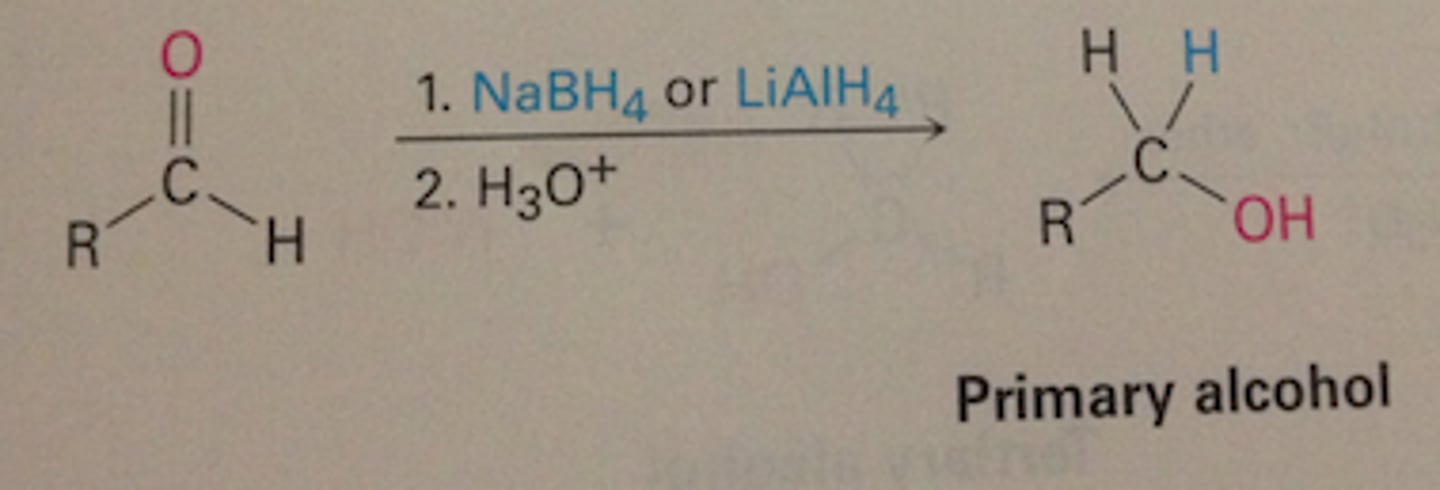CHE 321- Oxidizing and reducing agents in alcohols
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is oxidation? How does it work in alcohols?
a decrease in the hydrogen content or an increase in