Chemistry - States of Matter, Phase Change, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Solids
form of matter that has a definite shape and volume
shape of solid doesn’t depend on the shape of its container
particles in a solid are packed tightly together and orderly arranged
solids are almost incompressible (difficult to squeeze into a smaller volume)
solids expand only slightly when heated
Liquids
particles are in close contact, but are not orderly arranged
particles in a liquid are free to flow —> liquids take the shape of its container
volume of a liquid is fixed/constant
almost incompressible
tend to expand slightly when heated
Gases
take both the shape and volume of its container
particles in a gas are much farther apart than the particles in a liquid
the space between particles allow gases to be easily compressed into smaller volumes
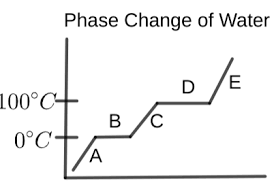
What is happening in letter A?
the water is a solid (ice)
temperature is increasing
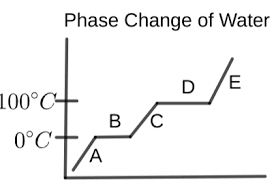
What is happening in letter B?
melting is occurring
ice and liquid water are present
temperature remains the same
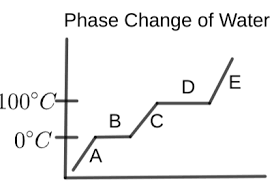
What is happening in letter C?
the water is a liquid
temperature is rising again
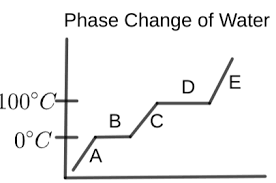
What is happening in letter D?
vaporization is occurring
liquid water and water vapor are present
temperature is constant
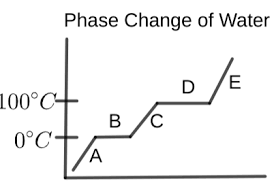
What is happening in letter E?
the water is a vapor
temperature is increasing
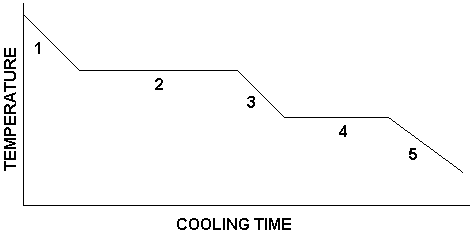
What is happening in number 1?
substance is a gas
temperature is decreasing
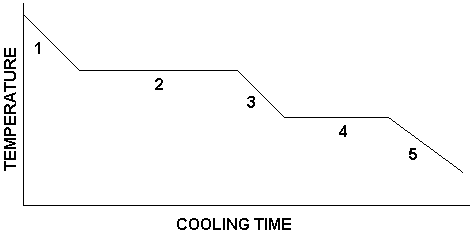
What is happening in number 2?
condensation is occurring
gas and liquid are present
temperature remains constant
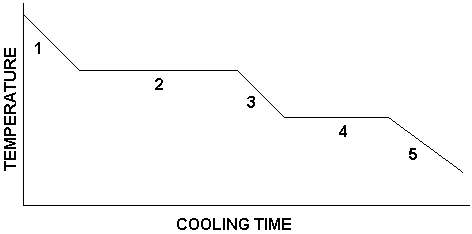
What is happening in number 3?
substance is a liquid
temperature continues to decrease
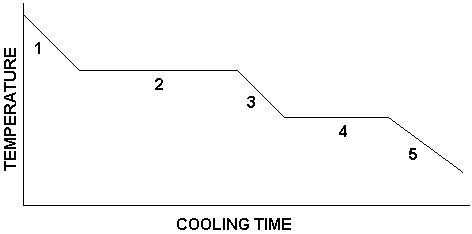
What is happening in number 4?
freezing is occurring
liquid and solid are present
temperature is constant
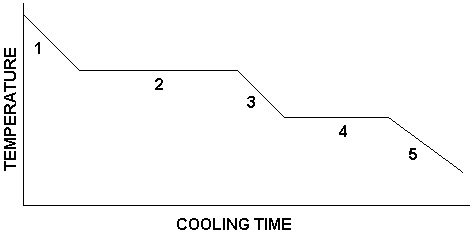
What is happening in number 5?
substance is a solid
temperature decreases
Melting
solid turns into a liquid
Condensation
gas turns into a liquid
Deposition
gas turns into a solid
rarely happens
Freezing
liquids turns into a solid
Sublimation
solid turns into a gas
rarely happens
Vaporization
liquid turns into a gas
Elements
shown on the periodic table by a symbol
always 1 or 2 letters
never more than 1 capital letter
pure substance
cannot be broken down by physical change or chemical change
made up of only 1 type of atom
Compounds
represented by a formula
at least two different element symbols
always more than 1 capital letter per formula
pure substance
form when two or more different elements bond together chemically
can be separated only by a chemical change
always exists as a molecule
Mixtures
not always the same concentration
form when elements and/or compounds are combined physically
can be separated by physical change
not a pure substance
Homogenous Mixture
particles are evenly distributed throughout the mixture
Heterogenous Mixture
particles are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture
Flotation
useful for separating mixtures that are composed of parts that have different densities
Sifting
involves a tool called a sieve
the sieve has holes that allow smaller materials—but not larger materials—to pass through
useful for mixtures composed of particles with different sizes
Magnet
useful for separating mixtures that contain magnetic and non-magnetic parts
Filtration
useful for separating a mixture that contains liquid and solid parts as well as mixtures that contain particles with different sizes
Distillation
a solution is heated until the solvent vaporizes
the solute does not change state and is left behind
useful for mixtures that contain parts with different boiling points
Panning
helps miners separate gold from sand and gravel
miners scoop up material from the stream bed and swirl it in a metal pan
useful for mixtures that are composed of particles with different sizes
Chromatography
useful for mixtures that contain parts that have a difference in solubility
Molecules
two or more atoms combine or bond
Subscripts
indicate the number of each atom present in a molecule
Coefficients
indicate the number of molecules or atoms involved in a reaction