Systemic Anatomy - The Endocrine System
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture and lab material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
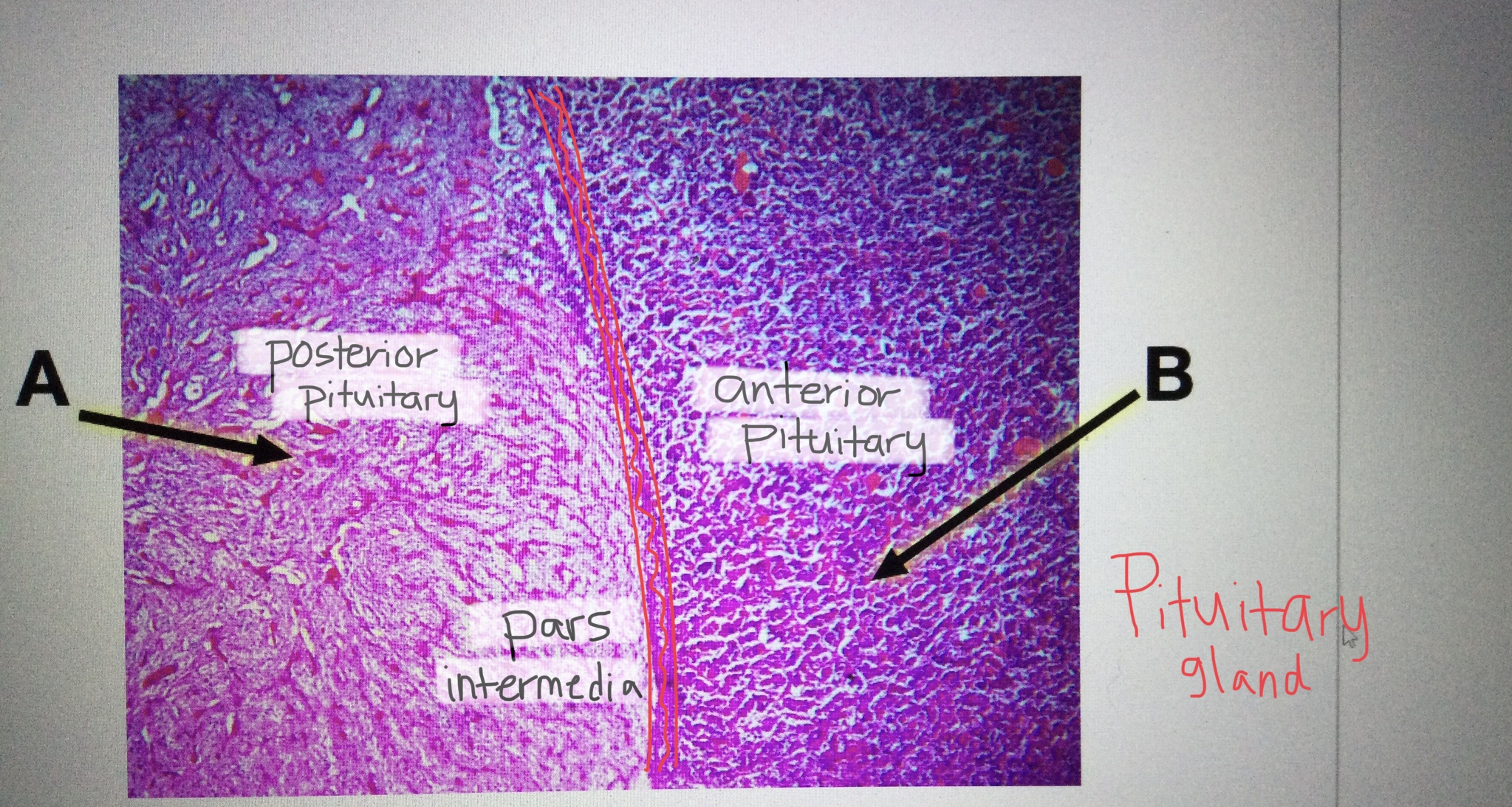
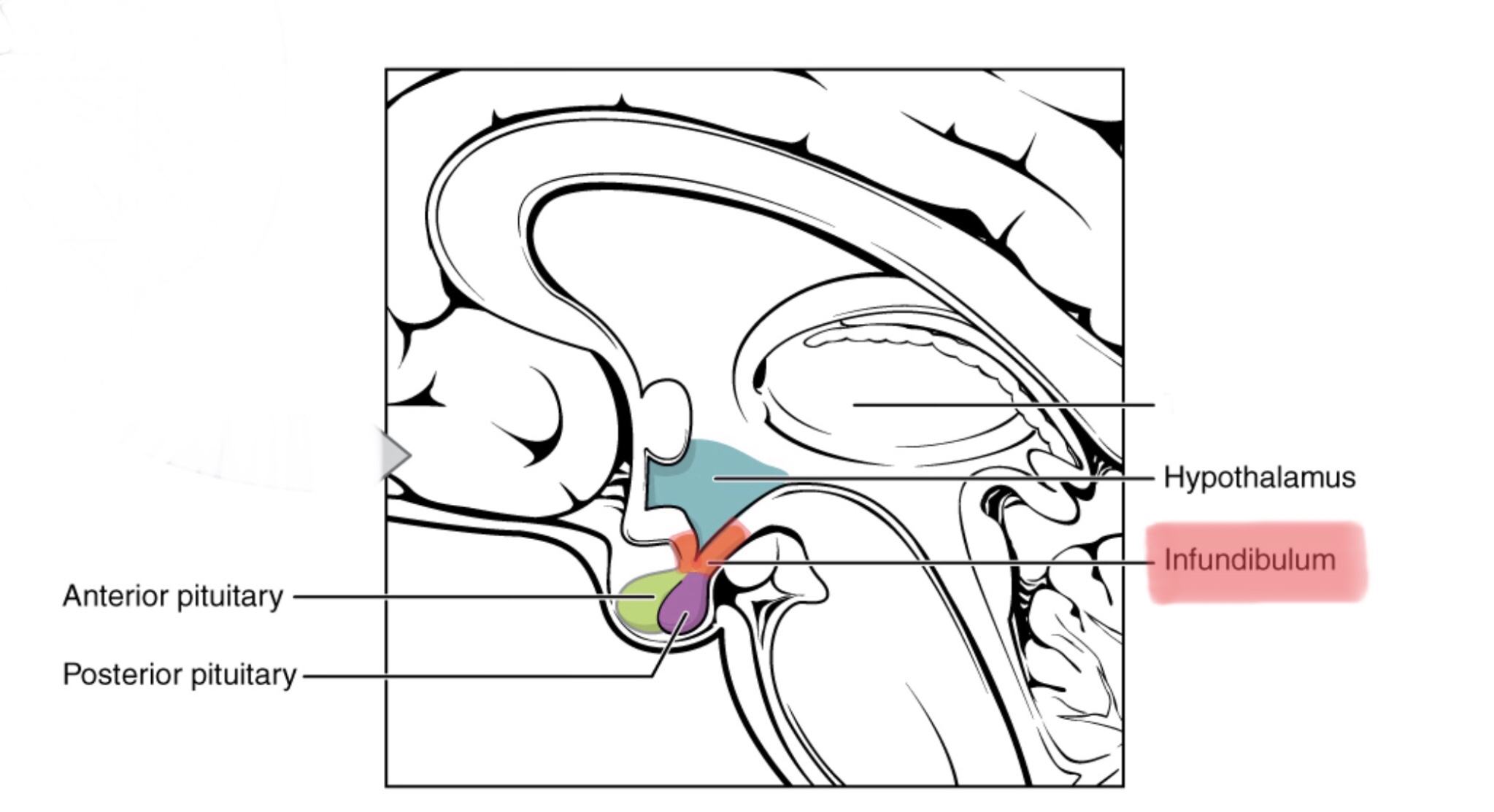
Identify pituitary tissue.
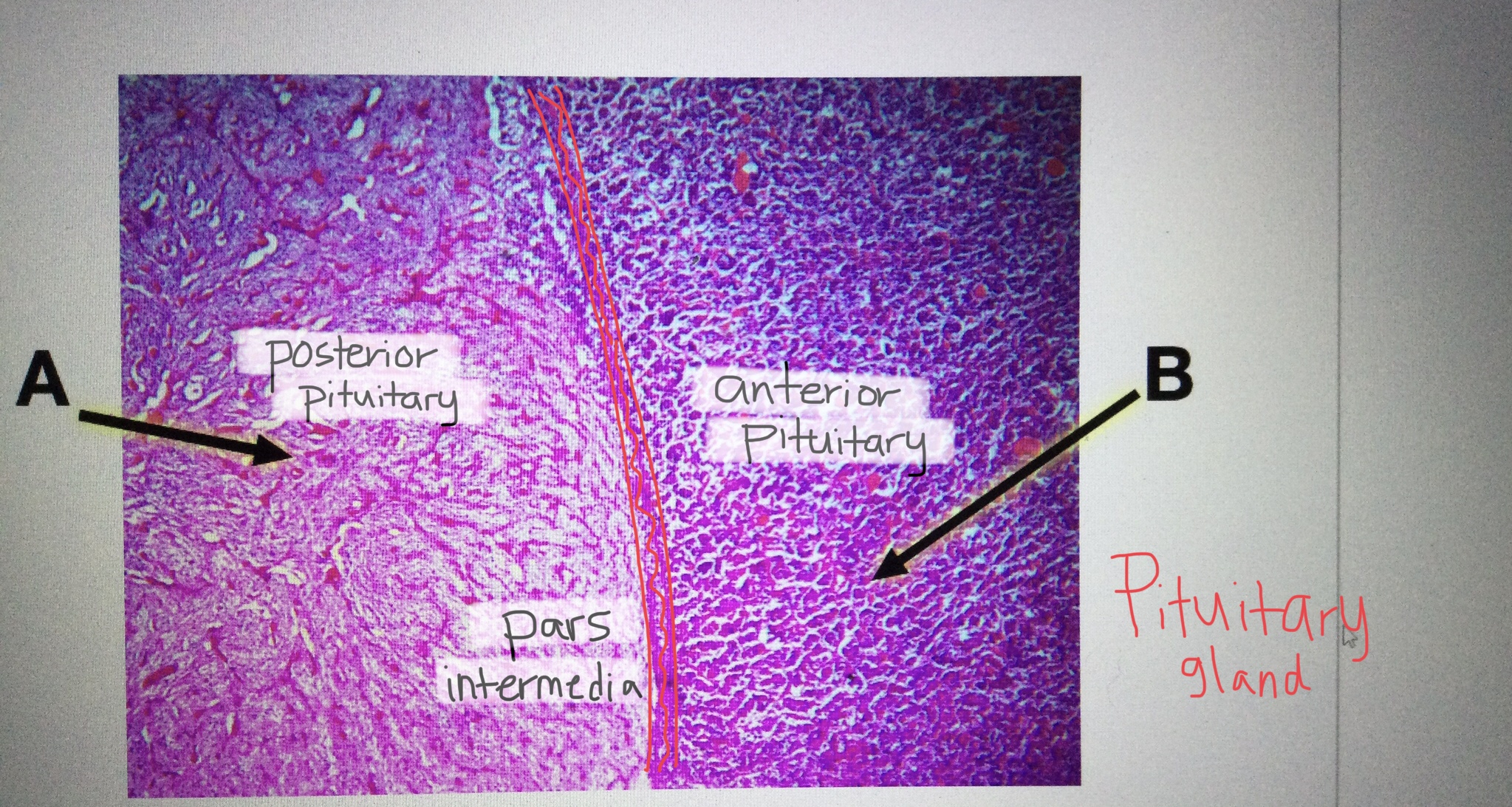
Identify anterior pituitary tissue.
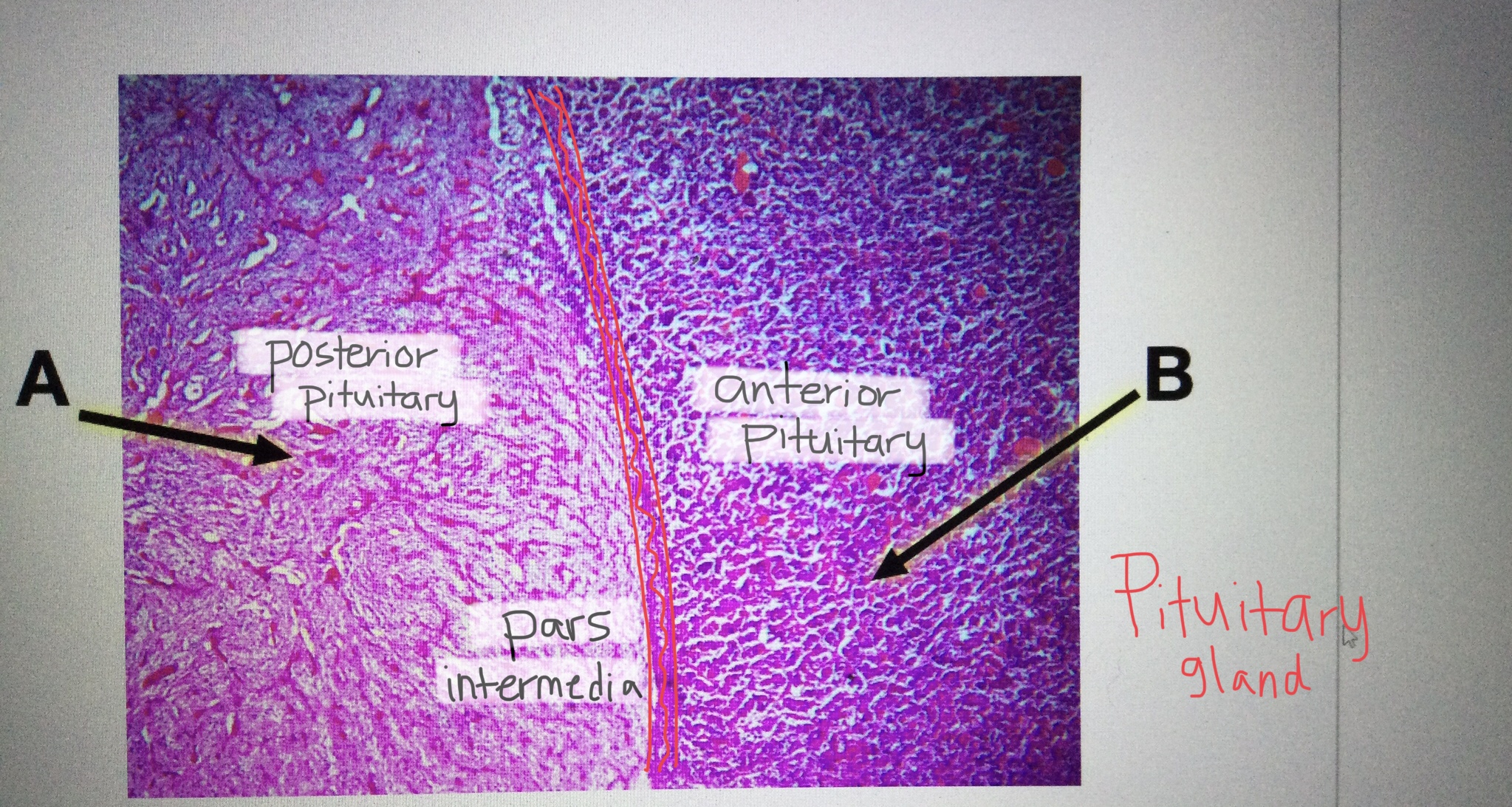
Identify posterior pituitary tissue.
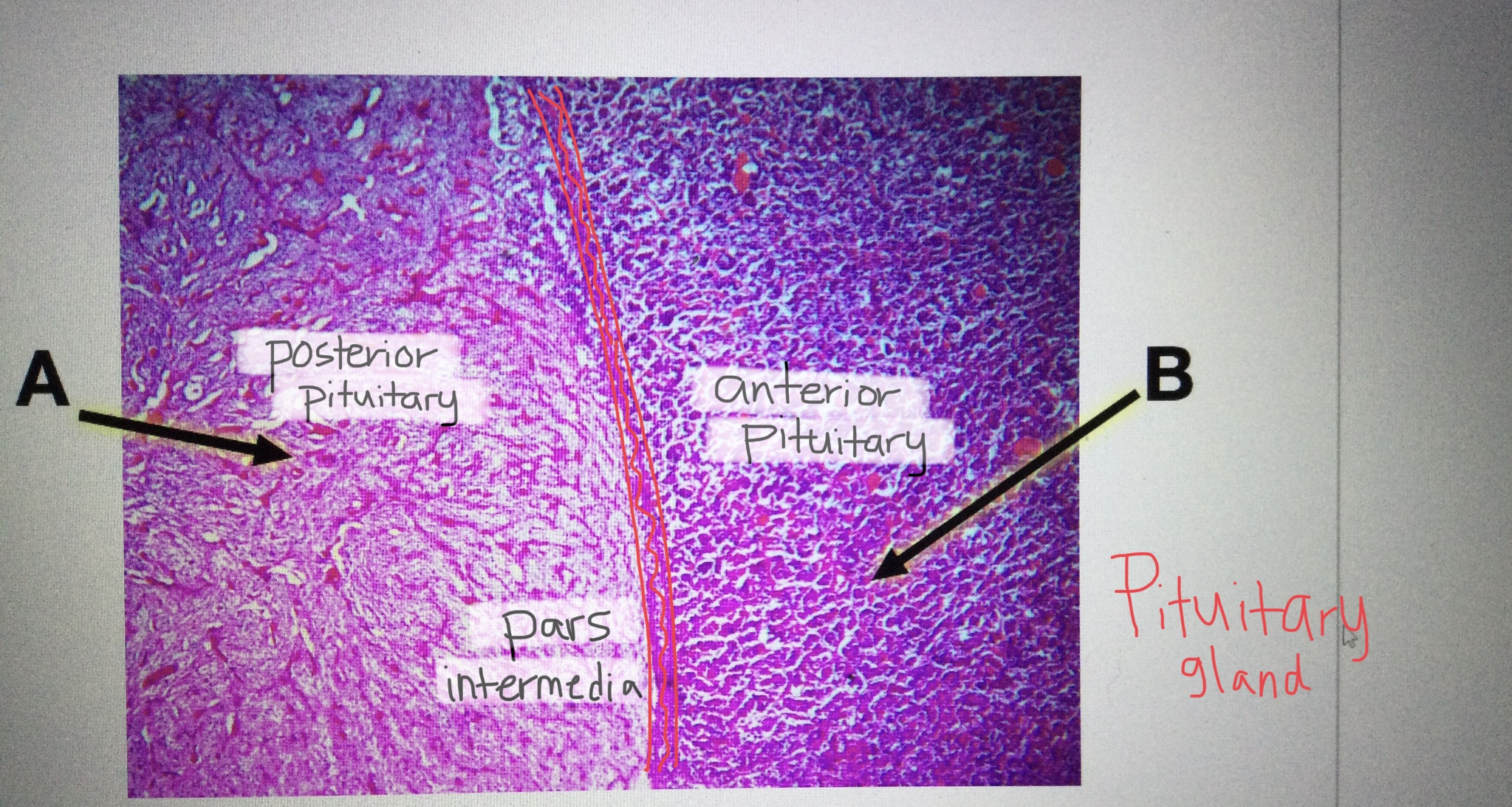
Identify the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland.
Identify the infundibulum.
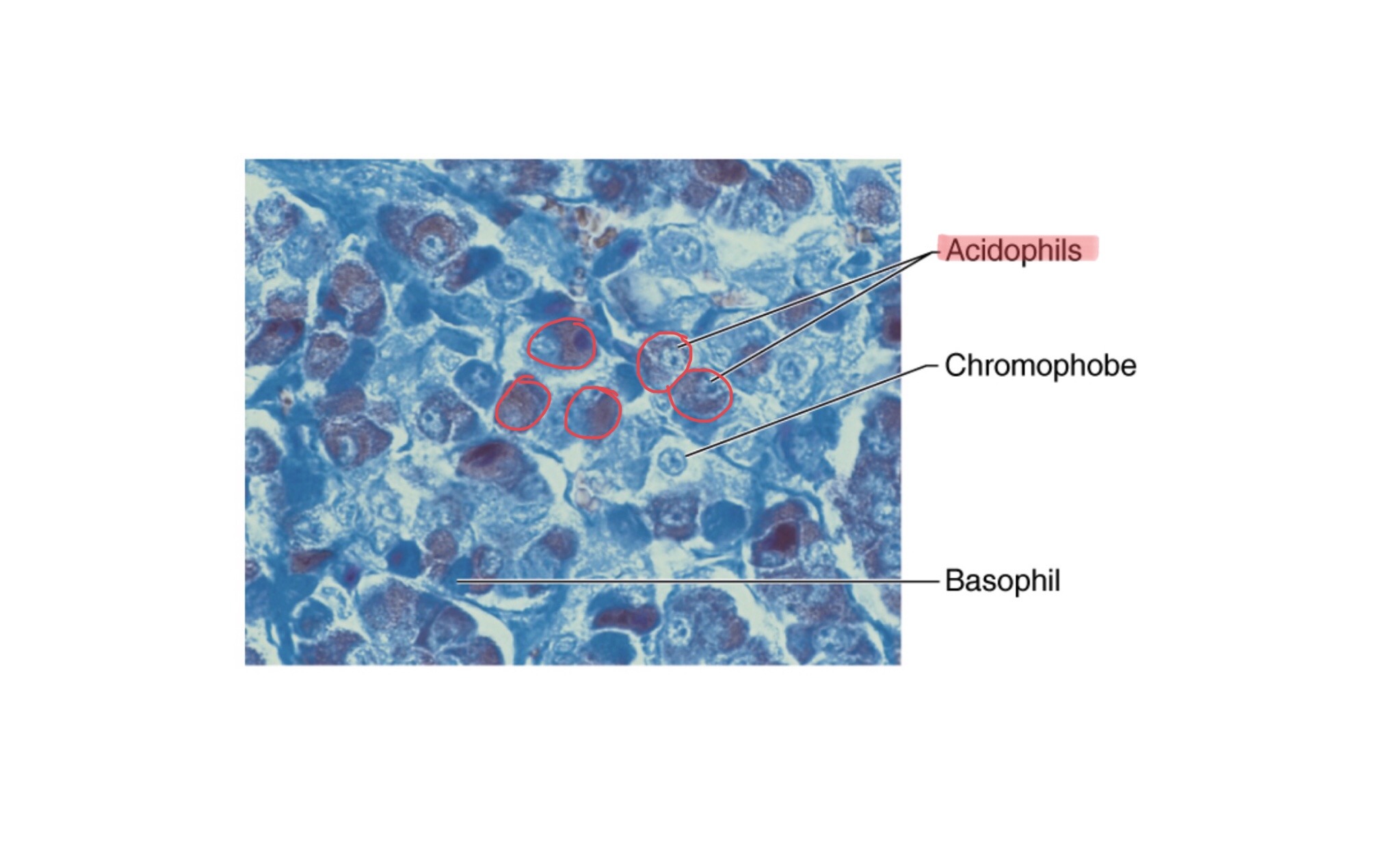
Identify the acidophils of the anterior pituitary gland.
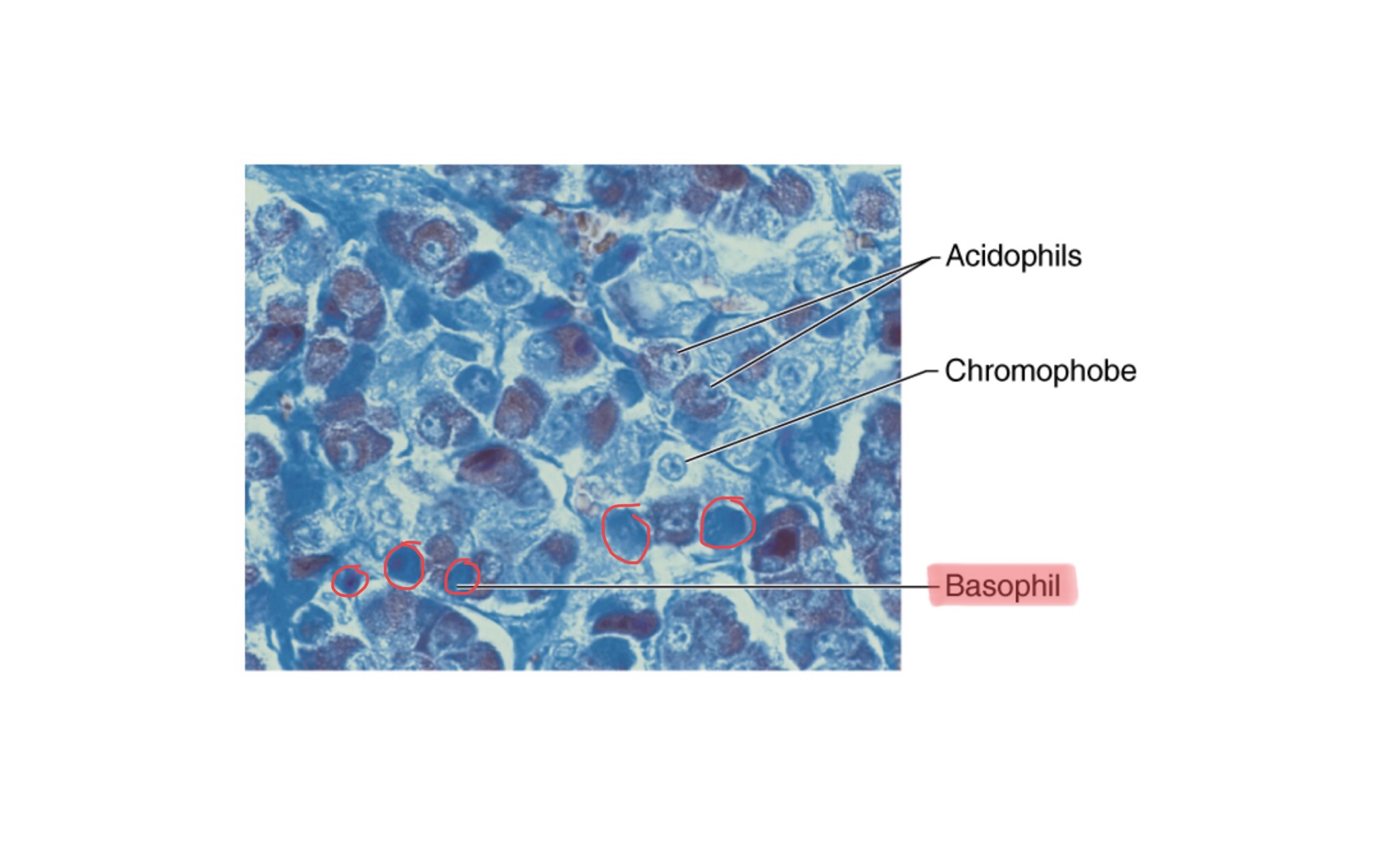
Identify the basophils of the anterior pituitary gland.