content of oxygen or other electronegative elements .
What is Jones reagent and what does it do?
Jones reagent is a strong oxidizing agent which generally turns alcohols into carbonyls.
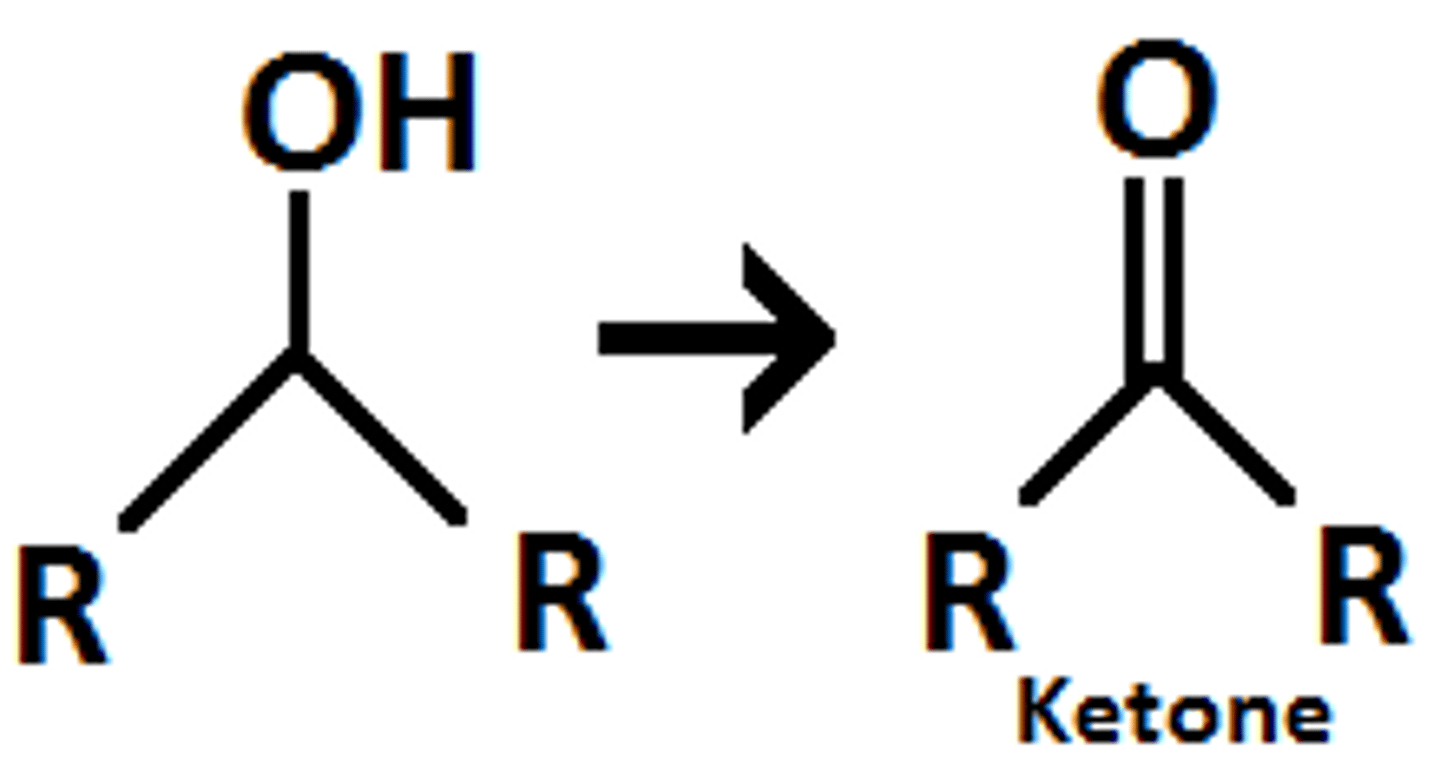
