14) embryology of the neural tube
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
derivations of the ectoderm
nervous system
sensory epithelia of the eye, ear, nose
epidermis of skin and its appendages (hair and nails)
mammary glands
pituitary gland, enamel (ameloblasts), parotid
derivations of the mesoderm
connective tissue (cartilage, bone, blood)
striated and smooth muscles
cardiovascular system
genitourinary system
spleen
serous membranes lining the body cavities (pericardial, pleural, peritoneal)
derivations of the endoderm
epithelial lining of the GIT, respiratory tract, bladder and urethra
thyroid and parathyroid glands, liver, pancreas, submandibular gland
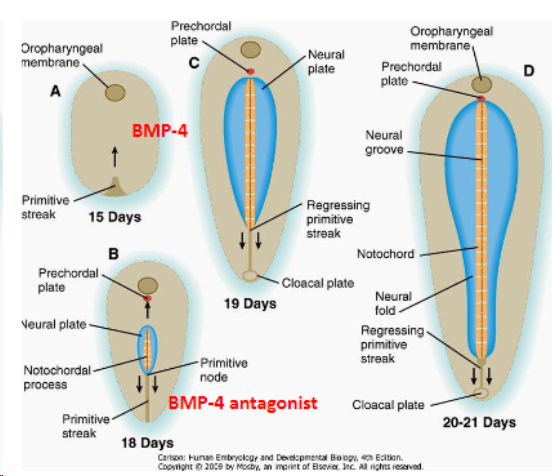
BMP-4
Ectoderm exposed to BMP-4 (from endoderm and mesoderm below) which develops into skin.
role of the primitive node
The primitive node secretes BMP-4 antagonists: that allow a region of the ectoderm to develop into nerve tissue.
Primitive node induces the development of notochord which in turn will induce the development of neural tube
BMP-4 and antagonist
Epidermis - develops as a response to BMP-4 agonist
Neural plate - does not develop into the epidermis due to BMP-4 antagonist
notochord
germ layer and position
Mesodermal
In the midline, forms the central axis
In all chordates
function and remnants of the notochord
Induces the development of the nervous system (main function then starts regressing)
Remnants- nucleus pulposus in IVD
neurulation
formation/development of the neural tube
primary neurulation
function
Folding, elevation, closing and fusing of the neural tube along the dorsal midline
Results in the functional separation of the ectoderm and mesoderm forming non-neuronal tissue
Up to mid-lumbar enlargement of the spinal cord
primary neurulation
steps
Notochord is the inducer
Neural plate - ectodermal
Neural groove and folds
Neural folds fuse -> neural tube
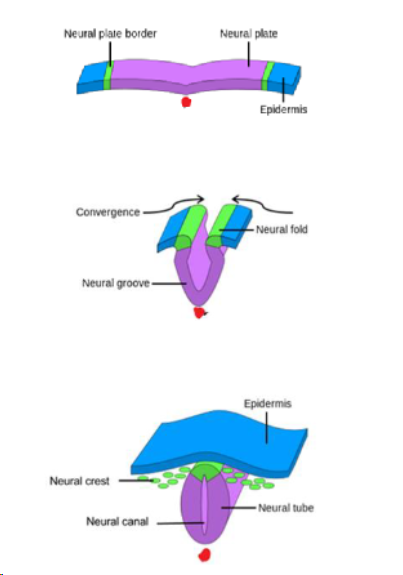
where do neural crest cells come from
Neural crest cells (dislodged cells from the neural folds)
Go everywhere from the cranial cavity to sacrum
neuropore
openings at the caudal and cranial end of the primitive streak which are in the process of closing
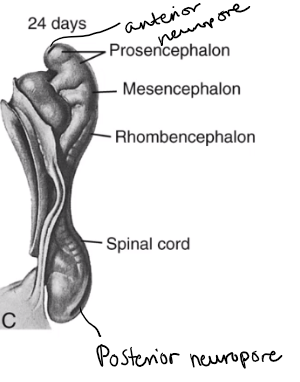
when do the neuropores close
The anterior neuropore closes around day 25.