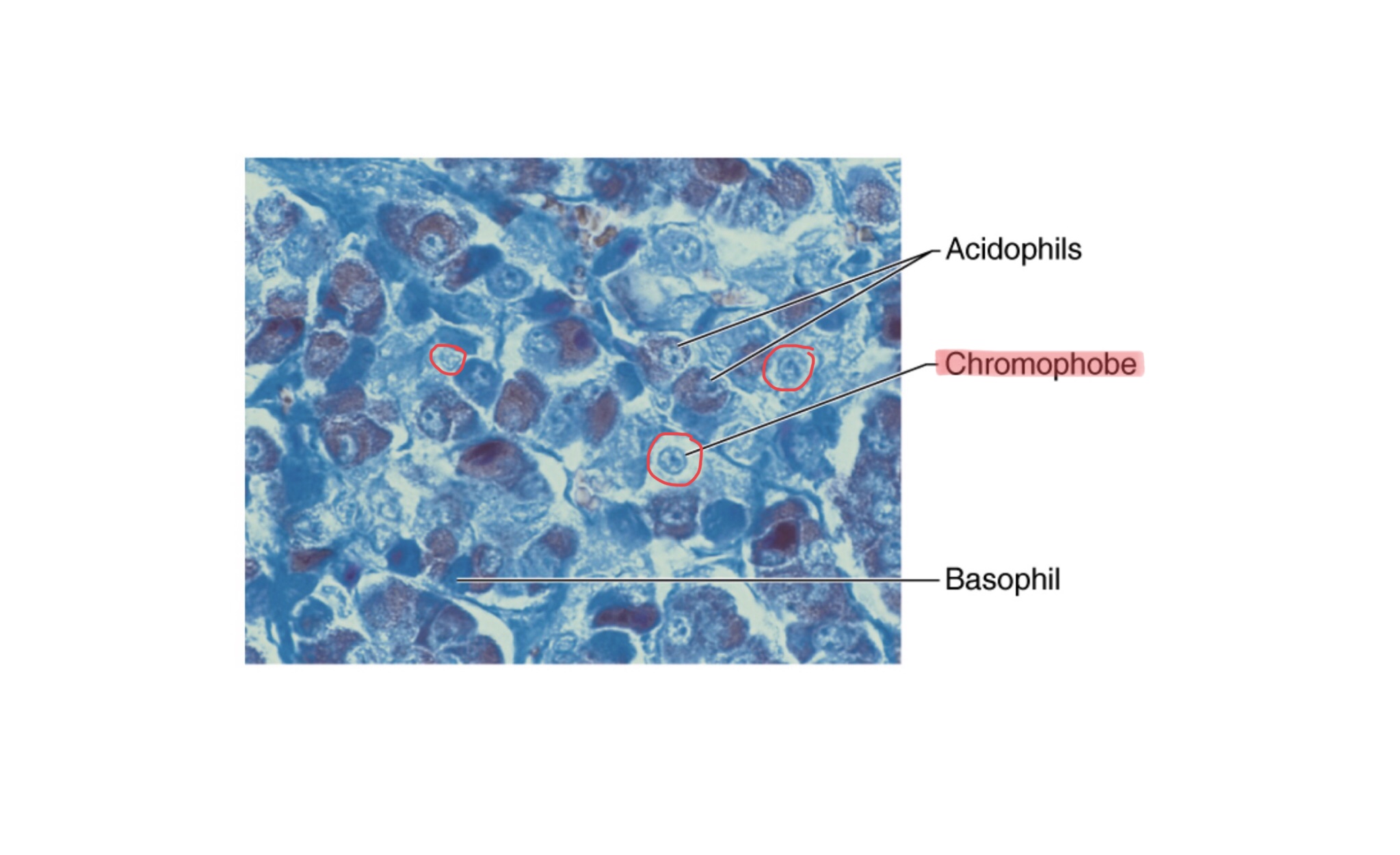
Identify the chromophobes of the anterior pituitary gland.
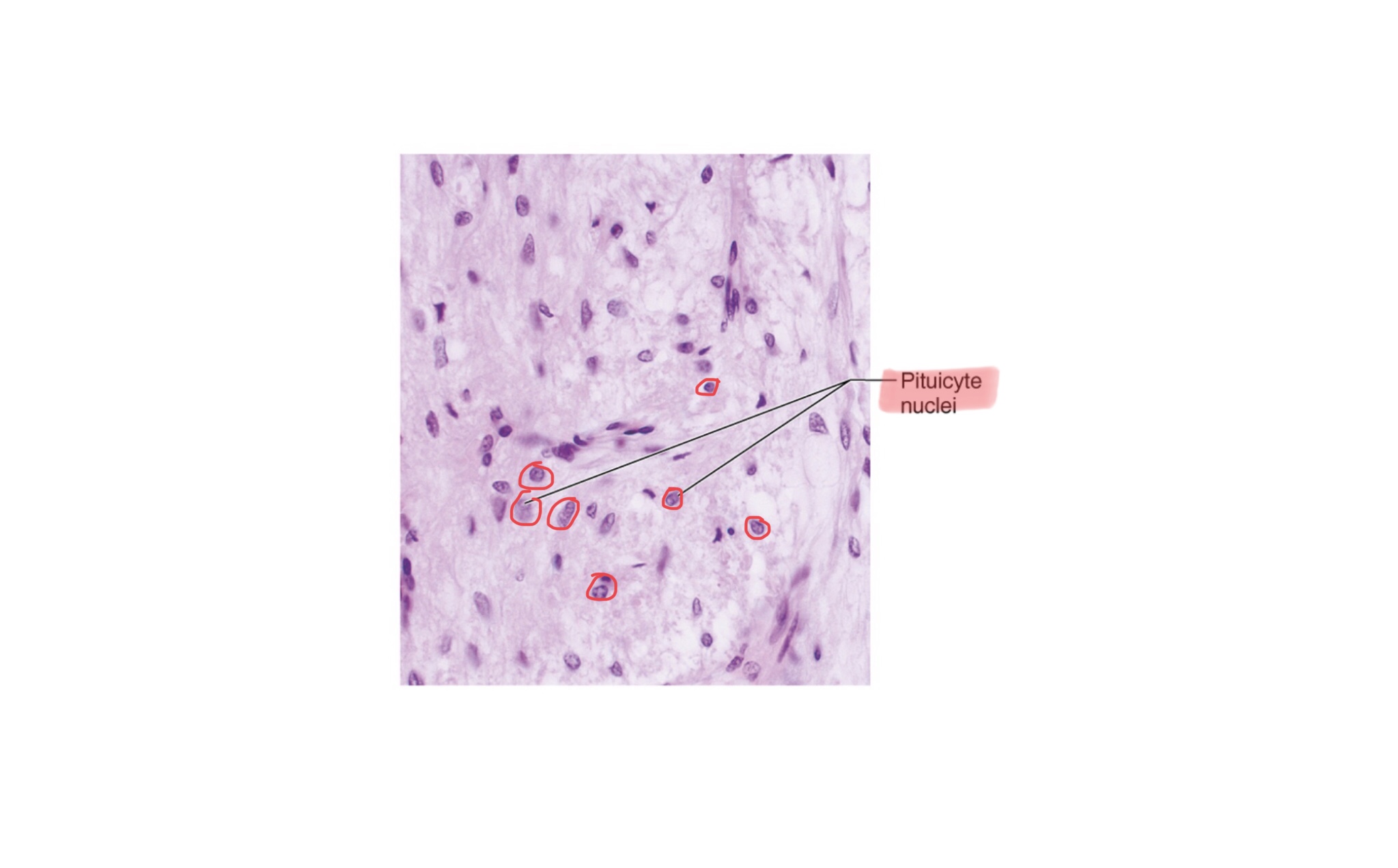
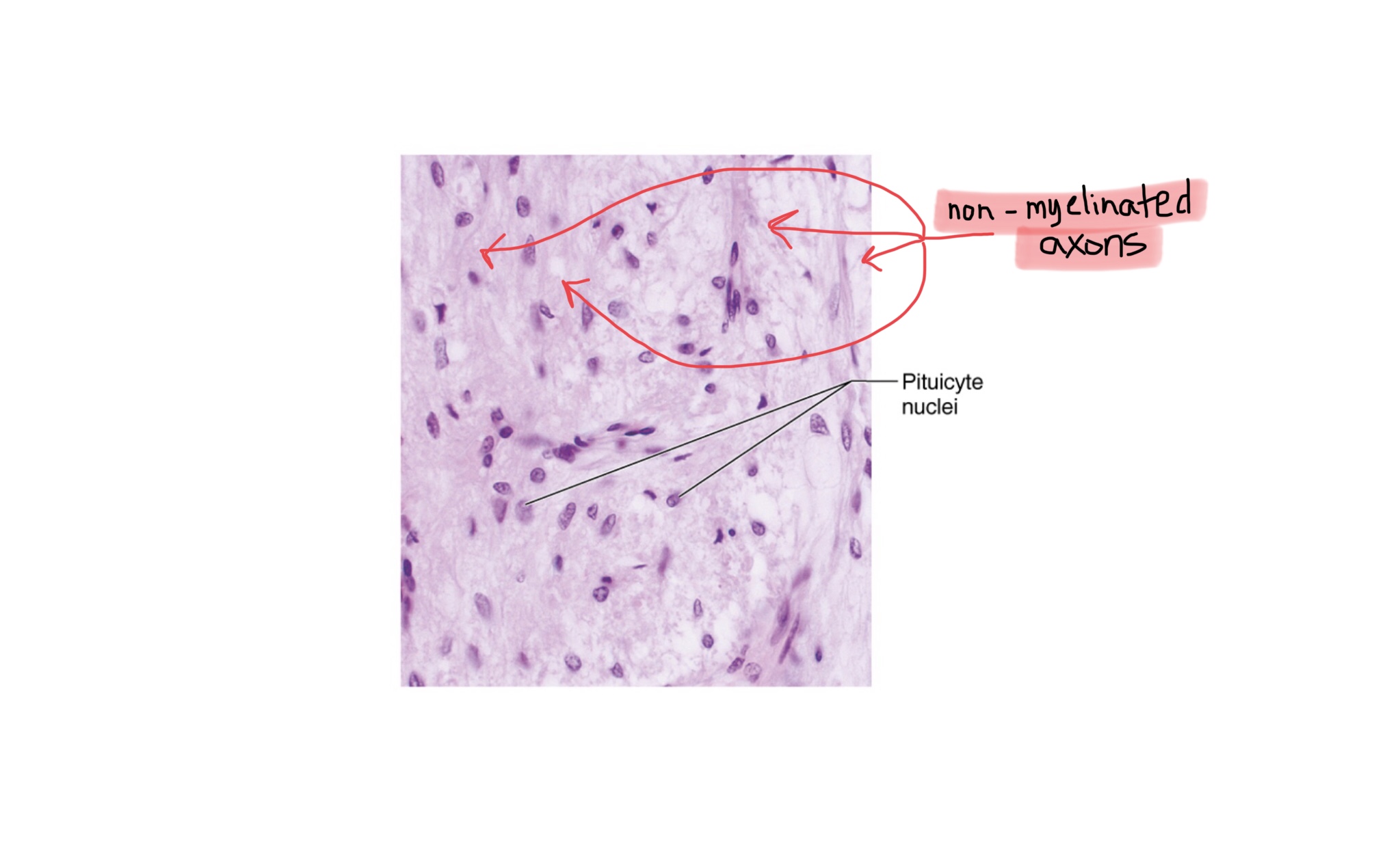
Identify the pituicyte nuclei of the posterior pituitary gland.
Identify the non-myelinated axons of the posterior pituitary gland.
What hormones do the acidophils of the anterior pituitary gland secrete?
The acidophils of the anterior pituitary gland secrete somatotrophs (growth hormone) and mammotrophs (prolactin).
What hormones do the basophils of the anterior pituitary gland secrete?
The basophils of the anterior pituitary gland secrete thyrotrophs (thyroid-stimulating hormone), gonadotrophs (follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone), and corticotrophs (adrenocorticotropic hormone).
What are chromophobes?
Chromophobes of the anterior pituitary gland are acidophils and basophils that have released their hormones.
What hormones does the posterior pituitary store?
The posterior pituitary stores antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) produced by the hypothalamus.
Identify thyroid tissue.
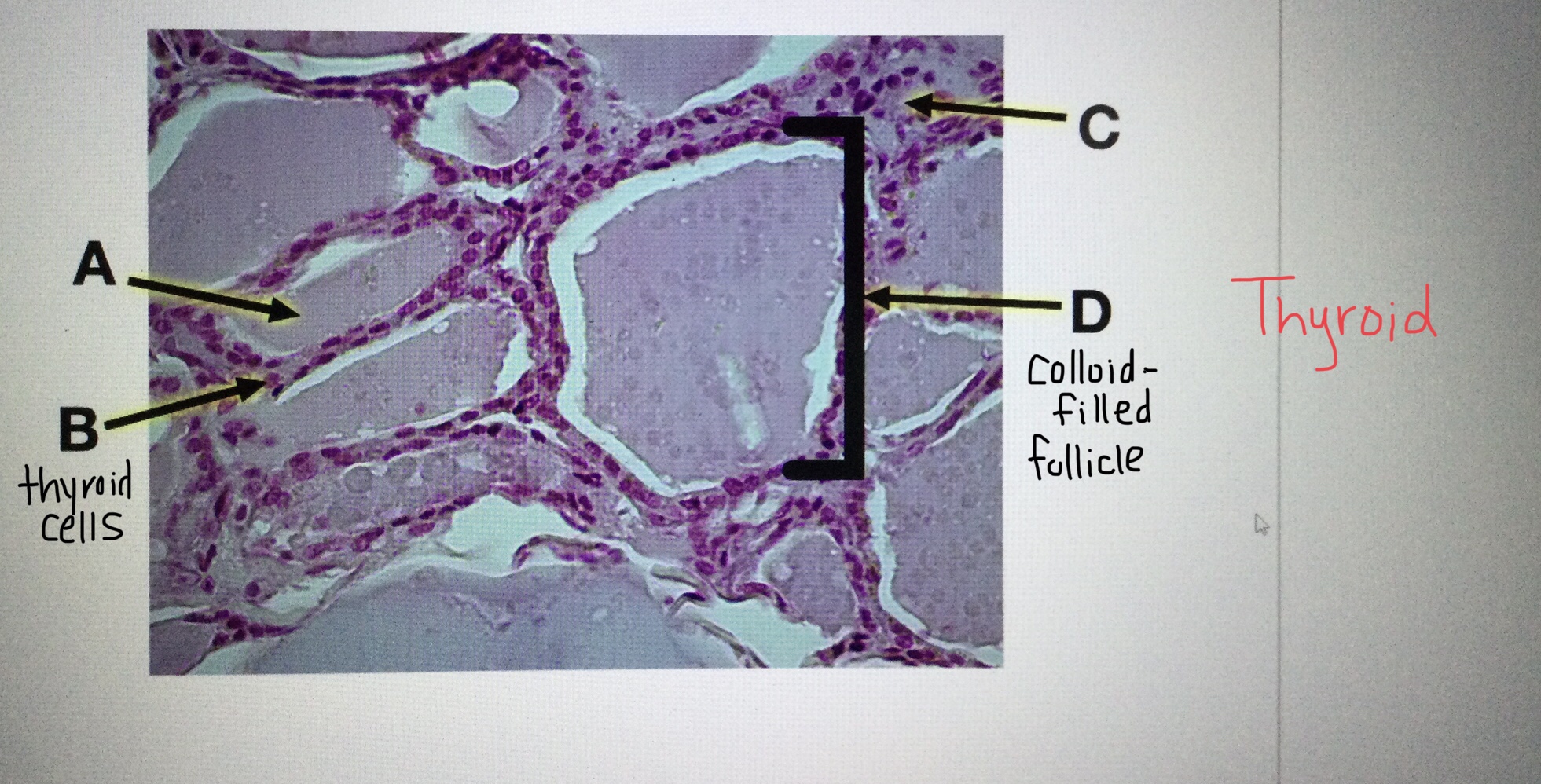
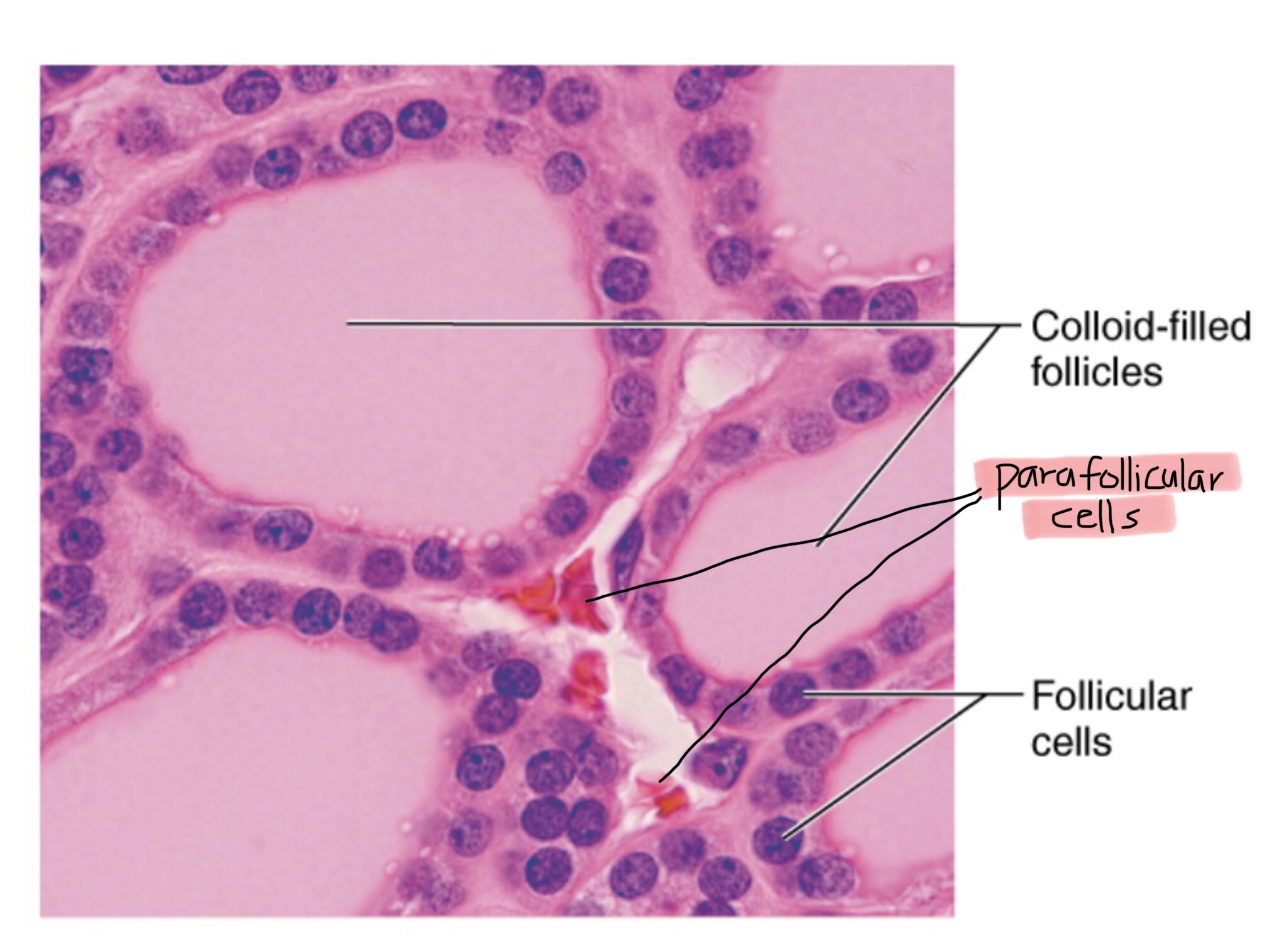
Identify the colloid-filled follicles of the thyroid gland.
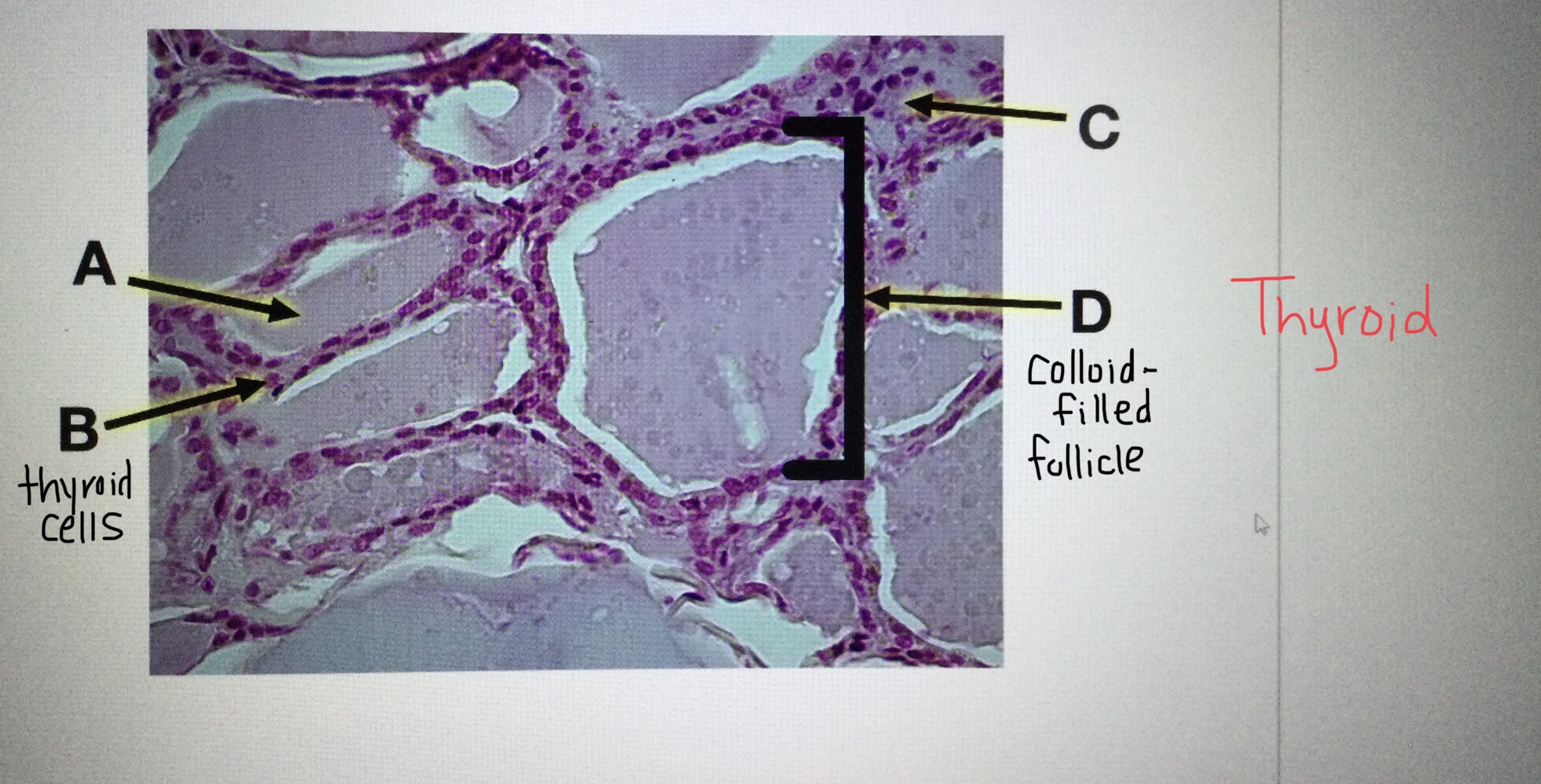
Identify the follicle cells of the thyroid gland.
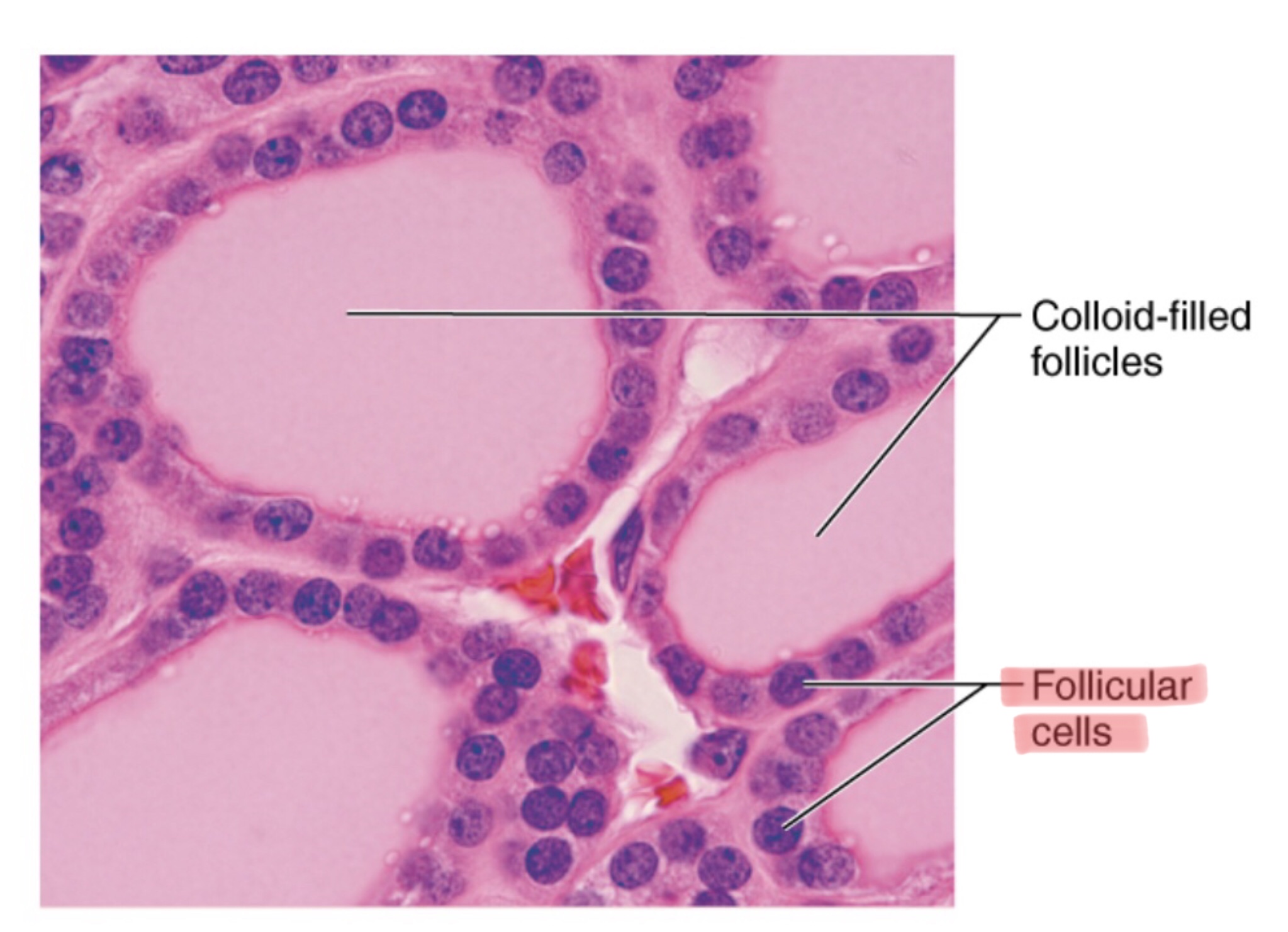
Identify the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland.