What is jones reagent effect in secondary alcohols?
secondary alcohols are turned into ketones
what does LiAlH4/ H+ do to a ketone
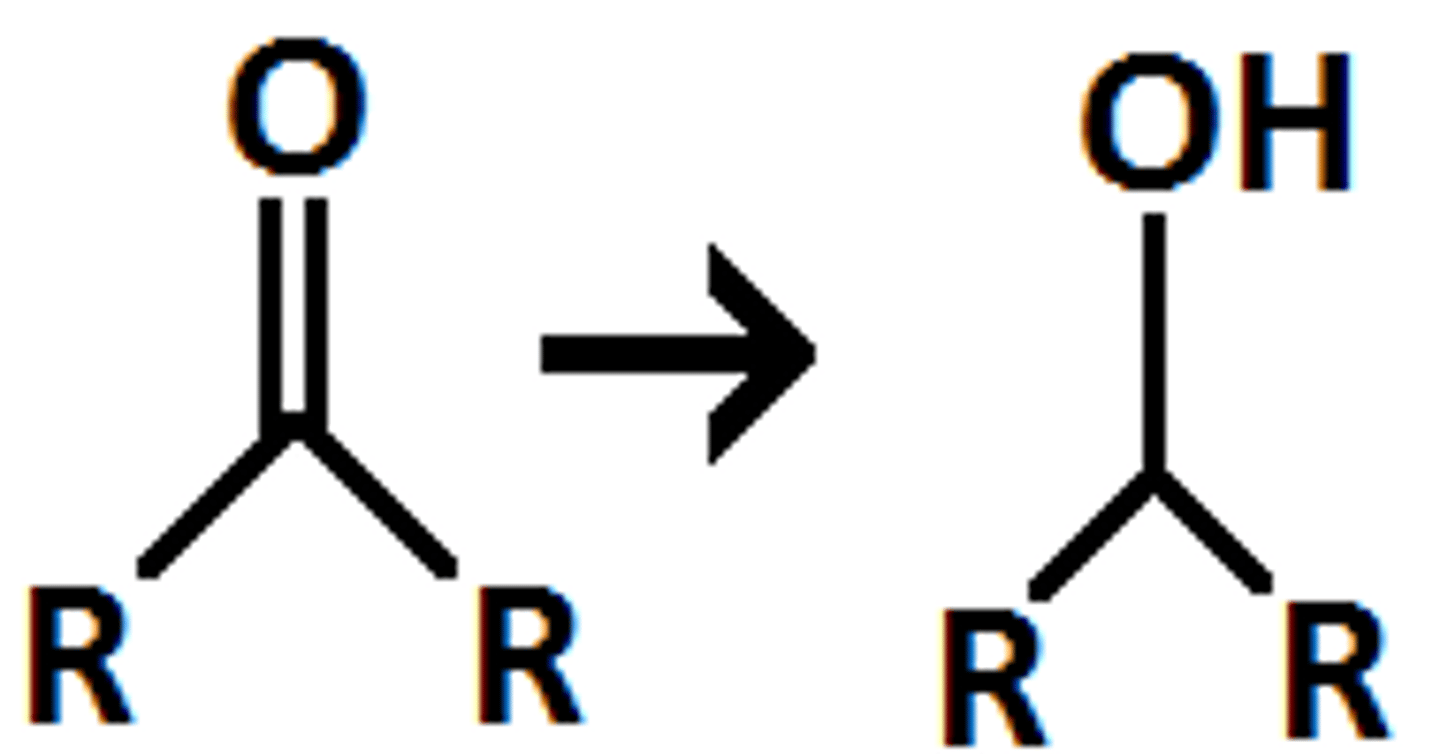
ketone reduces to a secondary alcohol
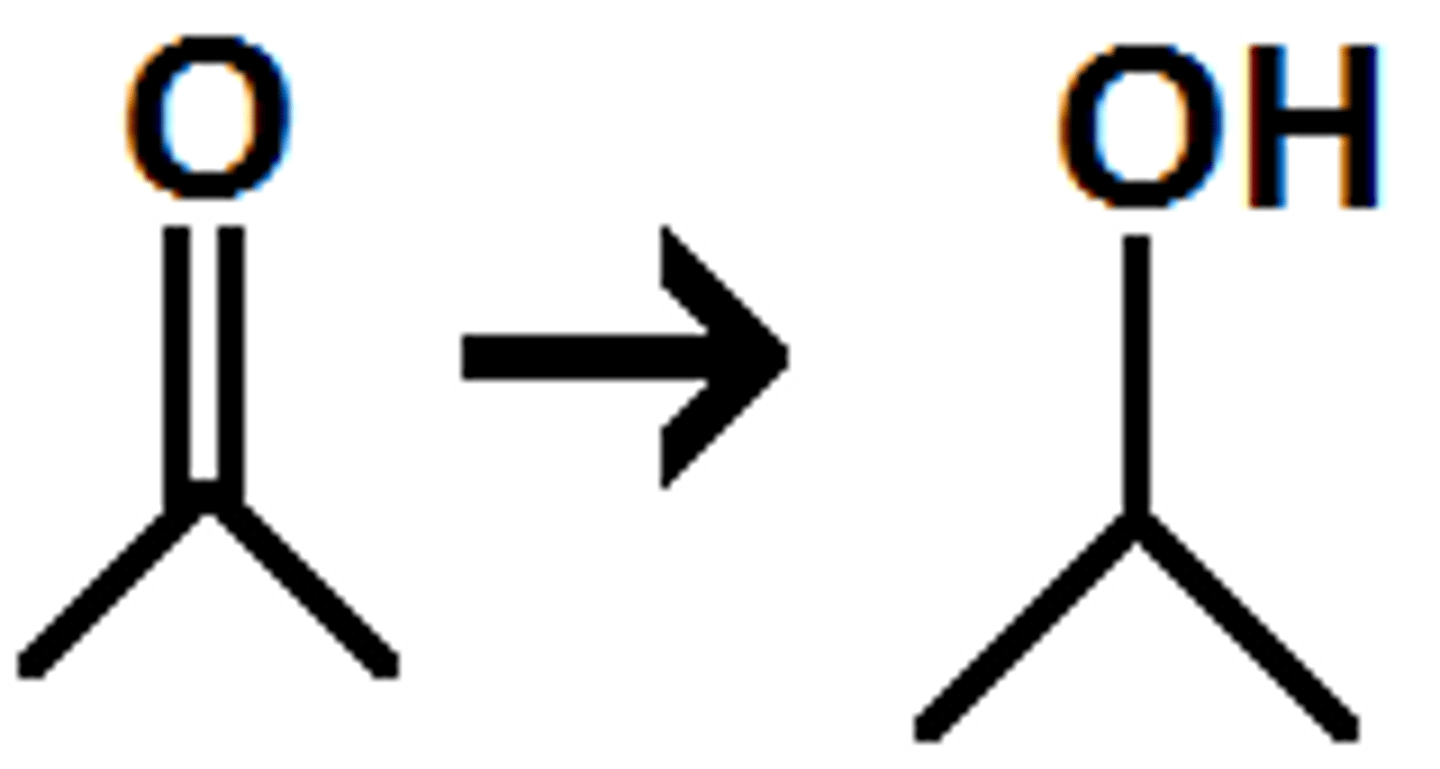
