SHS: Lab One
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Abduction
The movement of vocal folds away from the midline
Adduction
The movement of vocal folds toward the midline
Laryngeal Airway Resistance
The opposition provided by the larynx to the mass flow of air through it
Vocal fold abduction/adduction
The main contributor to glottal size and configuration
Longitudinal tension exerted by the cricothyroid muscles and activation of the muscles within the vocal folds (thyroarytenoid muscles)
The major contributors to vocal fold stiffness
VII (7)/ X (Vagus)
The intrinsic laryngeal muscles are innervated by
Degree of coupling between the trachea and the pharynx
Protection of the pulmonary airways
Containment of the pulmonary air supply
Sound generation
Functions of laryngeal functions
Separate at the bottom first and return to the midline at the bottom first (Also called “vertical phase difference” or Mucosal wave)
The medial surfaces of the vocal folds…
The rate of vocal fold vibration (expressed in Hertz, Hz, cycles/second), perceived as pitch. (The measurement of sound)
Fundamental Frequency
Vocal fold stiffness and their effective vibrating mass; the stiffer the vocal the higher the rate at which they vibrate. (Shorter movements)
Fundamental frequency is determined by…
A measure of the acoustic signal (in decibels, dB), perceived as loudness.
Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
Fundamental frequency - Sound pressure level composition
Spectrum
Laryngeal voice source and the “filter” that shapes it
Voice quality is dependent on…
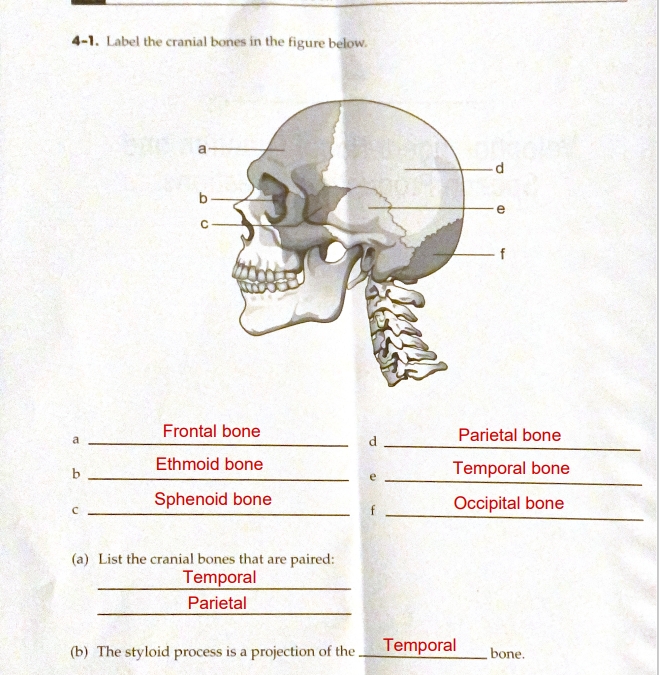
Eight
Temporal (two)
Parietal (two)
Occipital (one)
Frontal (one)
Sphenoid (one)
Ethmoid (one)
There are _____ cranial bones…
14
Maxillary (two)
Palatine (two)
Vomer (one)
Inferior nasal conchae (two)
Lacrimal (two)
Nasal (two)
Zygomatic (two)
Mandible (one)