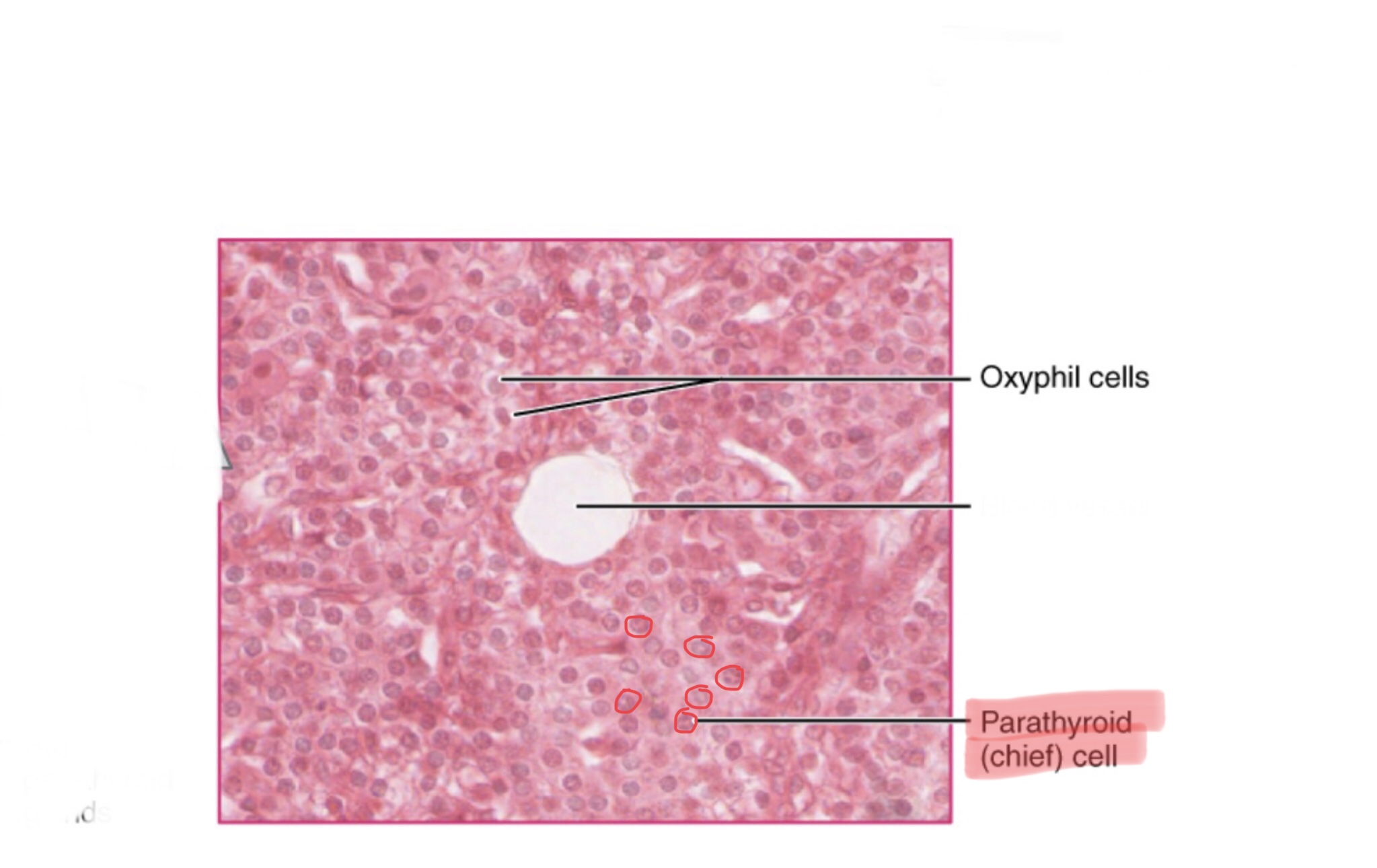
Identify parathyroid tissue.
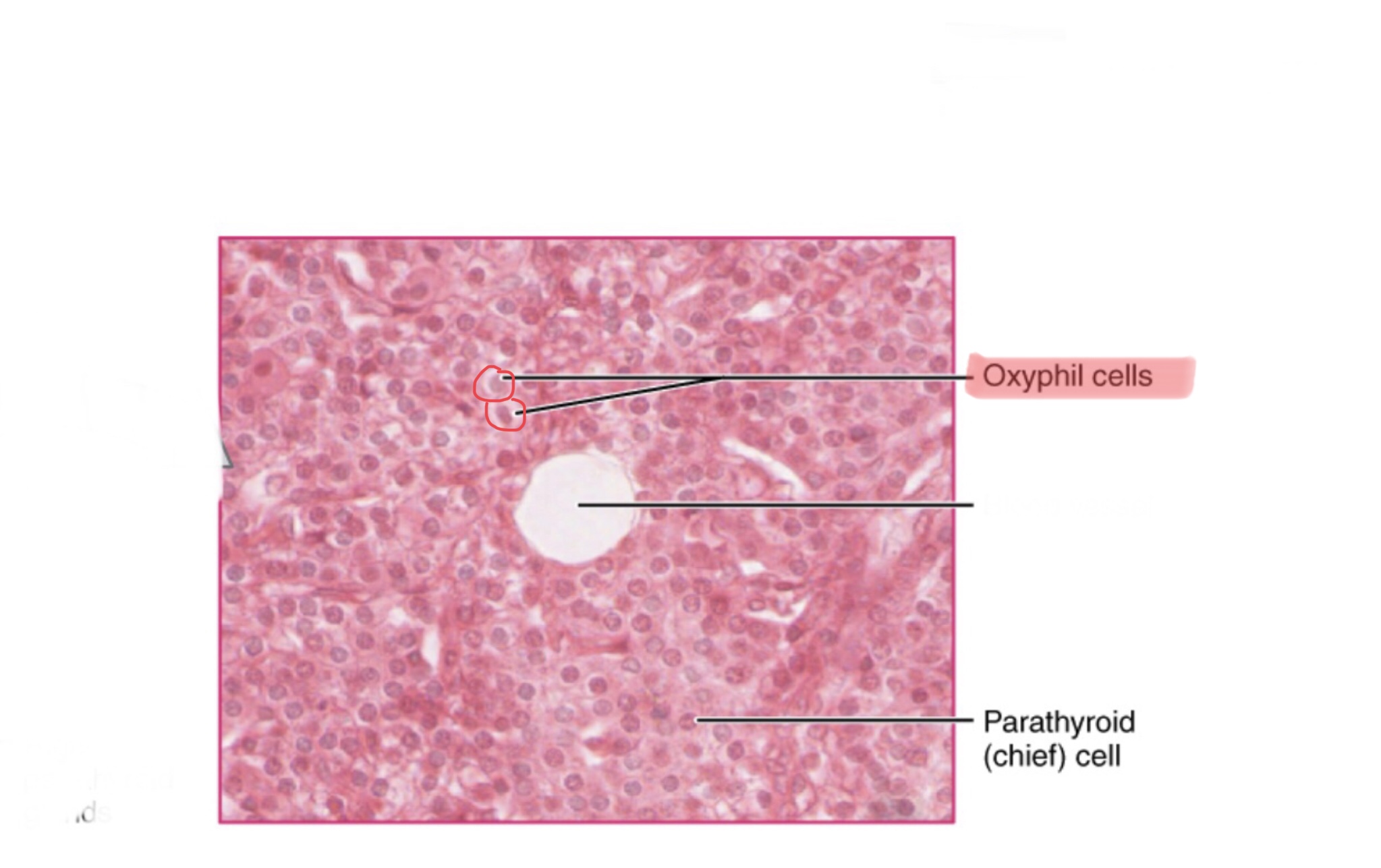
Identify the oxyphil cells of the parathyroid gland.
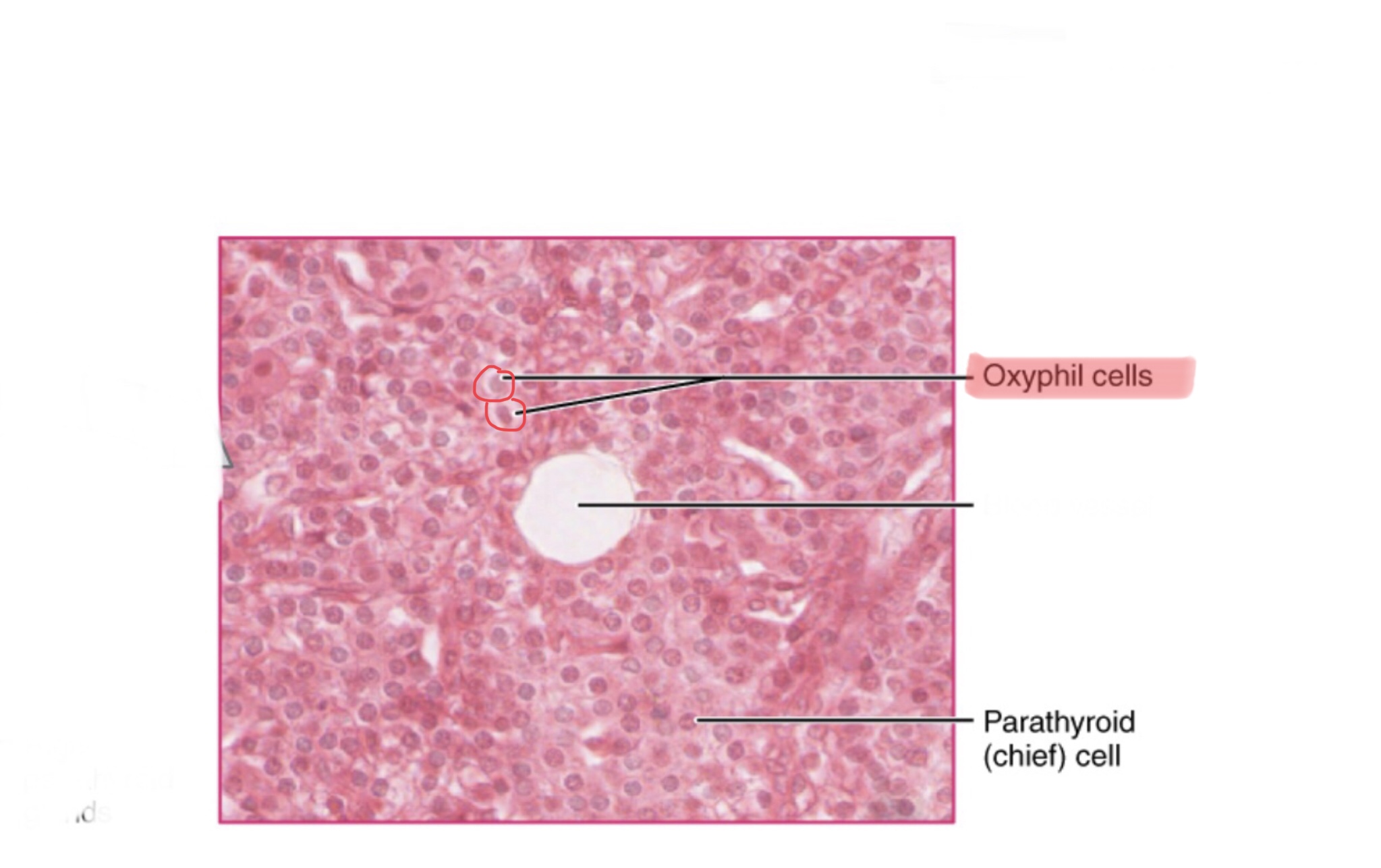
Identify the chief cells of the parathyroid gland.
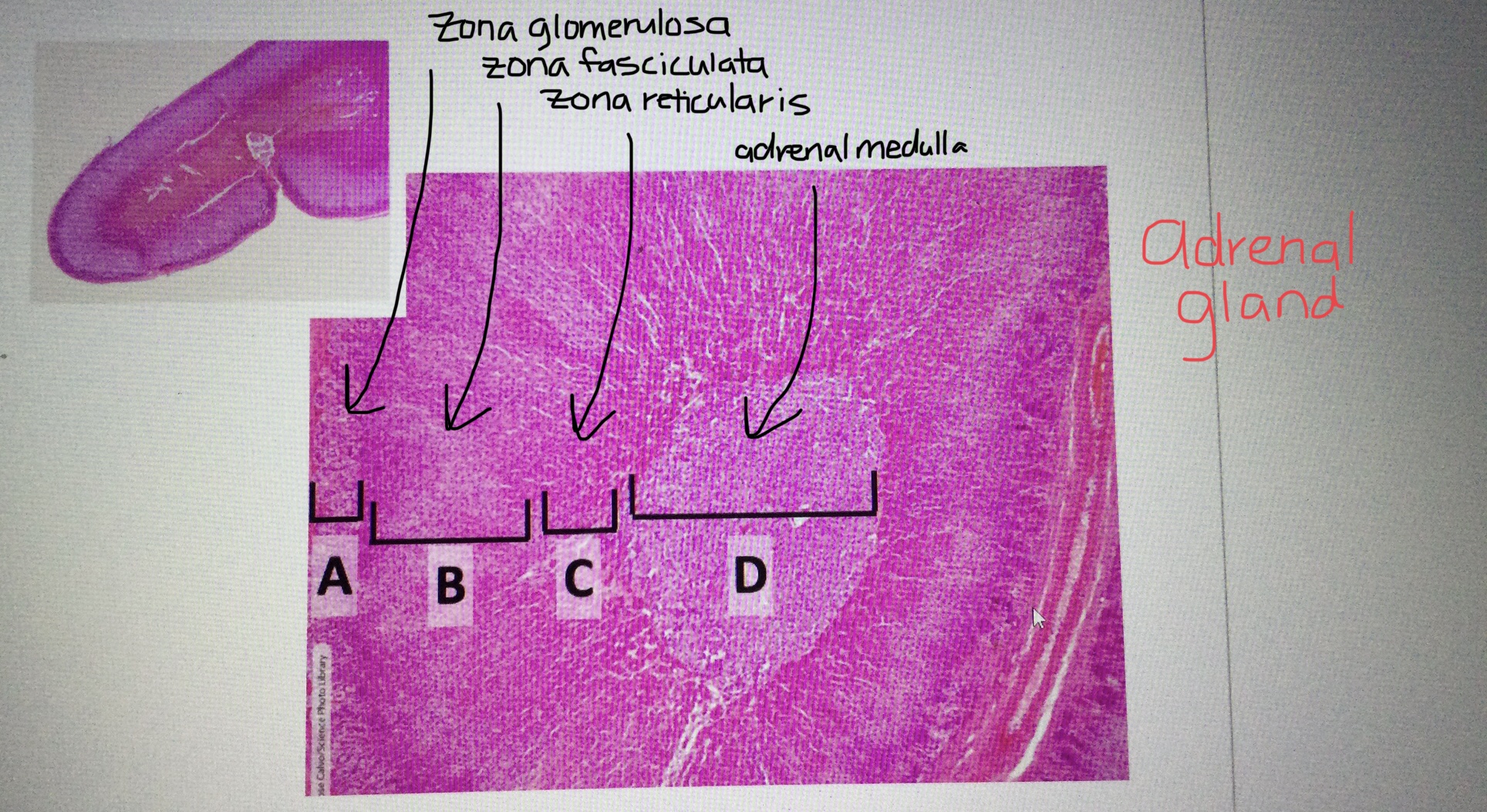
Identify adrenal tissue.
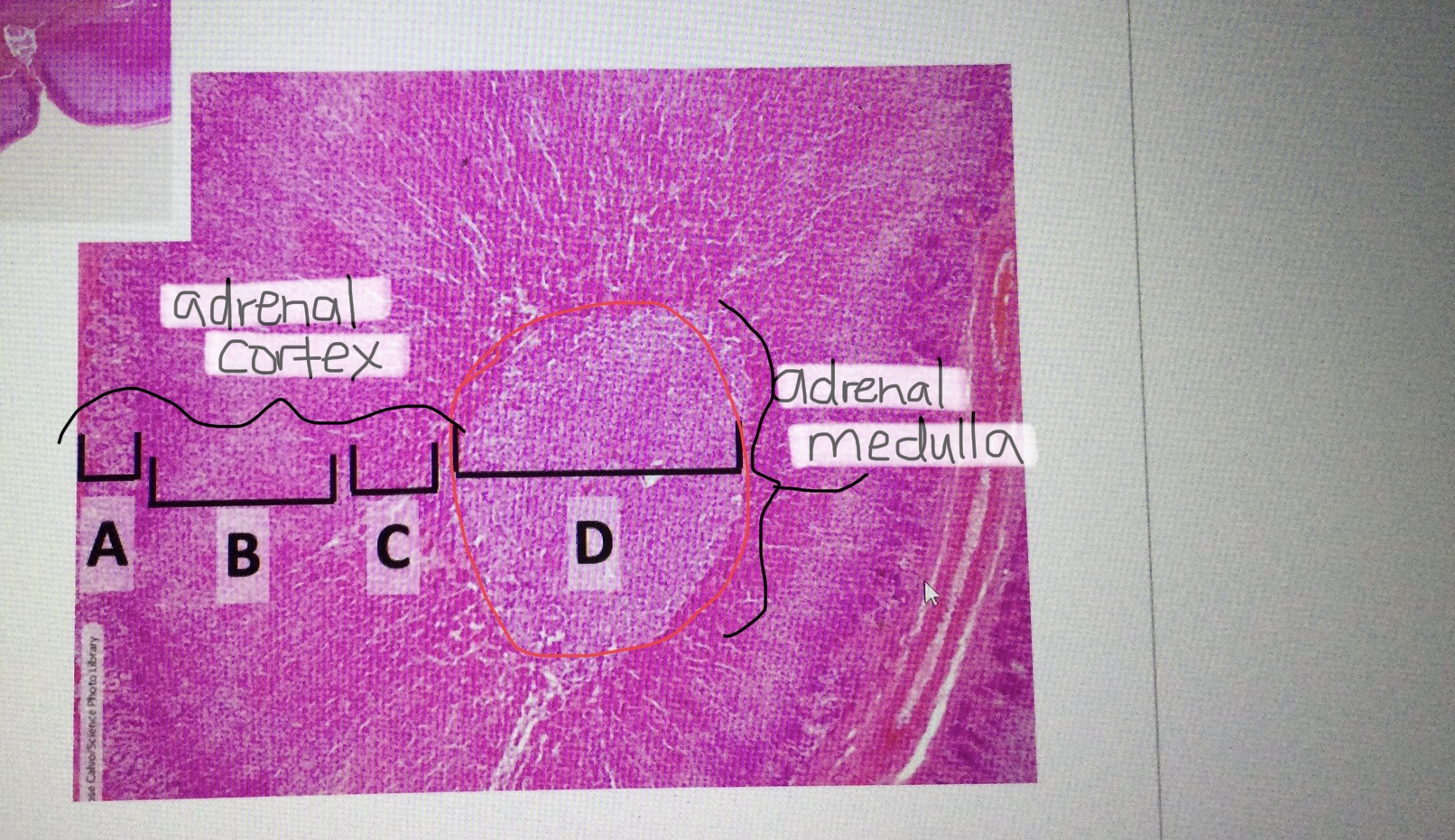
Identify the adrenal cortex.
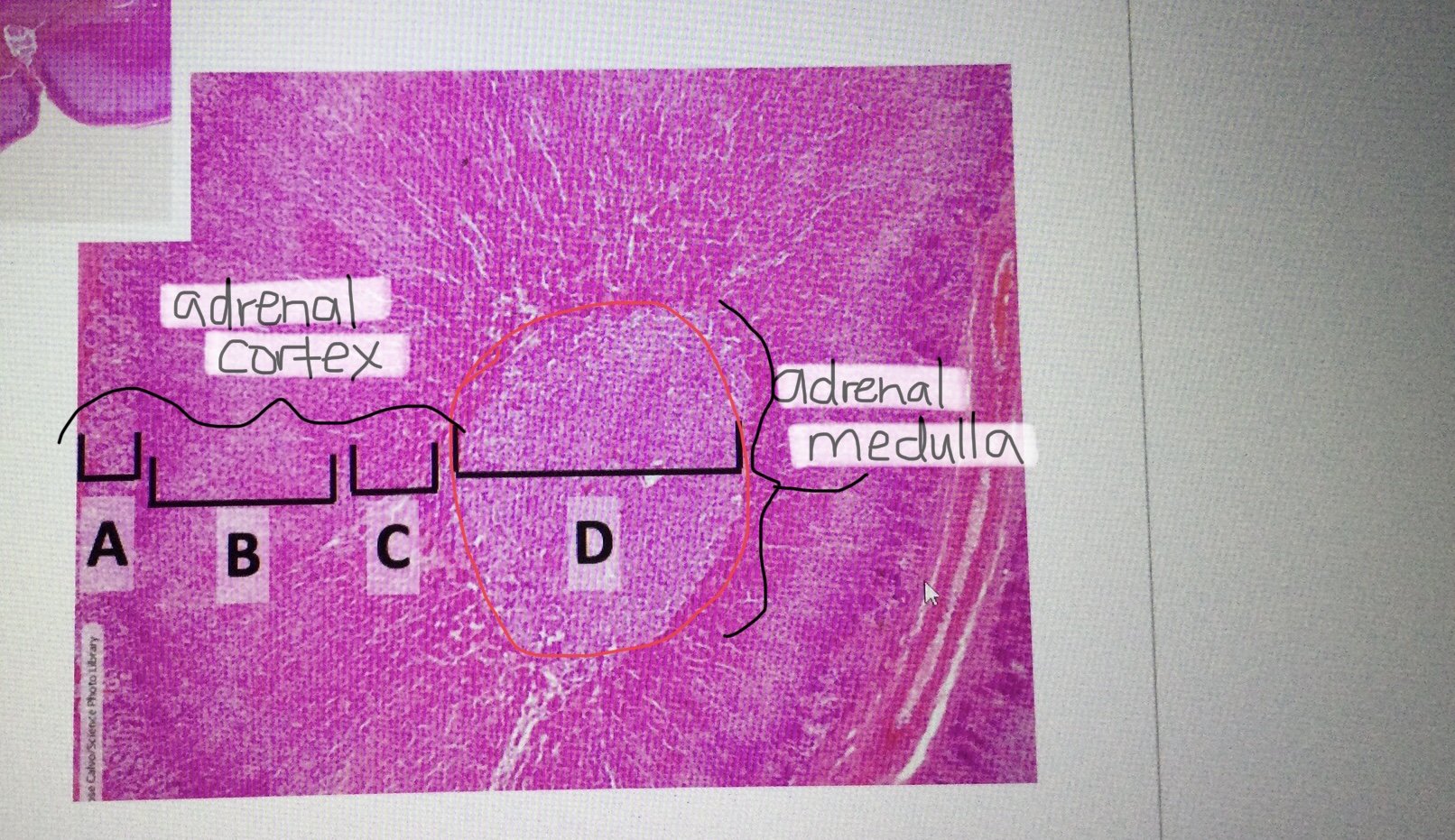
Identify the adrenal medulla.
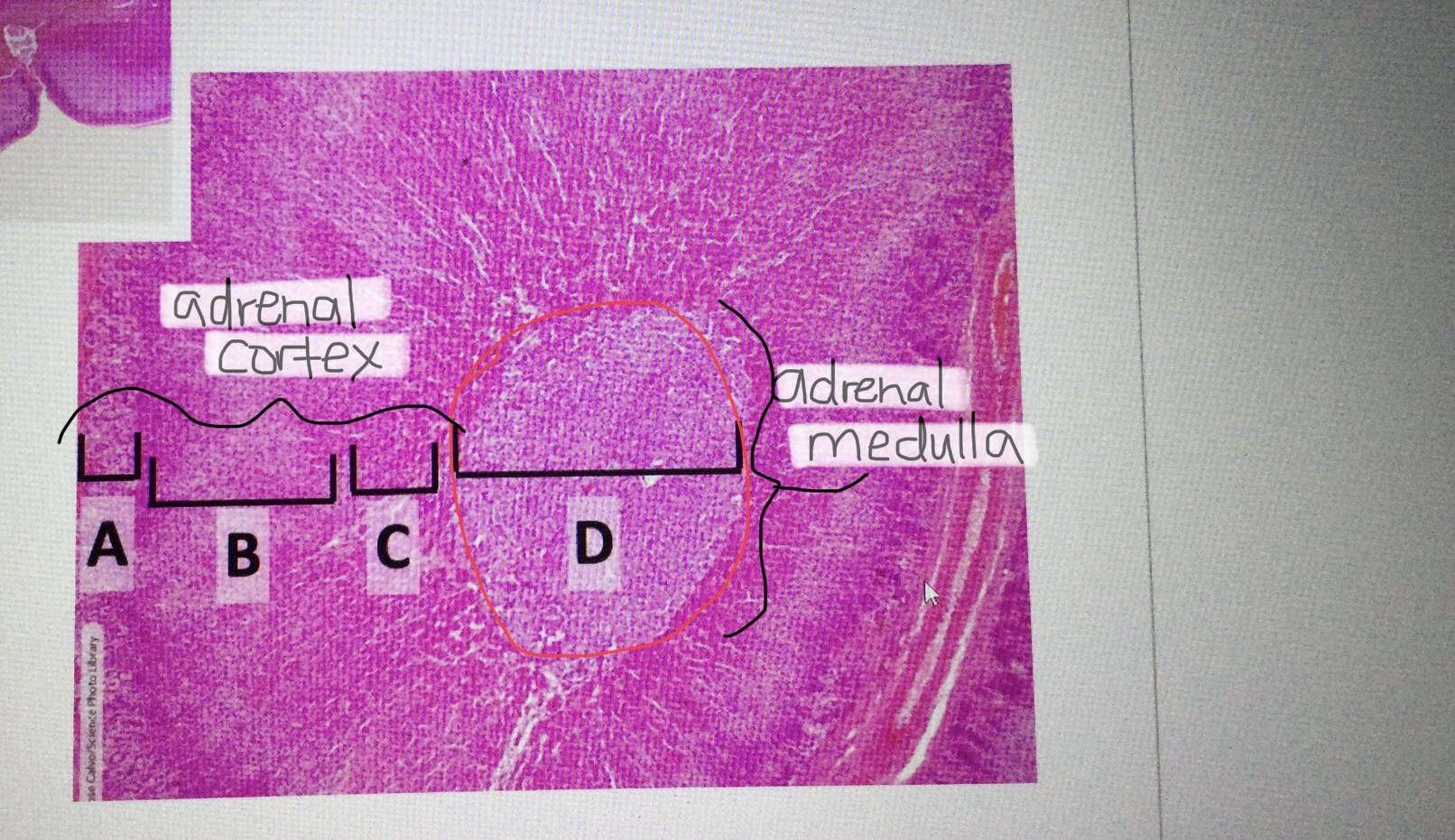
Identify the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex.
