Lec 5 - Cancer treatment and classiciation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are some ways we can suppress cancer besides chemotherapy? (4)
tyrosine kinase inhibitors
histone deacetylase inhibitors (SIRT pathways)
angiogenesis inhibitors
immunotherapy
Reduce cell proliferation and increase apoptosis
What is tyrosine kinase? What will tyrosine kinase inhibitors do?
Tyrosine Kinase promotes survival and proliferation of some cells
TK is over-active in cancer cells
May play a role in modulating p53 as well
TK inhibitors will decrease this activity
Block signal pathways that cause cells to proliferate - stop pathway for cell division
upregulate pathways that cause apoptosis
What do Histone deacetylase inhibitors do? How does it work?
Plays important role in gene expression
Abnormal activity of HATs (histone acetyltransferase) or HDACs (histone deacetylase) can either promote or inhibit suppessor or promotor genes
Factor in acute promyelocytic leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and some types of colorectal and gastric carcinoma
May re-sensitize cells to drugs, chemotherapy
Can affect expression of suppressor genes (epigenetic)
What is angiogenesis? What do angiogenesis inhibitors do? **exam
This is a vital in tumour growth
provides oxygen and nutrient supply
allows for metastasis
Inhibitors reduce formation of blood vessels (choking cells, by cutting off blood supply)
Limit growth and metastasis
Eg. Vasostatin, Angiostatin, Thalidomide, Sorafenib
What is immunotherapy?
AKA biologic therapy which boost body’s own immune response
Recognition of cancer cells
Slow or stop growth of cells/ kill cells
Stimulating immune response to cancer cells
What are some immunotherapy treatments? **exam (know each and one sentence describing what each is )
monoclonal antibodies
oncolytic virus therapy
t-cell therapy
cancer vaccines
What is interferon/interleukins therapy treatment? What does each do and how?
Are cytokines in the immune response
Interferons increase resistance in normal body cells
Blocks growth of cancer cells
Causes cancer cells to send out cytokines (identifiers)
Makes cancer cells more susceptible to the cytotoxic (killer) T cells
Interleukin 2 increases activity of T-cells
Inhibits growth in cancer cells
Can be used in most cancers
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Lab-made antibodies
Can increase body’s own antibodies and response
Can block protein activity in cancers (targeted therapy)
Cancer cells “hide” by activating immune checkpoints
Body uses these normally to recognize its own cells
Antibodies can turn off these checkpoints
Amplify bodies response to the cancer
Eg.Ipilimumab, Nivolumab Avelumab Durvalumab
How are monoclonal antibodies made? What do they help to do?
Made from clones of one cell (antigen)
Help to bind Killer T cells
Help to bind radioactive and immunotoxins
Can trigger apoptosis
What is targeted therapy? Exmaple?
Therapies are specific to the genetic changes in that tumour, rather than just location in body
Can target proteins specific to the cancer
Eg. Monoclonal antibodies can attack
Small synthetic molecules
Block or turn off cell growth and division signals
Shorten cell lifespan
Directly destroy cancer cells
What is oncolytic virus therapy? What cancer was it used for?
Inject a genetically modified virus into tumour
doesn’t enter healthy cells
Virus enters the cancer cells to replicate
Causes cancer cells to rupture and die
proteins released from dying cells trigger immune system to target any cancer cells that have the same proteins
May cause symptoms – fever, fatigue, nausea
Has been used on melanomas
Clinical trials for others
What are challenges with oncolytic virus therapy? (2)
Innate immune response may attack the virus before entry or before immune response is developed
Tumour may suppress immune response
What is t-cell therapy? What cancer is it used for?
Aka chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy
Remove patients’ T-cells (cancer cells or WBC…)
Modify / add receptors that will recognize the cancer cells
Re-inject into patient to kill cancer cells
May trigger fever, seizure, confusion,
Can be used for blood cancers
Testing being done on other cancers
What are types of cancer vaccines? (2)
Treatment vaccines
Expose body to cancer cells or proteins (antigens) or DNA segments to trigger an immune response
Being studied
Preventive
Eg. HPV vaccine
Prevents viral infection that can be causative in cancer
What are the top age-related cancers? (5)
lung
breast
prostate
colorectal
bladder
What is the fastest increasing cancer in Canada?
Melanomas
more so on east than west
can be higher in AB due to out altitude
What cancers have the poorest survival rate?
Pancreas and lung cancers
breast cancer rates have decreased by a lot
What are the general risk factors for cancers? (7)
Genetics
Aging
Diet / Exercise / obesity
Alcohol
Smoking
Ethnicity
Chronic inflammation
Pre-existing diseases
What is hyperplasia in cancer?
Overgrowth of cells
Triggered by stimulus
(eg. Hormones, pressure, deficiency)
Stops when stimulus removed
What is neoplasm in cancer?
Independent and excessive growth
Cells are different in appearance
abnormal cells
What is neoplasia?
Tumour
Fast growth of cells
grow more rapidly than normal cells
What are characteristics of benign tumours? **exam
tumour is encapsulated and has clearly defiend edges
doesn’t metastasize and has limited growth potential (grows slower)
differentiated - resembles tissue from which it grew
like dysplasia and hyperplasia…
What are characteristics of malignant tumours? **exam
invades normal tissue - no encapsulation
does metastasize and forms tumours in distant locations (cells pull off)
abnormal tissue - rapid, uncontrolled growth
neoplasia…
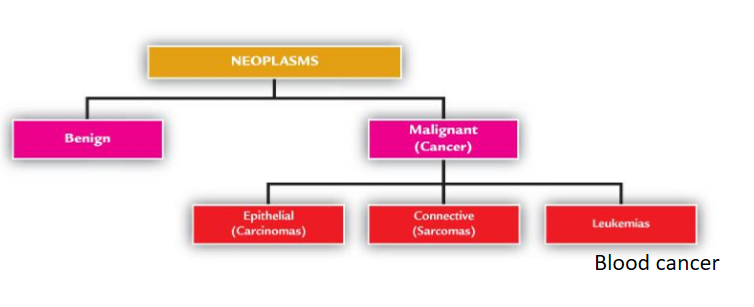
How can neoplasms be classified? How are they classified? **exam
into benign or malignant (cancer)
Malignant has 3 types
epithelial (carcinomas)
connective tissue (sarcoma)
leukemias (blood cancer)
Classified according to:
Appearance and growth pattern
Type of body tissue from which they arise
What is carcinoma? **exam
neoplasm of the epithelial cells
Largest group of malignancy
Skin as well as epithelial linings (mucous membranes etc.)
What is adenocarcinoma?
Occurs in epithelial tissues with glandular origin
type of carcinoma
What is sarcoma? Mixed cancer? **exam
Sarcoma
Neoplasms of connective tissue
Mixed Cancer
epithelial and connective tissue
What are tumours? (3) **exam
Melanoma
Malignant neoplasm of melanocytes
Glioma
tumours of glial cells of brain
Lymphoma
neoplasms of Lymphoid tissue and blood-forming organs
What is leukemia? **Exam
Happens in white blood cells
can be lymphocytic leukemia or myelocytic leukemia
When does cancer present as we age?
Peak age of diagnosis – age 65
Cancer cell growth can slow down after the age of 75
Lower metabolic rates with age
How can cancer invade and metastasize? (3 examples)
Carcinomas and epithelial tissue neoplasms commonly spread
Sarcomas shed cells into bloodstream
Lymph nodes filter cancer cells
Absence of lymph node involvement favourable