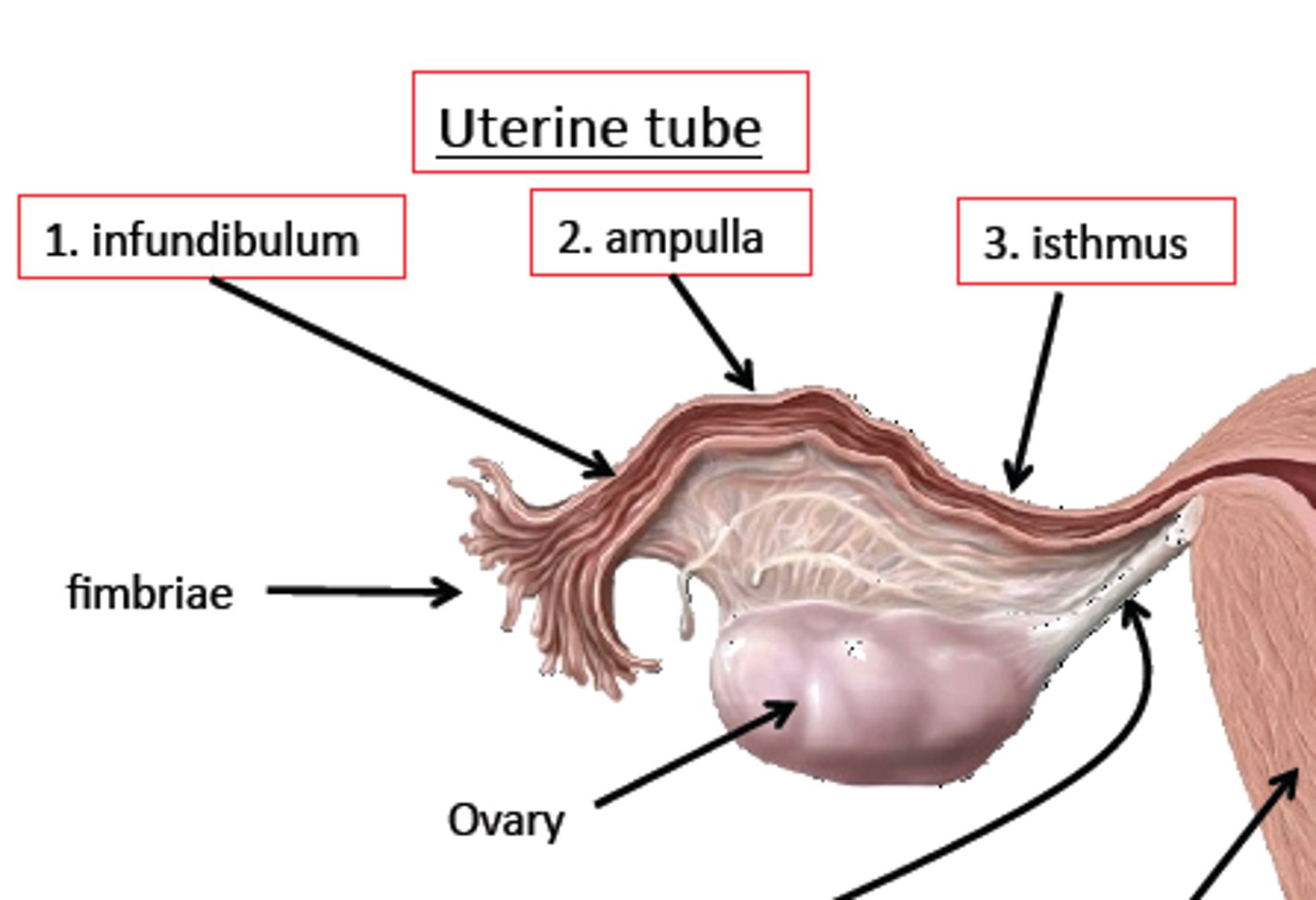
Uterine tubes empty into the superolateral region of the uterus via the ____________.
isthmus
Utering tubes expand distally around the ovary forming the ____________.
ampulla
The ampulla ends in the funnel-shaped, ciliated _______________ containing fimbriae.
infundibulum
True or False? The uterine tubes are directly connected to the ovaries.
false (they have no contact with the ovaries)
The ovulated oocyte is cast into the peritoneal cavity. How is it carried toward the uterus?
by peristalsis and ciliary action
What is the mesosalpinx?
visceral peritoneum that supports the uterine tubes
What is the uterus? Where is it located?