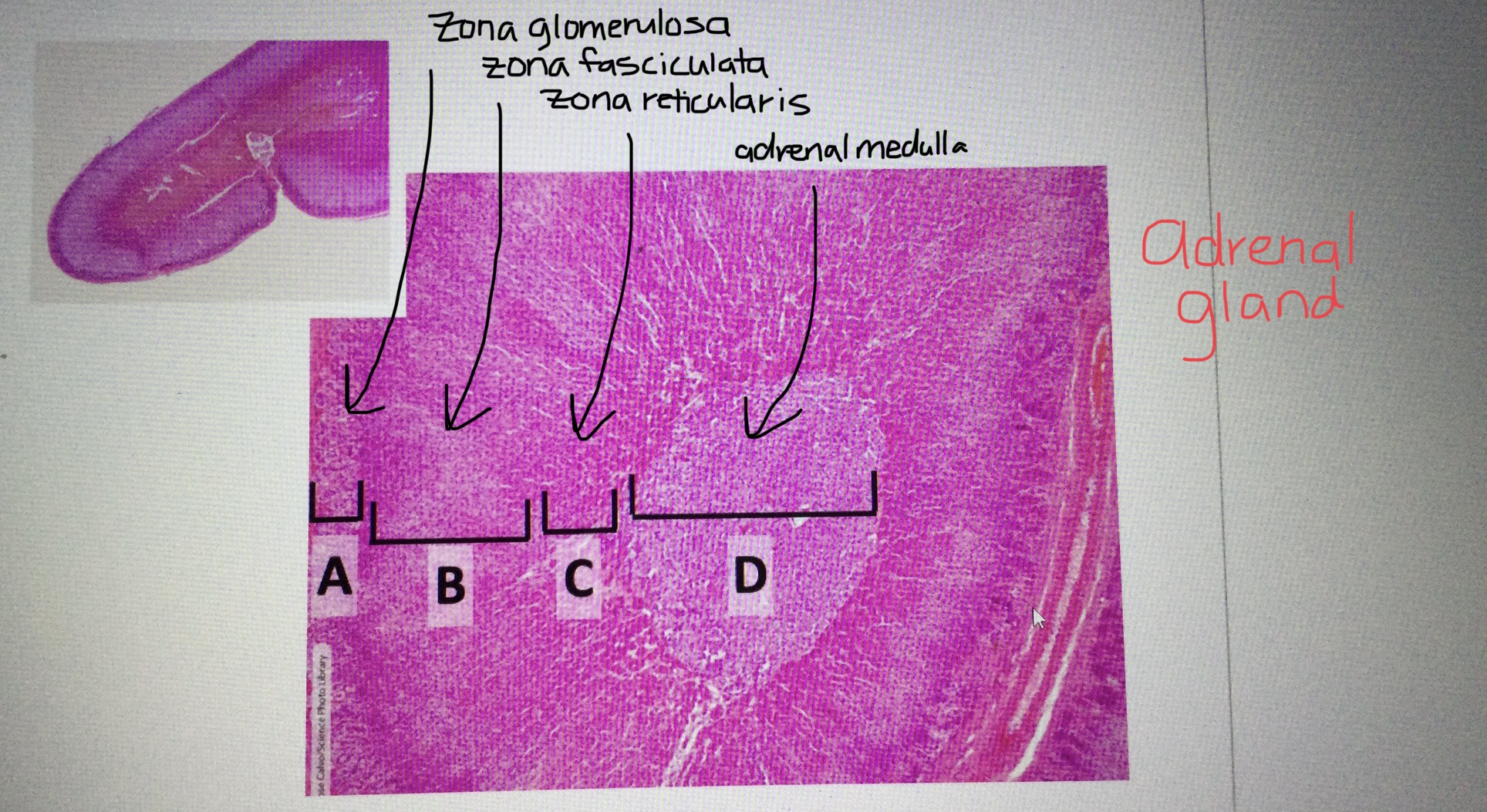
Identify the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex.
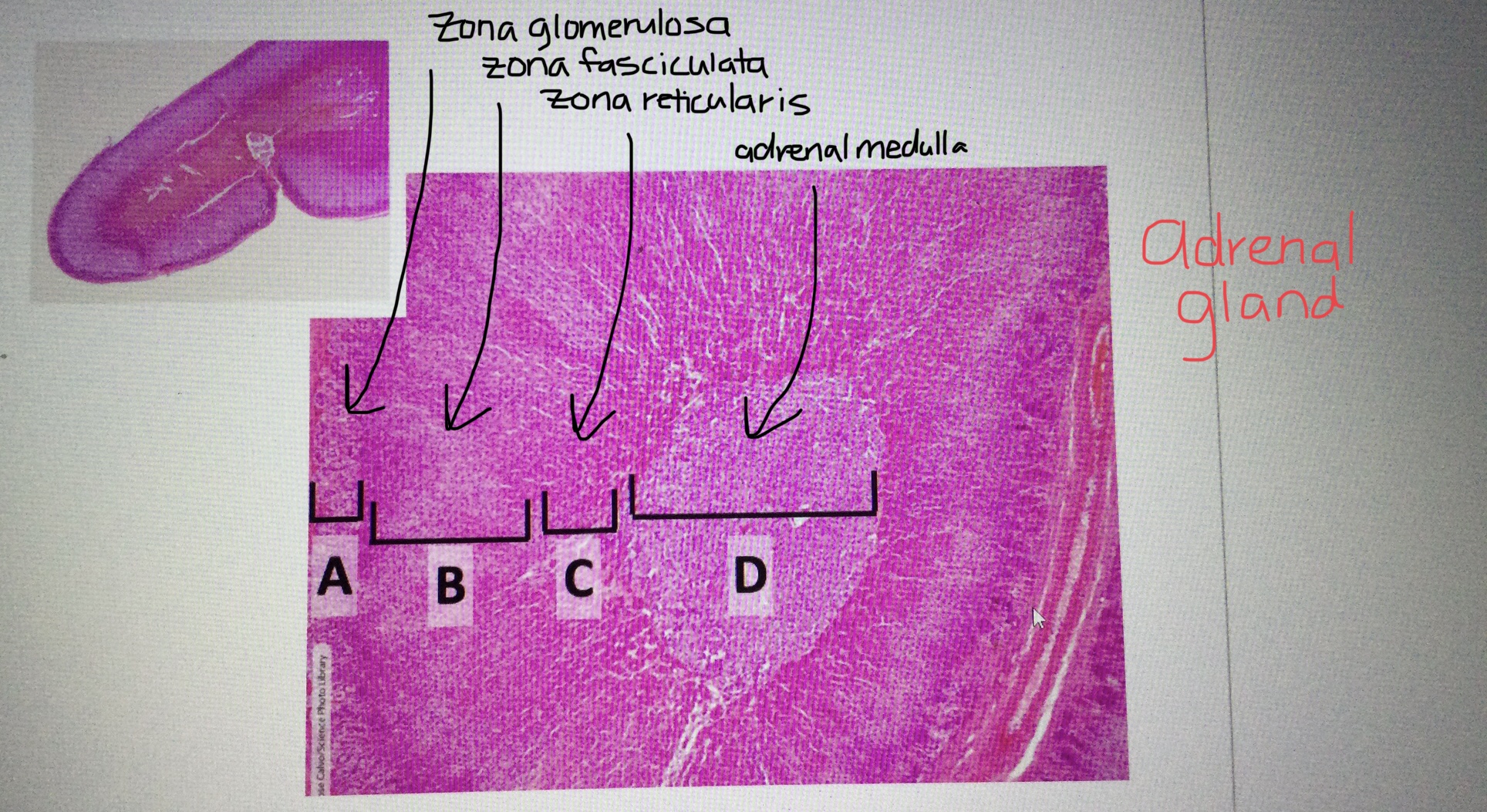
Identify the zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex.
Identify pancreatic tissue.
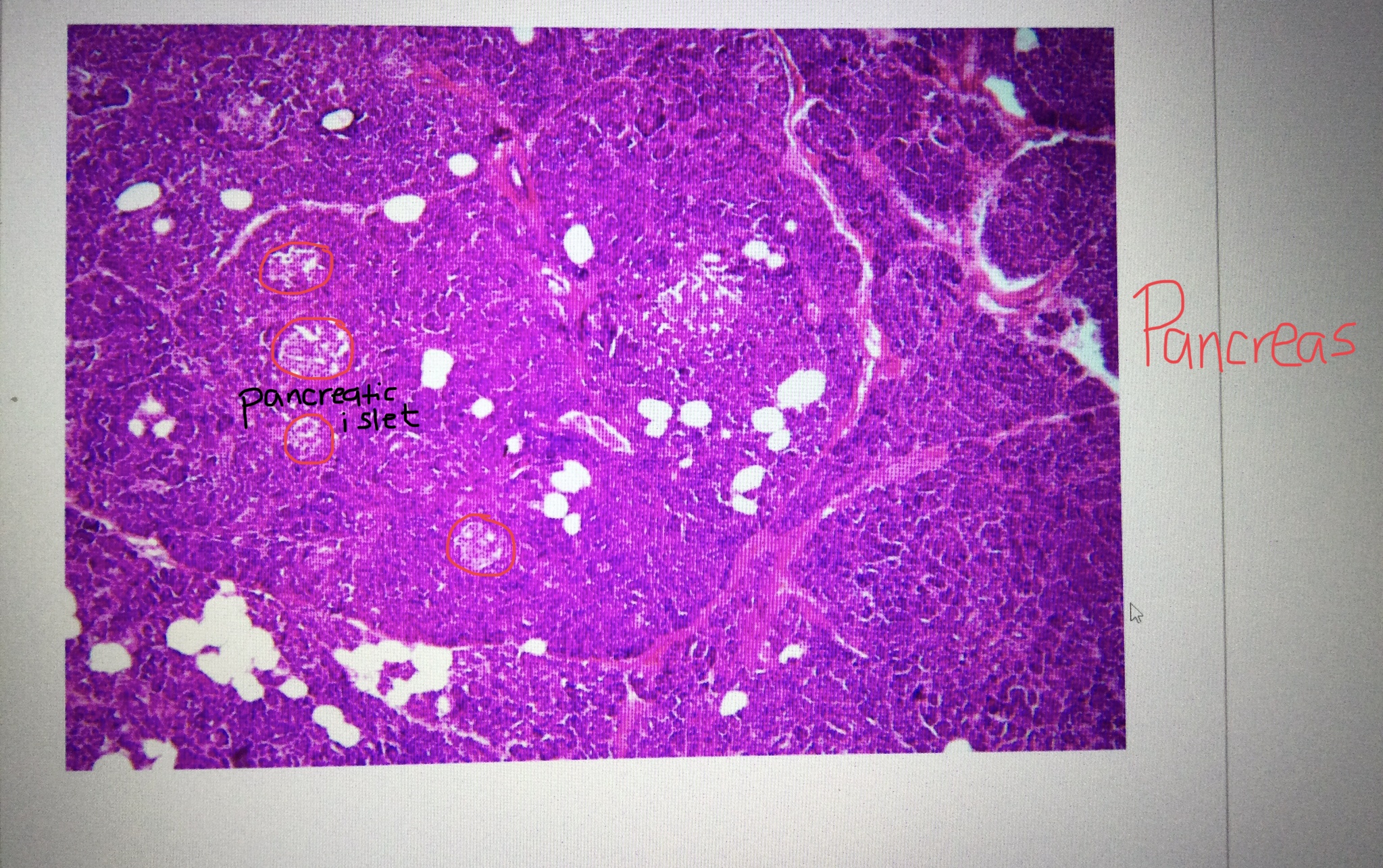
Identify the pancreatic islet cells.
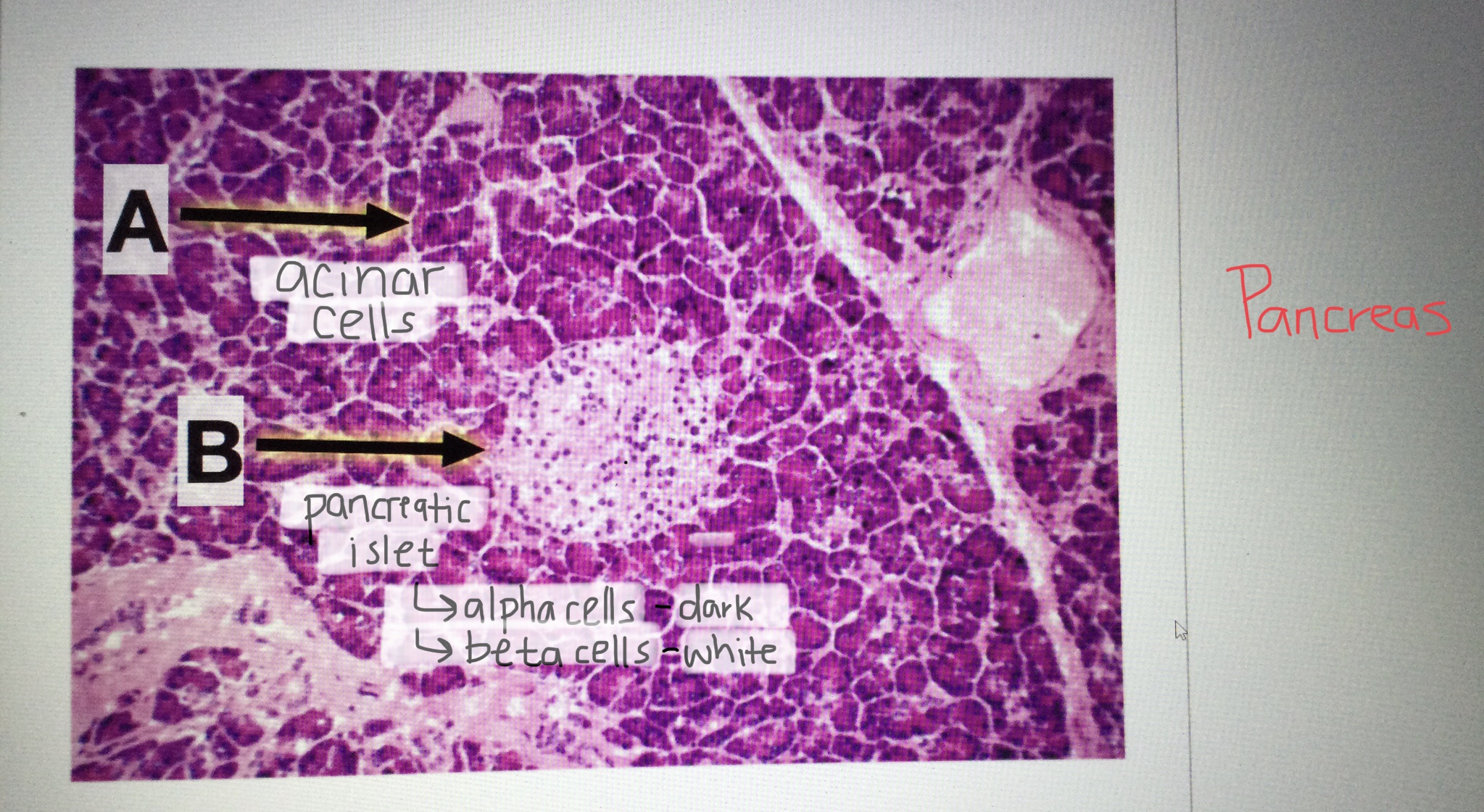
Identify the acinar cells of the pancreas.
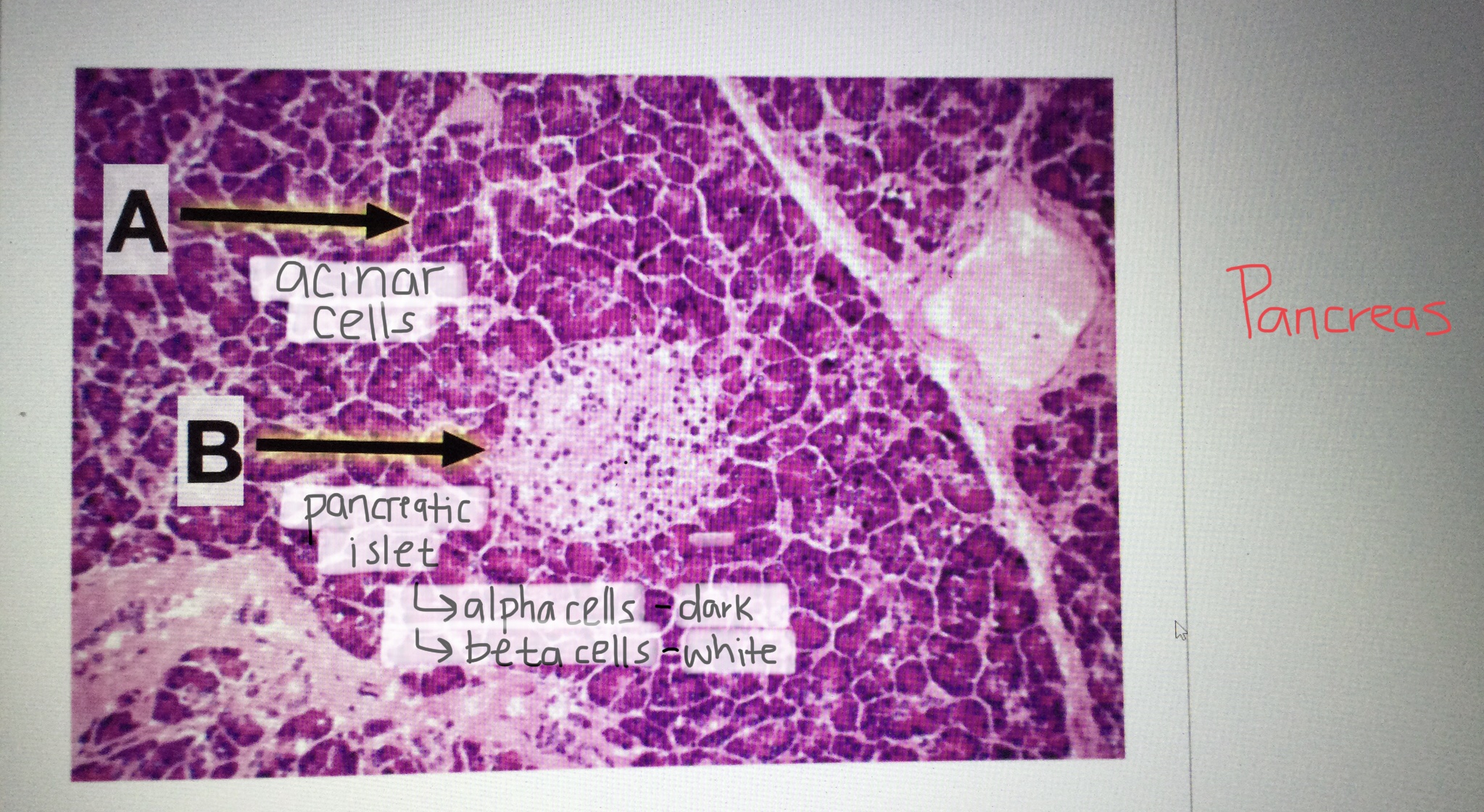
Identify the alpha cells of the pancreas.
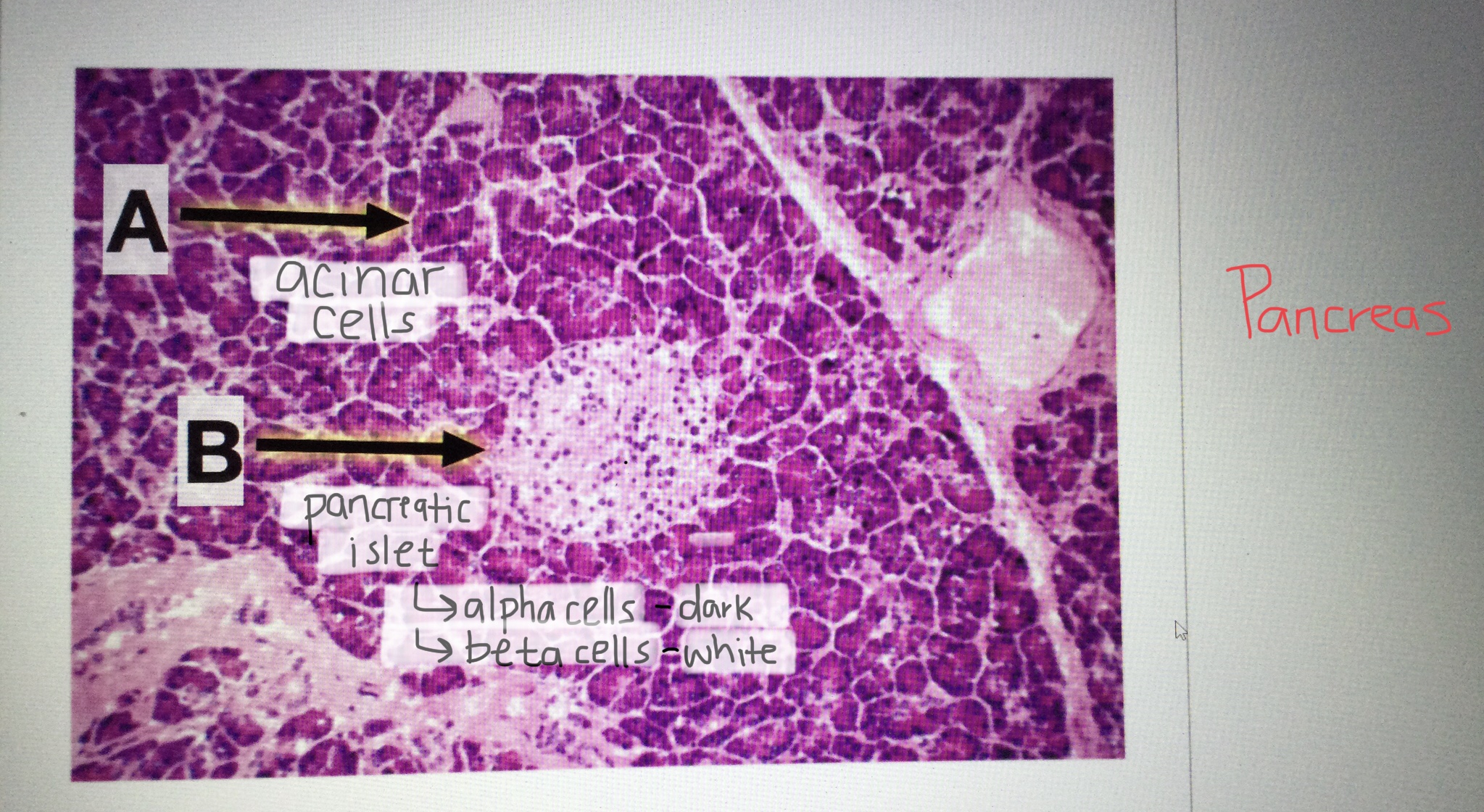
Identify the beta cells of the pancreas.
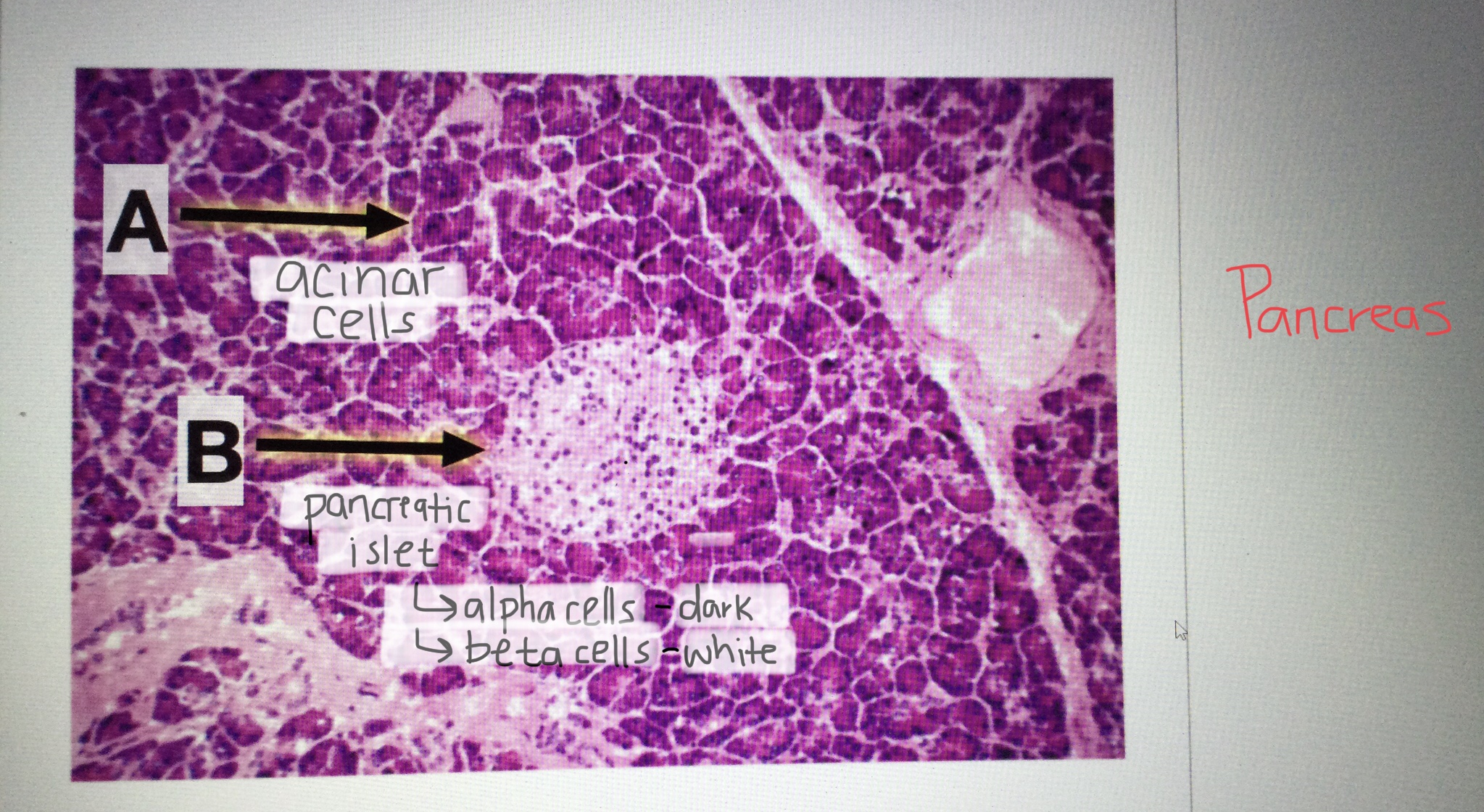
What is the function of acinar cells of the pancreas?
