reactions of carboxyllic acids and esters
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what happens since the carboxylic acid group is polarised
the c + is open to be attacked by nucleophilles
the o- may be attacked by a + charged species (H+)
the H+ may be lost as H+
What happens if the H from OH- group is lost
a carboxylate ion is formed
what does the formation of a carboxylate ion defined as and why is this good
delocalisation
more stable ion
features or carboxylic acids in reactions
as they are weak acids there equilibrium is shifted to left, strong enough to react with sodium hydrogen carbonate to form carbon dioxide
carboxylic acids donate
protons
with what do they form ionic salts
more reactive metals
does the hydrolysis of an ester go to completion
no
what does the acid catalyst do?
affect rate at which equilibrium is reached, not the equilibrium composition of mixture
what are triesters made from
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
why are esters used as cleaning products eg, soap
long hydrocarbon chain is non polar (mix with grease)
COO- group is polar and ionic (mix with water)
glycerol features
forms hydrogen bonds and is very soluble in water
plasticiser - molecules to slip over each-other + flexible
solvent
attracts water so prevent creams drying out eg, pharmaceutical industry
name a type of renewable fuel
biofuel
fatty acid number derivative
3C17H35COOH
show acid hydrolysis of esters
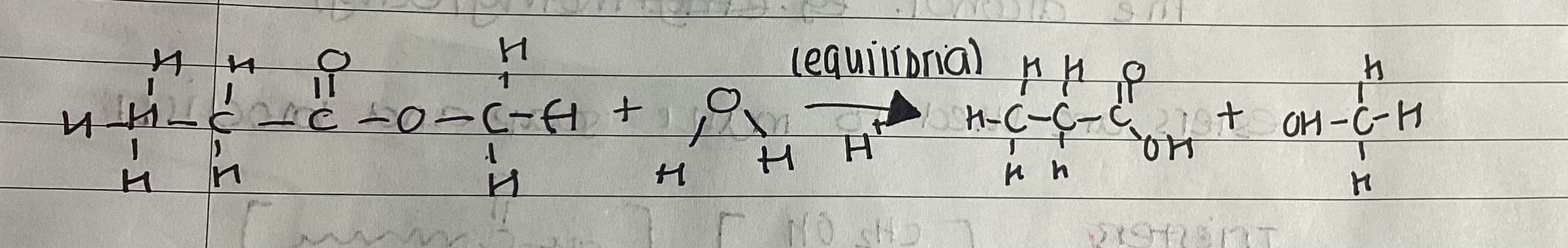
show full base hydrolysis of an ester using NaOH
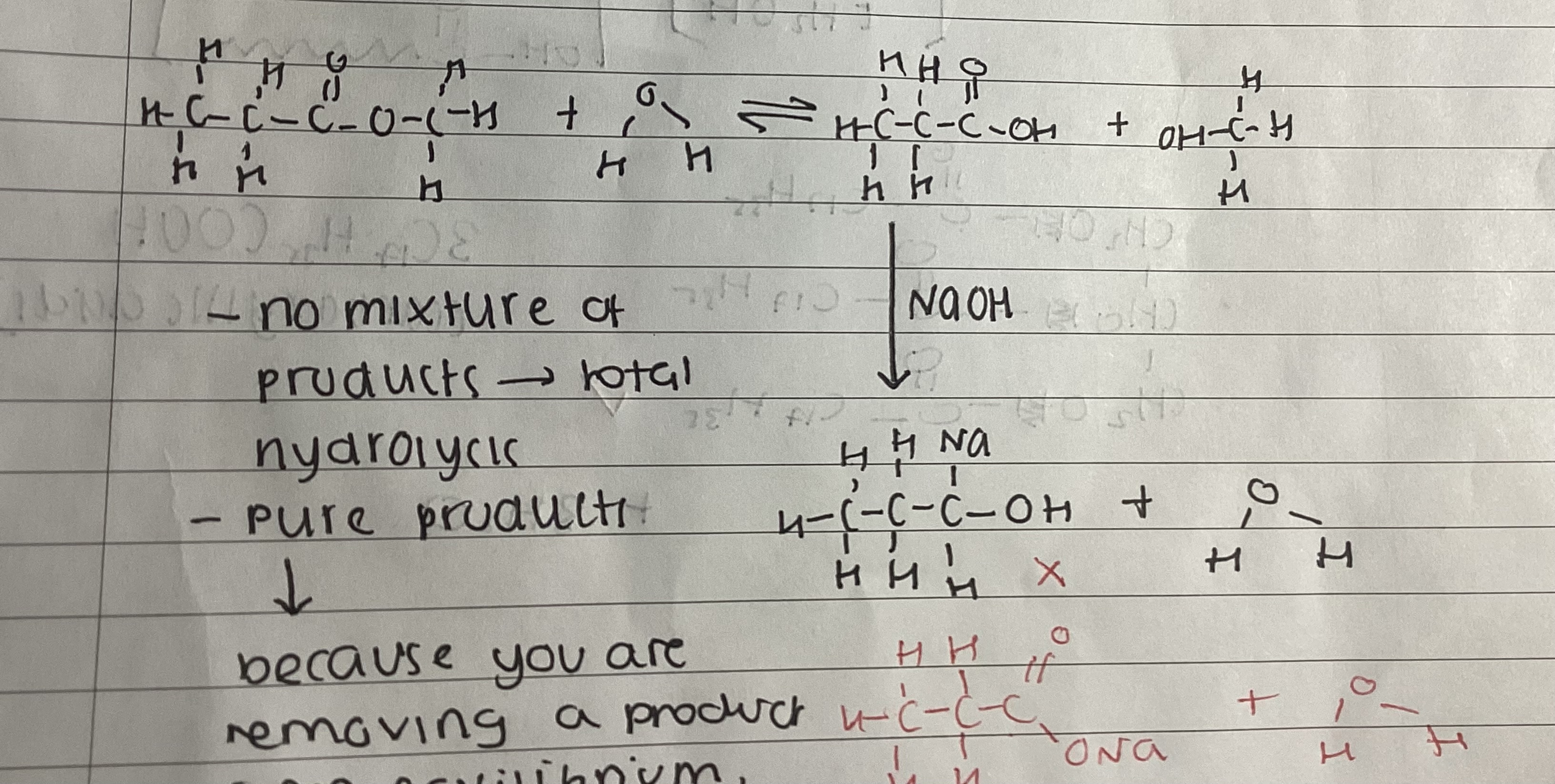
show complete final equation for base hydrolysis using NaOH
CH3CH2COOCH3 + NaOH → CH3CH2COONa + CH3OH
what is the name of CH3CH2COONa
sodium propanoate