what does LiAlH4/ H+ do to a carboxylic acid?
LiAlH4/ H+ reduces a carboxylic acid to primary alcohol
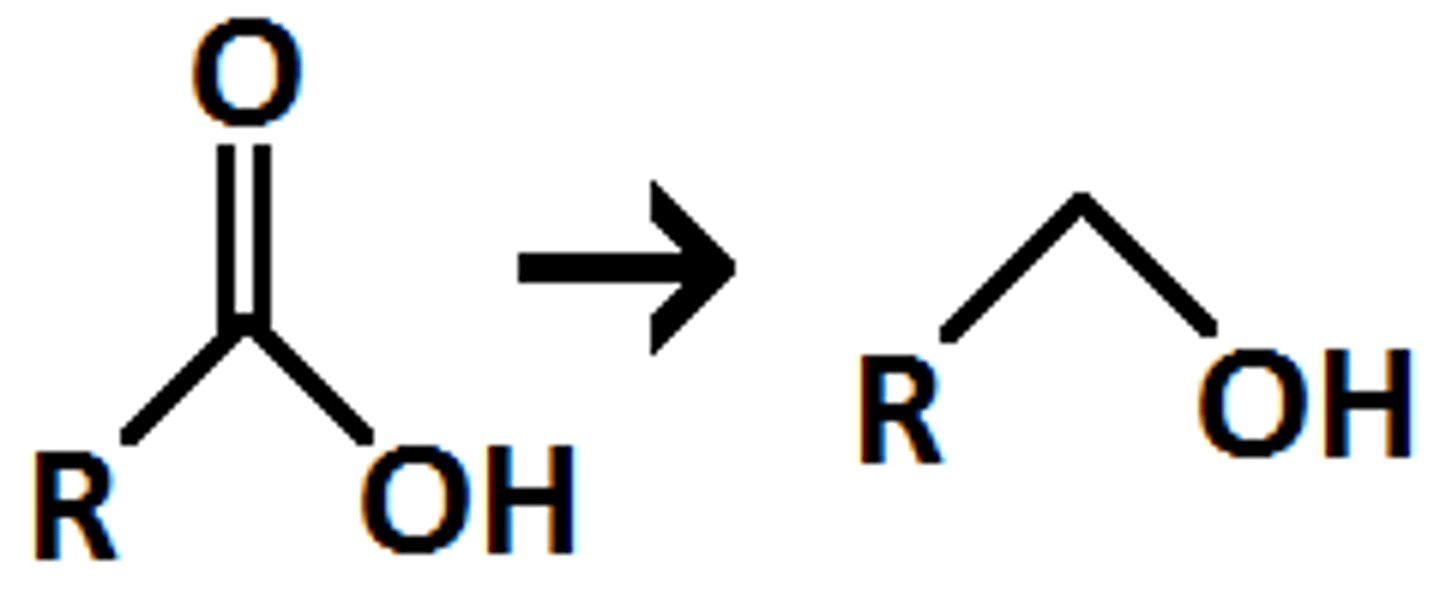
what does LiAlH4/ H+ do to an ester
esters are turned into primary alcohols
What are the oxidizing agents ?