The posterior neuropore closes around day 28.
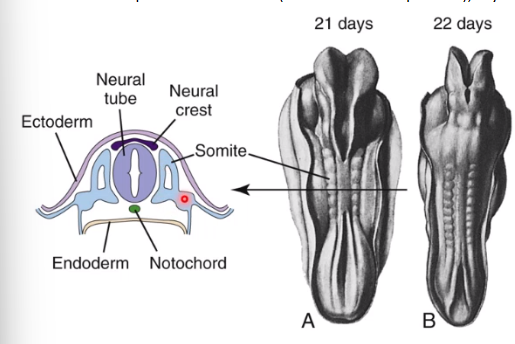
somite
Somite made from mesoderm
Each somite develops into sclerotome (vertebral developments), myotome and dermatome
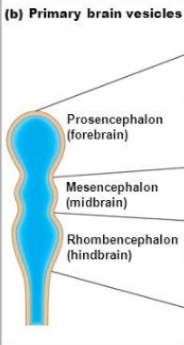
development of ventricles
Neural tube expands differently in its cranial and caudal ends
Cranial end - enlarge to form 3 primary brain vesicles
subsequent enlargement to form secondary brain vesicles
Caudal end - stays tubular for the spinal cord
primary brain vesicles
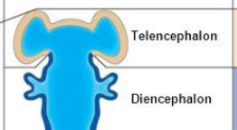
secondary brain vesicles from the forebrain
secondary brain vesicles from the midbrain

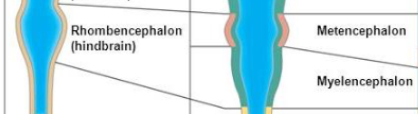
secondary brain vesicles from the hindbrain
adult brain structures from the telencephalon
and neural canal regions
cerebrum: cerebral hemispheres (cortex, white matter, basal nuclei)
lateral ventricles
adult structures from the diencephalon
diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus)
Buds of the diencephalon smooths out to form the retina and optic nerve to the eyes
third ventricle
adult structures from the mesencephalon
midbrain
cerebral aqueduct
adult structures from the metencephalon
pons
cerebellum
fourth ventricle
adult structures from the myelencephalon
medulla oblongata
fourth ventricle
flexures of the brain
simple
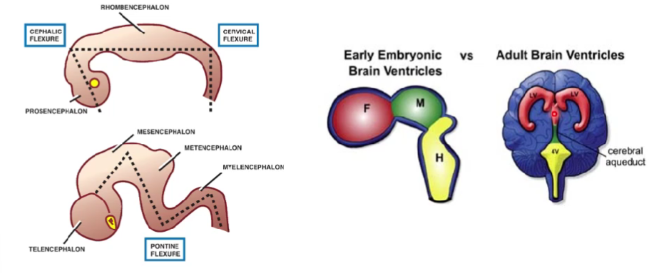