Acinar cells are the exocrine cells of the pancreas and secrete digestive enzymes.
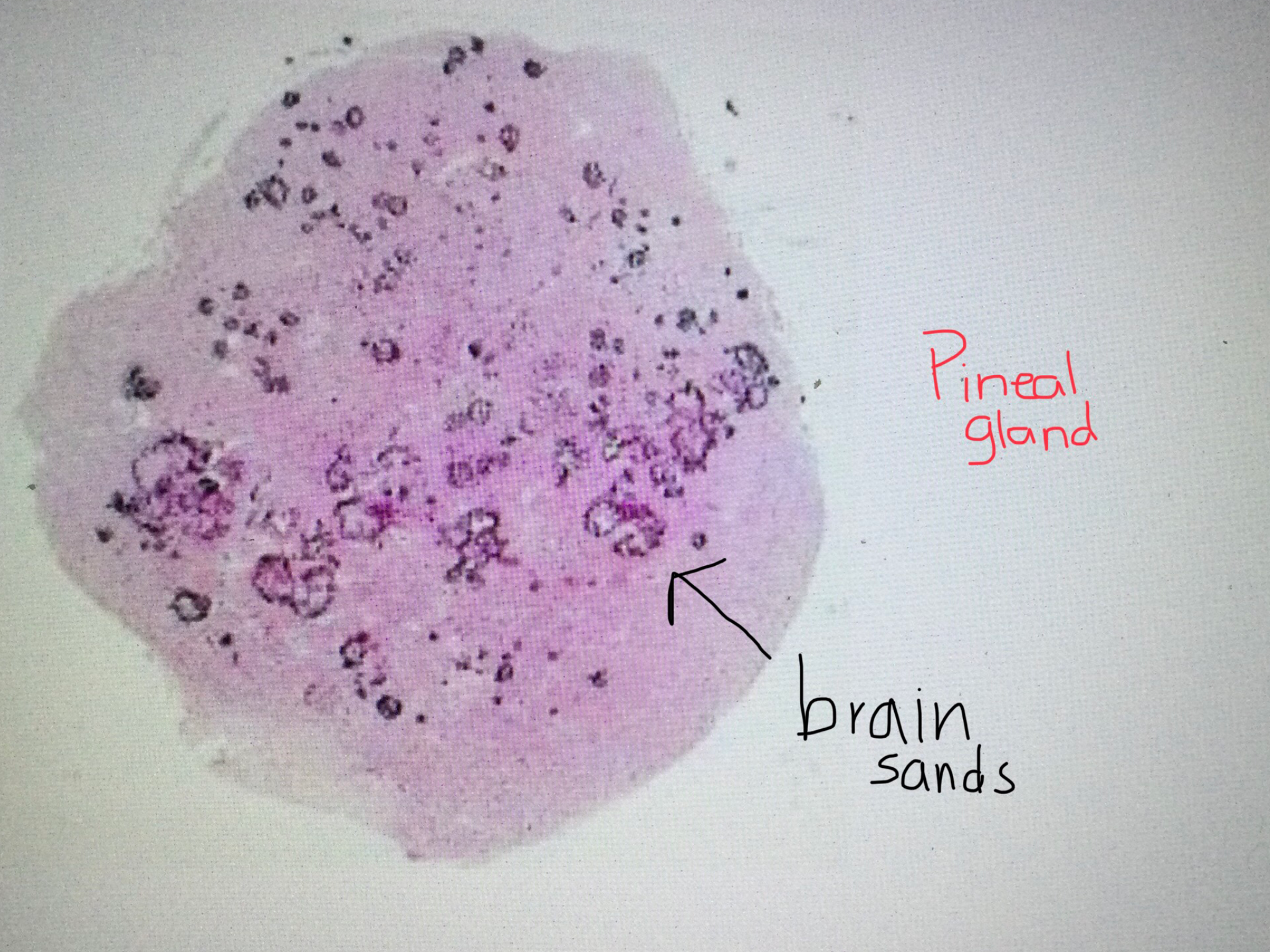
Identify pineal tissue.
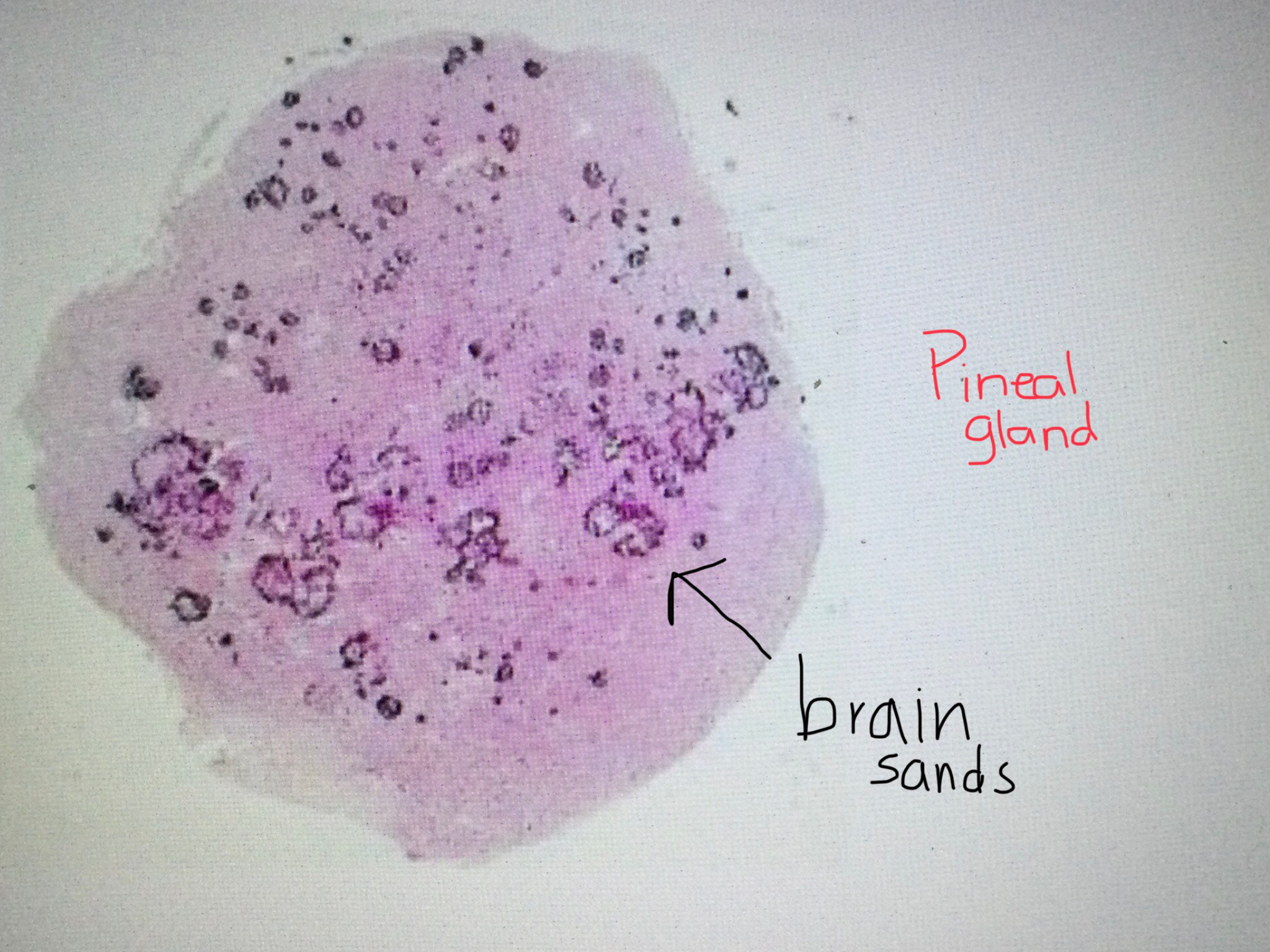
Identify the brain sands of the pineal gland.
Identify thymus tissue.
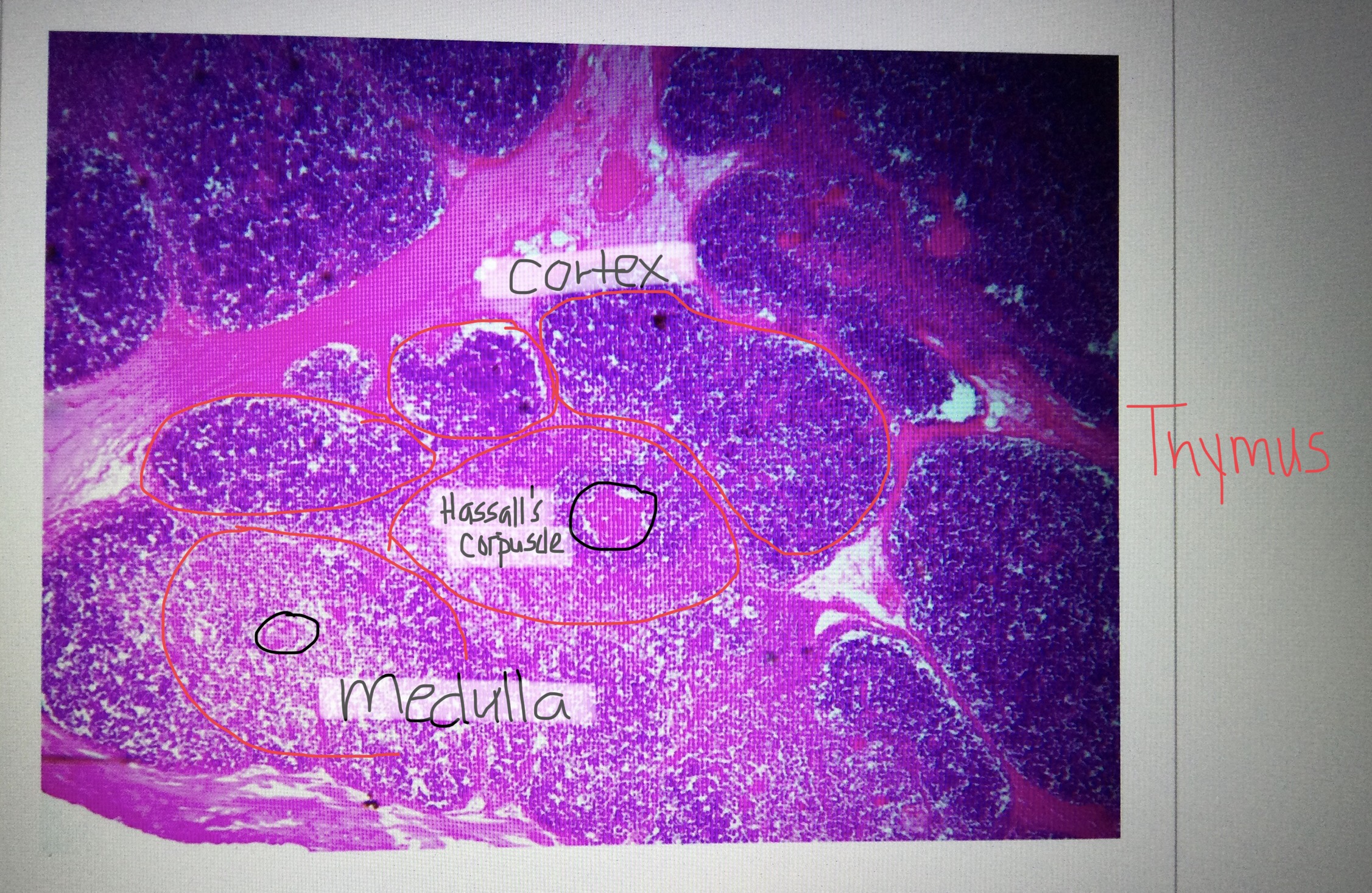
Identify a cortex of the thymus.
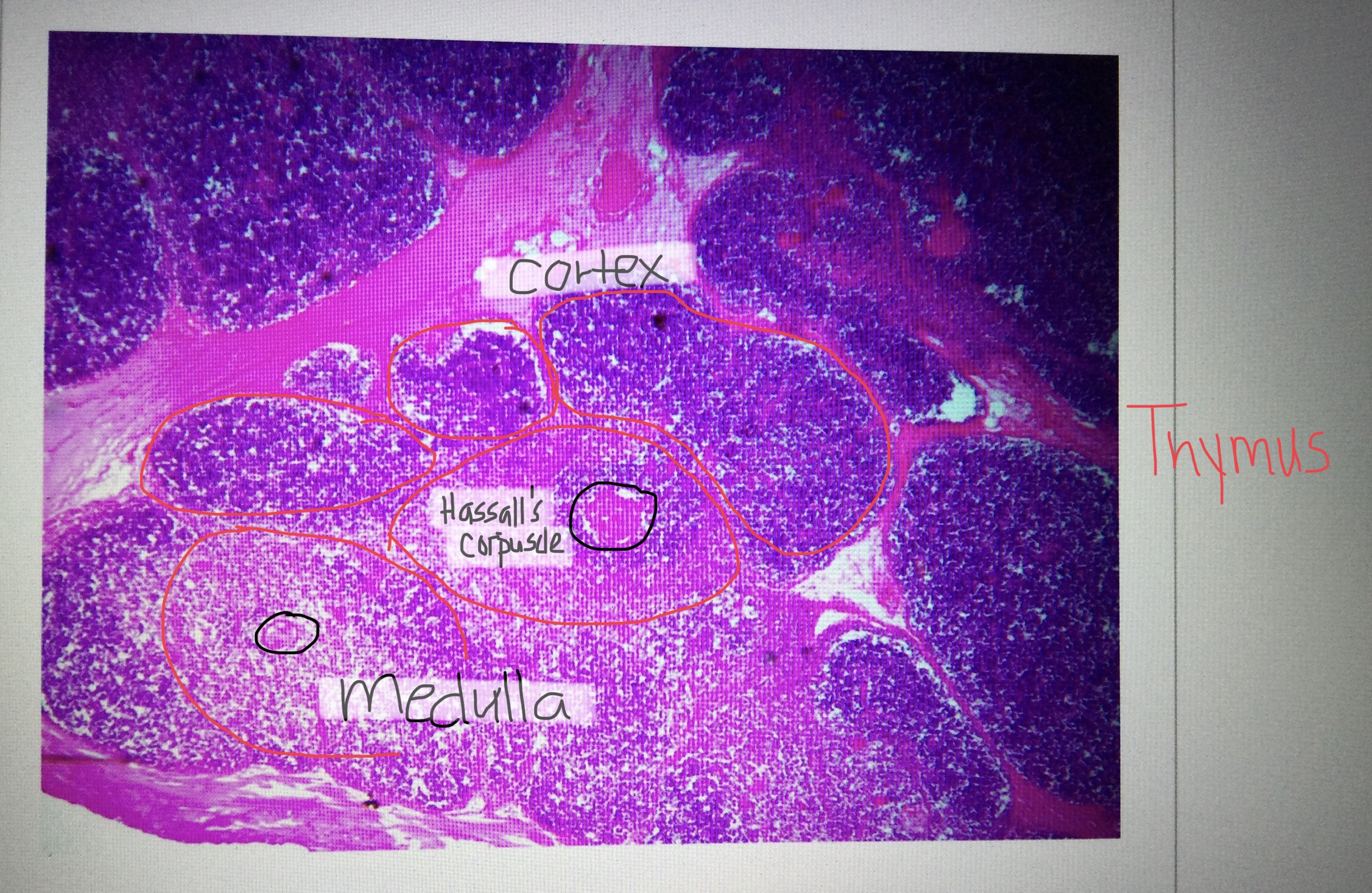
Identify a medulla of the thymus.
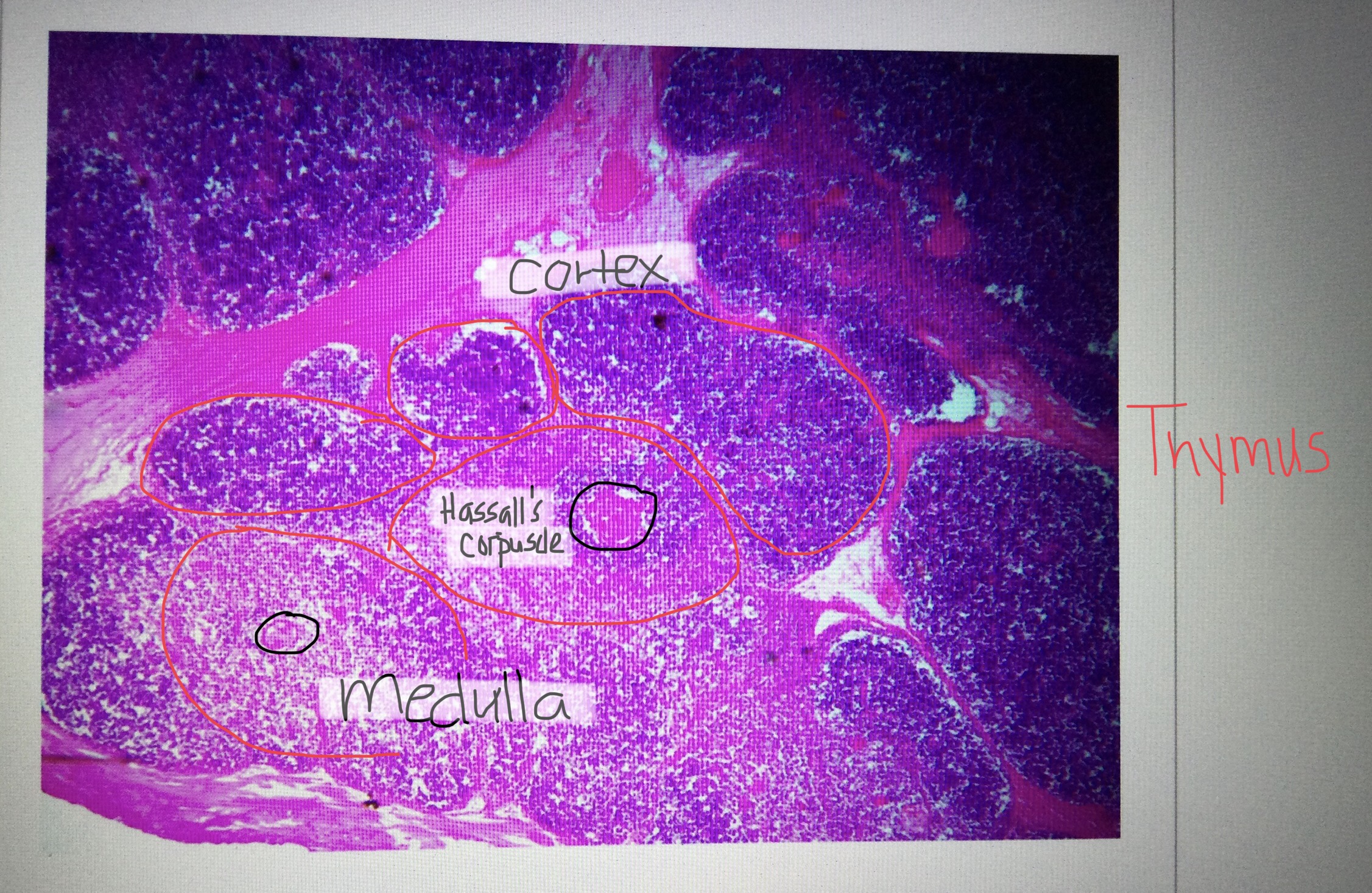
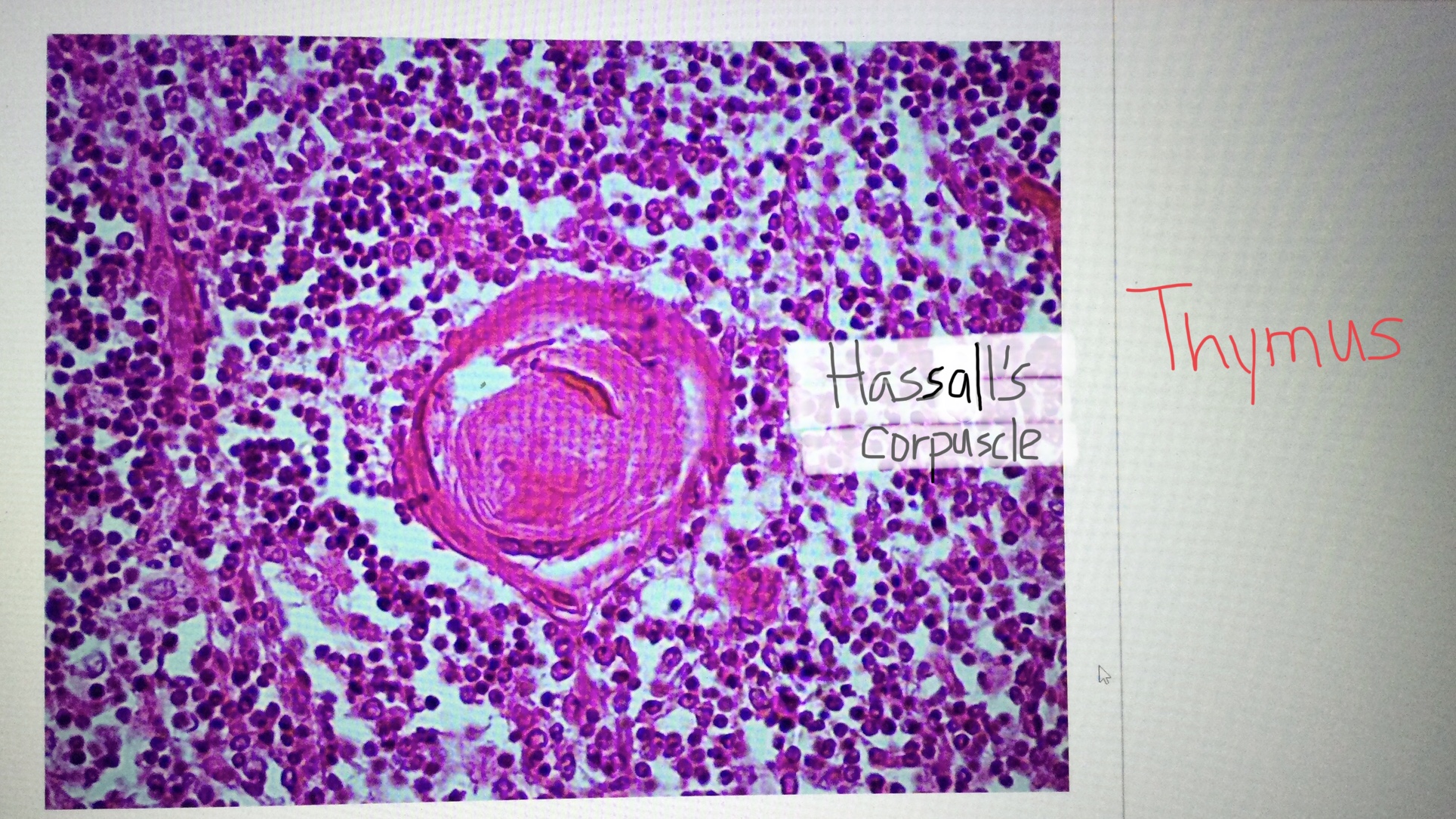
Identify the Hassall’s corpuscles of the thymus.
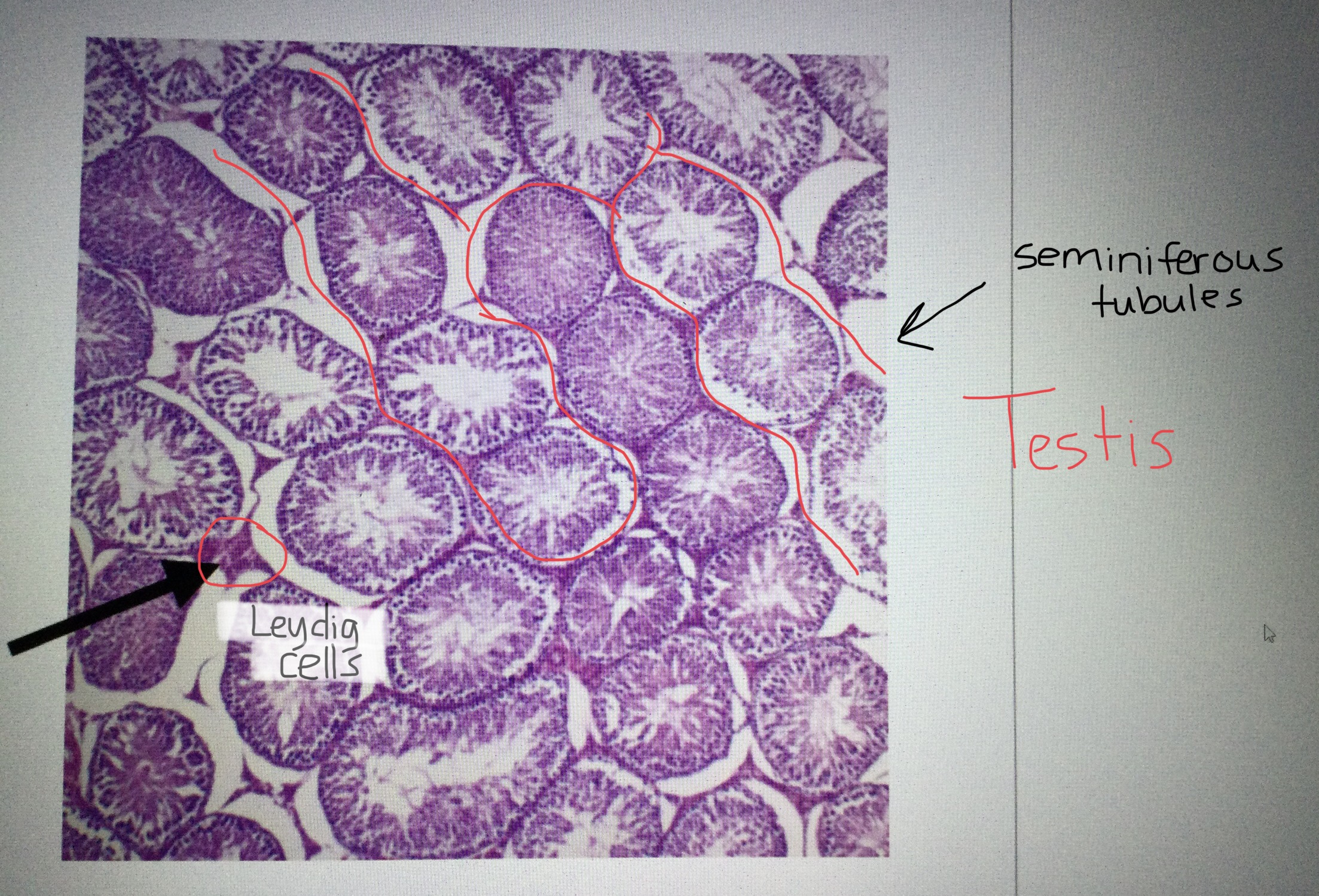
Identify testis tissue.
