Group 7- The Halogens
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the trend in boiling point down the group?
Increases
More electrons
Therefore stronger van der Waals forces
What is the trend in reactivity down the group?
Decreases
Atomic radius increases because there are more energy levels
Weaker attraction between positive nucleus and outer energy level due to increased distance
Therefore harder to attractive force pulling an electron in
What does trend in reactivity tell us about the oxidising ability (as oxidising agents) of each halogen?
Oxidation is the loss of electrons
Oxidising agents cause another species to be oxidised and are themselves reduced
This means that fluorine and chlorine will be the strongest oxidising agents because halogens want to gain an electron upon reaction, causing the species they react with to be oxidised
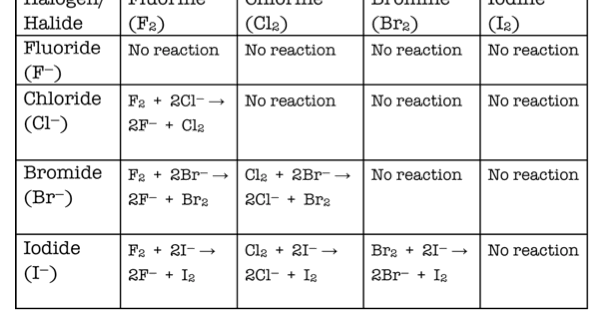
Describe and explain halogen displacement reactions, including displacement equations and what can be observed
Chlorine, bromine and iodine as diatomic molecules in solution are pale green, orange and brown respectively
When a more reactive halogen reacts with a less reactive halogen in solution, a displacement reaction takes place
Chlorine is more reactive than bromine and iodine so it displaces them and cannot be displaced by them
When added to bromide ions in solution, the colour changes from pale green to brown- the colour change is caused by the diatomic molecule in solution
Bromine is more reactive that iodine but less reactive then chlorine so it cannot be displaced by iodine but can be displaced by chlorine
Iodine is the least reactive so it cannot displace either of them and will be displaced by both of them
What is the ionic and overall equation for the reaction of chlorine with water?
Ionic equation: Cl2 + H2O ⇌ 2H+ + Cl- + ClO-
Overall equation: Cl2 + H2O ⇌ HCl + HClO
How is the reaction of chlorine with water used?
Used in swimming pools and drinking water- halogens are good antimicrobial agents
Chlorine is used in water supplies as it is toxic to bacteria/microbes
Adding it to water supplies is beneficial for the population
Why is chlorine which is toxic used in drinking water?
The benefits of adding chlorine to our drinking water outweighs the risks
It provides safe drinking water and the chlorine is in too low concentrations to be harmful to humans, but is enough for bacteria
What is the reaction of chlorine with water in direct sunlight?
2Cl2 + 2H2O → 4HCl + O2
Give the symbol equation for the reaction of chlorine with cold, aqueous sodium hydroxide
2NaOH (aq) + Cl2 (g) → NaClO (aq) + NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
What is the reaction of chlorine with cold, aqueous sodium hydroxide used for?
Household bleach commonly contains the chlorate (I) ion in the form of sodium chlorate (I), formed when chlorine reacts with cold, aqueous sodium hydroxide
Bleach acts as an oxidising agent against organic compounds in food stains, bacteria and dyes
What are the reactions of chlorine with water and cold, aqueous sodium hydroxide examples of?
Disproportionation reactions
What are reducing agents?
The cause other species to be reduced and are themselves oxidised
Electron donors
What is the trend in reducing ability of the halogens?
Reducing ability increases as you go down the group
Chlorine is the weakest reducing agent and iodine is the strongest
This is because Iodine’s ionic radius is the greatest and there is the greatest shielding between outer electrons and the positive nucleus due to more energy levels
This means it is easier to lose and electron, making iodine the strongest reducing agent
What test can we do to see the difference in reducing ability between the halogens?
Reactions of X- ions with concentrated sulfuric acid
Give the equation for the reaction between chloride ions in potassium chloride and concentrated sulfuric acid and any other resulting reactions. Then state what tests can be done to test the reducing ability of chloride ions.
KCl (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → KHSO4 (aq) + HCl (aq)
Fizzing- gas formed
Universal indicator turns red when hovering over solution- acidic gas given off
Misty white fumes when ammonia is held at the mouth of test tube- HX gas is produced (HCl)
Oxidation states tell us this is not a redox reaction
Give the equation for the reaction between bromide ions in potassium bromide and concentrated sulfuric acid and any other resulting reactions. Then state what tests can be done to test the reducing ability of bromide ions.
KBr (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → KHSO4 (aq) + HBr (aq)
2HBr (g) + H2SO4 (aq)→ SO2 (g)+ Br2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Fizzing- gas formed
Universal indicator turns red when hovering over solution- acidic gas given off
Misty white fumes when ammonia is held at the mouth of test tube- HX gas has been produced (HBr)
Reacts with K2Cr2O7/H+ paper (potassium dichromate paper) and its turns from orange to green - SO2 gas produced:
Orange gas produced (Br2)
This is a redox reaction
Why is SO2 hazardous?
It’s a choking gas
Give the equation for the reaction between iodide ions in potassium iodide and concentrated sulfuric acid and any other resulting reactions. Then state what tests can be done to test the reducing ability of iodide ions.
KI (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → KHSO4 (aq) + HI (aq)
HI (g) + H2SO4 (aq) → SO2 (g) + I2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
6HI (g) + H2SO4 (aq) → S (s) + 3I2 (g) + 4H2O (l)
8HI (g) + H2SO4 (aq) → H2S (g) + 4H2O (l) + 4I2 (g)
Fizzing- gas formed
Universal indicator turns red when hovering over solution- acidic gas given off
Misty white fumes when ammonia is held at the mouth of test tube- HX gas has been produced (HBr)
Reacts with K2Cr2O7/H+ paper (potassium dichromate paper) and it turns from orange to green- SO2 gas produced
Purple gas produced (I2)
Yellow solid produced (sulfur)
Lead acetate paper turns black- H2S gas produced
This is a redox reaction
How can we test for halide ions?
Add acidified silver nitrate
F- stays colourless
Cl- forms a white precipitate
Br- forms a cream precipitate
I- forms a yellow precipitate
Why is silver nitrate acidified when testing for halide ions?
Add acidified silver nitrate- acidified allows us to get rid of ions causing false positives like CO3- and OH- ions
AgOH masks other results
Ag2CO3 forms a cream precipitate that could be mistaken for bromine
How can we differentiate between chloride, bromide and iodide ions when tested for with acidified silver nitrate as they may appear to be similar colours?
Add dilute ammonia
Silver chloride ions turn colourless, but silver bromide and iodide ions have no visible change
Add concentrated ammonia
Silver bromide ions turn colourless but silver iodide shows no visible change
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between halide ions and silver nitrate?
Ag+ (aq)+ X- (aq)→ AgX (s)
What is the reaction for the addition of ammonia to silver halides?
AgX (s) + 2NH3 (aq) → [Ag(NH3)2]X (aq)
How can we test for ammonium (NH4+) ions and what is the ionic equation for this?
Add NaOH and warm (in a water bath)
Hold damp red litmus paper over mouth of test tube
Red litmus paper turns blue
NH4+ + OH- → NH3 + H2O
NH3 is an alkaline gas
How can we test for ammonium ions?
Add NaOH and warm
Hold damp red litmus paper of the mouth of the test tube
Damp red litmus papers turns blue