flexures of the brain
not simple
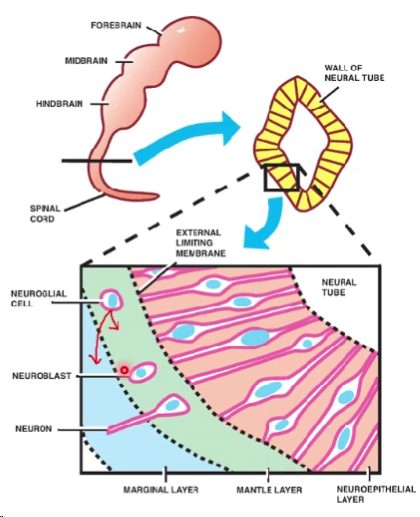
neural tube
initial cell type
Initially lined by a single layer of pseudostratified cells - germinal layer (ependymal layer and epithelium of choroid plexus)
mantle layer of the brain
Some cells migrate to the mantle layer and stay there
These develop into neuroblasts or glioblasts (supporting cells)
Grey matter - neurones and neuroglia/glioblasts
marginal layer of the brain
Some glioblasts migrate further into the marginal layer
Axons of neurones also migrate further
White matter - axons and neuroglia/glioblasts
migration of the cells
diagram
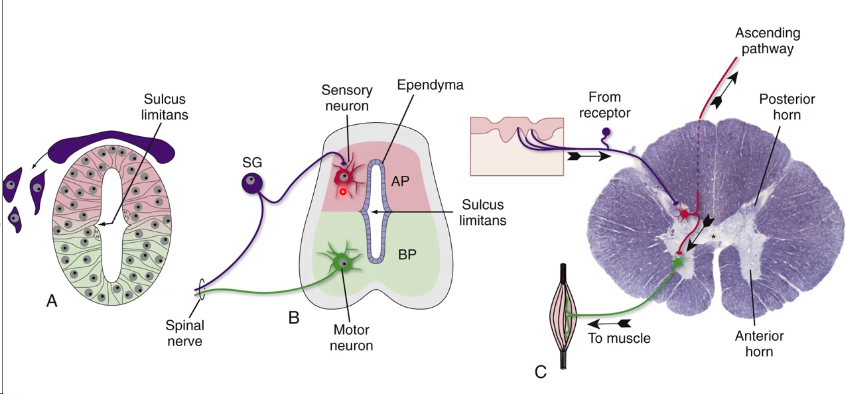
neural tube → spinal cord
Migration to form grey matter
Migration to form white matter
Posterior part develops sensory neurones
Anterior part develops motor neurones
pseudostratified layer of cells remains called the ependyma
cortical grey of the cerebrum and cerebellum
Neuroblasts migrate further outside forming cortical grey matter layer
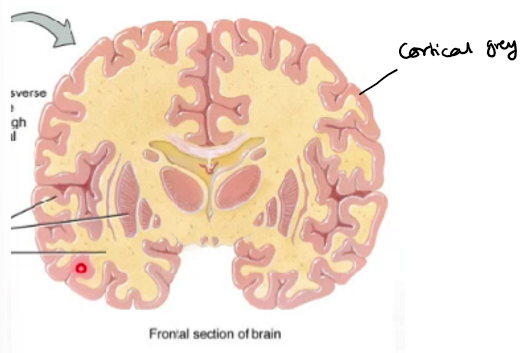
pathologies associated with cortical neuronal migration
Pathologies associated with cortical neuronal migration can cause disorders e.g. autism spectrum disorder (ASD), epilepsy
neural crest cells
change in cell type
At the time of neurulation, cells of the lateral most edge of the neural plate are induced to form neural crest cells