Jones reagent [Cr (VI) CrO3, H2CrO4,Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7) in aqueous acid/acetone... PCC
what is PCC and what is its effect in a primary alcohol?
PCC can turn a primary alcohol into an aldehyde
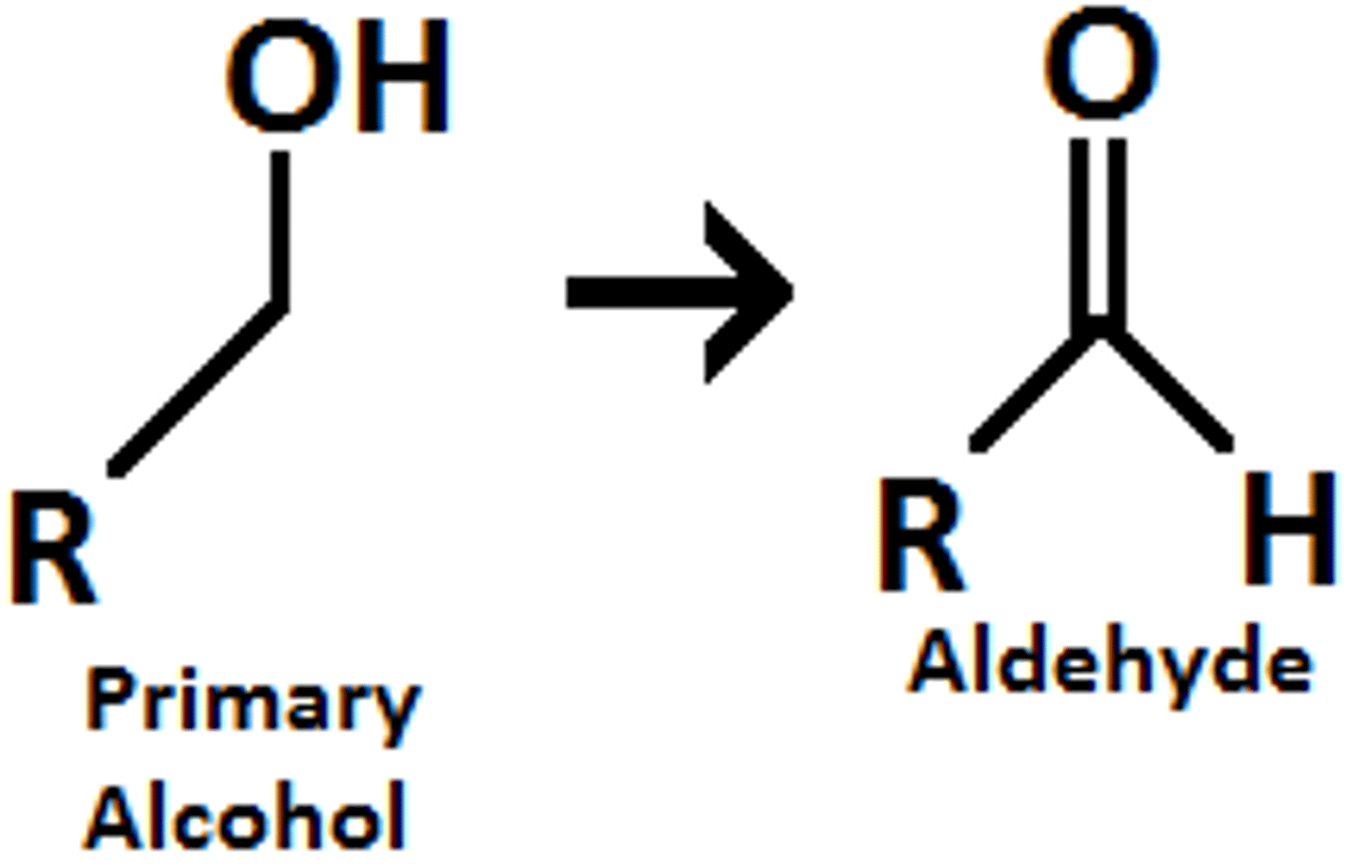
what is PCC effect on a secondary alcohol?