- hollow, thick organ
- anterior to rectum, posterior to bladder
What are 5 parts of the uterus?
1) body
2) fundus
3) isthmus
4) cervix
5) cervical canal
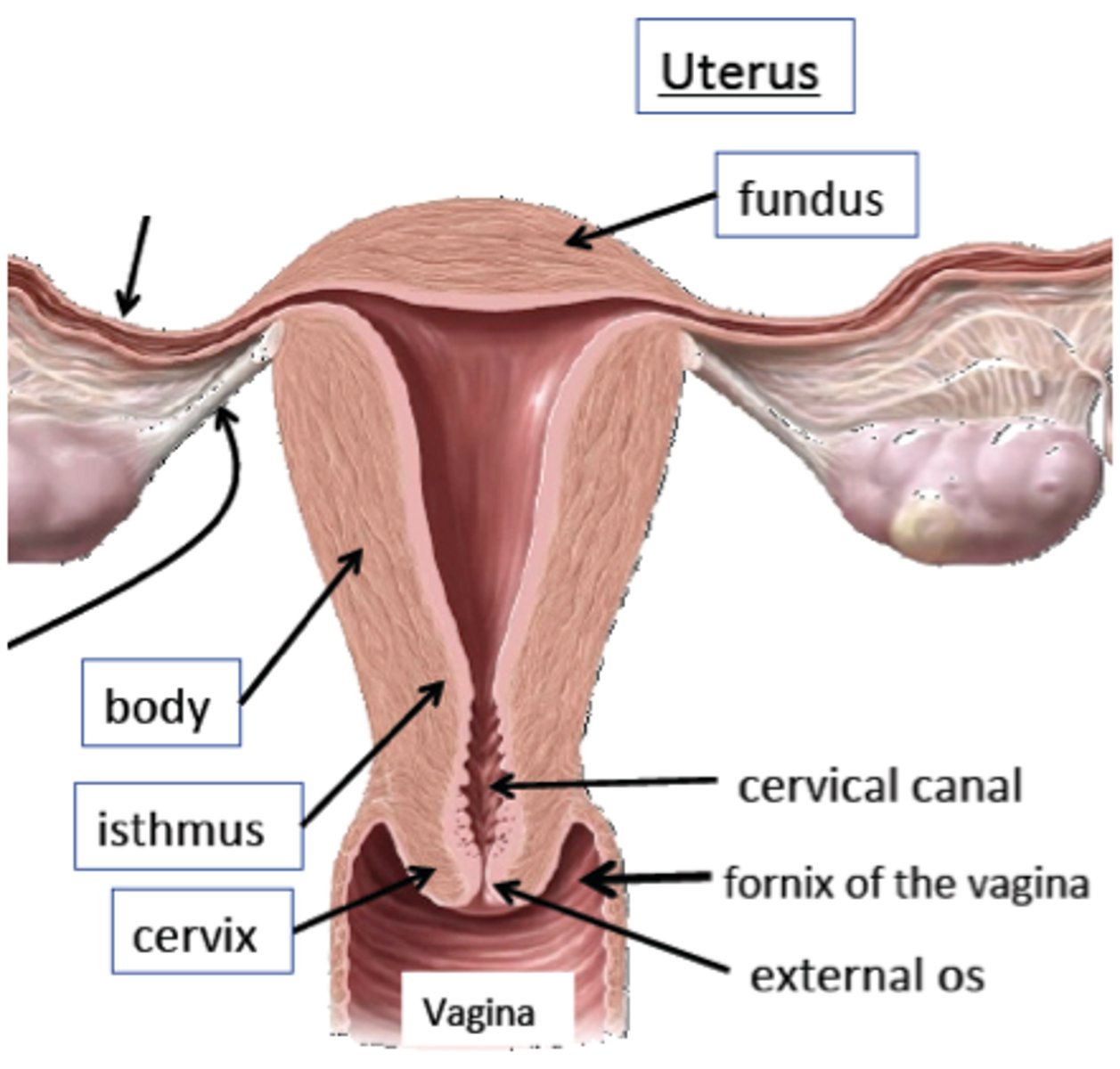
Describe the...