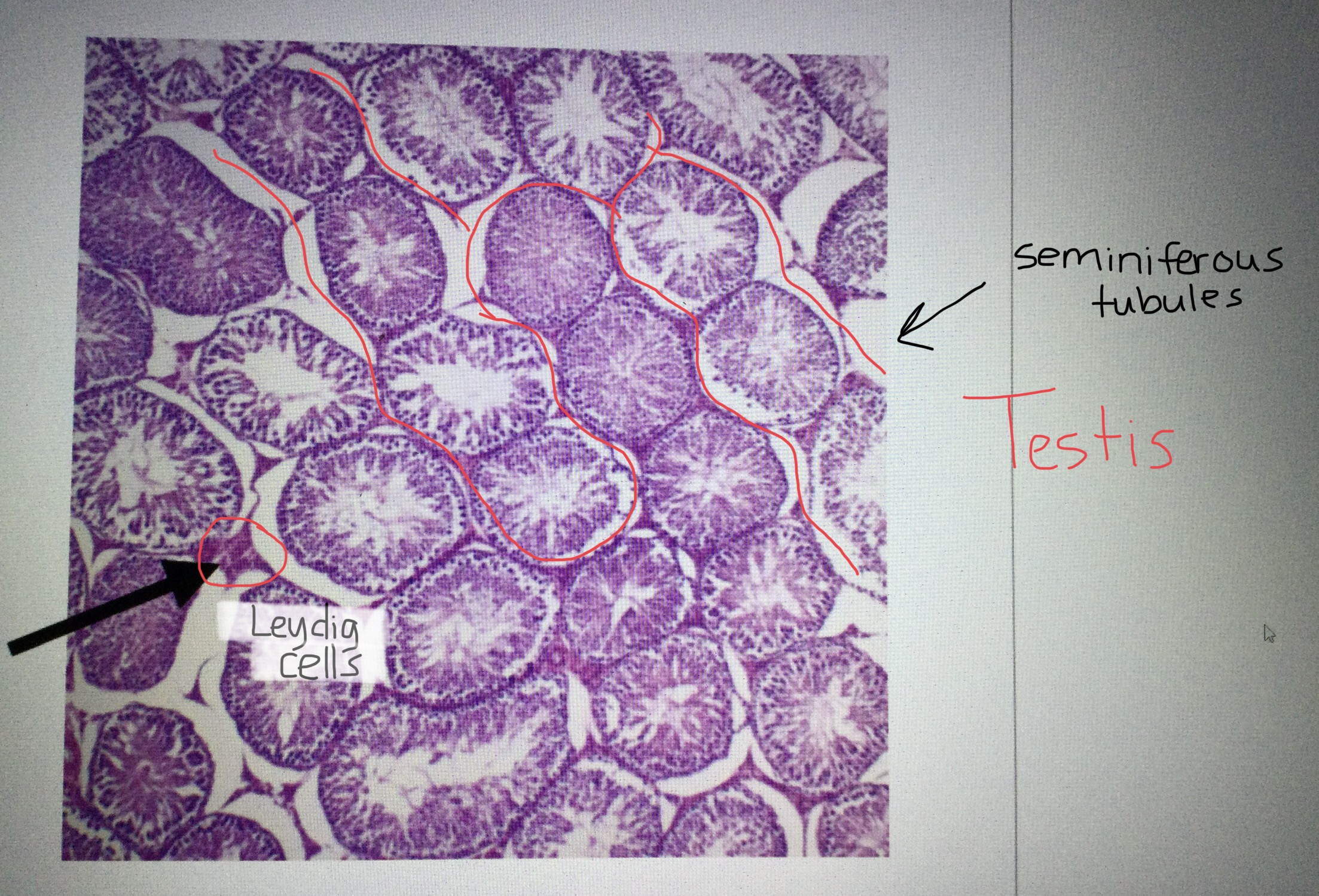
Identify the Leydig cells of the testis.
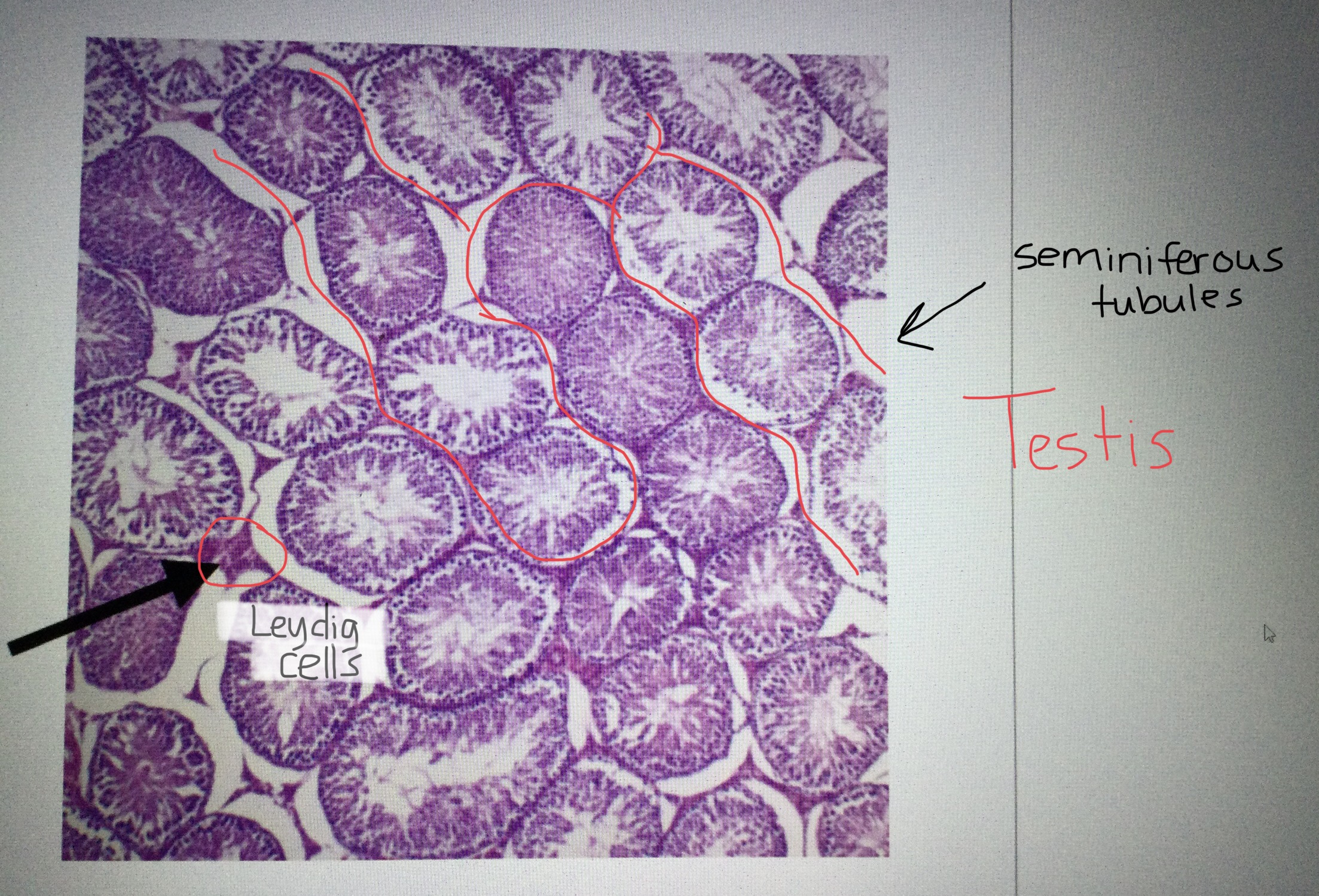
Identify the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
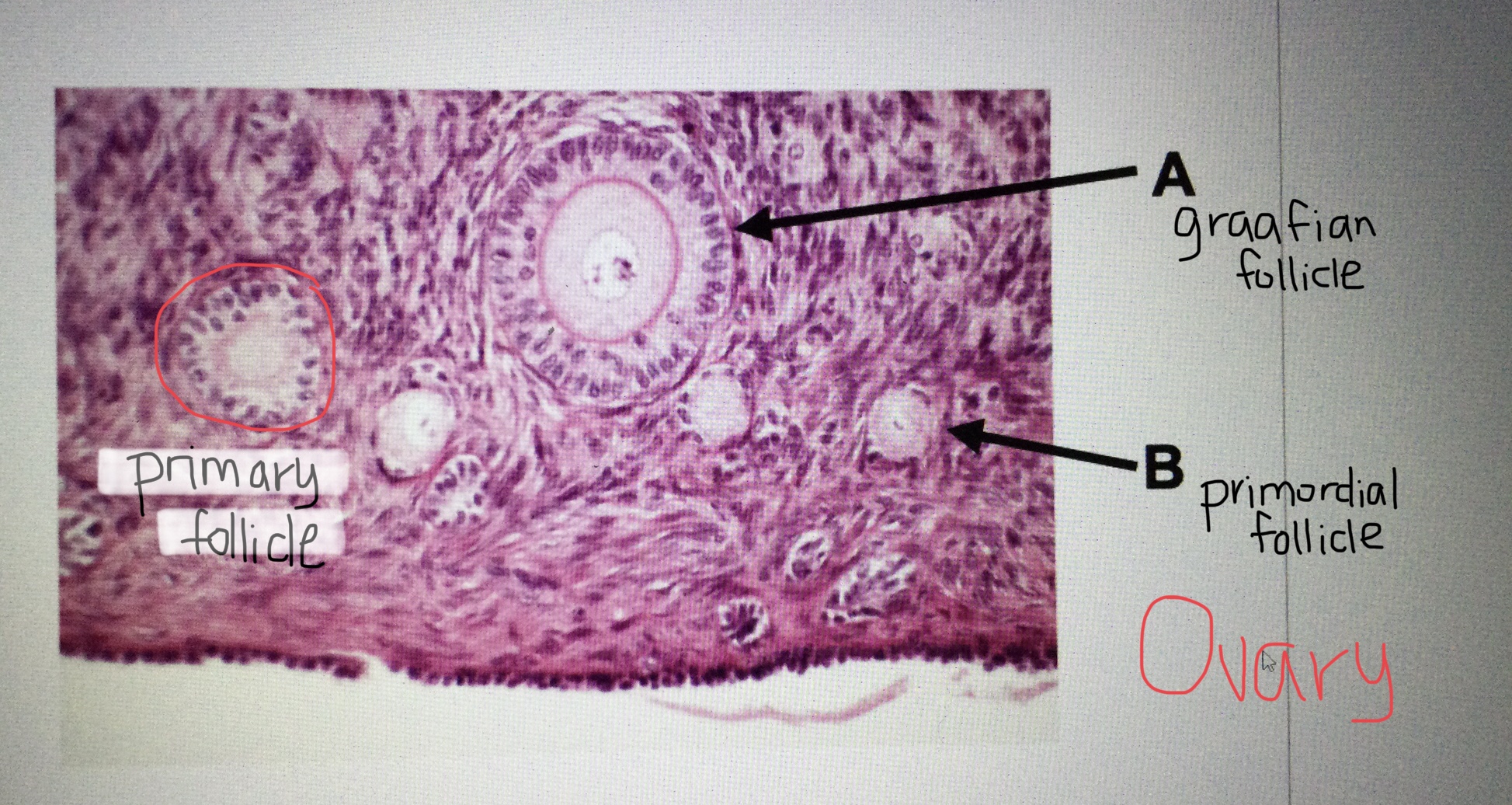
Identify ovarian tissue.
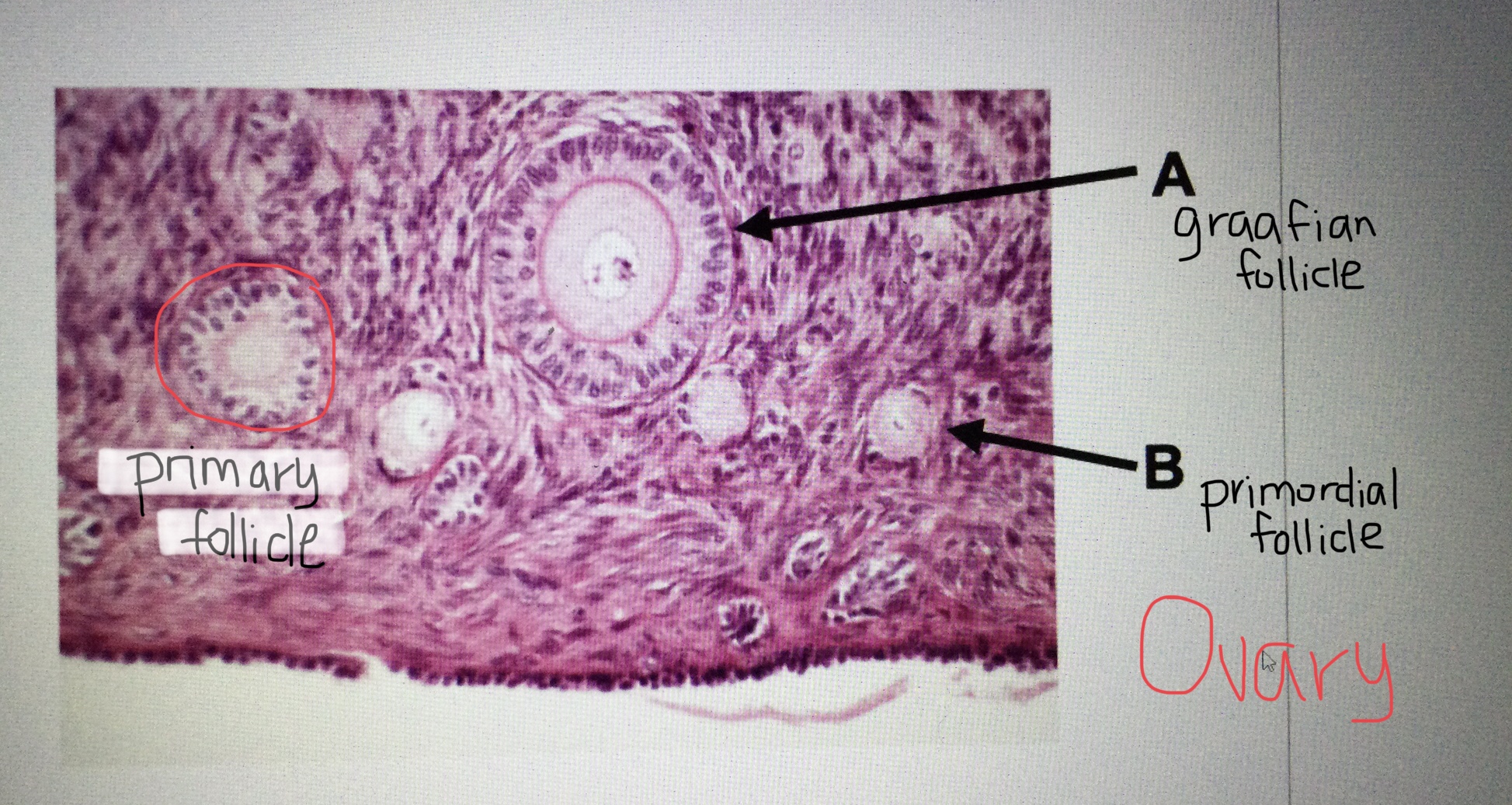
Identify a primordial follicle of the ovary.
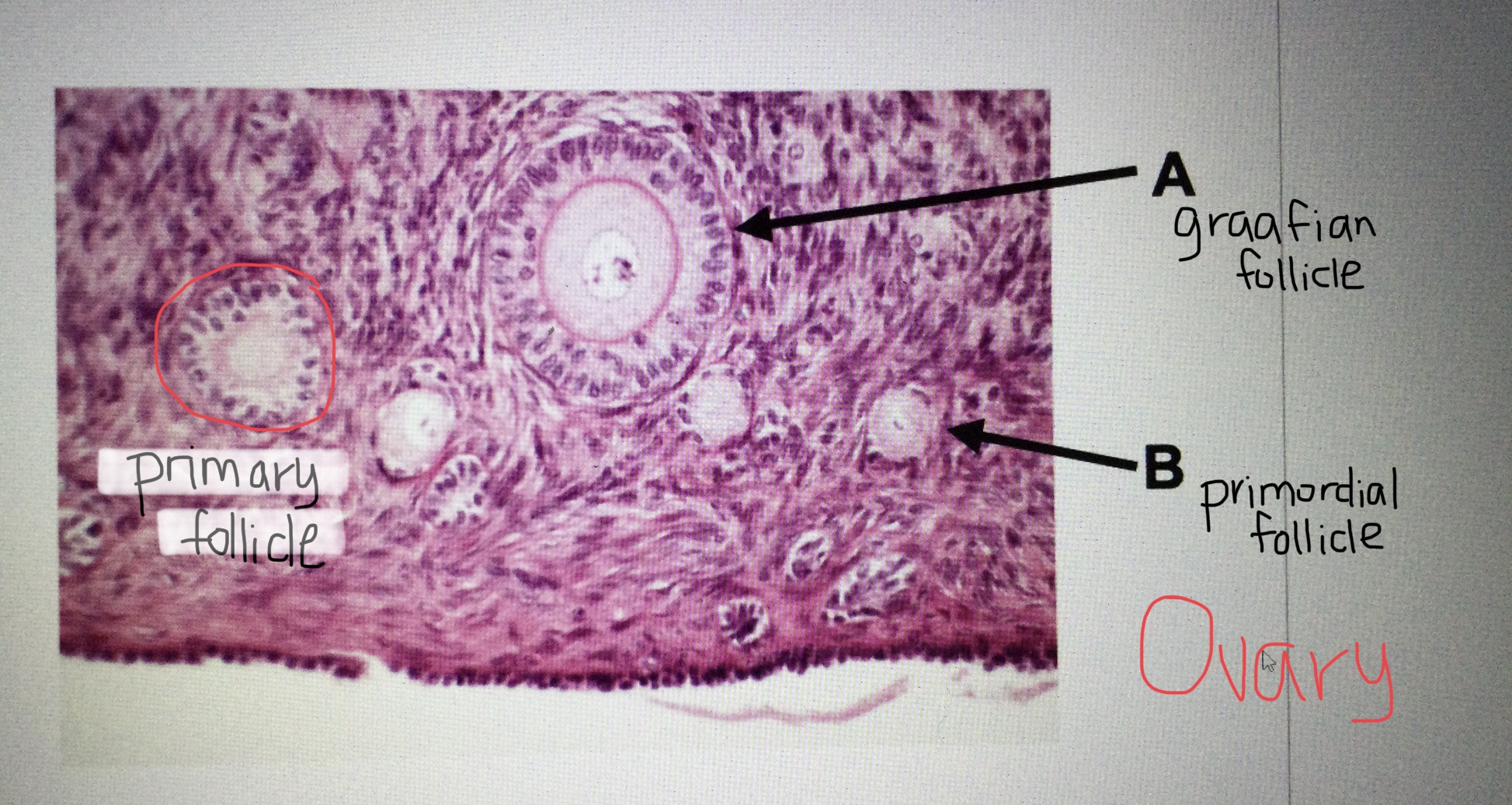
Identify a primary follicle of the ovary.
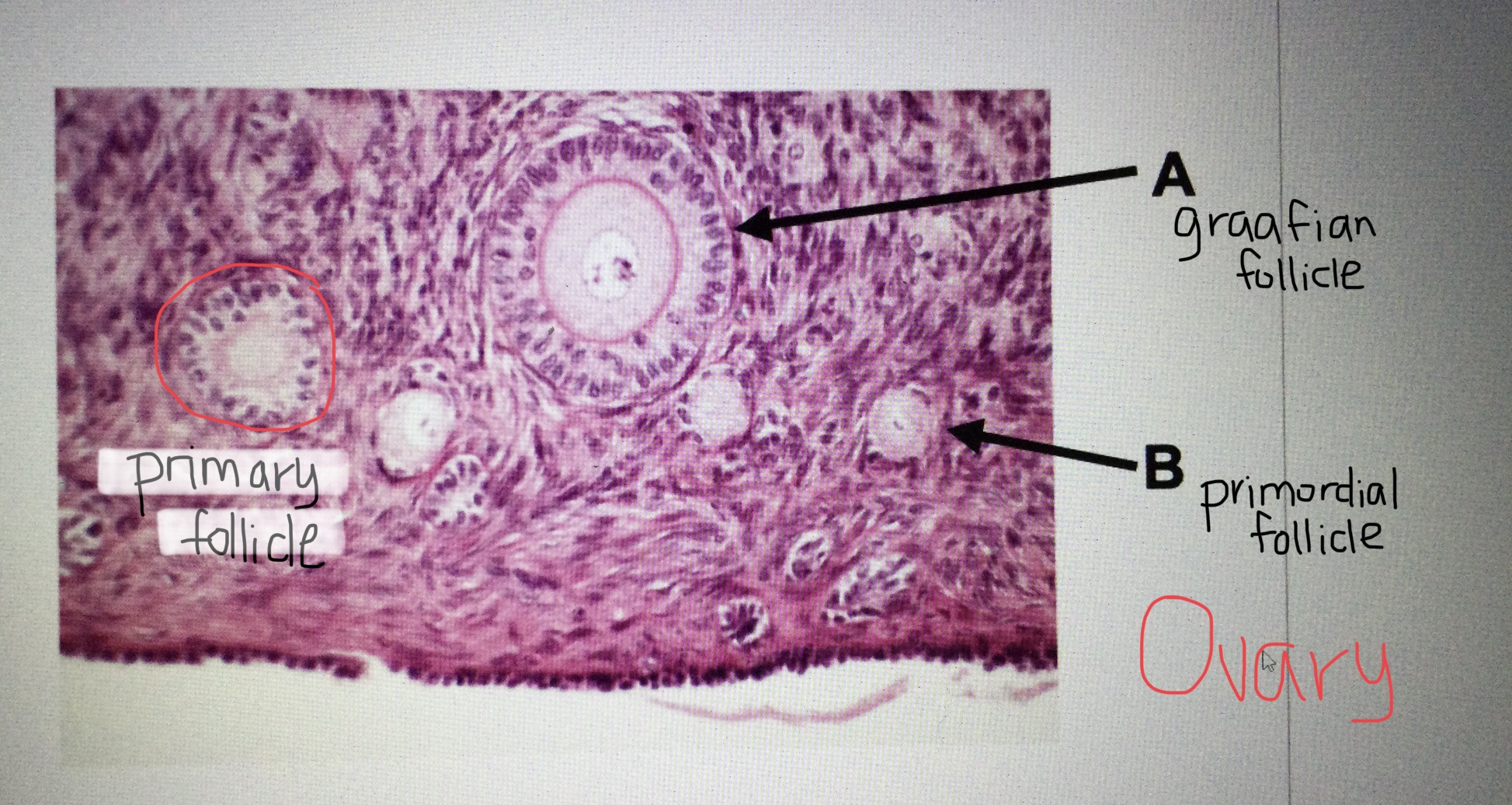
Identify a Graafian follicle of the ovary.
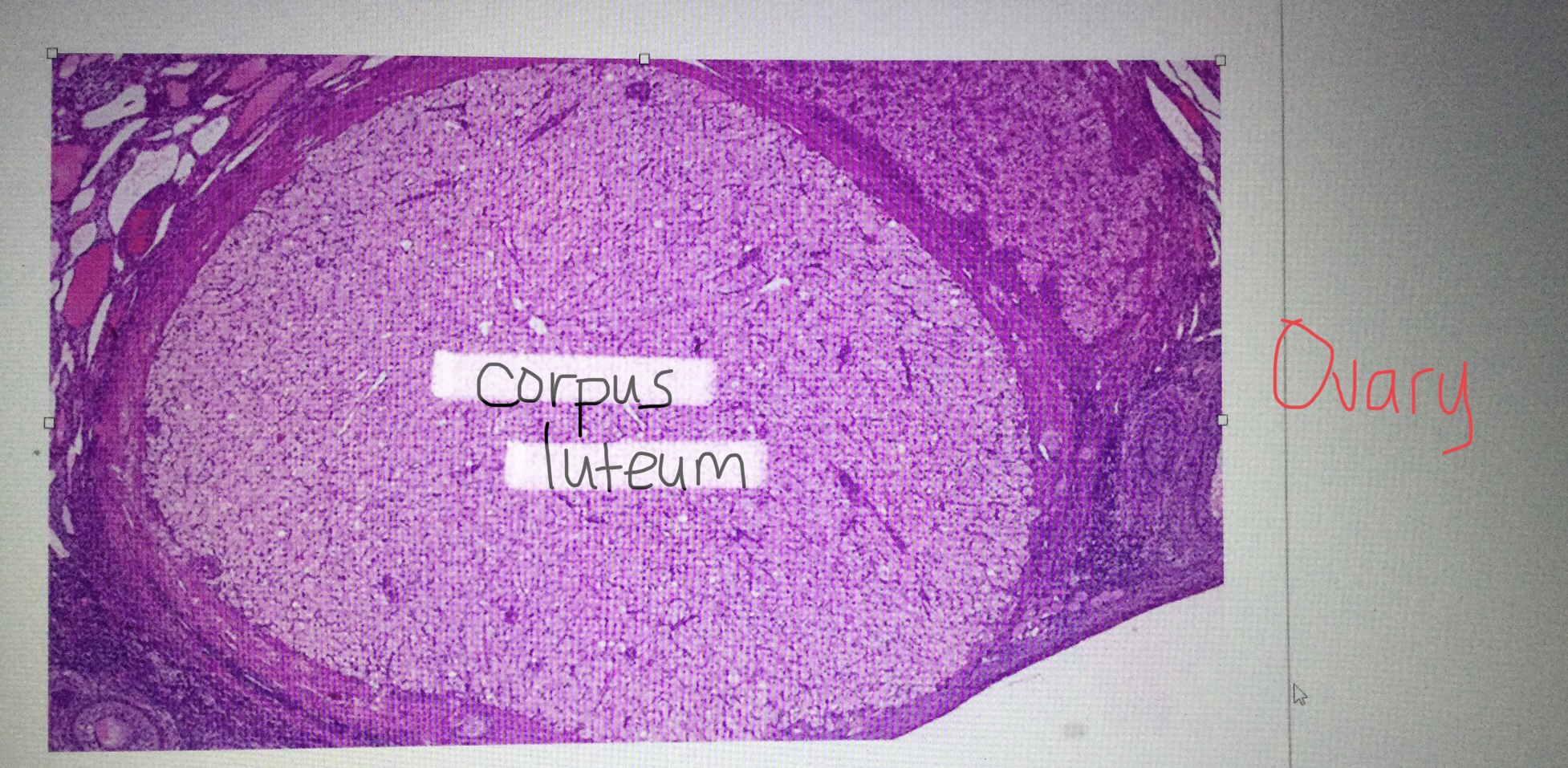
Identify a corpus luteum of the ovary.