PCC can turn a secondary alcohol into a carbonyl/ketone
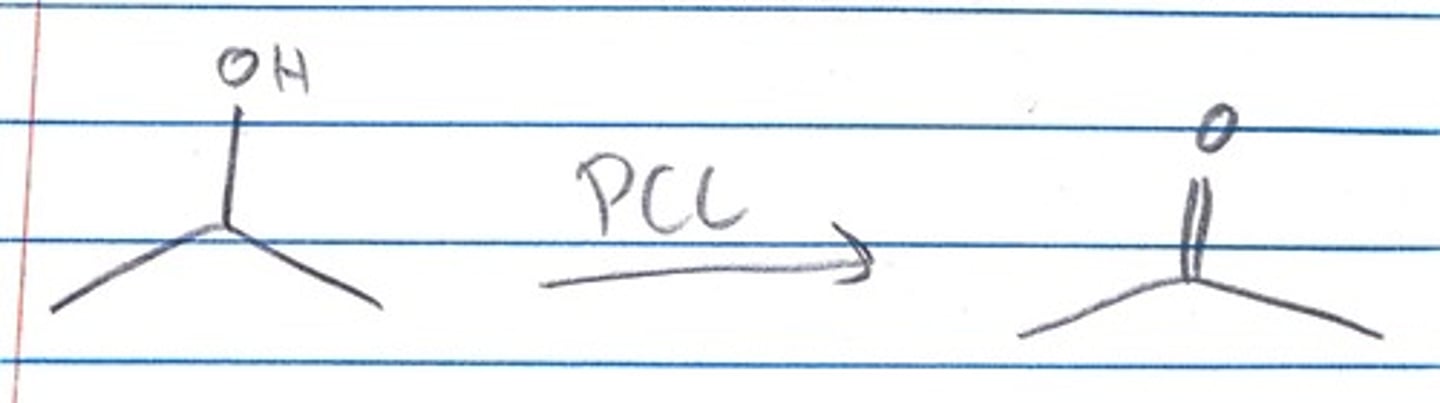
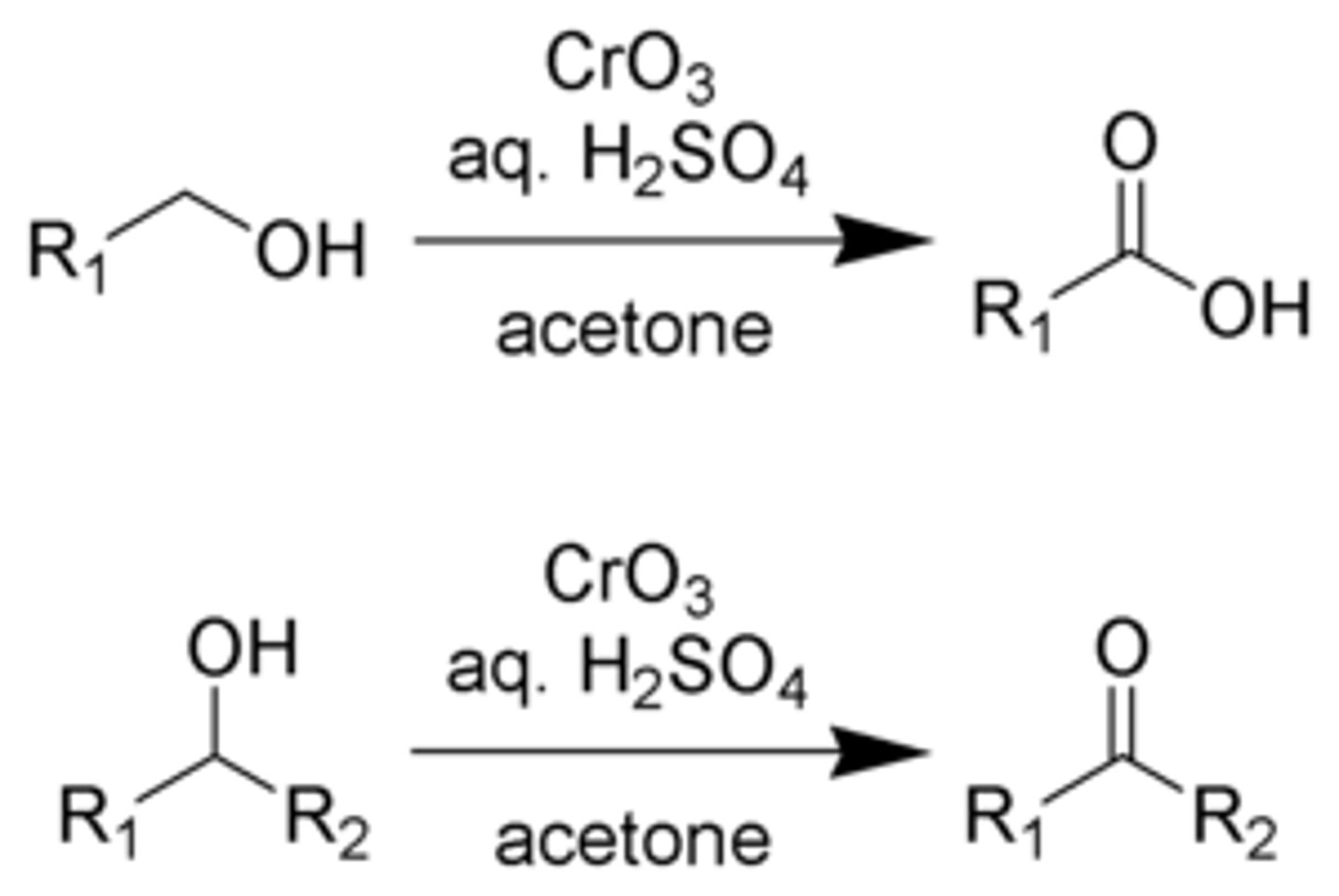
What is jones reagent effect in primary alcohols?
primary alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids via the aldehyde and aldehyde hydrate
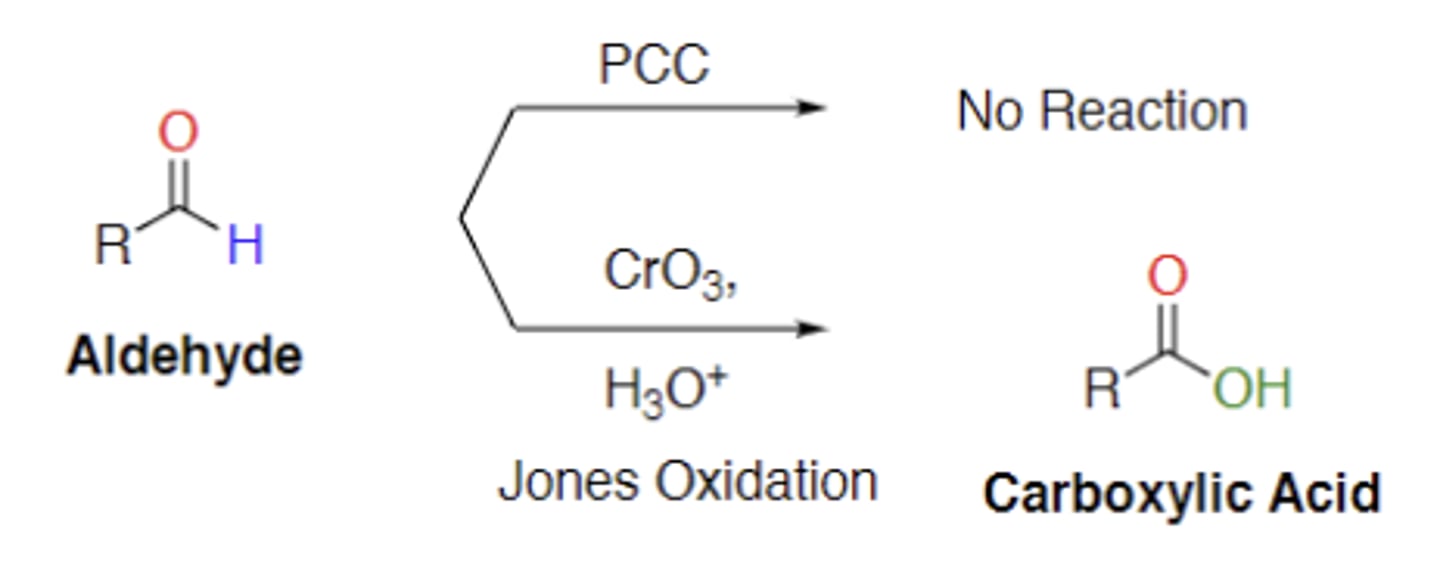
What is jones reagent effect in aldehydes
Jones reagent turns aldehydes into carboxylic acids
What is reduction? what does reduction do in alcohols?