a) body
b) fundus
c) isthmus
d) cervix
a) major portion
b) rounded region superior to the entrance of uterine tubes
c) narrowed region btwn body and cervix
d) narrow neck, projects into vagina
For the cervical canal,
a) what is it
b) what does it communicate with (and via what)
a) cavity of the cervix
b) vagina via external os; uterine body via internal os
What is the function of cervical glands?
secrete mucus that covers the external os + blocks sperm entry (except during midcycle)
What are 4 supports of the uterus?
1) mesometrium
2) lateral cervical ligaments
3) uterosacral ligaments
4) round ligaments
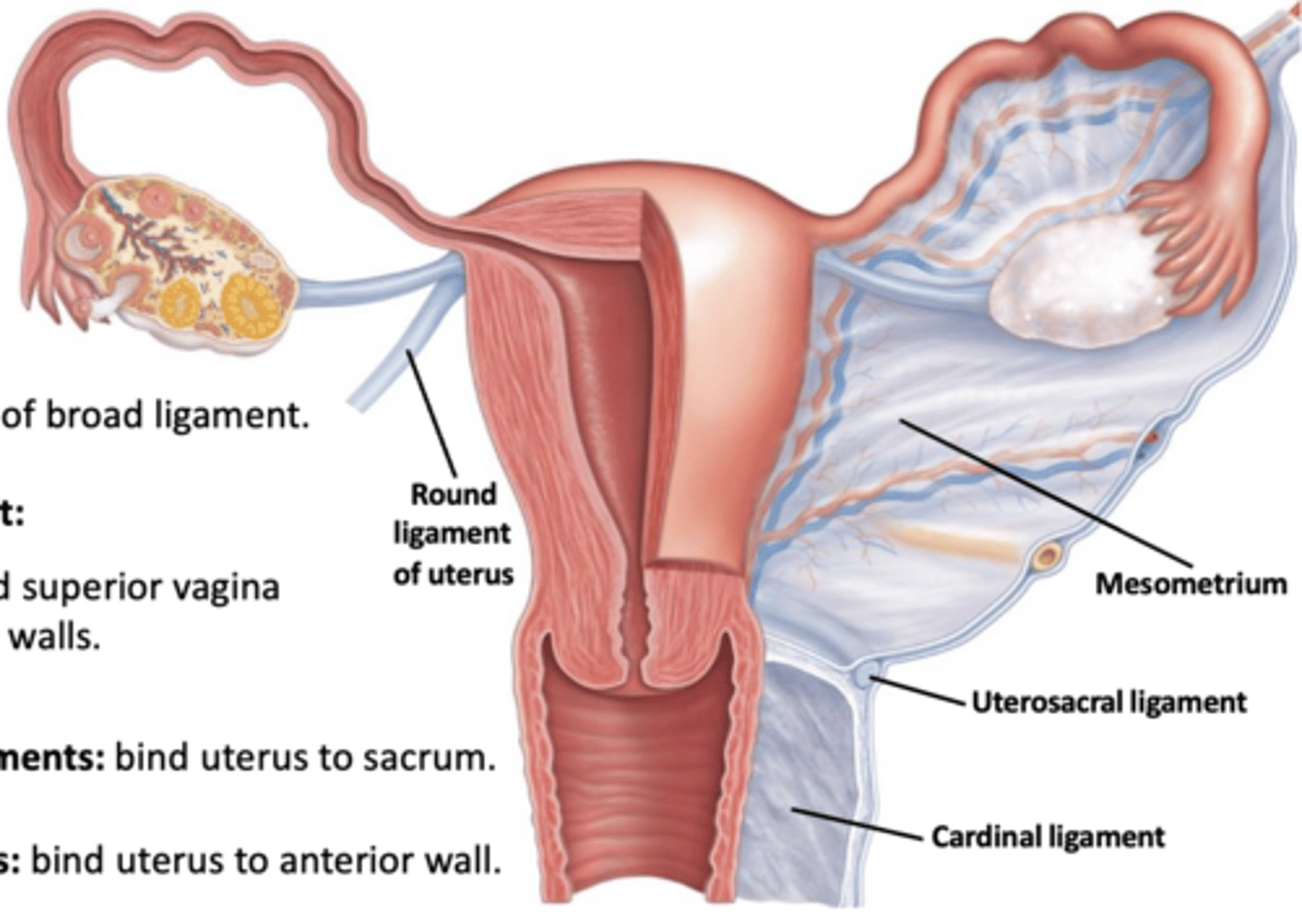
What does each do?