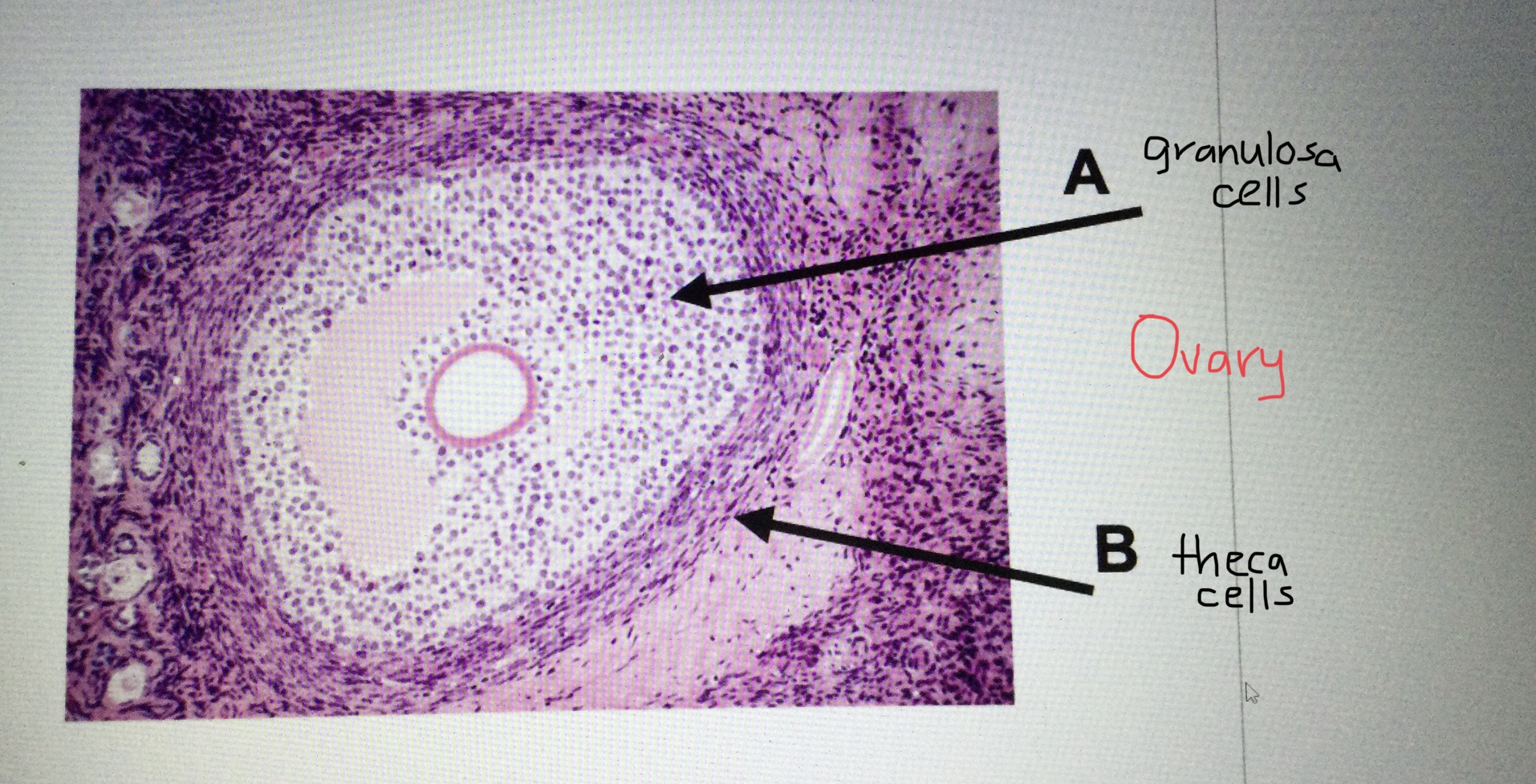
Identify the theca cells surrounding an ovarian follicle.
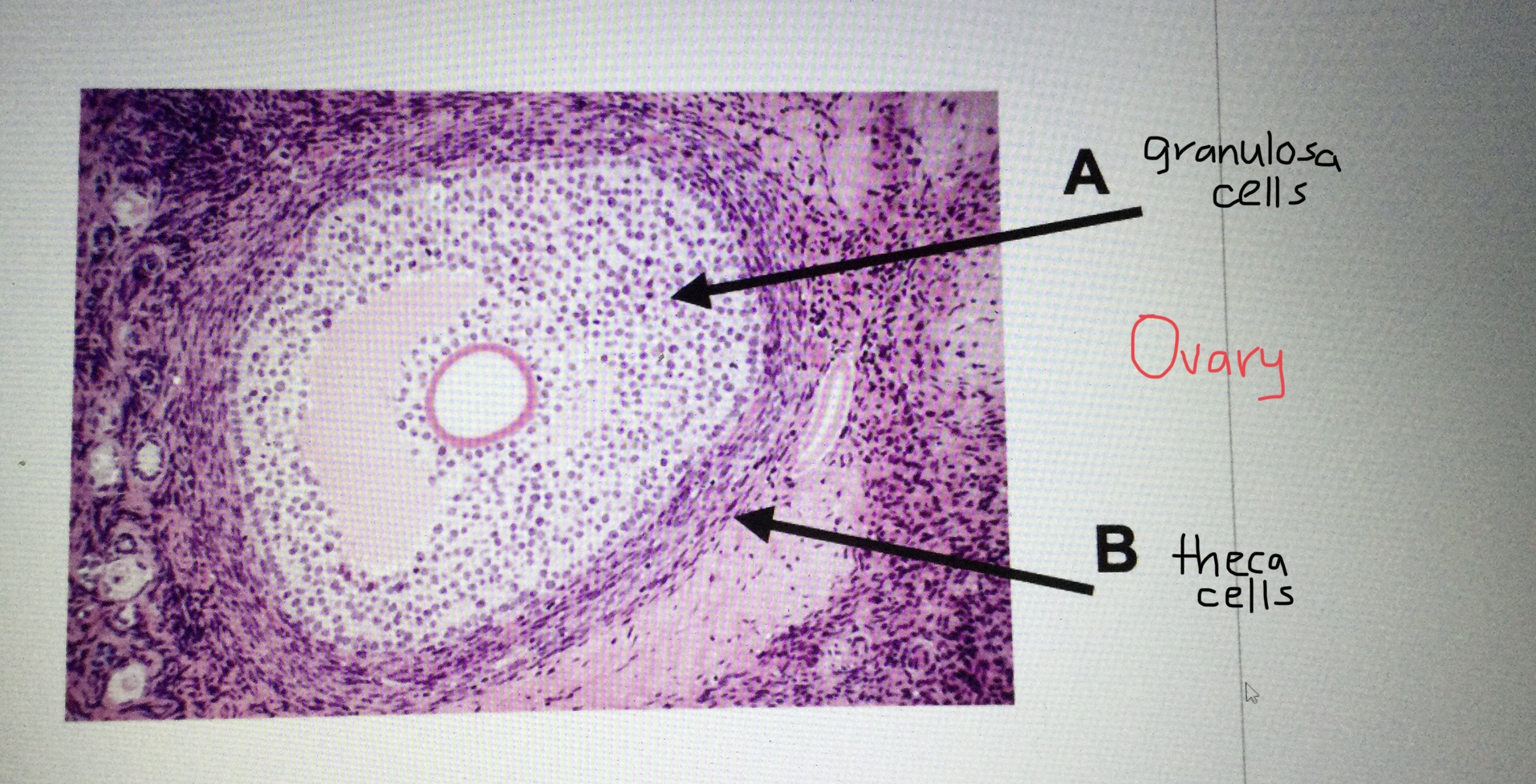
Identify the granulosa cells inside an ovarian follicle.
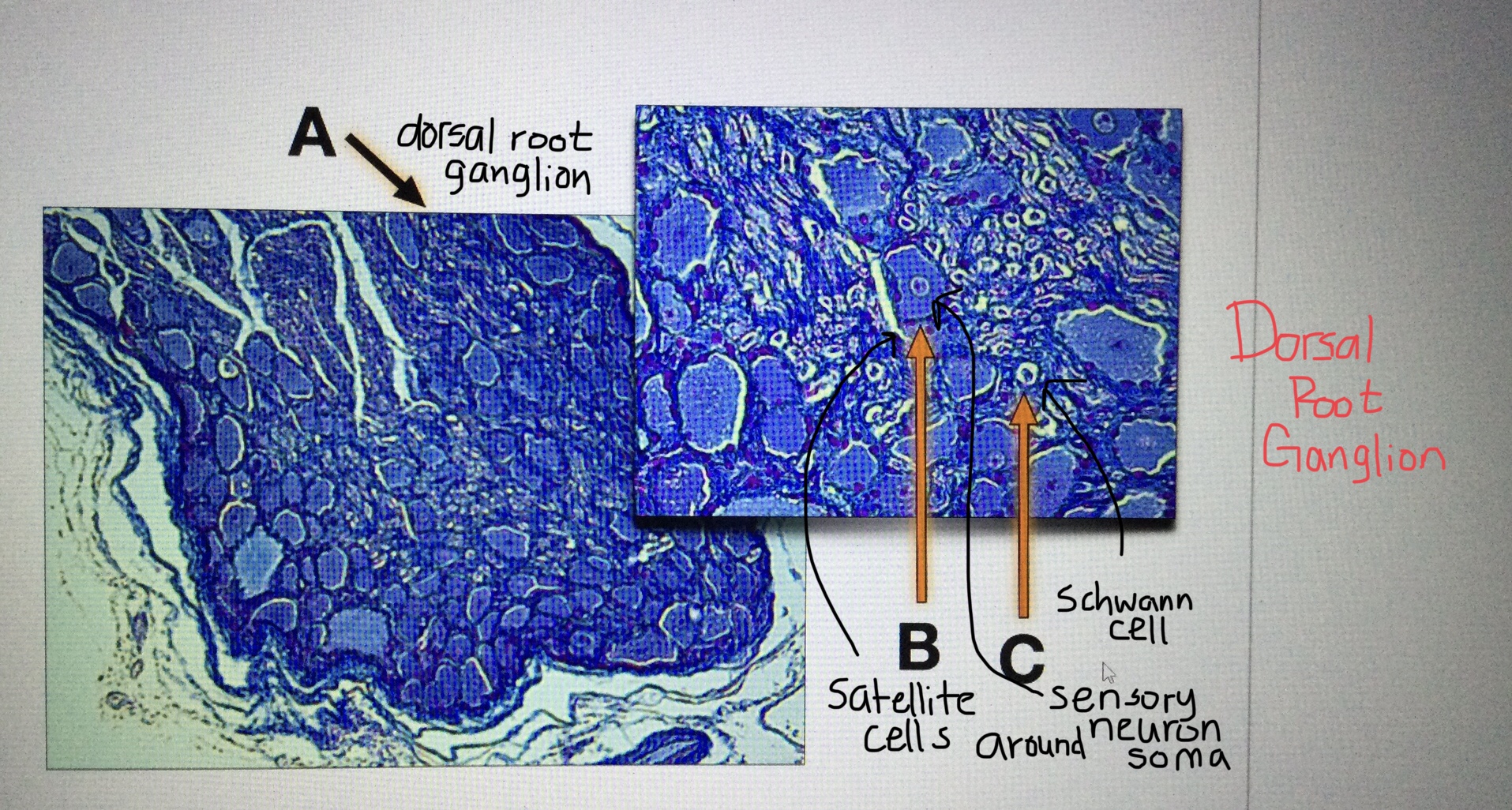
Identify dorsal root ganglion tissue.
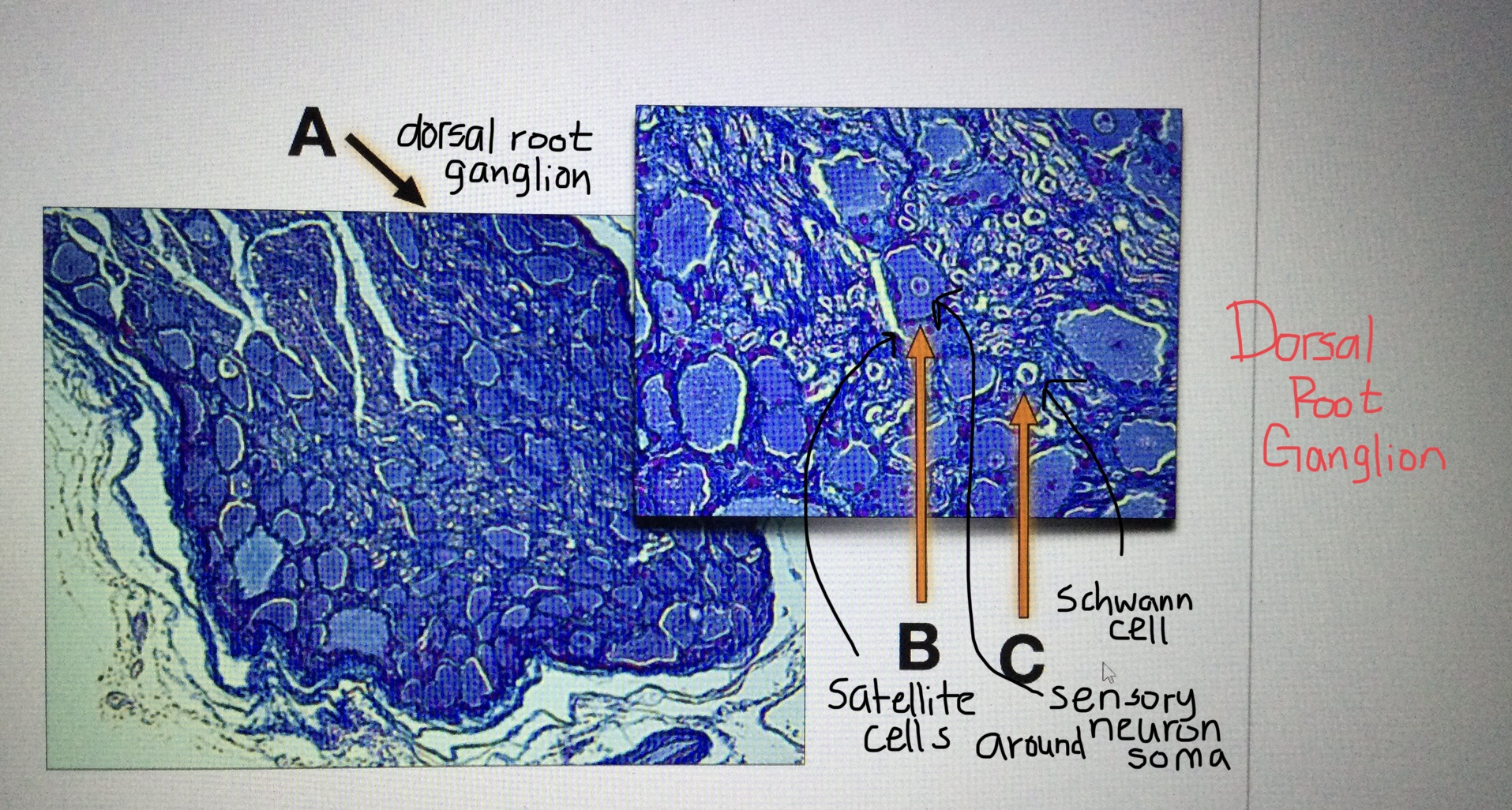
Identify a sensory neuron of the dorsal root ganglion and its support cells.
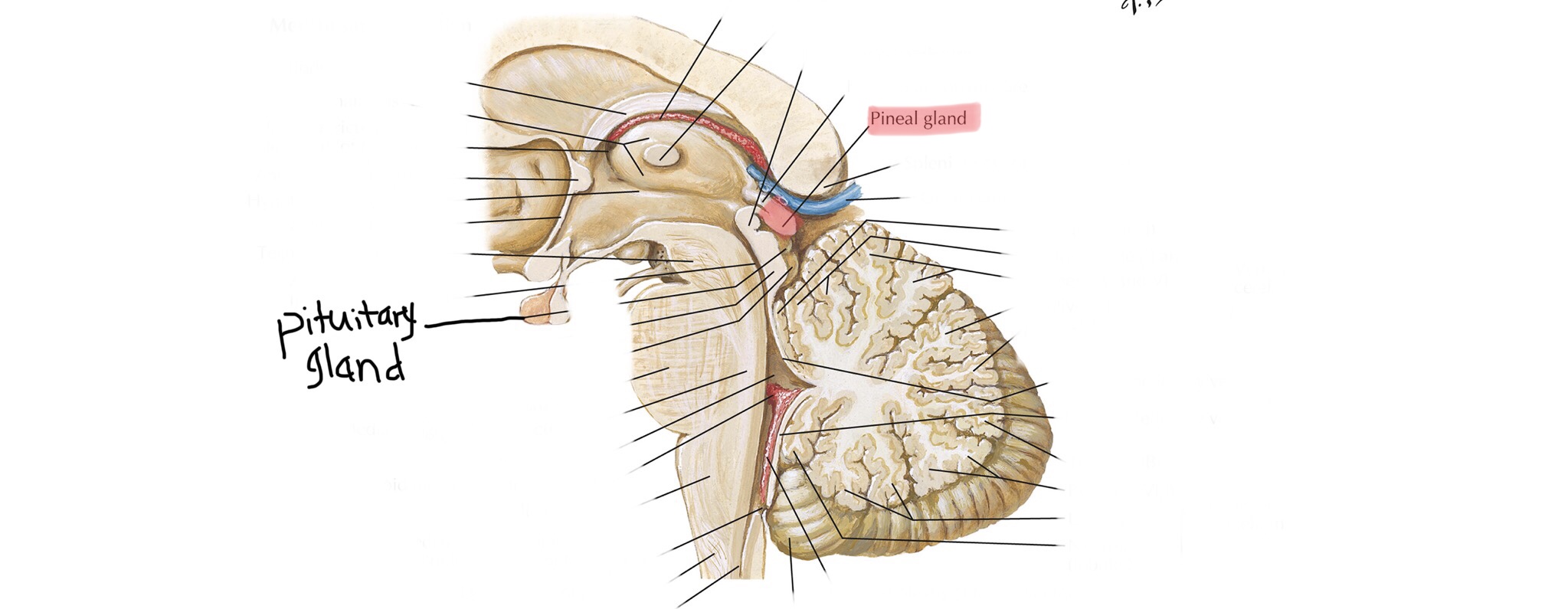
Identify the pituitary gland.
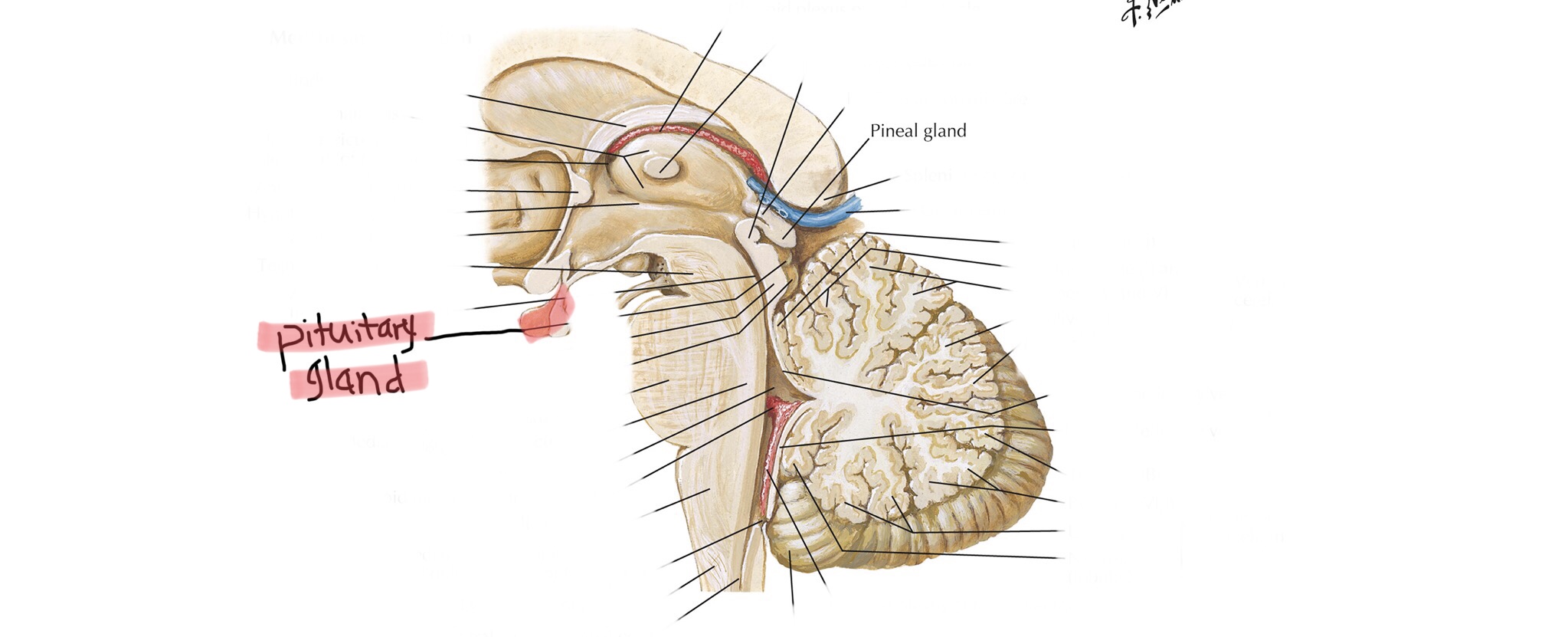
Identify the pineal gland.
Identify the thyroid gland.
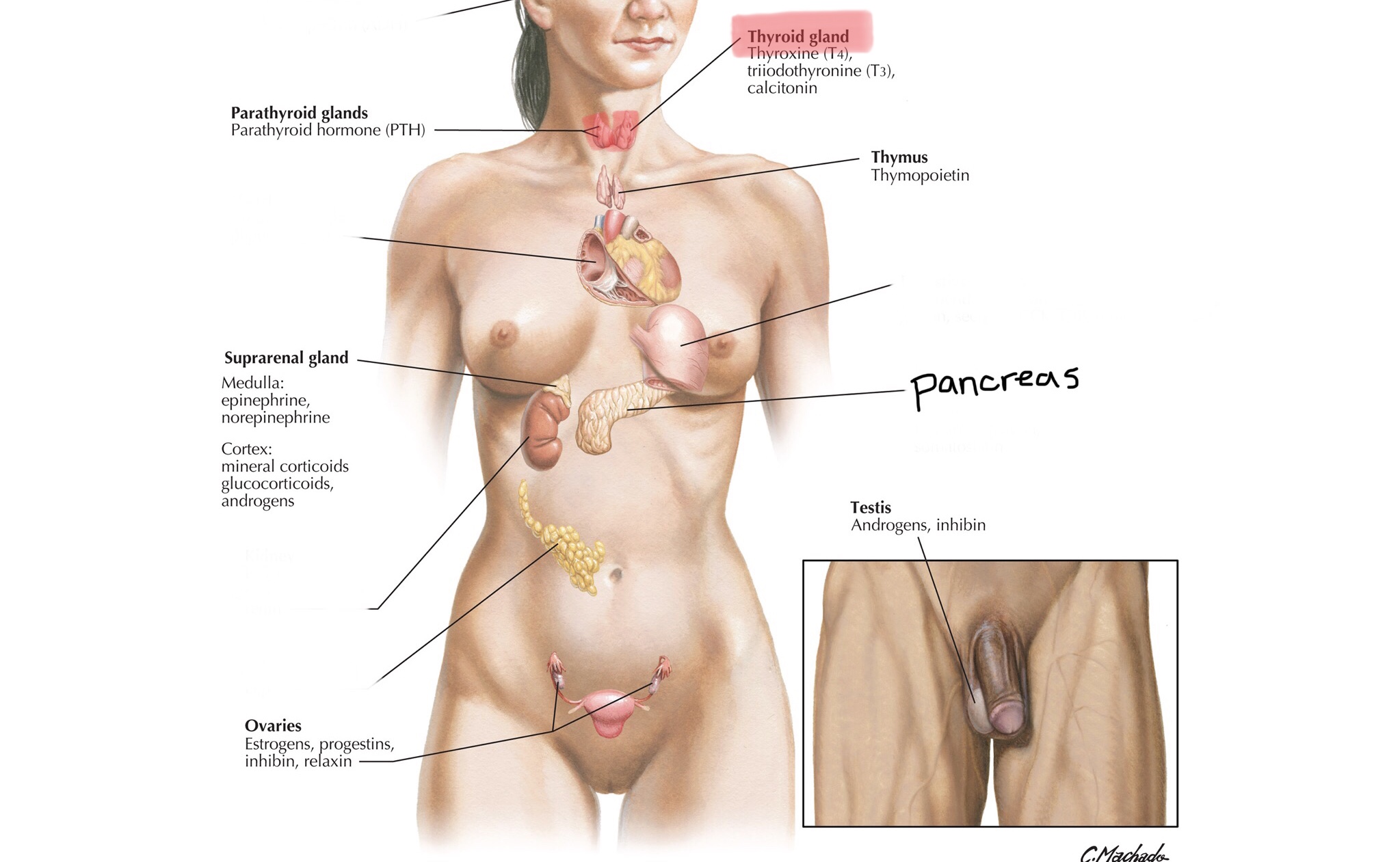
Identify the parathyroid glands.