There are ______ facial bones…
8
Frontal sinus
Ethmoidal
Maxillary
Nasal passage
Superior nasal concha
Middle nasal concha
Inferior nasal concha
There are _______ sinuses
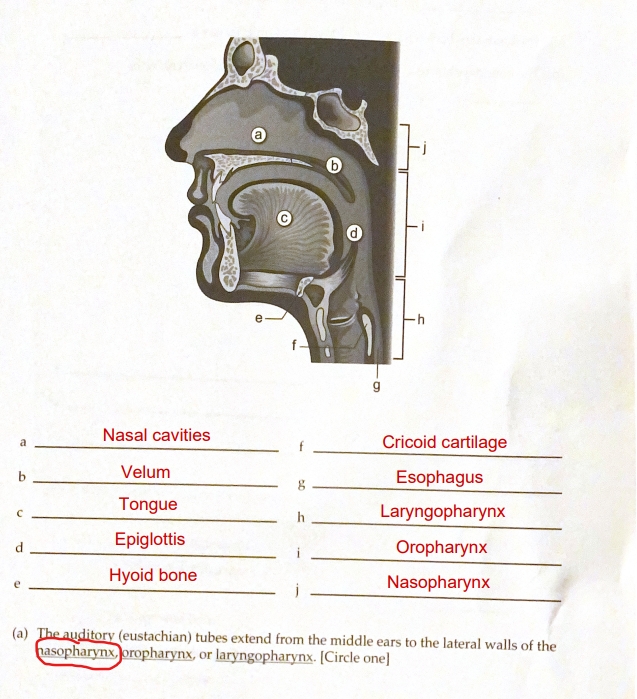
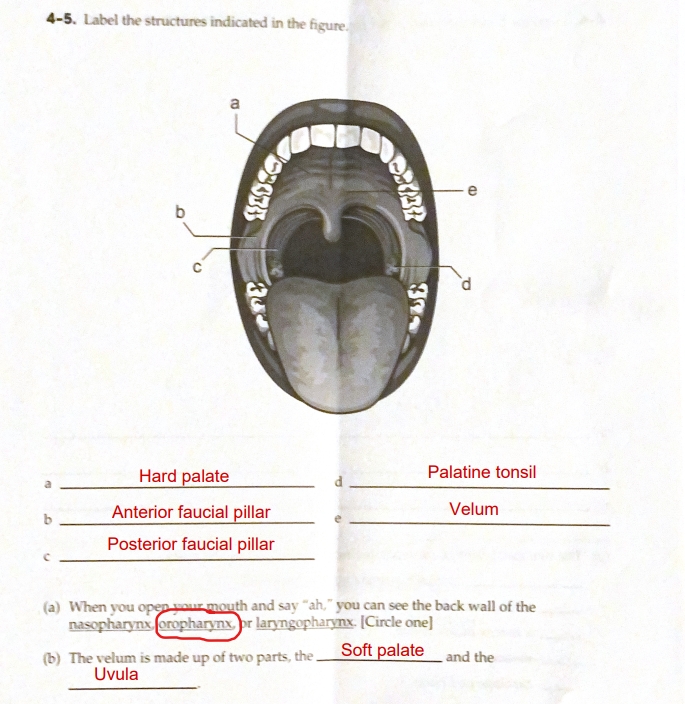
Nasopharymx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
The three cavities of the pharynx…
Two champers of the nasal cavity
The septum (Cartilage) separates…
• Recoil of muscles, cartilages, and connective tissues
• Surface tension
• Gravity
• Aeromechanical forces
Name passive forces of the velopharynx
• Muscles of the pharynx
• Muscles of the velum
• Muscles of the outer nose
Name active forces of the velopharynx
Superior, Middle, and Inferior
The sections of the constrictor muscles…
Thyropharyngeus (upper) and cricopharyngeus (lower) muscles
The inferior constitutor contains….
Swallowing by constricting the pharyngeal tube; by pulling pharyngeal walls inward and forward to constrict the pharyngeal tube
The main function for the constrictor muscles…
Constricts the pharynx
The superior constrictor…
Constricts the pharynx
The middle constrictor
Constricts the pharynx
The inferior constrictor…
Constricts and raises the pharynx
The salpingopharyngeus…
Widens and raises the pharynx
The stylopharyngeus…
Constricts and raises the pharynx
The palatopharyngeus…
Pulls the velum upward and backwards
The palatal levator…
Pulls the velum upward and shortens and increases the bulk of velum
The uvulus…
Pulls the velum downward and upward
The glossopalatine
Pulls the velum backward and forward
The pharyngopalatine…
Clavicles and scapulae
Components of the pectoral girdle
Coxal, sacral, and coccygeal (Vertebrae)
Components of the pelvic girdle
Lungs and airways
Pulmonary apparatus is…
Rib cage wall, abdominal wall, diaphragm, and abdominal content
Chest wall is…
Alveoli
Gas exchange occurs in….