a) mesometrium
b) lateral cervical ligaments
c) uterosacral ligaments
d) round ligaments
a) part of broad ligament; supports uterus laterally
b) goes from cervix/superior vagina to walls of pelvis
c) paired; secure uterus to sacrum
d) bind anterior wall to labia majora
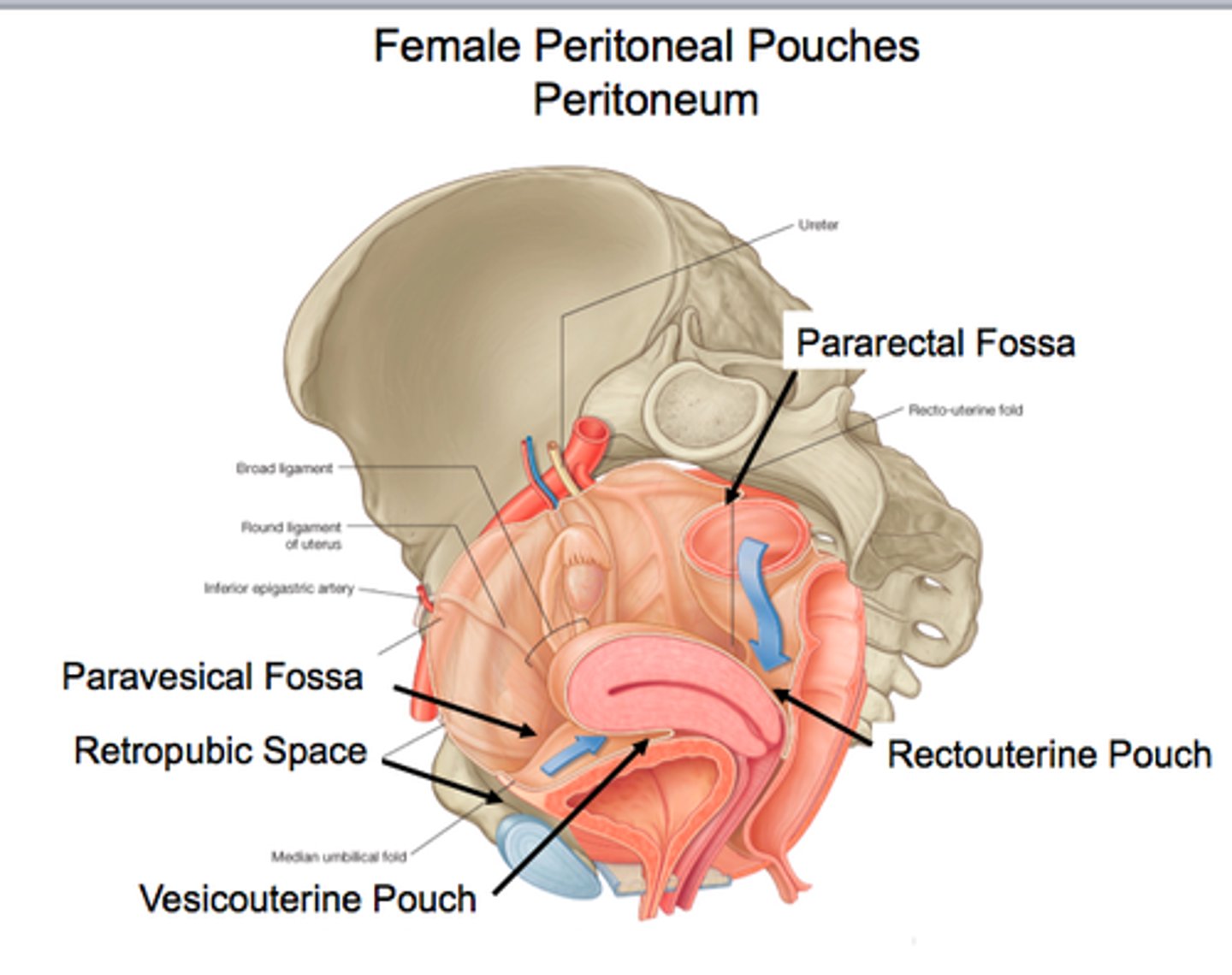
Several cul-de-sacs of peritoneum exist around the uterus. What are these 2 pouches?