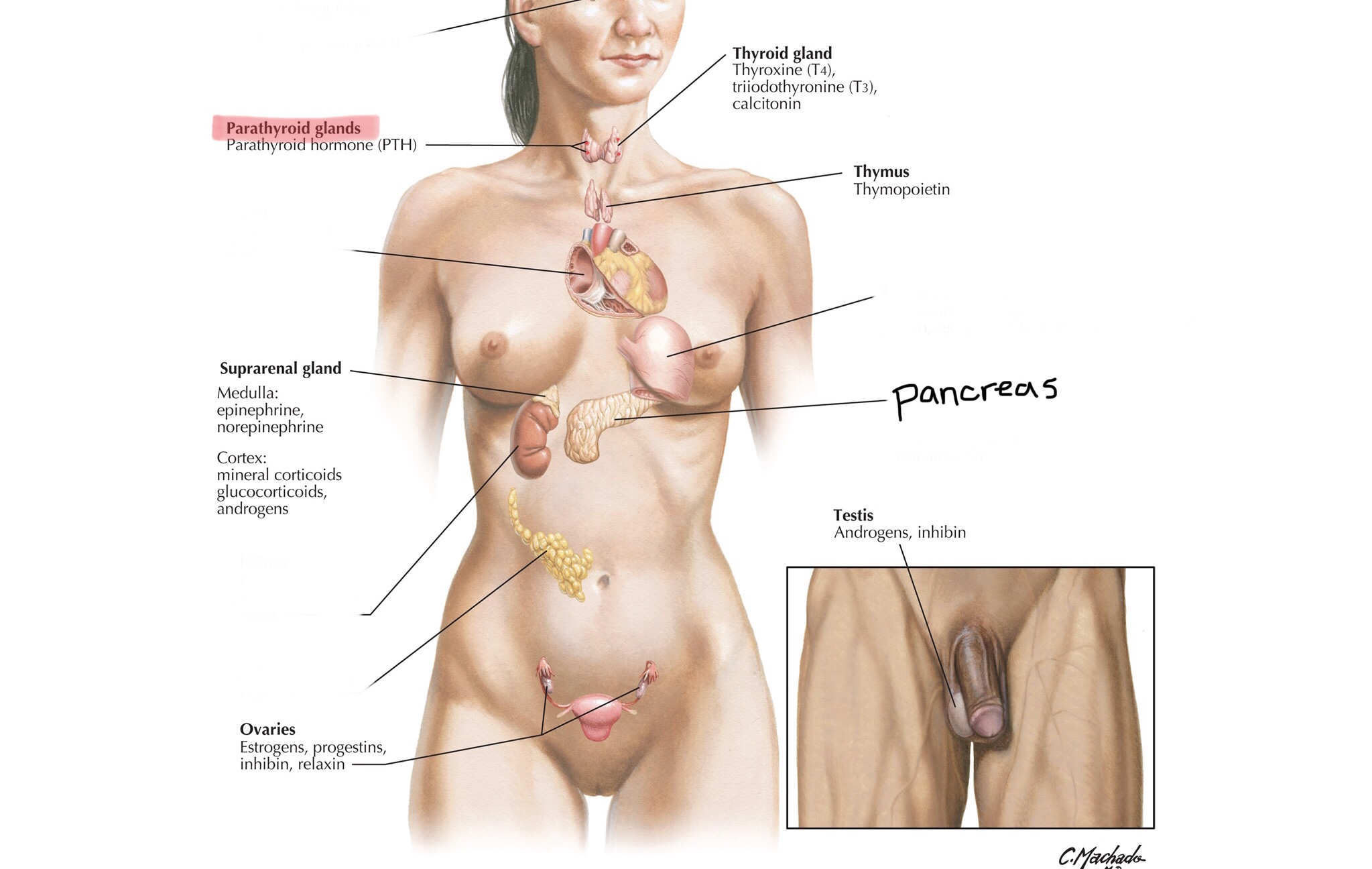
Identify the thymus.
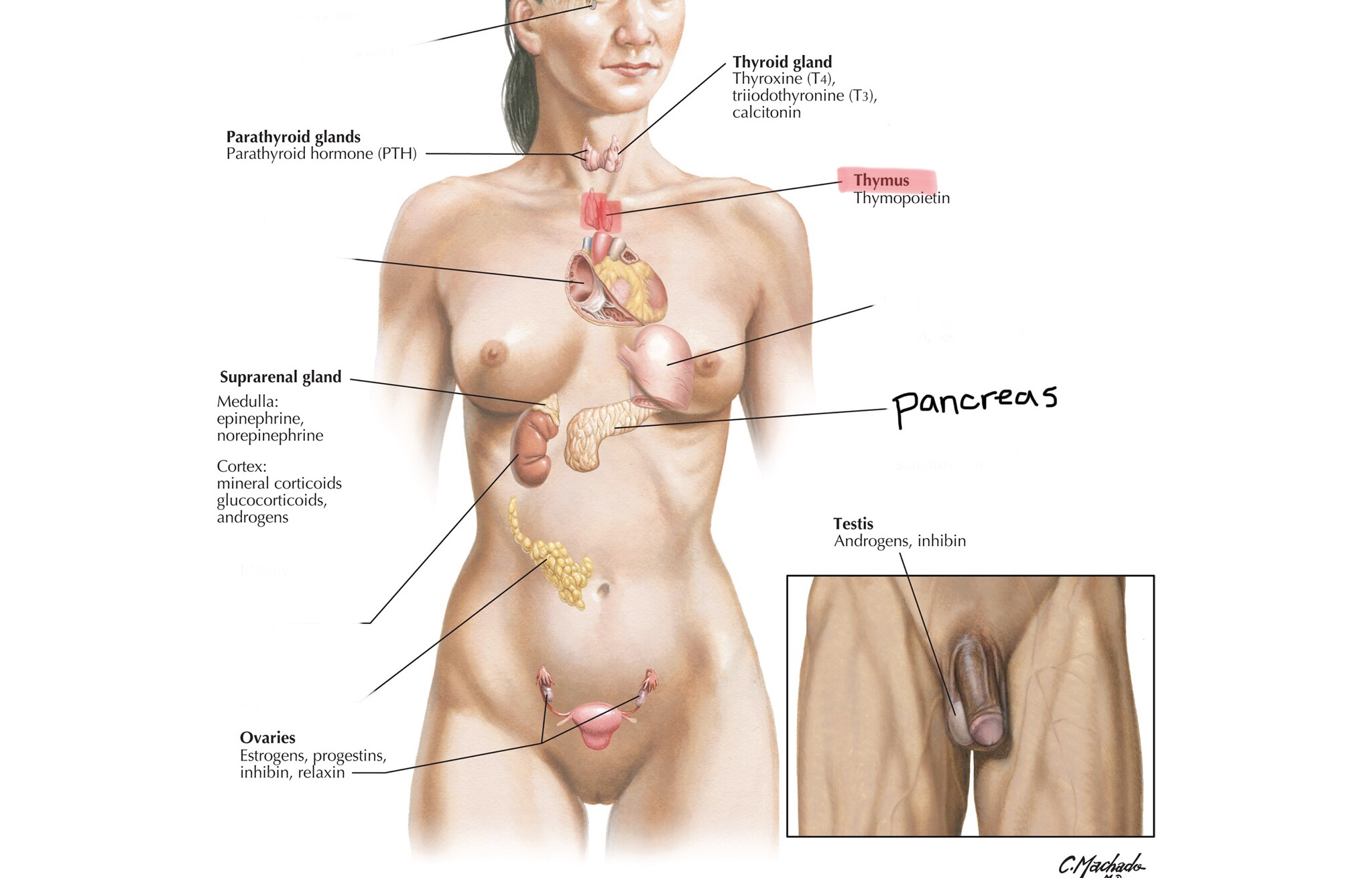
Identify the pancreas.
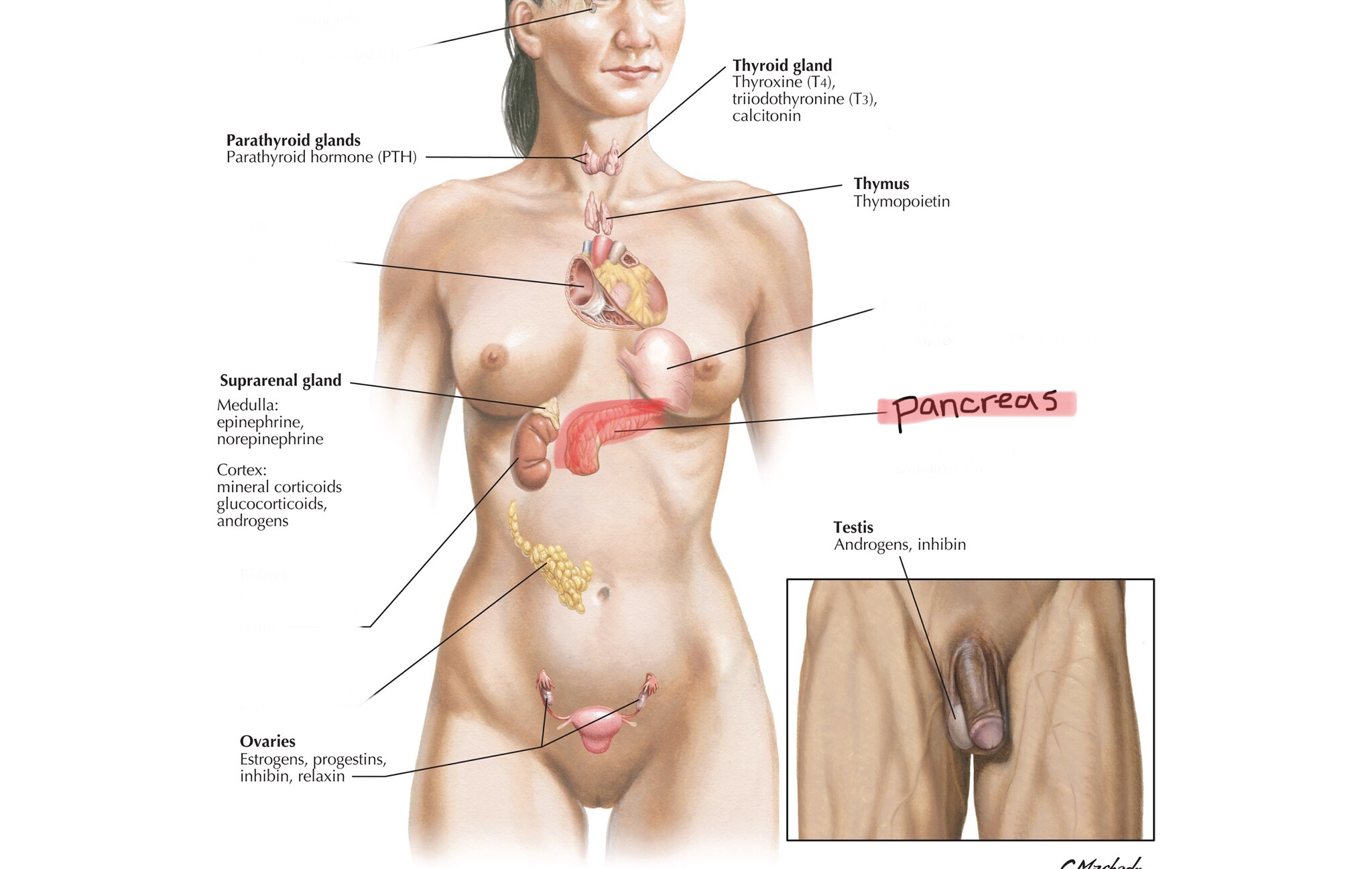
Identify the adrenal glands.
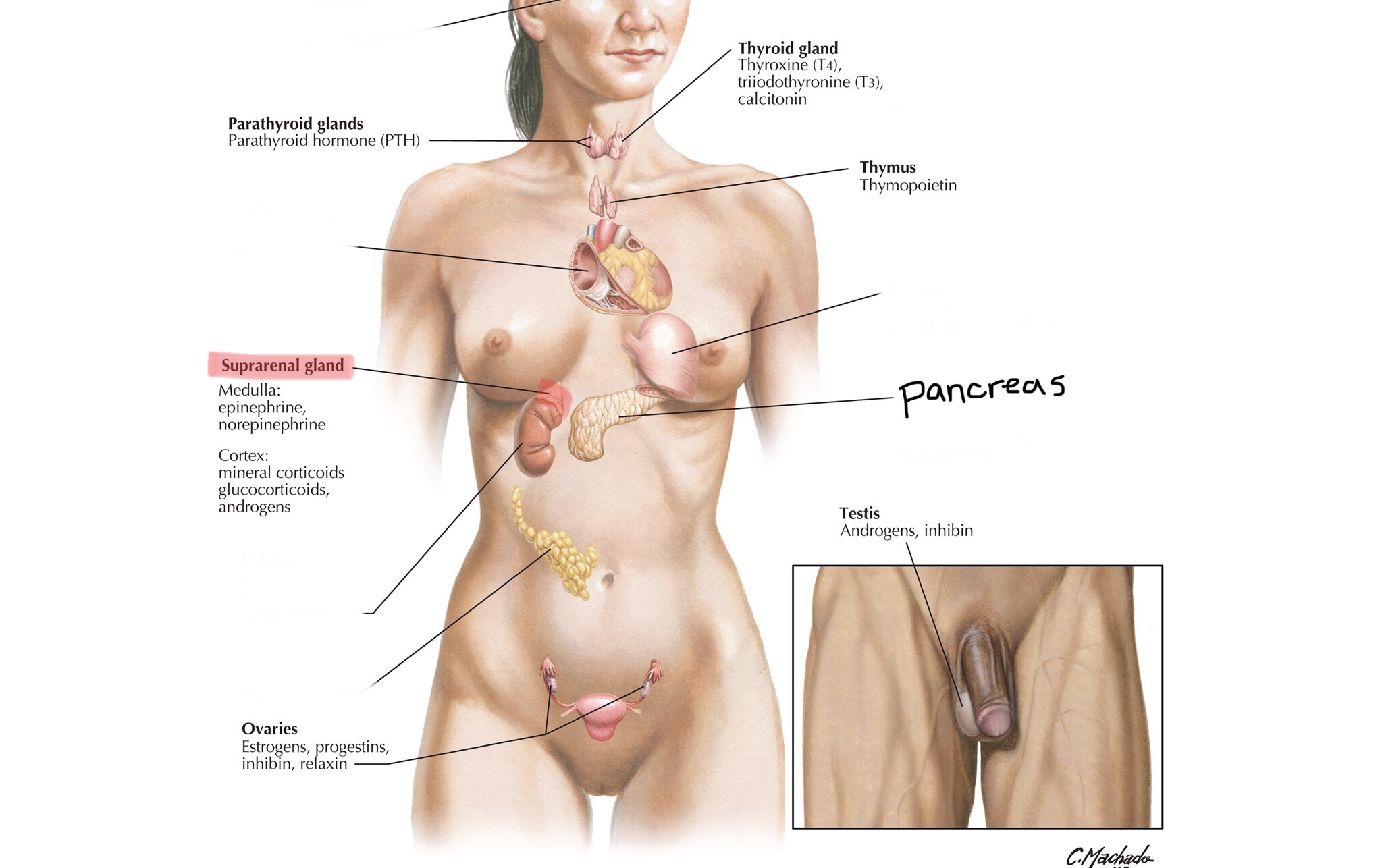
Identify the testes.
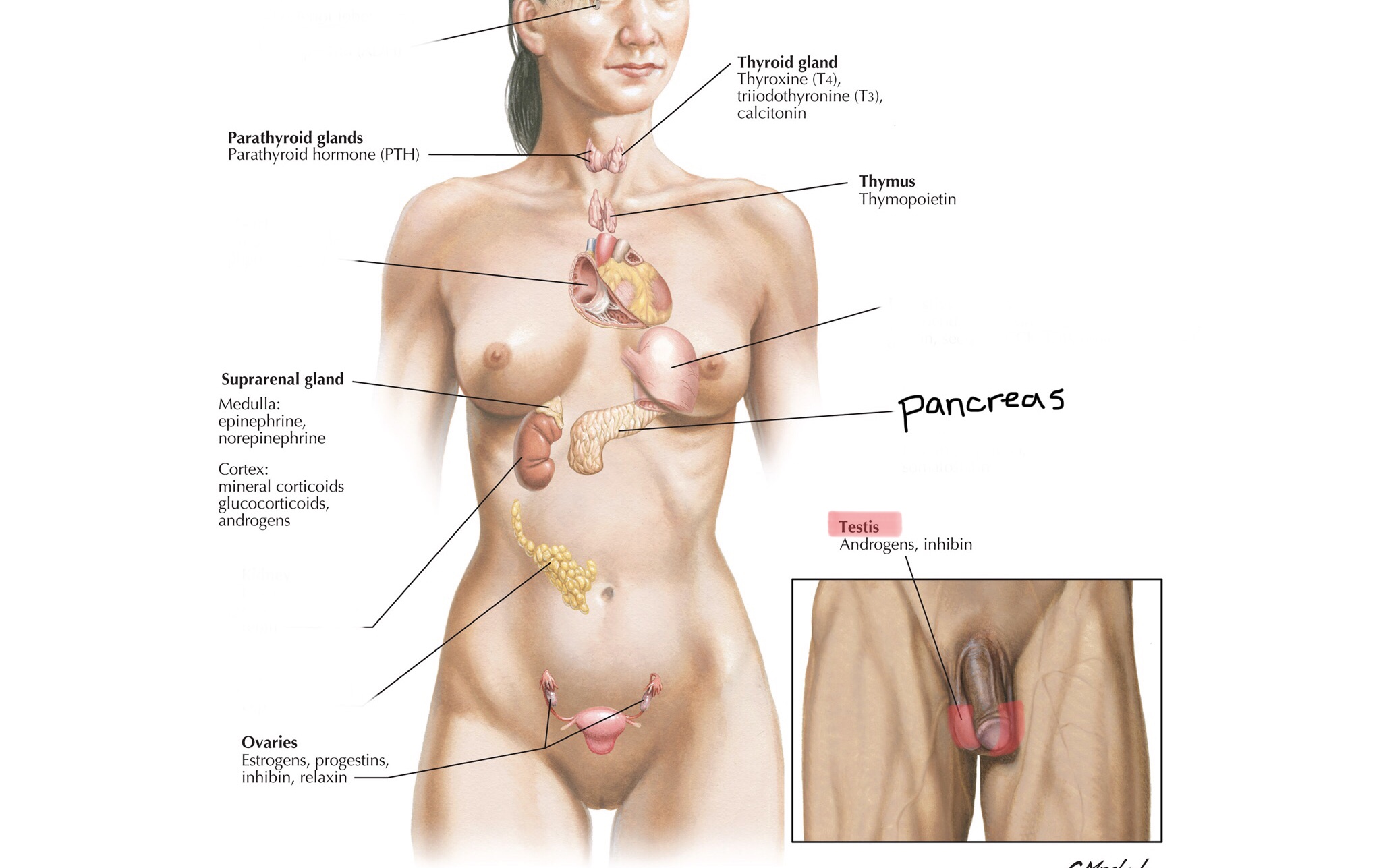
Identify the ovaries.
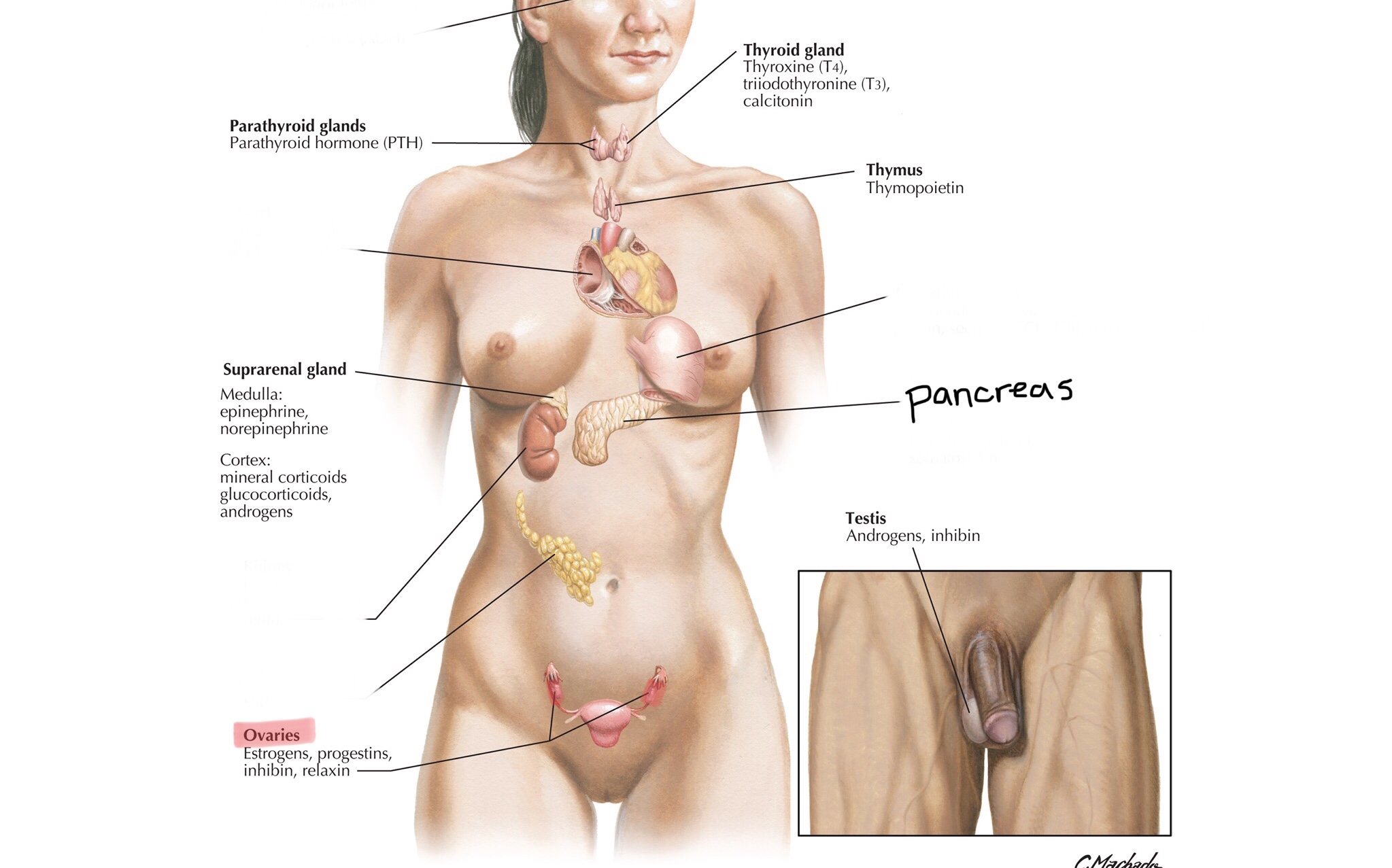
What is the main function of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system maintains homeostasis by sending long-distance chemical signals via hormones to communicate with the rest of the body.
What are endocrine glands?
Endocrine glands are ductless tissues or organs that secrete hormones directly into surrounding extracellular fluid.
What are the two main types of hormones?
Hormones can be divided into two groups, those that are derived from lipids (steroids) and those that are derived from amino acids (amines, peptides, proteins).
What are some examples of amine hormones?
Some important amine hormones include melatonin, epinephrine, and norepinephrine.
What are some examples of peptide/protein hormones?
Some important peptide/protein hormones include antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
How does the chemical makeup of a hormone effect its function?
In order for hormones to have an effect on the body, they must be able to bind to intracellular hormone receptors. Lipid-based hormones are able to diffuse freely across the cell membranes of targeted cells, whereas amino acid-based hormones require some help.
How do lipid-based hormones cause an effect on target cells?
Lipid-based hormones diffuse freely across the lipid bilayers of the target cell outer membrane and nuclear envelope. Once bound to a receptor, it becomes a receptor-hormone complex, which triggers gene transcription/production of proteins.
How do protein-based hormones cause an effect on target cells?
Protein-based hormones cannot freely diffuse across a plasma membrane. Instead, they bind to membrane receptors, initiating a signaling cascade. In most mechanisms, after the protein-based hormones bind with a surface receptor, a G protein on the intracellular side of the receptor activates, causing adenylyl cyclase enzymes to convert adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). cAMP then activates protein kinases in the cytosol to initiate a phosphorylation cascade, ultimately resulting in a change in cellular activity.
What is the function of the posterior pituitary gland?
The posterior pituitary gland does not synthesize any hormones, rather it stores and releases antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) produced by the hypothalamus. Its secretions are regulated by the hypothalamus.
How does the anterior pituitary gland receive signals to produce hormones?
Hormones from the hypothalamus travel down the hypophyseal portal system (a double capillary bed) into the hypophyseal portal veins of the anterior pituitary gland, triggering production and secretion of its hormones.
What are the four tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
The four tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland are thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
What are the three non-tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
The three non-tropic hormones of the pituitary gland are growth hormone (GH), beta endorphin, and prolactin.
What is the function of tropic hormones?
Tropic hormones regulate functions of other endocrine glands by turning them on or off.
What is the function of luteinizing hormone?
LH works on the reproductive system by increasing the production of sex hormones.
What is the function of follicle-stimulating hormone?
FSH works on the reproductive system by increasing the production/maturation of sperm and eggs.
What is the function of thyroid-stimulating hormone?
TSH works on the thyroid to increase production of thyroid hormone.
What is the function of prolactin?
Prolactin works on the mammary glands to increase milk production.
What is the function of growth hormone?
GH works on the liver, bones, and muscles to increase growth. GH also directly works on metabolism by increasing fatty acid levels in the blood for fuel.
What is the function of adrenocorticotropic hormone?
ACTH works on the adrenal glands to regulate metabolism and stress/release corticosteriods.
What is the function of antidiuretic hormone?
ADH works on the kidneys to control water balance.
What is the function of oxytocin?
OT works on the female reproductive system during labor to facilitate contractions/regulates smooth muscle contractions.
What is the main function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland regulates metabolism.
What is a goiter?
A goiter refers to the overgrowth of the thyroid gland caused by excess storage of hormone components. When the thyroid is unable to successfully synthesize hormones, it does not release, causing the colloid-filled follicles to swell and overgrow.
What hormones does the thyroid secrete?
The thyroid secretes thyroid hormone (TH), including triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), calcitonin, and parathyroid hormone (PTH).
What is the function of thyroid hormone (TH)?
Thyroid hormone works directly on the body’s metabolism.
What is the function of calcitonin?
Calcitonin is produced in the prescence of high blood calcium levels to antagonize parathyroid hormone.
What hormones does the parathyroid gland produce?
Parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH).
What is the function of the parathyroid and parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
The parathyroid glands and PTH regulate blood calcium levels, increasing levels when they get low.
What hormone does the pineal gland secrete?
The pineal gland secretes melatonin.
What is the function of melatonin?
Melatonin regulates the circadian rhythm.
What are brain sands made of?
Brain sands of the pineal gland are concretions of calcium that develop as we age.
What is the function of the thymus?
The thymus helps develop T-lymphocytes of the immune system.
What hormones does the thymus secrete?
The thymus secretes thymulin, thymopoetin, and thymosin.
What are the three distinct layers of the adrenal cortex from most superficial to most deep?
The three layers of the adrenal cortex include the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata, and the zona reticularis.
What class of hormones are produced and secreted by the zona glomerulosa?
The zona glomerulosa produces mineralcorticoids, such as aldosterone.
What is the function of aldosterone?
Aldosterone regulates electrolyte concentrations.
What class of hormones does the zona fasciculata produce?
The zona fasciculata produces glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone.
What is the function of cortisol?
Cortisol is a stress resistor.
What class of hormones does the zona reticularis produce?
The zona reticularis produces gonadocorticoids, such as androgen.
What is the function of androgen?
Androgen is the weak sex hormone and converts to testosterone or estrogen, leading to the development of secondary sex characteristics, female sex drive, and the source of estrogen during menopause.