Inner chest wall covered by thing membrane
The parietal pleura is…
Thoracic vertebrae, ribs, costal cartilages, sternum, and pectoral girdle
Rib cage wall consists…
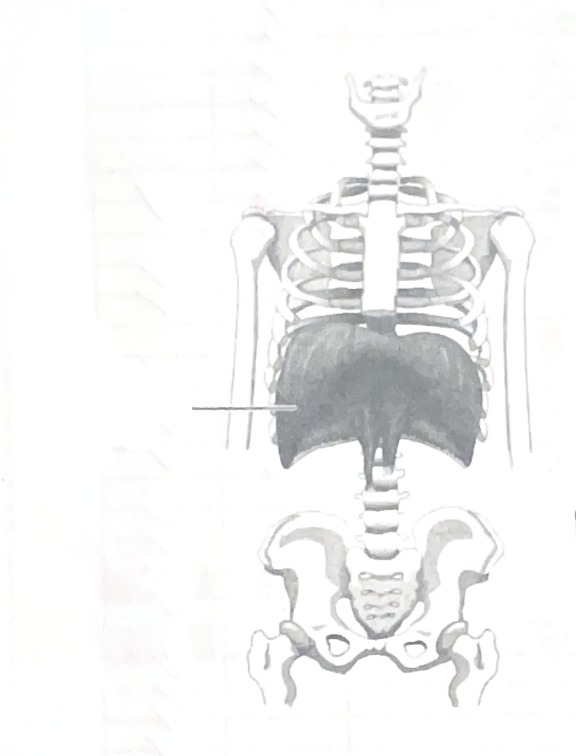
Floor of the thorax
The diaphragm forms…
Natural recoil of muscles, cartilages, ligaments, and lung tissue
Surface tension of the alveoli
Pull of gravity
What are passive forces of breathing apparatus….
Rib cage wall muscles, diaphragm, muscle, abdominal wall muscles
What are active forces of breathing apparatus….
Alveolar pressure
Pressure most important for speech production that is inside the lungs…
Pulls downward on the central tendon to enlarge the thorax vertically (flattened)
and/or
Elevates the lower six ribs to enlarge the thorax circumferentially (Domed)
Movements of the diaphragm…
Lung volume
Alveolar pressure
Chest wall shape
Variables of breathing….
Size of the breathing apparatus
Breathings relation to volume…
Volume of air in the pulmonary apparatus after a maximum inspiration
Total lung capacity is…
Sum of all passive and active forces operating on the breathing apparatus
Alveolar pressure represents…
Inversely related when the breathing apparatus is closed (Boyle’s Law)
Lung volume and alveolar pressure are…
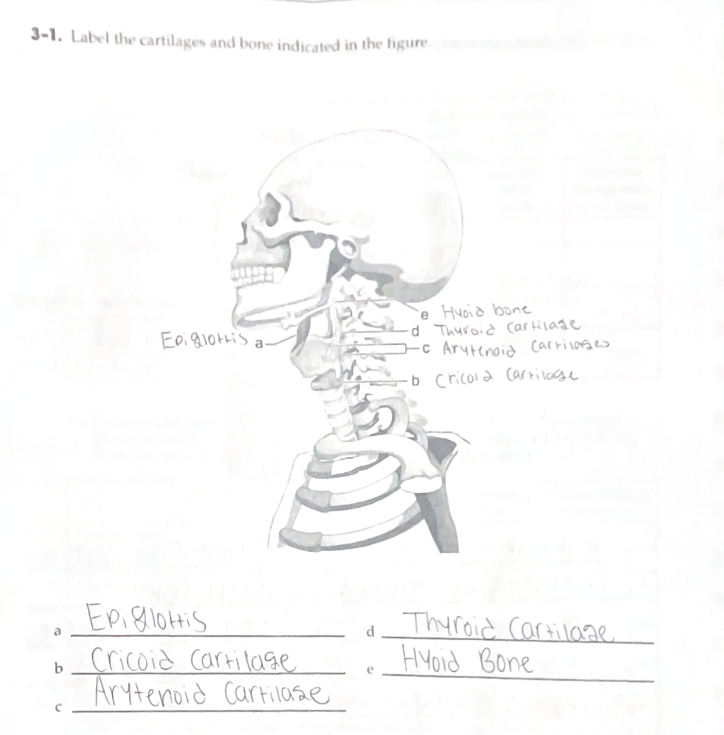
Cricothyroid and cricoarytenoid
The laryngeal joints are…
*Rotating and gliding
The cricothyroid joints motions are…
*Rocking and gliding
The cricoarytenoid joints motions are…
• Epithelium: squamous cells
• Superficial lamina propria: a few elastic
fibers; also called Reinke’s space
• Intermediate lamina propria: many elastic
fibers
• Deep lamina propria: many collagenous
fibers
• Muscle: muscle fibers (thyrovocalis)
Layers of the vocal folds are…
Both inside the larynx
Intrinsic ligaments and membranes connect…
One attachment inside the larynx and one outside the larynx
Extrinsic ligaments and membranes connect…
Both attachments outside the larynx; actions influence the larynx through the hyoid bone
Supplementary ligaments and membranes connect…
…
Infrahyoid and suprahyoid > Supplementary
Recoil of muscles, cartilages, and connective tissues
Surface tension
Gravity