Neural crest cells transform from epithelial cells to migratory mesenchymal cells (which are mesodermal) that contribute to forming many tissues in the body so are able to migrate
Failure of migration gives rise to different types of abnormalities
embryological origin and migration of neural crest cells
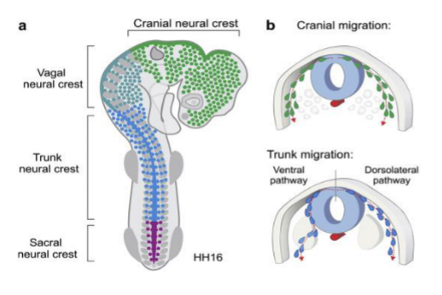
main neural crest cell contributions
Craniofacial skeleton
All ganglia (sympathetic ganglia, parasympathetic ganglia…)
Adrenal medulla
Cardiac septa
C cells of thyroid
Pharyngeal arch contribution
Odontoblast in teeth and deposition of dentine
NTDs
causes
Maternal diabetes
Maternal obesity
Folic acid deficiency (main cause)
Mutations in folate dependant or folate responsive pathways
Antiepileptic drugs like valproic acid
Delayed or failure of closure of neural tube: usually defects in primary neurulation
what arises from secondary neurulation
Distal lumbar cord, conus medullaris and filum terminale
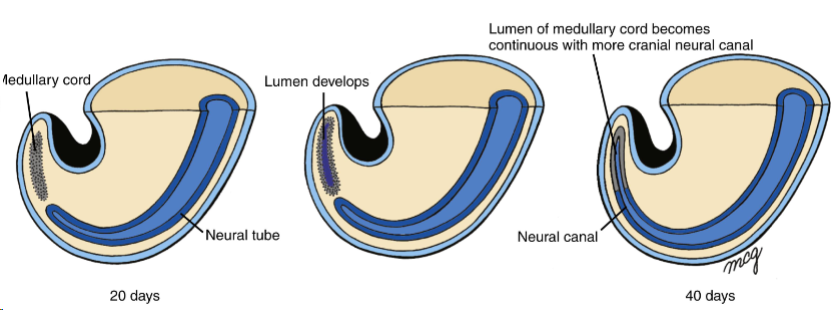
secondary neurulation
Medullary cord - new cord of cells in caudal end of embryo
Gets canalised
Two canals fuse and the cavity continues
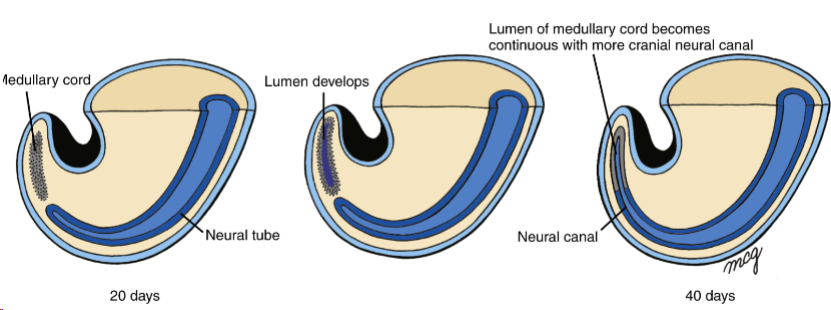
secondary neurulation
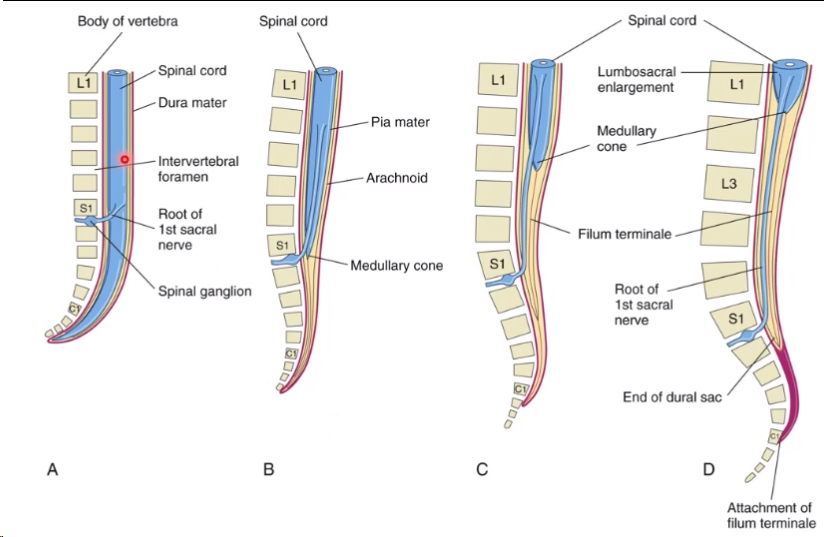
position of spinal cord
At this point the spinal cord ends at the end of the coccyx.