1) vesicouterine pouch
2) rectouterine pouch
What does each peritoneal pouch lie between?
a) vesicouterine pouch
b) rectouterine pouch
a) bladder and uterus
b) rectum and uterus
What are the 3 layers of the uterine wall?
1) perimetrium
2) myometrium
3) endometrium
What is each layer?
a) perimetrium
b) myometrium
c) endometrium
a) outermost serous layer; the visceral peritoneum
b) middle layer of smooth muscle
c) mucosal lining of uterine cavity
Does the endometrium contain glands?
yes, it has numerous uterine glands
What are the 2 layers of the endometrium?
1) stratum functionalis
2) stratum basalis
What is the function of each?
a) stratum functionalis
b) stratum basalis
a) responds to ovarian hormones + sheds during menstruation
b) doesn't repond to ovarian hormones + forms new stratum functionalis after menstruation
What causes the stratum functionalis to shed during menstruation?
degeneration/regeneration of spiral arteries
What is the pathway of uterine vascular supply?
1) internal iliacs
2) uterine arteries: sides of uterus + send branches into uterine wall
3) arcuate arteries: in myometrium
4) radial branches: in endometrium
What do radial branches give off?
1) spiral arteries to stratum functionalis
2) straight arteries to stratum basalis
For the vagina...
a) what is it
b) what does it lie between
c) what is embedded in the anterior wall
d) how many coats does its wall have
a) thin-walled tube
b) btwn bladder and rectum
c) the urethra
d) three
What is the function of the vagina?
- provides a passageway for birth and menstrual flow
- organ of copulation
What are the 2 parts of the vagina (and define each)?
1) hymen: incomplete partition near vaginal orifice
2) vaginal fornix: upper end of vagina surrounding cervix
What are 6 female external genitalia (vulva/pudendum)?
1) mons pubic
2) labia majora
3) labia minora
4) greater vestibular glands
5) clitoris
6) perineum
What is the...
a) mons pubis
b) labia majora
c) labia minora
d) greater vestibular glands
a) fatty area overlying pubic symphysis
b) hair-covered, fatty skin folds; counterpart of male scrotum
c) skin folds within labia majora; counterpart of ventral penis
d) pea-sized glands flanking the vagina
Regarding the clitoris,
a) what is it homologous to
b) what are 2 parts of it
a) penis
b) prepuce: hoods (covers) erectile tissue + glans (exposed portion)
For the perineum,
a) what is it
b) what is it bordered by laterally
a) diamond-shaped region btwn pubic arch and coccyx
b) ischial tuberosities
What are mammary glands?
modified sweat glands
What are 3 parts of mammary glands?
1) areola
2) suspensory ligaments
3) lobes w/glandular alveoli
What does each do?
a) areola
b) suspensory ligaments
c) lobes w/glandular alveoli
a) pigmented skin surrounding the nipple
b) attach breast to underlying muscle
c) produce milk in lactating women
Alveolar glands pass milk to _______________________, which open to the outside.
lactiferous ducts
Semen is a milky white, sticky mix of _________________________________.
sperm + accessory gland secretions
What are 3 functions of semen?
1) provides a transport medium + nutrients (fructose) for sperm
2) protects + activates sperm
3) facilitates sperm movement
What happens to semen immediately after ejaculation?
clotting factors coagulate it