The passive forces for laryngeal forces…
Intrinsic muscles
Extrinsic muscles
Supplementary muscles
The active forces for laryngeal forces…
Internal (thyrovocalis) and external (thyromuscularis) thyroarytenoids
Parts of the thyroarytenoid…
Originates below the hyoid bone
Infrahyoid means…
Originates above the hyoid bone
Suprahyoid means
Diaphragm
Inspiratory
Sternocleidomastoid breaths…
Inspiratory
Scalenus anterior, medius, and posterior breathes…
Inspiratory
Pectoralis major breathes…
Inspiratory
Pectoralis minor breathes…
Inspiratory
Subclavius breathes…
Inspiratory
Serratus anterior breathes…
Inspiratory
External intercostals breathes…
Expiratory
Internal intercostals (between ribs) breathes…
Inspiratory
Internal intercostals (between costal cartilages) breathes…
Expiratory
Transversus thoracis breathes…
Both inspiratory and expiratory
Latissimus dorsi breathes…
Expiratory
Serratus posterior inferior breathes…
Inspiratory
Lateral iliocostalis cervicis breathes…
Expiratory
Lateral iliocostalis lumborum breathes…
Both inspiratory and expiratory
Lateral iliocostalis thoracis breathes…
Inspiratory
Levatores costarum breathes…
Expiratory
Quadratus lumborum breathes…
Expiratory
Subcostals breathes…
Inspiratory
Diaphragm breathes…
Expiratory
Rectus abdominis breathes…
Expiratory
External oblique breathes…
Expiratory
Internal oblique breathes…
Expiratory
Transversus abdominis breathes…

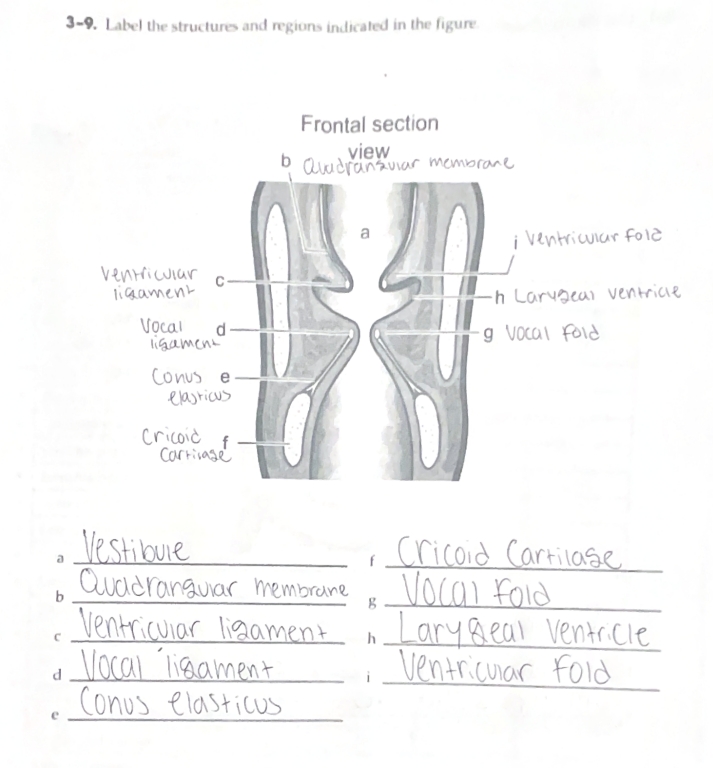
Shortening, tensing, and abducting the vocal folds
Thyroarytenoid muscles influence the vocal folds by…
Lengthening and abducting vocal folds
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscles influence the vocal folds by…
Adducts/compresses vocal folds
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles influence the vocal folds by…
Adducts/compresses vocal folds
Arytenoid muscles influence the vocal folds by…
Tenses and lengthens vocal folds
Cricothyroid muscles influence the vocal folds by…
Downward and forward movements in housing
Sternothyroid muscles influence the housing by…
Upward and downward movements in housing
Thyrohyoid muscles influence the housing by…
Downward movements in housing
Sternohyoid muscles influence the housing by…