In adults spinal cord ends at lower border of L1
In children spinal cord ends at upper border of L3
how does the spinal cord end up at the higher spinal levels
Shortening of medullary cord so it ends at lower border of L1
Conus medullaris and filum terminale forms
Dural sac is pulled up (regresses) - so long spinal nerves form
proposed theories of NTDs
Neural tube fails to close: abnormalities in cellular behaviour (inefficient proliferation, disorganised cellular death and poor collective cell movement)
Closed neural tube reopens: possibly due to a breakdown in critical cell-cell adhesion junctions
spina bifida
vertebral arch defect (may be said to be an NTD but is incorrect)
1 to 2/1000 live births world-wide
Failure of fusion of two vertebral arches
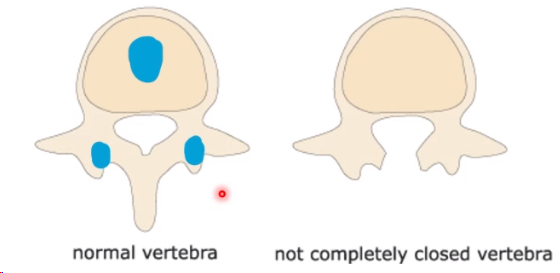
four types of spina bifida
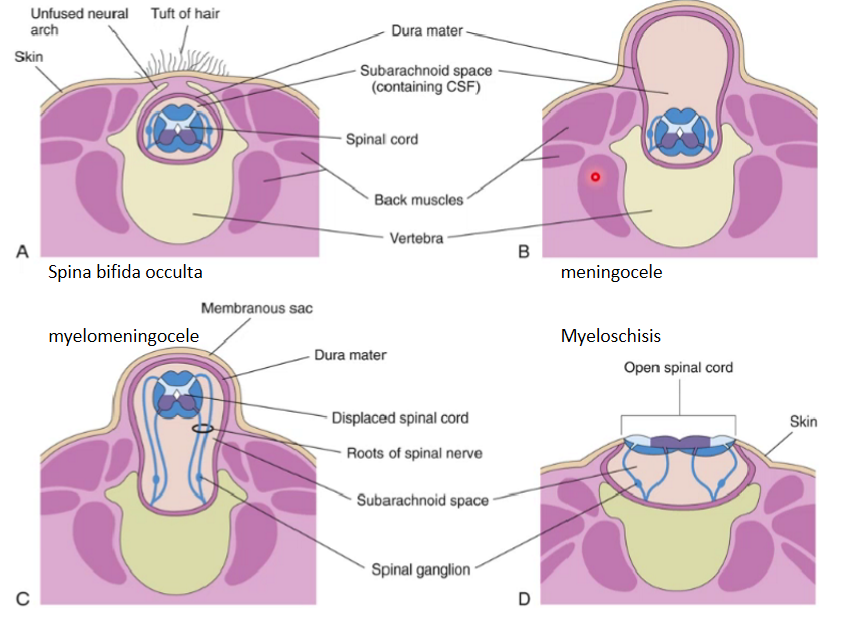
-cele
Cystic mass
myelo-
nervous tissue
closed spina bifida
closed as skin is covering it
does not break through the skin
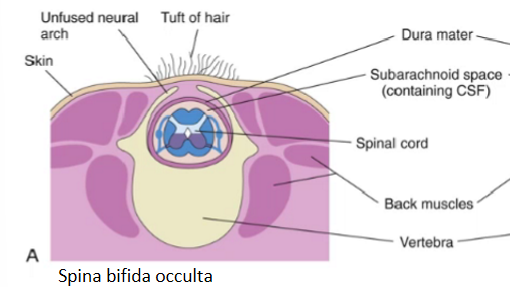
spina bifida occulta
delayed or failure of closure of neural tubes AND vertebral arches fail to fuse
Nervous tissue is still inside spinal canal
Asymptomatic
May just be seen as pathologies of that area (tuft of hair, dimple, excessive lordosis)
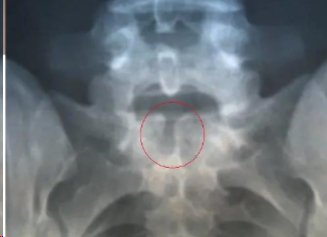
spina bifida occulta
x-ray
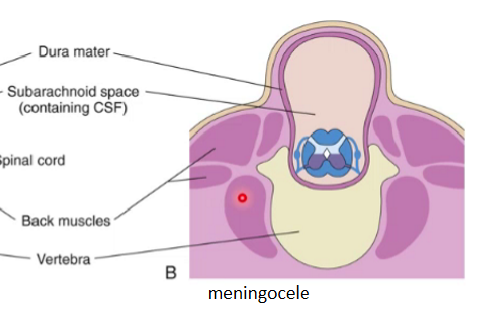
meningocele
(spina bifida cystica)