Reduction is an increase in hydrogen content or a decrease in the content of oxygen or other electronegative elements. Reducing agents generally reduce ketones, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids to alcohols
What is NaBH4?
NaBH4 is a reducing agent .
What does NaBH4 do to a ketone?
NaBH4 reduces a ketone to a secondary alcohol
What does NaBH4 do to aldehydes ?
NaBH4 reduces aldehydes to primary alcohols
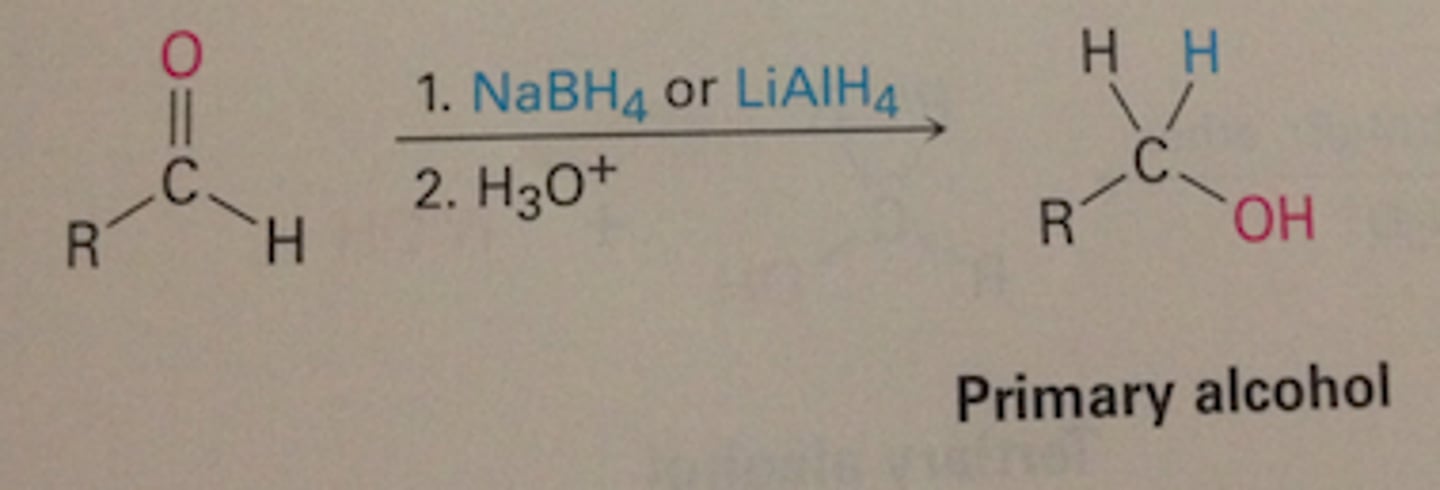
What is LiAlH4/ H+
reducing agent that is much more reactive than NaBH4.
-reduces ketones and aldehydes
-reduces esters and carboxylic acids
what does LiAlH4/ H+ do to an aldehyde
aldehydes reduce to an primary alcohol in the presence of LiAlH4/ H+.