Fluctuating (as there's fluid which when touched moves) midline cystic mass covered with skin
Only meninges protrude
Spinal cord is still intact
May be associated with neurological defects
May develop defects like:
Weakness of legs
Trouble with bowel and bladder control
These issues may change or progress as children grow
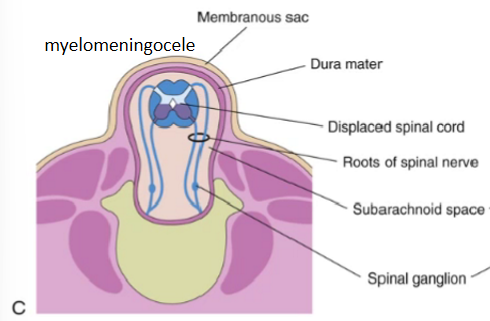
myelomeningocele
Meninges and nervous tissue protrude
Nervous roots gets stretched excessively
Neural defects are always present
myelomeningocele
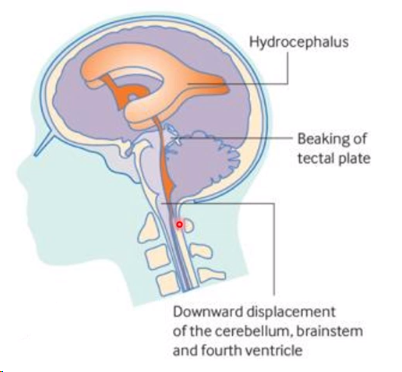
changes to the brain
Chiari II (downward herniation of the cerebellum through the foramen magnum)
Hydrocephalus (enlargement of the ventricles of the brain)
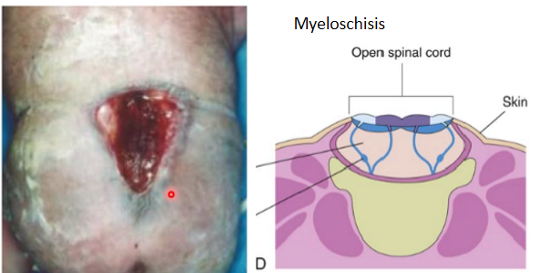
myeloschisis
spinal cord is exposed to the outside
diagnosis of spina bifida
USG and blood test between 12 to 20 weeks
Raised maternal serum alpha foetoprotein level in NTDs
alpha foetoprotein
Alpha foetoprotein secreted from inside the neural tube
The protein is in direct communication with the amniotic fluid so the maternal alpha foetoprotein blood levels increase
management of spina bifida
In utero cellular therapies (human embryonic stem cell, pluripotent stem cells etc.)
Foetal intervention/postnatal surgery
prevention of spina bifida
Daily 400 microgram folic acid supplement in addition to dietary sources for all women planning pregnancy till 12 weeks of pregnancy
further reading of neurological defects
DiGeorge syndrome
Congenital megacolon